PLTW HBS Exam 1.2.1-1.2.6
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
rotation motion
turning movement of a bone around its own axis
circumduction motion
draw around; cone shape or circular motion of a limb
abduction
movement away from the midline of the body
adduction
movement toward the midline of the body
depression motion
movement of a body part inferiorly
elevation movement
movement of a body part superiorly
flexion
decreases the angle of a joint; bending a joint
extension
increases the angle of a joint; straightens joint
hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position
plantar flexion
bends the foot downward toward the ankle
dorsiflexion
backward flexion; pointing your toes to the sky
ligament
connects bone to bone
tendon
connects muscle to bone
range of motion (ROM)
total range possible in a joint, describe by the terms related to body movements (i.e., ability to flex, extend, abduct, adduct); measured in degrees
goinometer
instrument used to measure joint angles
medial
toward the midline of the body
lateral
away from the midline of the body
anterior
front of the body
posterior
back of the body
medial collateral ligament (MCL)
distal end of the femur to the promised end of the tibia located on the medial side of the leg; major purpose is to prevent the knee from valves and external rotating forces
lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
distal end of the femur to the proximal end of the fibula (may also touch the tibia as well) located on the lateral side of the leg; main purpose is to prevent the knee from varus
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
attached to anterior tibia; prevents forward sliding of the tibia and stops hyperextension of the knee
posterior cruciate ligament
attaches to the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau; prevents posterior movement of the tibia on the femur
anterior drawer test
indicates ACL tear; pulls the knee
posterior drawer test
indicates PCL; pushes on the leg
valgus stress test
tests for MCL injury
varus stress test
tests for LCL injury
varus
inward bending or twisting force
valgus
bending or twisting outward
lymphatic drainage KT tape
placing tape to pull up in skin and allow easier movement of fluid in the body; used right after injury or surgery to reduce swelling
ligament correction KT tape
playing tape with tension to activate mechanorecpetors; used for stability
types of joints
synovial, fibrous, and cartilaginous
synovial joint
freely movable joints were bones are enclosed by a fluid filled capsule, allowing a wide range of motion
synovial membrane
protects the joint
joint cavity and synovial fluid
The space between the bones that contains synovial fluid which lubricates the cavity and reduces friction and nourishes cartilage
meniscus
provides cushioning between the bones
ball and socket joint
spherical head of one bone fits into a cap like socket of another, allowing for the greatest range of motion; shoulder and hip joints
hinge joint
The convex end of one bones fits into the concave end of another allowing for movement in a singular plane, similar to a door hinge; elbow and knee joints
pivot joint
A rounded portion of one bone rotates within a ring formed by another bone and/or ligaments, allowing for rotation around a single axis; c1 and c2 that allows you to shake your head no
condyloid/ ellipsoid joint
an oval articular surface of one bone fits into a shallow depression in another bone, allowing for movement in two planes; radiocarpal (wrist) joint
saddle joint
both articulating surfaces are saddle shaped (concave in one direction, convex in the other) and allow for greater movement than condyloid joints; carpometacarpal (joint base of the thumb) joint
plane/ gliding joint
articulating surfaces are flat or slightly curved, allowing for short, gliding movements between the bones; joints between carpal and tarsal bones
3 types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
hyaline cartilage
located at the end of bones (articular, cartilage), nose, trachea, and ribs. Provides a smooth, resilient surface for joints, allowing movement.
elastic cartilage
located on the ear, epiglottis, and parts of the larynx. Provide support with flexibility.
fibrocartilage
located on the intervertebral discs, menisci of the knee, and tendinous insertions. Offer strength and shock absorption, acting as a cushion between bones.
skeletal muscle
muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones. Striated and voluntary
smooth muscle
involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body that is not striated
cardiac muscle
Striated, involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart
Sliding filament theory
The concept that a sarcomere shortens as the thick and thin filaments slide pass one another; part of muscle contraction
actin
thin filaments, attached to Z disc, need calcium to bind
myosin
sick filament, needs ATP to release, pulls on other fiber
sarcomere
contractile unit of muscle
z disc
separated the sarcomeres from each other
calcium
required to free actin by binding to troponin, moving the tropomyosin, and allowing it to bind with myosin
ATP
Chemical energy required for myosin to release actin
rigor mortis
temporary stiffening of muscles after death, caused by lack of ATP production
muscle atrophy
lack of muscle activity; reduces muscle size, tone, and power
acetylcholine (acH)
neurotransmitter chemical released at the end of nerve cells
neuromuscular junction
The synapse between a somatic motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber
t-tubules
tubes that the neurotransmitter goes down to spread the action potential into the interior of the muscle fiber
sarcoplasmic reticulum
organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium
cross bridges
connections between the heads of the myosin filaments and receptor binding sites on the actin filaments
power stroke
action of the myosin pulling the actin (sliding)
hydrolysis
breaks ATP to ADP + Pi
ATP + h2o —> energy + ADP + Pi
dehydration synthesis
brings ADP + Pi back to ATP
energy + ADP + Pi —> ATP + h2o
ATP equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
solution that produces the greatest percent contraction?
ATP in salt solution
endomysium (3)
connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
epimysium (1)
connective tissue that surrounds entire muscle
perimysium (2)
connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
origin
attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction
insertion
attachment of a muscle to movable bone
muscle always…
pulls
muscles work in…
opposing pairs
sprain
injury to a ligament
strain
injury to a tendon
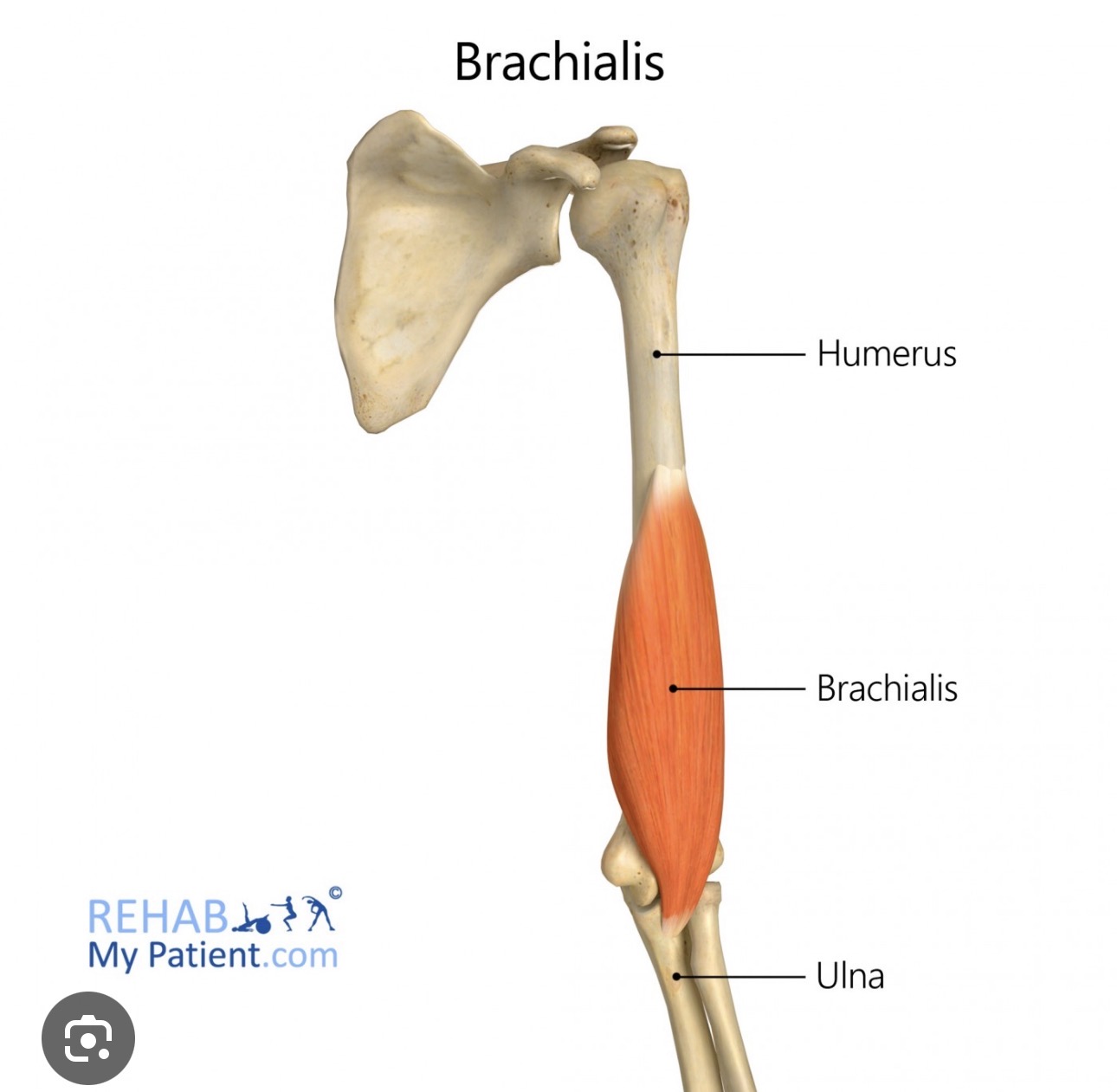
Brachialis
Origin- halfway down humorous
insertion- proximal ulna
action- flexes elbow
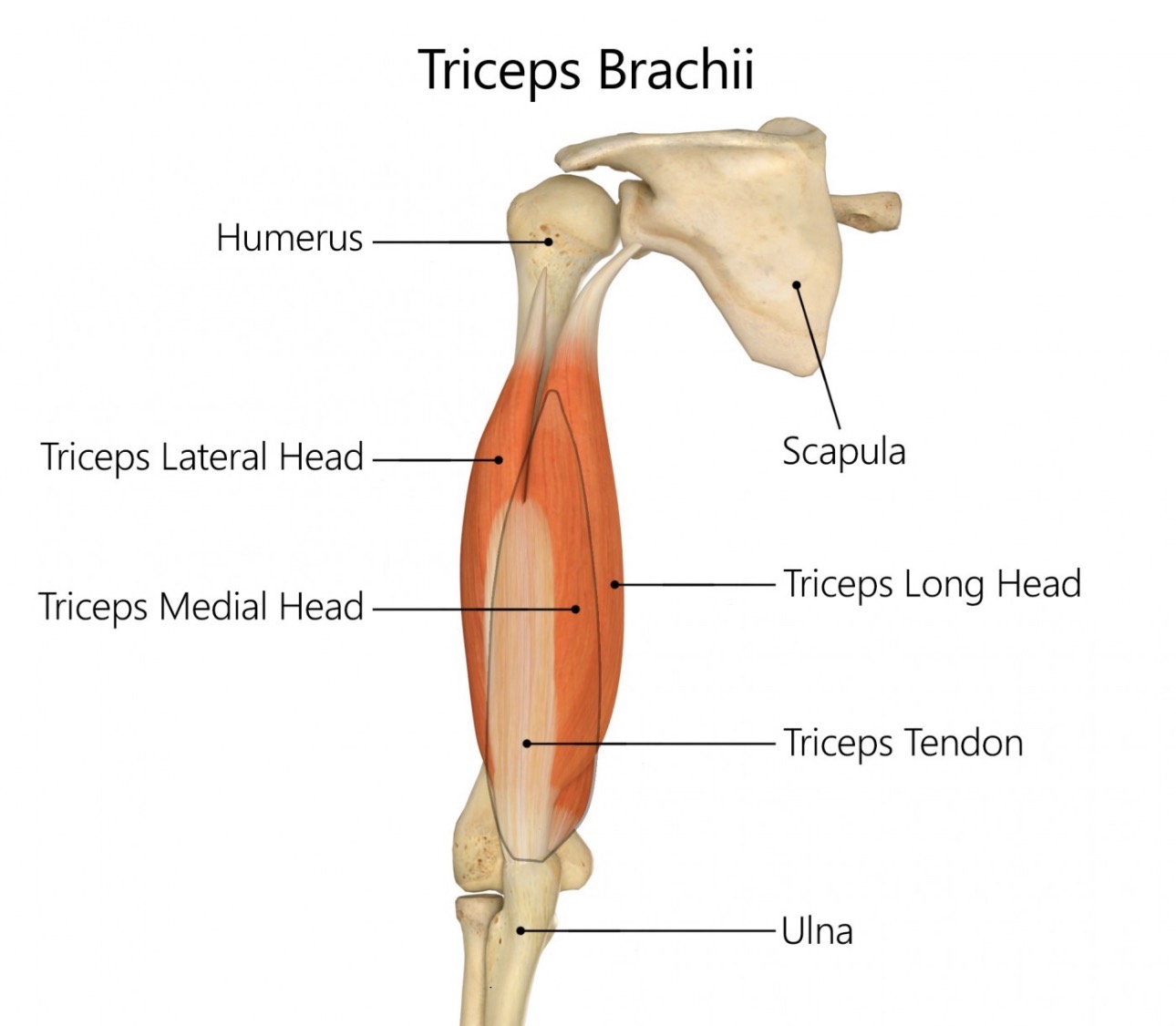
triceps medial head
Origin- humorous
insertion- proximal ulna
action- extend elbow
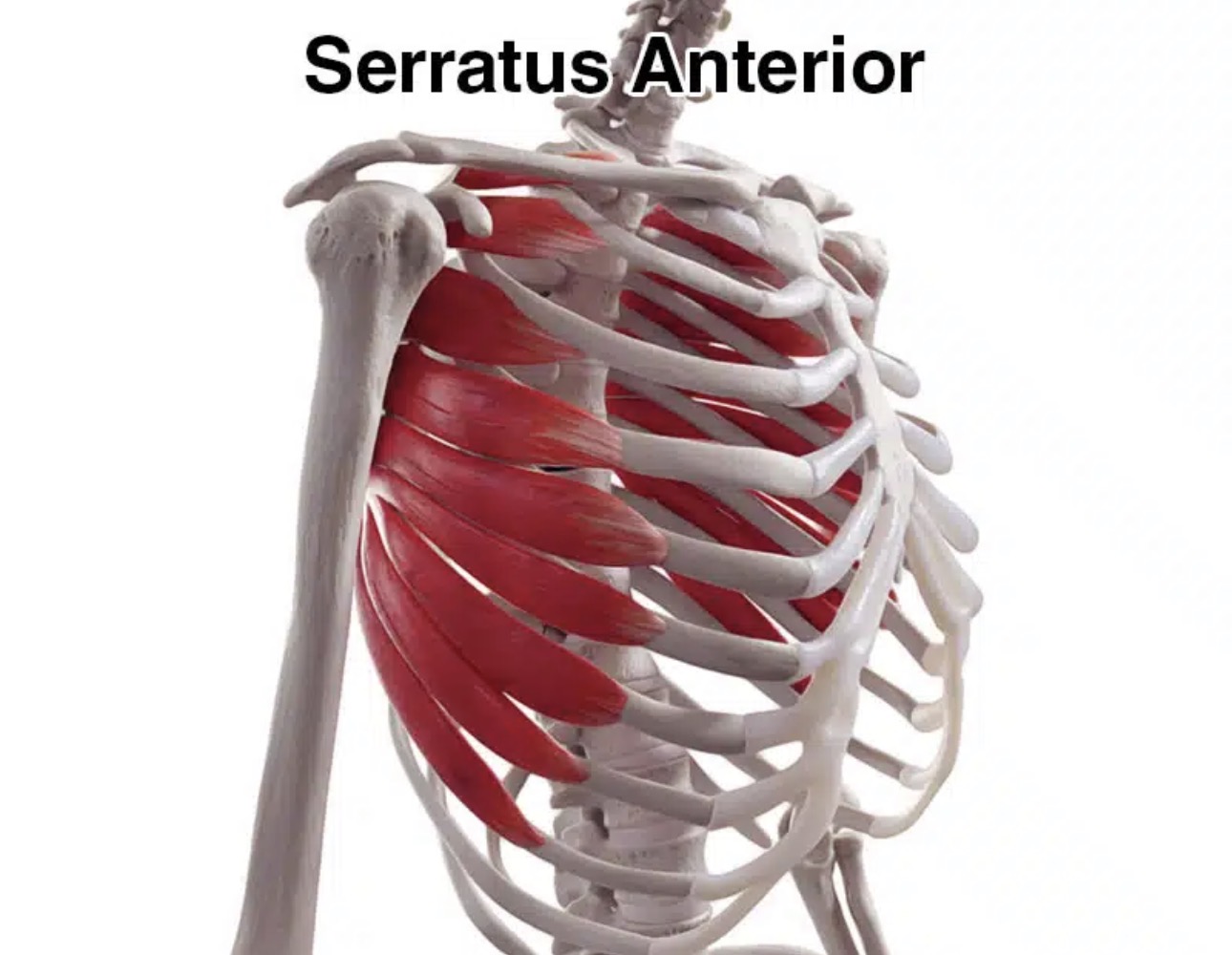
serratus anterior
Origin- ribs 1-8
insertion- anterior medial border of scapula
action- pulls scapular anterior and downward
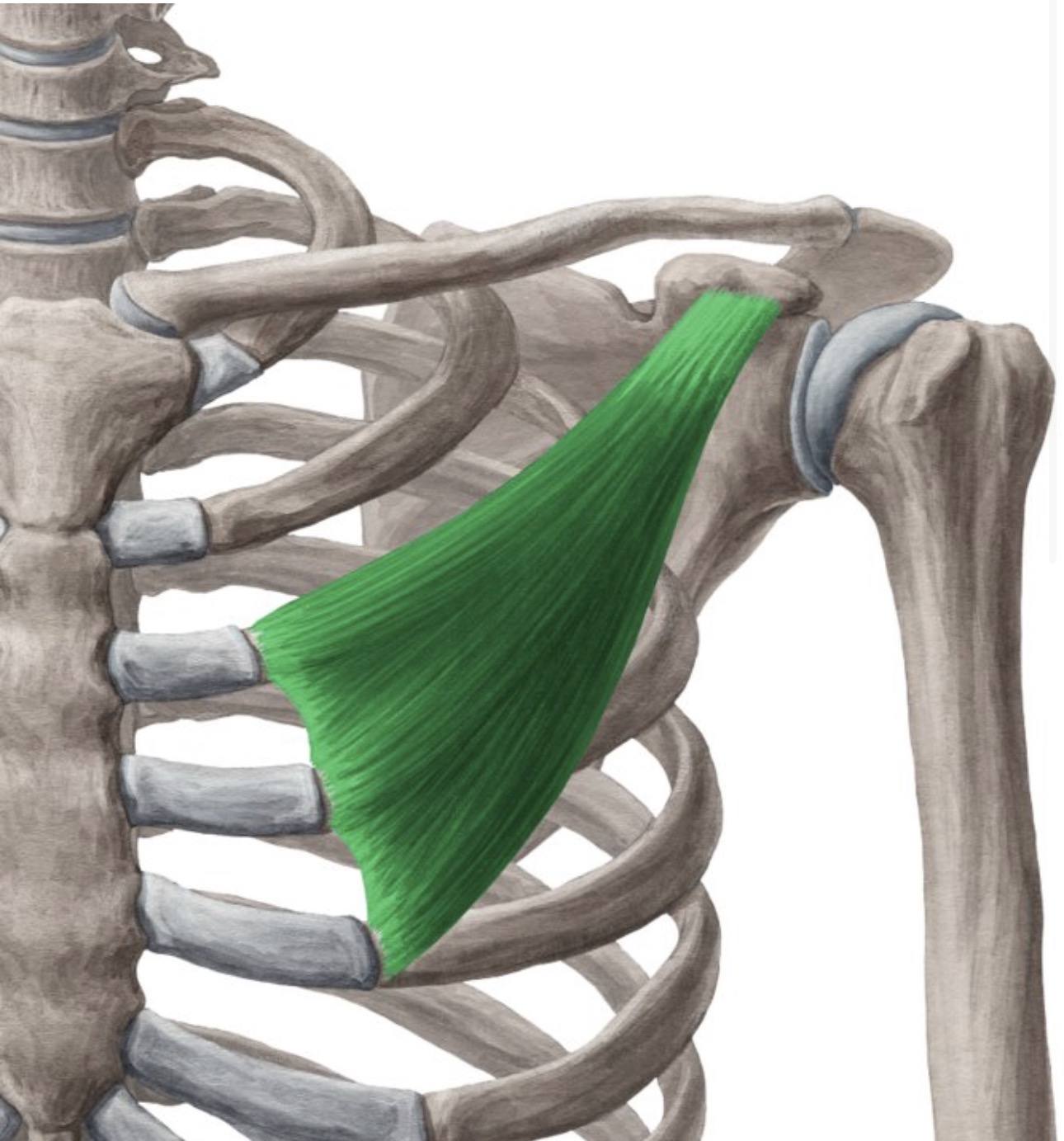
pectoralis minor muscle
Origin- ribs 3-5
insertion- piece of the scapula visible on the front
action- rotates the shoulder forward
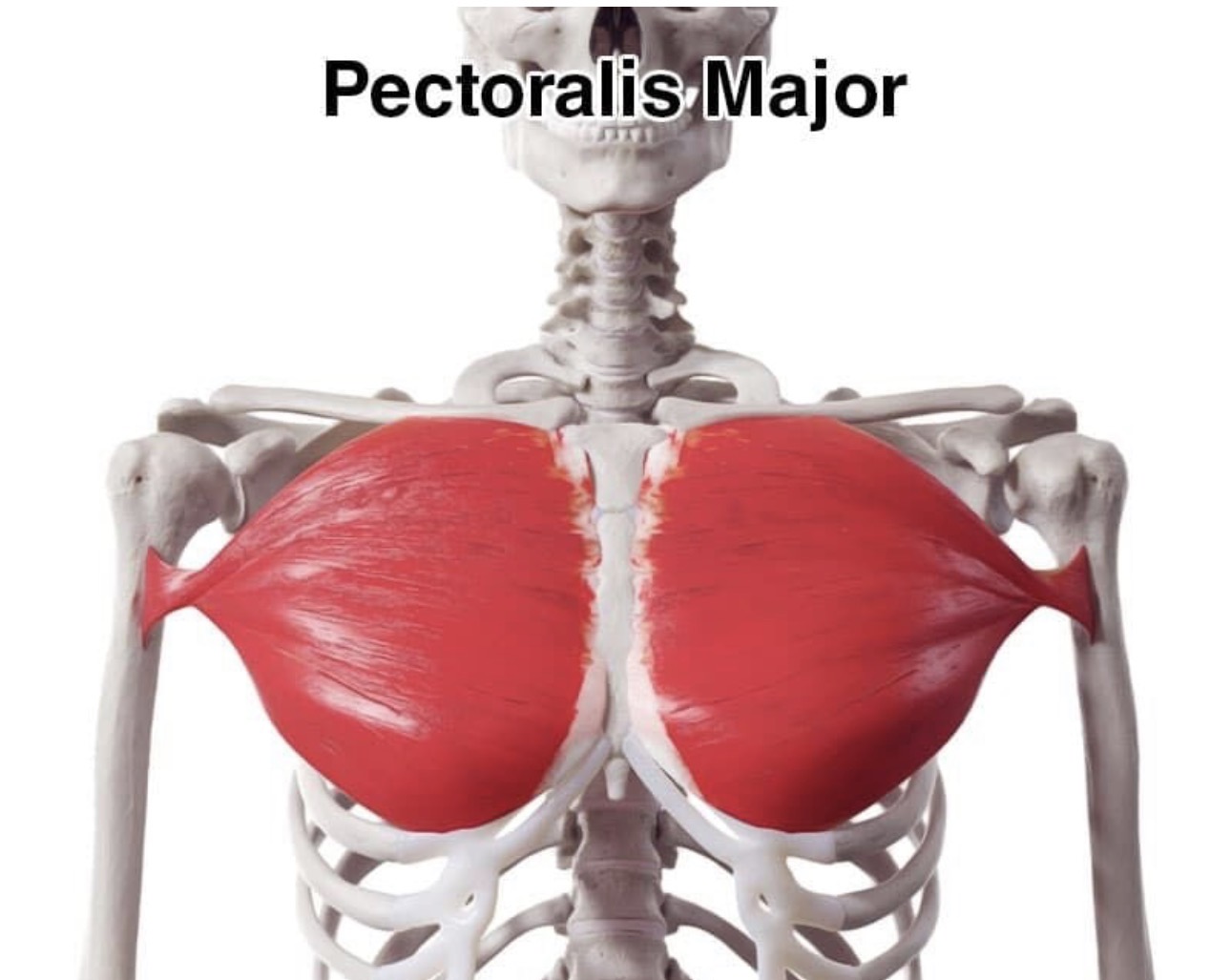
pectoralis major
adducts and flexes humerus
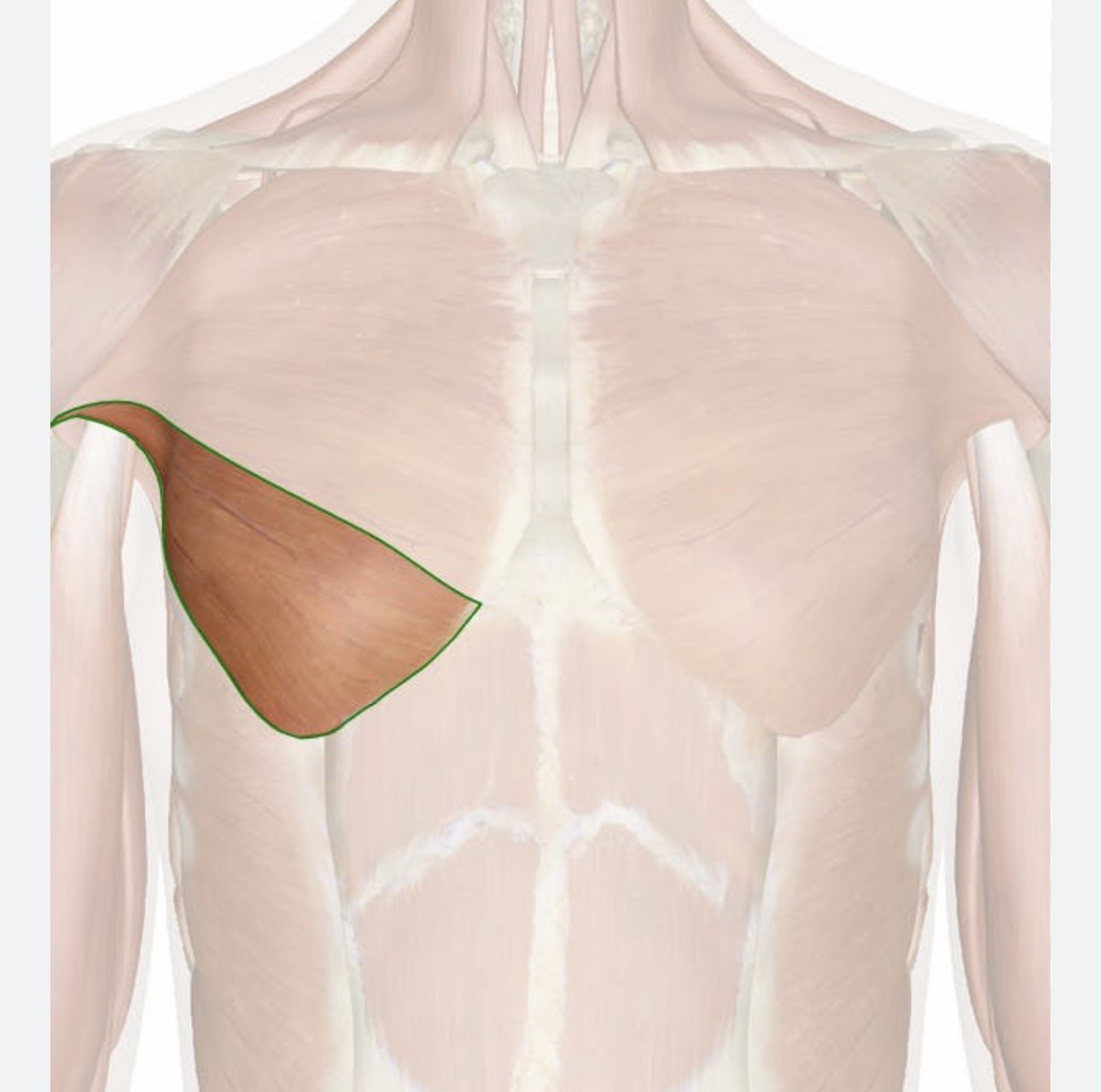
pectoralis major abdominal head
Origin- ribs 5-7
insertion- lateral edge of most proximal part of humerus
action- arm extension and flexion
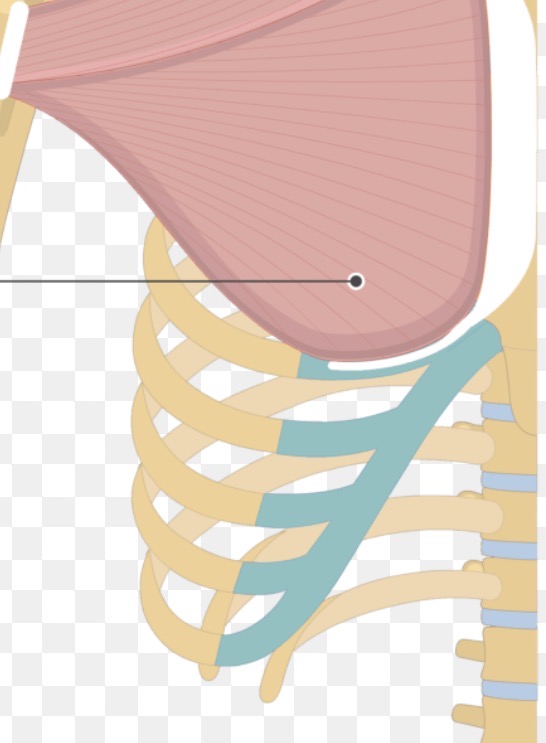
pectoralis major sternal head
Origin- ribs 1-5 on lateral edge of sternum
insertion- lateral edge of humerus
action- adduction of humerus