Exam 4 Vocab/Notes
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Albedo
measurement of reflectance
Snow and ice have high albedo so they resist warming
Carbon dioxide
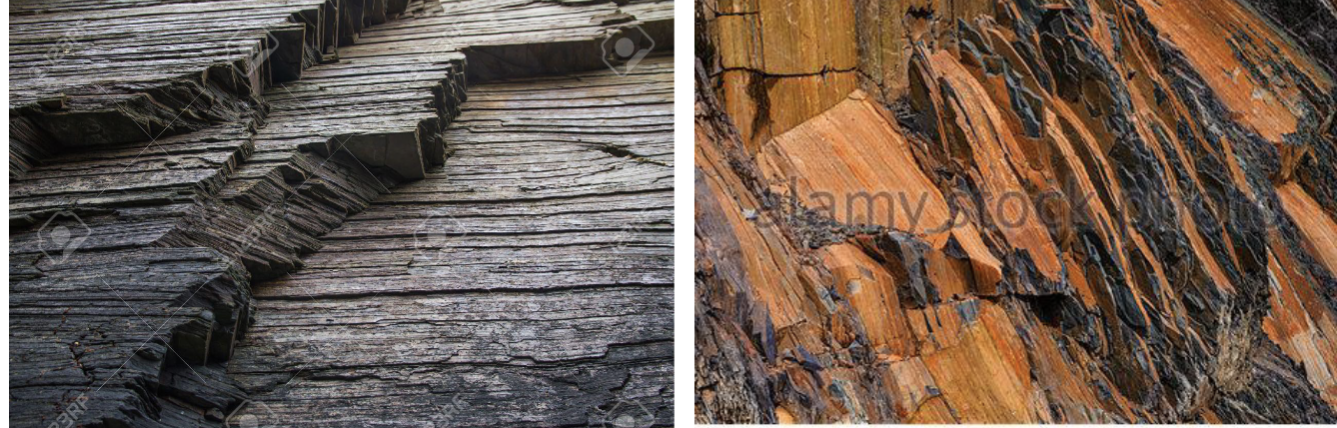
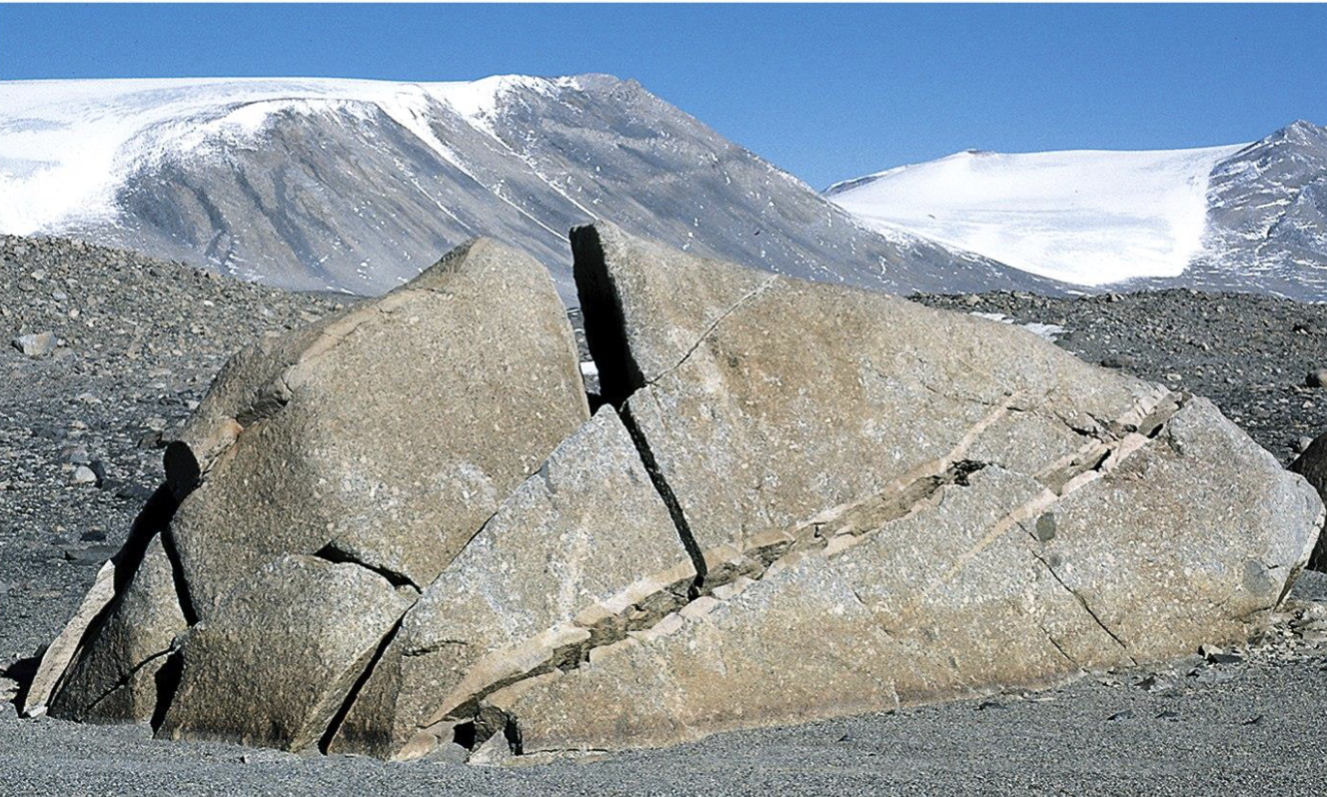
Mechanical/Physical Weathering
Frost wedging
Salt Crystal Growth
Sheeting
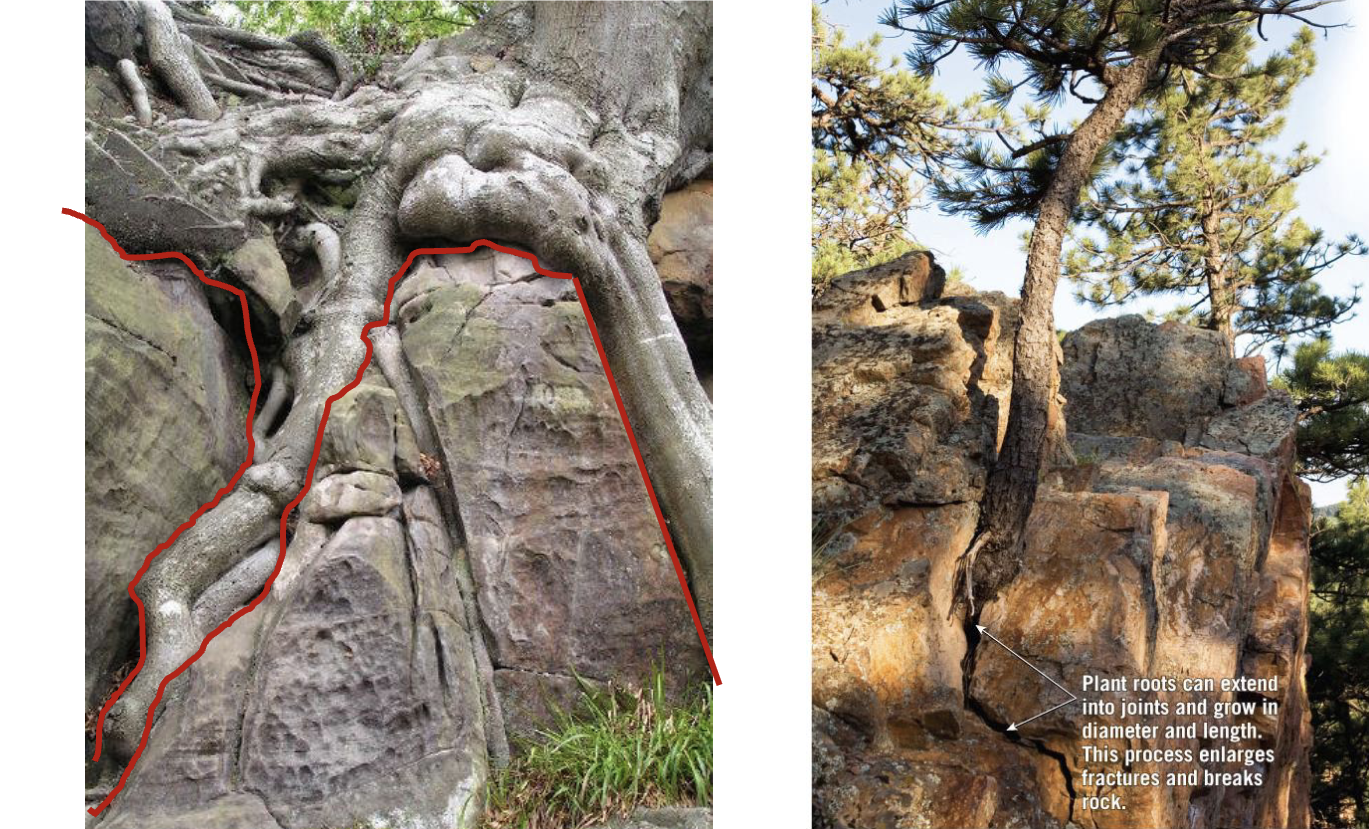
Biological activity
Humus
Soil Erosion
Snow Line
Till
Plucking
Glacial Eratic
Glacia retreat
Fall
Scarp
Longwave Radiation
Radiation emitted by Earth is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere
Such as carbon dioxide and water vapor
Greenhouse Gas

Chemical Weathering
1) Oxidation
Oxygen dissolves in water
Minerals oxidize or rust
2) Carbon acid
Carbon dioxide dissolves in water
Co2 + H2o → H2CO3
H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3-
Topsoil
Dust Bowl
Firn
Zone of accumulation
Rock flour
End moraine
Positive Feedback loop
Slide
Rockslide
Shortwave Radiation
solar radiation passes through the atmosphere and heats the Earth
Atmospheric Window
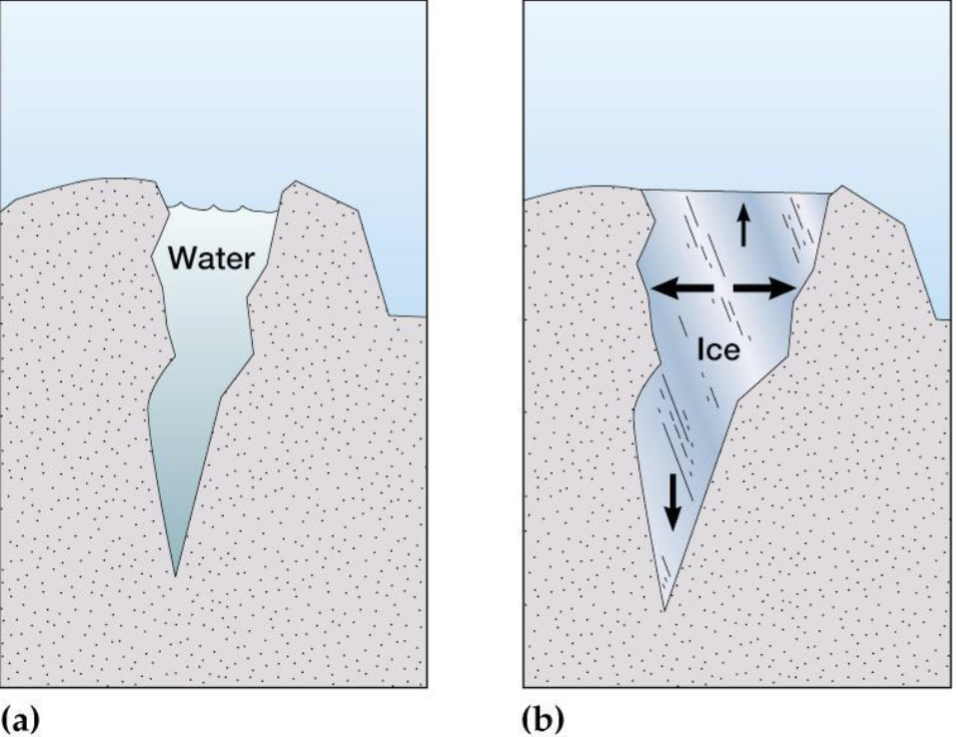
Frost Wedging

O horizon

Biological activity
Zone of wastage
Tillite
Crevasse
Glacial budget
Mass Wasting
Creep
Rockfall
Greenhouse Effect
Heating the atmosphere
long-wave radiation heats the atmosphere, whoch radiates heat both out into space and back to Earth.
This selective absorption and reheating of Earth is called the greenhouse effect and results in warming of the atmosphere
Climate vs Weather
Weather:
instantaneous atmospheric condition
Can change rapidly
Prevails over a short area
Only limited predicability
depends primarily on density (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another
Climate:
average atmospheric conditions
sustains over 30 years
prevails over a large region
is almost constant
depends on latitude, distance to the sea, vegetation, presence or absence of mountains, and other geographical factors
Climate is what you expect, weather is what you get
Carbonic acid
A horizon
Oxidation
Ice sheet
Zone of fracture
Alpine glacier
Glacial advance
Angle of repose
Slump
Earthflow
Absorbed →
causes warming
Reflected →
no warming
Solar Energy =
short wave radiation
Grenhouses Gases
Water vapor, H2O
Carbon Dioxide, CO2
Methane, CH4
Nitric Oxide, NO2
Ozone, O3
Hydrocarbons
Chlorofluorocarbons
Non-Greenhouse Gases
Nitrogen, N2
Oxygen, O2
Argon, Ar
Carbon Monoxide, CO
Sulfur Dioxide, SO2
Greenhouse Effect
Natural
Would still be operating in the absence of human life
necessary for our planet to be habitable
Humans are changing how strong the greenhouse effect is by altering the amount of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere
Climate and Soil Formation
Tempature and precipararion most important
Determines whether mechanical or chemical weathering predominates
Determines the depth of soil formation:
Warm, wet climates produce a tick layer of chemically weathered soil
Cool, dry climates produce a thin layer of mechanically weathered soil
Paths of Incoming Solar Energy
50% of solar energy passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed on Earth’s surface
20% is absorbed by clouds and atmospheric gases
Including oxygen and ozone
30% is reflected back into space
By clouds, atmosphere, snow, and ice
Rising CO2 levels
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas
short-wavelength solar radiation passes through to Earth but slows long-wavelength Earth radiation from passing back into space
Humans add CO2 to the atmosphere
Burning fossil fuels
Deforestation
CO2 levels are highest in the past 600,000 years
Oxygen Isotope Analysis
The precise measurement of the ratio of 18O/16O
Ratios are trapped in calcium carbonate shells or marine organisms
Ration varies with the amount of sea ice and water tempature
Climate change recorded in glacial ice
Some ice cores represent more than 200,000 years of climate history
Ice can be analyzed for:
a. Oxygen isotope analysis
b. Carbon dioxide and methane (air bubbles trapped in the ice)
c. Dust, volcanic ash, pollen
Tree Rings: Archives of environmental history
Growth rings are added each year
The thickness and density of rings reflect environmental conditions
In certain regions, ring chronologies extend back thousands of years
Other types of proxy data
Fossil pollen
Pollen can provide high-resolution records of vegetation changes in a region
Regional vegetation is climate-dependent
Corals
With oxygen isotope analysis, corals are used as paleothermometers and precipitation proxies
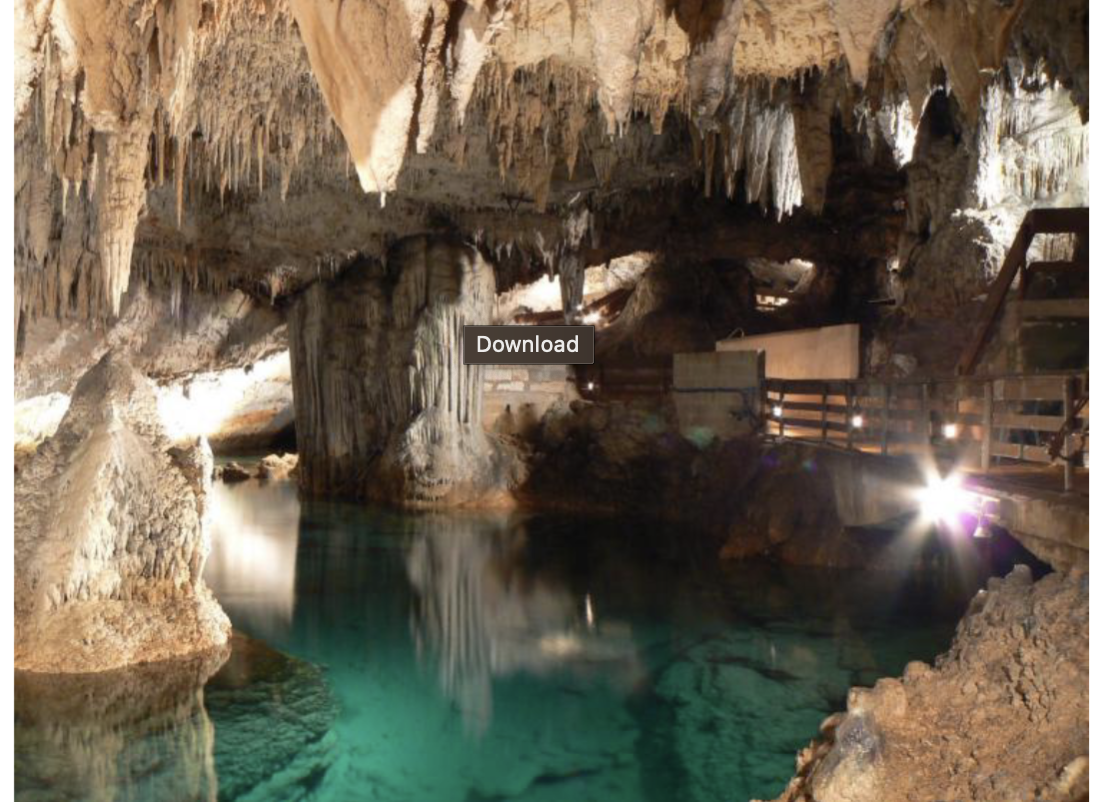

Chemical Weathering
water
rain water and carbonic acid

Differential Weathering
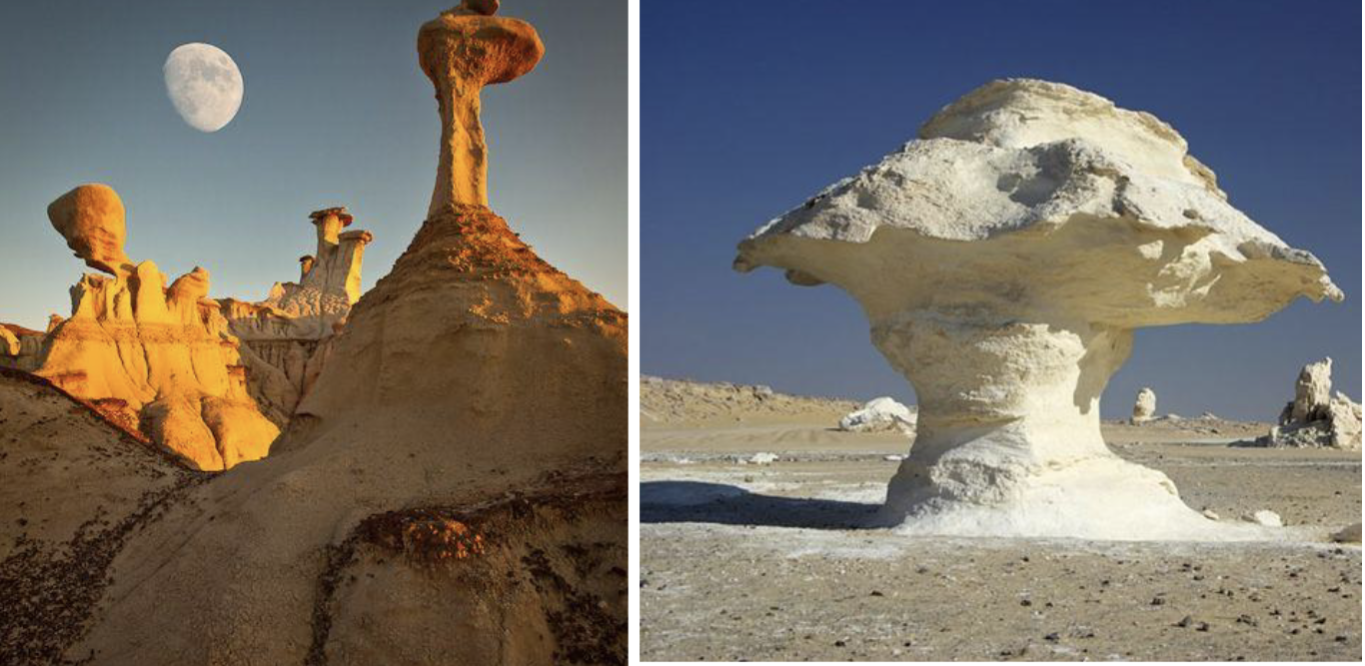

Formations of Landforms
Erosion cuts vertically down into rocks
If streams alone were creating landform, the valley would be deep and very steep sided
Mass wasting creates river valleys wider than they are deep
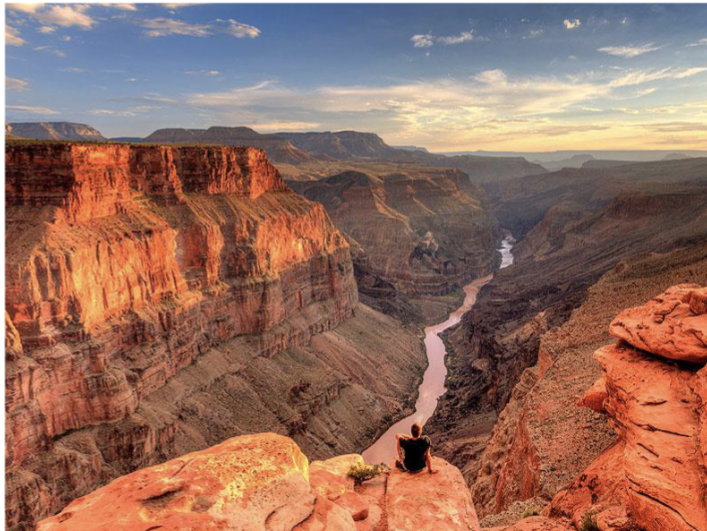

Mass Wasting
Downslope movement of rock and soil under the direct influence of gravity
Can be fast or slow
Includes mudslides, lahars, landslides, rock avalanches, soil creep
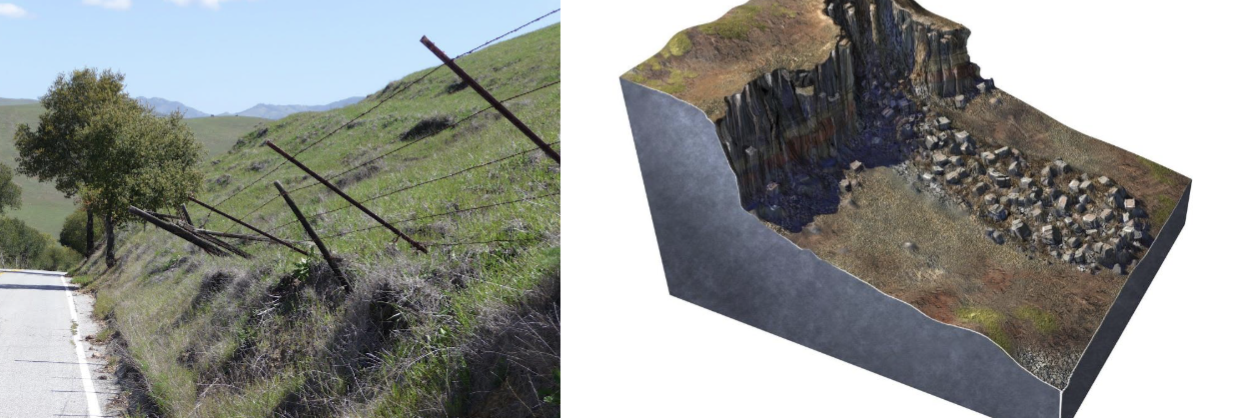
Controls on Mass Wasting: Oversteepened slopes
Consolidated soils or rocks can experience overstepping
Steepness that can be maintained depends on the material present
Won’t move immediately like unconsolidated material
Will eventually lead to mass wasting & less steep slopes → restores stability
Controls on Mass Wasting: Removal of Vegetation
Roots bind soil and regolith together
Protect against raindrop impact and erosion
Cutting down trees for agriculture
Replacing deep-rooted plants with shallow-rooted plants
Wildfires all increase the likelihood of mass wasting
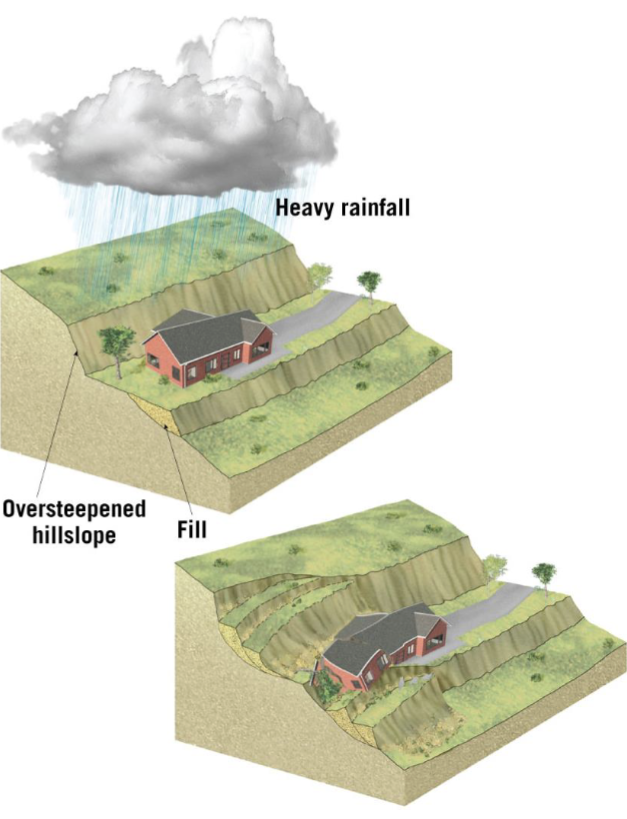
Triggers of Mass Wasting Events: Addition of Water
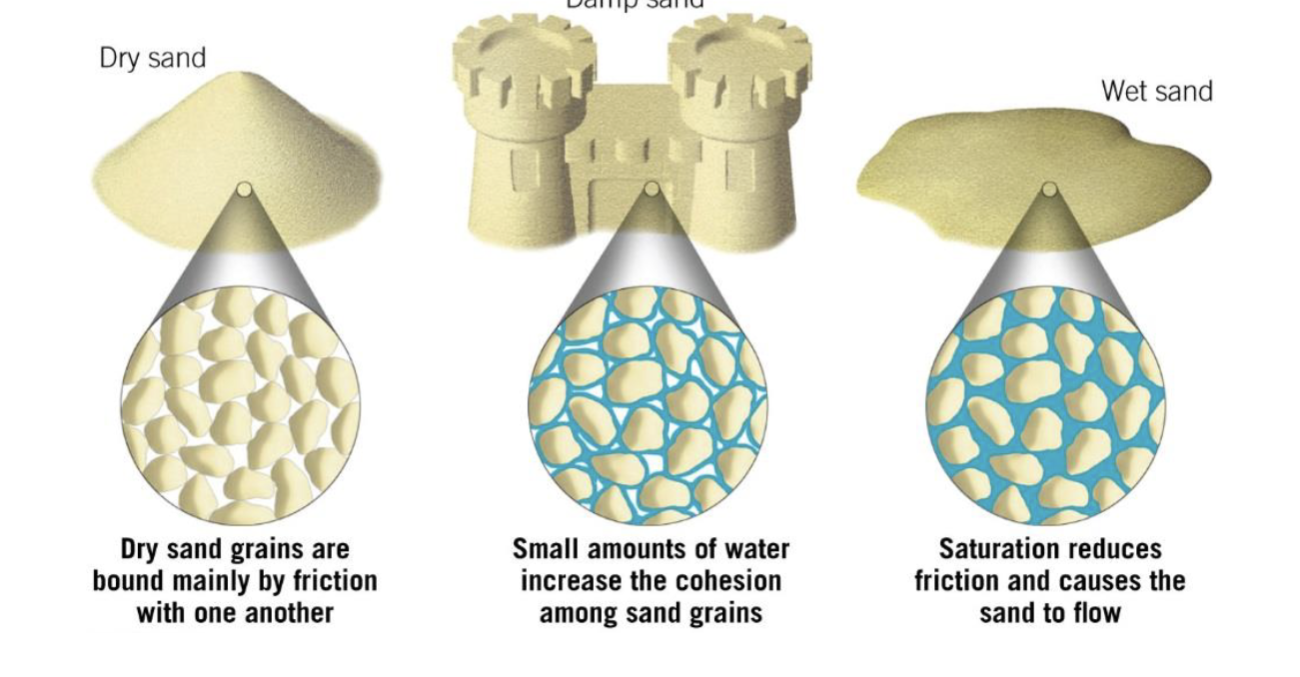
water foes not transport the material, but weakens cohesion
“Lubrication’ of grains allows gravity to move the material more easily
Adds weight to the sediments, increasing the effects of gravity
Heavy rains, melting glaciers
Triggers of Mass Wasting Events: Oversteepened slopes
Unconsolidated particles assume a stable slope at the angle of repose
different for various materials
Natural processes, such as stream cuts, oversteepen a slope
Triggers of Mass Wasting Events: Earthquakes
Conditions that favor mass wasting can exist for a long time before anything happens
Shaking from an earthquake may trigger any kind of mass wasting event
Intense shaking of water-saturated materials may cause them to behave like a liquid in a process known as liquification
Triggers of Mass Wasting Events
No specific Trigger
Sometimes rapid mass wasting events happen with no discernible trigger
Slope materials gradually weaken due to long-term weathering and the infiltration of water
Eventually gives out and falls
Process essential random and very difficulty to predict in terms of timing
Classification of Mass Wasting Events: Material
Soil or regolith - Debris, mud, earth
Bedrock = Rock
Classification of Mass Wasting Events: Motion
Fall= free fall of detached pieces
Slide= distinct zone of weakness
Flow= move as a viscous fluid to create lobes or tongues
Classification of Mass Wasting Events: Rate of Movement
Fast
Intermediate
Slow = Creep
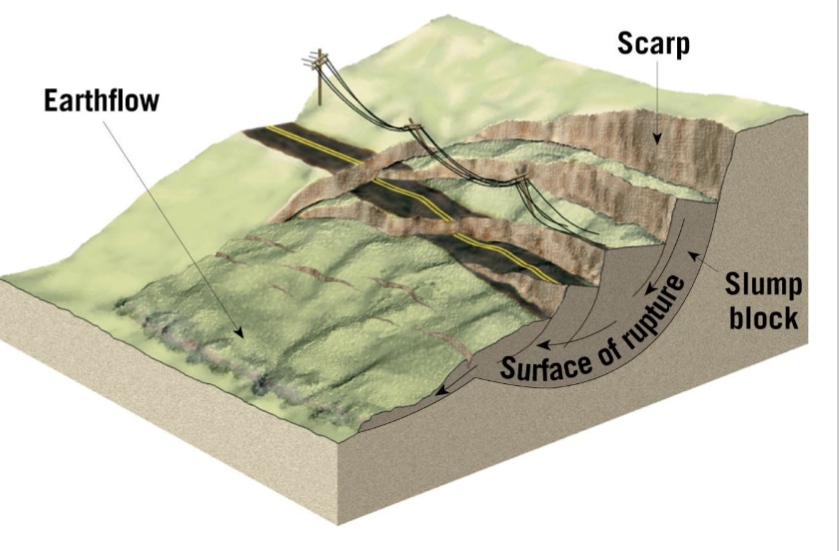
Slump
The movement of a mass of rock or unconsolidated material as a unit along a curved surface
can involve a single mass or multiple blocks
Occurs along oversteepened slopes
Moderate speed
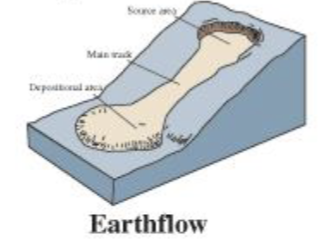
Earthflow
Earthflows form on hillsides in humid regions during heavy
precipitation or snowmeltCommonly involve materials rich in clay and silt
Create a tongue or teardrop-shaped mass that flows
downslopeTravel between 1 mm a day to several meters a day
Commonly associated with large slumps