AP Pysch U3 Development and Learning
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Chronological development
development from infancy to adulthood in chronologically ordered events
Lifespan development
developmental patterns of growth, change, and stability in behavior that occur throughout the entire life span
Stability and change
Certain aspects of our persona, such as temperament, remain consistent (Stability). Conversely, factors like our social attitudes exhibit more variability, particularly during the transformative adolescent years (Change).
Nature and nurture
Genetic traits (Nature) such as temperament and personality influence social behavior, while environmental factors (Nuture) such as parenting styles, peer relationships, and cultural norms and values shape social development.
Continuous development vs Discontinuous development
Growth is a gradual and continuous process, vs biological maturation leading to distinct stages or phases.
Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that harm the embryo/fetus during prenatal development
Fine motor coordination
small muscle groups
finger dexterity and/or skilled manipulation of objects with the hands
Gross motor coordination
Large muscle movements as in running, walking, skipping, and throwing.
Maturation
Biological processes changing our behavior as we age, uninfluenced by external factors.
Reflexes
specific patterns of motor responses triggered by specific patterns of sensory stimulation
Rooting reflex
infant reflex
when touched on the cheek, infant turns towards source for touch, opens mouth, and searches for nipple
Visual cliff
device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
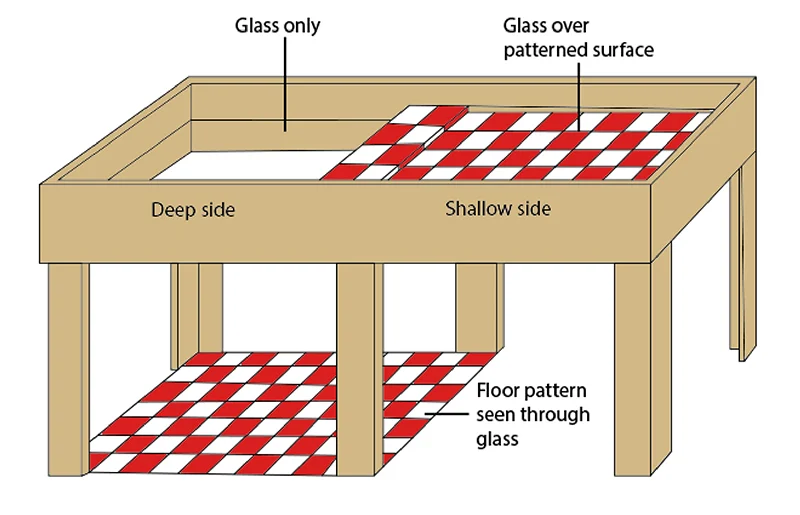
Critical periods
Periods of time in developmental sequence where certain kinds of environmental/social/sensory experiences
Sensitive periods
time periods when specific skills develop most easily, brain is especially receptive to certain stimuli
Imprinting
the process by which certain animals form strong attachments during an early-life critical period
Growth spurt
something I didn’t have smh
The relatively sudden and rapid physical growth that occurs during puberty (and infancy). Each body part increases in size on a schedule: Weight usually precedes height, and growth of the limbs precedes growth of the torso. (that’s why guys have gangly arms and legs)
Puberty
sexual maturation, a person becomes capable of reproducing
Primary sex characteristics
characteristics directly relating to reproduction, ex.(ovaries, testes, and external genitalia)
Secondary sex characteristics
non-reproductive sexual characteristics, ex. body hair, breasts, deep male voices, etc.
Menarche
first menstrual cycle
Spermarche
first ejaculation
Menopause
menstrual cycles stop, around 50 years of age.
schemas
mental concepts/frameworks we use to label and understand the world.
Assimilation vs Accommodation
interpreting new information using our existing schemas vs adapting schemas to fit new information
sensorimotor stage
from Piaget's theory, 0-24 months, infants interpret the world via sensory impressions and motor activities
In sensory motor stage: Object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived
Preoperational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
In this stage: Mental symbols
represent objects in the real world
Pretend play
make-believe activities in which children create new symbolic relations, acting as if they were in a situation different from their actual one
Conservation
the principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects.
Reversibility
the capacity to think through a series of steps and then mentally reverse direction, returning to the starting point
Animism
Belief that objects, such as plants and stones, or natural events, like thunderstorms and earthquakes, have a discrete spirit and conscious life.
Egocentrism
Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty to comphrend another’s point of view
Theory of mind
not everyone is exactly like you.
An awareness that other people's behavior may be influenced by beliefs, desires, and emotions that differ from one's own.
Concrete operational stage
7-12, elementary-intermediate
-2D thinking
-learn to think logically based on the things they have experienced
-math and science
ex: can do multiplication and division, but not algebra
Systematic thinking
approaches problems in a rational and analytical fashion
Formal operational stage
12+
-3D thinking
-Abstract reasoning (justice, love, fairness, etc)
-manipulate objects in our mind (i can do that :D)
-Hypothetical situations
-meta-cognition-thinking about thinking
-Plan ahead
Abstract thinking
Thinking about ideas and concepts, ex. what is love? baby don’t hurt me
Hypothetical thinking
bruh Thinking that is based on what is possible, and not just what is real, "if-then" thinking.
Scaffolding
temporary support to reach a new, higher level
Zone of proximal development
things the learner can do with help
Crystallized intelligence
Accumulated knowledge
Fluid intelligence
Reasoning + problem solving (working memory)
Dementia
Progressive decline in mental abilities and memory. Personality changes, thinking impaired
Phonemes
in language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
ex: cat has 3 c/a/t/
Morphemes
the smallest unit of meaning
ex; prefixes/roots/suffixes
ex: un/reach/able
Semantics
-the set of rules by which we derive meaning from morphemes, words, and sentences in a given language
- the meaning and interpretation of words, signs, and sentence structure
Grammar
Rules that allow us to communicate with and understand others
Syntax
Specific arrangement of words/phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language.
Cooing
0-6 months- early vowel-like sounds
Babbling
6-8 months- infant spontaneously utters nonsense sounds
One-word stage
age 1 to 2 - child speaks mostly in single words
Telegraphic speech
early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram—"go car"—using mostly nouns and verbs.
Overgeneralization of language rules
I goed to the park when I saw two mouses. There were some womans wered screaming
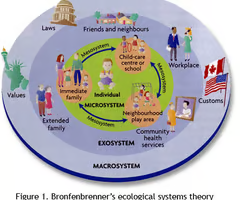
Ecological systems theory
Social environment effect on development
Microsystem
groups that have direct contact with you
ex: friends, parents, teachers, coworkers
Mesosystem
the relationships between groups in the microsystem
ex: how do these relationships guide development
ex: how does student-parent relationship effect development
Exosystem
indirect factors in an individual's life
ex: problems in the parents and teachers life that may effect the student
good picur
authoritarian
high demands/low responsiveness
-successful in future
-anxious
-insecure
Ex: authoritarian=dictator
authoritative
Optimal parenting style
high demand/high responsiveness
-gives freedom, but stay inside the box
-Grow up to be: confident, self reliant, happier, more successfu
Permissive
low demand/high responsiveness
-Will comfort you, but no demands
-Grow up to be: less mature, more impulsive, more dependent, more demanding, less successful
Neglectful
its not a vocab word but imma still do it
low demand/low responsiveness
-Neglectful
-No emotional bonds, often have low self esteem
Attachment Styles
behavior people exhibit in relationships, based on attachment to caregivers early in life
4 types: secure, dismissive, preoccupied, fearful
Secure attachment
Distressed when mother leaves, Positive and happy when mother returns.
self-assured, direct, responsive
develops trust
Insecure attatchment
Anxiety and avoidance of trusting relationships.
3 types: Avoidant, Anxious, and Disorganized
Avoidant attachment
No sign of distress when the the mother leaves, The Infant shows little interest when the mother returns.
Avoidance and lack of commitment in relationships
Anxious Attachment
Intense distress when the mother leaves, Mother in unable to comfort.
Clingy in relationships
Disorganized attachment
Inconsistent reactions to the caregiver's departure and return
yall tweaking in them relationships
Temperament
emotional reactivity and intensity
ex: difficult vs easy-going
Separation Anxiety
distress when caregiver is absent
Parallel Play
physically in same spot, but doing their own thing/play
Ability to like zone out
Pretend play
assigning different, symbolic roles to objects/people
so, roleplay
egocentrism
inability to comprehend other people’s perspectives
ex A young child covering their eyes and believing they are invisible.
Imaginary Audience
the tendency of adolescents to see themselves as the object of others' attention and evaluation
Ex: "they're all staring at me"
personal fable
A belief that they are special and unique, so much so that none of lifes difficulties or problems will affect them regardless of behavior
Ex: thinking they're invincible, so they take risks like drinking and driving
Social Clock
when adulthood begins and when major life events occur, ex marriage, dating, retirement, etc
Emerging adulthood
the transitional period from adolescence to adulthood, spanning approximately 18 to 25 years of age
stage theory of psychosocial development
people must resolve psychosocial conflicts at each stage of the lifespan (8 of them)
Trust and mistrust
1st year
-caregiver and environment must show care for baby, and baby trusts that they will (trust in humanity)
If doesn't happen: suspicion, fear of future events
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
2nd year
Needs to feel independence, and self adequacy
If doesn't happen: feelings of shame and self doubt
Intiative vs guilt
3rd-5th year
need to be a "self-starter" "friendships"
If doesn't happen: sense of guilt and inadequacy to be on ones own
Industry vs inferiority
6th year-puberty
Need to learn how things work, to understand organization
If doesn't happen: a sense of inferiority at understanding and organizing
"I can't keep up" "I'm a failure"
Identity vs Confusion
adolescence-25 years
Needs to become a unique and integrated person
If doesn't happen: confusion over who and what one really is
INDETITY CRISISIS
Intimacy vs Isolation
early adulthood 25-35
Need to make commitments to others, to love
if doesn't happen: inability to form affectionate relationships (what many people regret when older)
Generativity vs stagnation
middle age
Need family to care for and participate in society
If doesn't happen: concern only for self, one's own well being and prosperity, feeling of stagnancy.
Integrity vs despair
senior-death
Need a sense of integrity and fulfillment, a willingness to face death
If doesn't happen: dissatisfaction with life, despair over prospect of death
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
Stressful or traumatic experiences, including:
abuse
neglect
household dysfunction
domestic violence
growing up seeing substance abuse
mental disorders
parental discord
crime
among many other things.
Achievement (adolescent development)
Achieving identity as an adolescent through reflection and thought.
Diffusion (adolescent development)
You haven't begun to think things through about your identity
just living day by day
literally 90% of people literally im smh, so annoying when ppl don’t overthink their identity
Foreclosure (adolescent development)
your identity is based on what others want from you (parents say you are going to be this, or go to this school)
Moratorium
process of figuring out ur identity (me rn literally crashing out)
Racial/ethnic identity
ur race, ex african american
Sexual orientation
ex i’m gay
Religious identity
ex chirstian
Occupational identity
ex, i am a doctor
Familial identity
ex i am a daughter and sister
Possible selves
a person's ideas of what they might become, what they would like to become, and what they fear becoming, etc.
Behavioral perspective
All behaviors are learned through interactions with the environment, emphasizing stimulus-response relationships and conditioning.
Classical conditioning
a neutral stimulus, when repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus, eventually elicits a conditioned response
bell with food= saliva with bell