IB Biology Ecology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Saprotrophs
-Heterotrophs that obtain organic nutrients from dead organisms by external digestion.
-Secrete digestive enzymes into the material they are going to feed upon
-Usually fungi or bacteria
Heterotrophic Plants
-Venus Fly Trap
-Pitcher Plants
-Dodder (feeds on stems of other plants)
-Ghost Orchid (obtains carbon compounds from fungi living on the roots of trees)
Combustion in the Carbon Cycle
-Non-biological process
-Occurs naturally
-Biomass burns which releases CO2
-Over time, combustion has increased
Flux/gigatons year^-1 for Photosynthesis
-120
Flux/gigatons year^-1 for Combustion of fossil fuels
+6.4
Global Temperatures and Carbon Dioxide Concentrations
-To deduce carbon dioxide concentrations and temperatures in the past, columns of ice have been drilled in the Antarctic
-Deeper down the ice is older than ice on surface
-Bubbles of air trapped in ice can be used to get carbon dioxide concentration
-Global temperatures can be found from ratios of hydrogen isotopes from water molecules
Examples of Population
-All the bees in a hive
-All the pigeons in New York City.
Autotrophs
Organisms that make their own food
(Sunflowers, oak trees, roses)
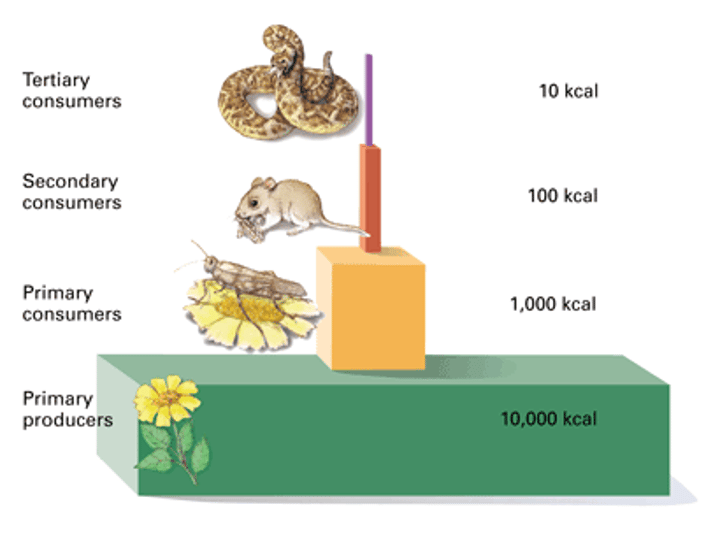
Energy Pyramid
Greenhouse Gases
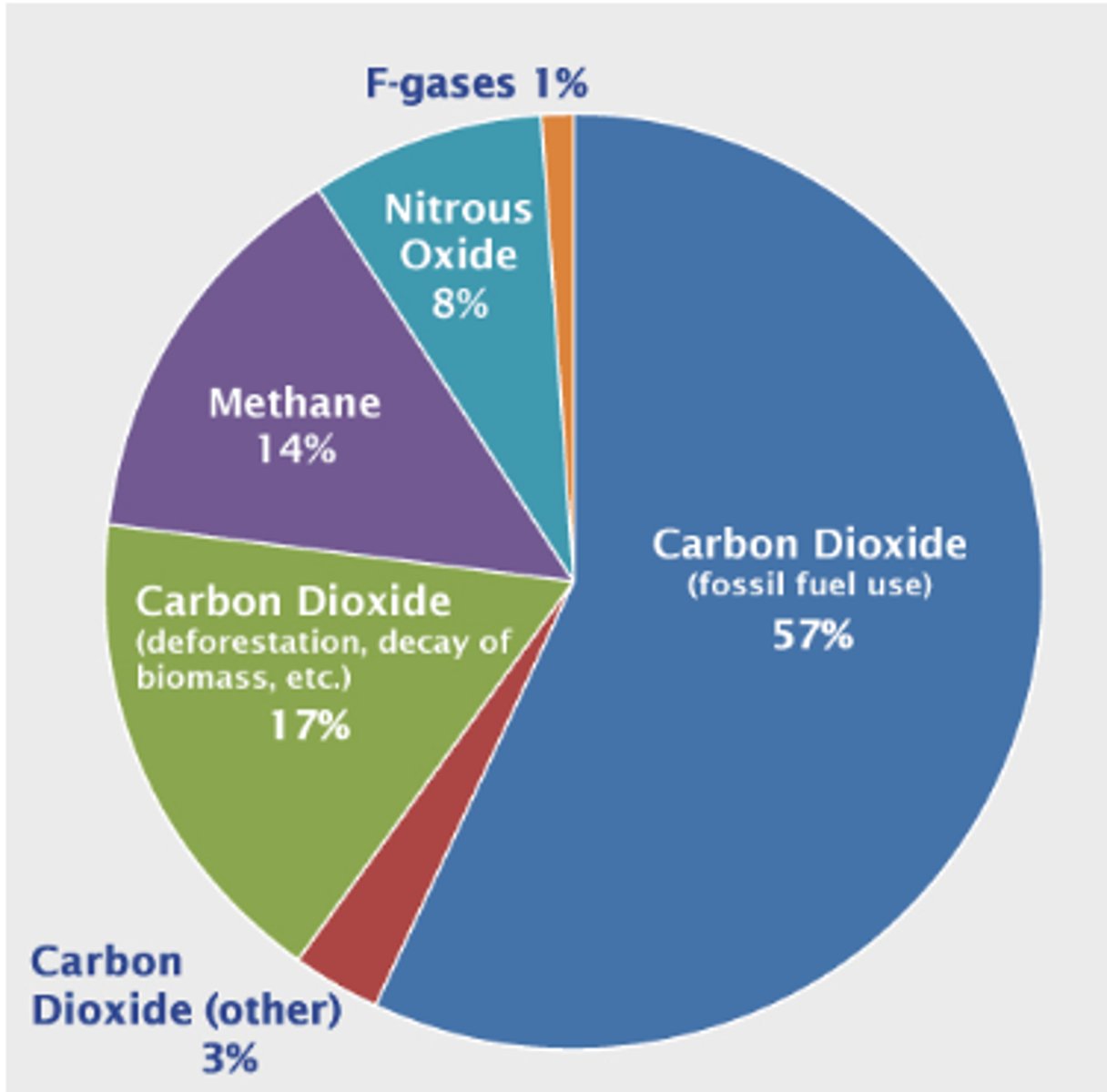
-Gases in the atmosphere that have the ability to trap long-wave radiation
-Carbon dioxide and water vapor are the most significant
-Water vapor isn't shown in charts because it is difficult to assess
Species
A group of organisms with similar characteristics, which can potentially interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Example of Species
Homo sapiens (humans)
Felis catus (domestic cats)
Pan troglodyte (chimpanzees)
Population
A group of organisms of the same species, who live in the same area at the same time
Members of a species may be reproductively isolated in separated populations, but as long as they could still interbreed if the populations came together again, they are the same species.
For example, the wood mouse lives in Britain and on Iceland.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that depend on other organisms for their food.
(Humans, tigers, deer, pandas)
Detritivores
-Heterotroph
-Obtain organic nutrients from dead organic matter (dead leaves, feces, decomposing animals)
Example of Detritivore
Larvae of the was moth feed upon old wax combs created by honey bees
Community
A group of different populations living together and interacting with each other in an area
Detritivores vs Saprotrophs
Saprotrophs secrete enzymes that digest dead material externally, whereas detritivores digest internally
Mesocosms
A small experimental area set up in an ecological research program
Considerations taken into creating a mesocosm
-Seal to prevent entry or exit of all chemical substances
-Autotrophs needed to produce carbon compounds and regenerate oxygen
Considerations taken into creating a mesocosm (pt. 2)
-Saprotroph needed to decompose dead organic matter and recycle nutrients
-Consumers and detritivores aren't necessary, but usually are included
-Large animals should NOT be included
Energy Source
1. Plants, algae, and some bacteria, convert light into chemical energy (photosynthesis)
2. Consumers, detritivores, and saprotrophs obtain energy from their food (chemical compounds get passed)
Energy Losses
-At each successive stage, energy is lost through three ways
-Some organisms die before they are eaten
-Some parts of organisms can't be eaten (like bones)
-Some organisms are undigestible (like cellulose for humans)
Trophic Levels
Producers -> Primary Consumers -> Secondary Consumers -> Tertiary Consumers -> Quaternary Consumers
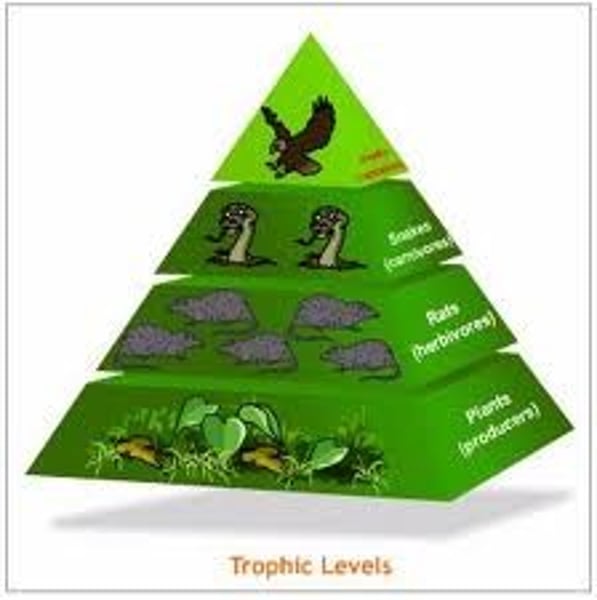
How much energy is passed to each successive level?
10%
Unit of Energy
kJ(m^-2)(y^-1)
Nutrient Recycling
The process of breaking down materials into a different form that can be used again
Energy
-Supplied to ecosystems in the form of light and converted to chemical energy by producers
-Chemical energy is used in living cell and is converted into heat, which can't be recycled
Ecosystems
-Have limited supplies of nutrients
-Supply of nutrients don't run out because nutrients can be recycled
Carbon Cycle
The movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back
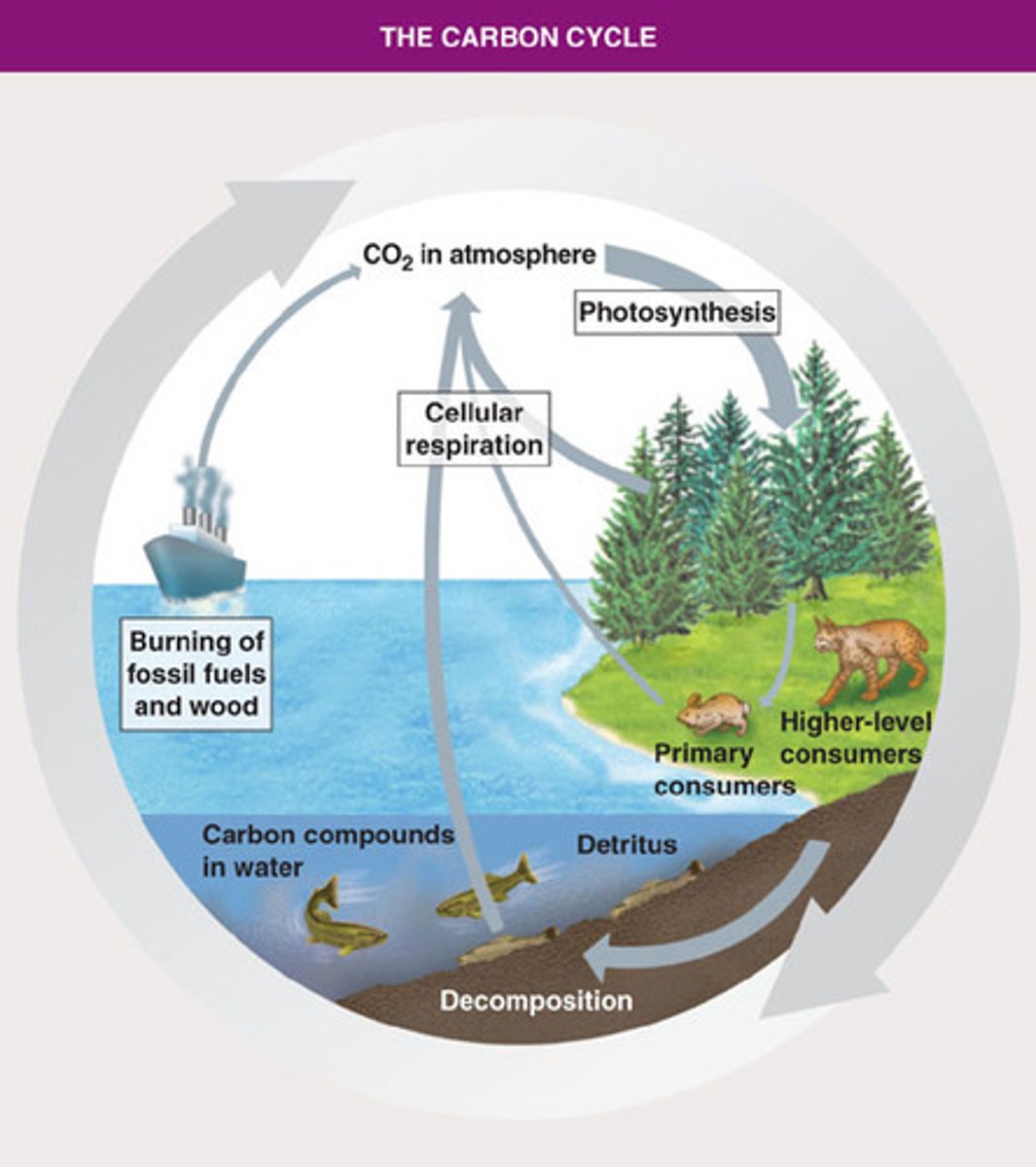
Fluxes in Carbon Cycle
-Transfers of carbon
-Thickness of arrow indicates size of a flux
Sinks of Carbon Cycle
-Methods of carbon storage in ecosystems
-Sink of methane in the atmosphere could be added and also methane fluxes
Methane in the Carbon Cycle
-Produced naturally by methanogenic archaeans (prokaryotes)
-Breaks down organic matter and produces methane as a waste product
-Methane accumulates in ground or diffuses in atmosphere
Flux/gigatons year^-1 for Cell Respiration
+119.6
Flux/gigatons year^-1 for Ocean Uptake
-92.2
Flux/gigatons year^-1 for Ocean Loss
+90.6
Flux/gigatons year^-1 for Deforestation and Land Use Changes
+1.6
Limestone in the Carbon Cycle
-Consists mainly of calcium carbonate (CaCO)
-Contains many fossils (e.g mollusk shells and skeletons of hard corals)
-These organisms absorb calcium and carbonate ions, then secrete calcium carbonate
-Fossils fall down to sea bed and builds up coral reefs
-Carbon is released when limestone reacts to anything that contains acid (like rainwater)
Peat and Coal
-Saprotrophs can't break down organic matter in acidic and anaerobic conditions
-Partially decomposed plant matter accumulates to form thick deposits called Peats
-Peat gets crushed and converted into coal
Silt
Fine soil found on river bottoms
Oil and Gas
-Silt is deposited on the bed of some shallow seas with remains of dead marine organisms
-Organic matter is not fully decomposed due to anaerobic conditions
-Silt is converted to shale with compounds from the organic matter becoming oil or gas trapped in pores in the rock
The Greenhouse Effect
-Warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere
-25% of short wavelength radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere with the rest of the radiation reaching Earth's surface
-Of the radiation that reaches Earth's surface, 70%-80% is trapped by gases in the atmosphere which causes heat to be trapped
Greenhouse Gases Chart
Correlation between Global Temperatures and Carbon Dioxide Concentrations
-Repeating pattern of rapid periods of warming followed by longer periods of gradual cooling
-Temperature correlates with CO2 concentrations
-CORRELATION DOES NOT EQUAL CAUSATION
Coral Reefs and Carbon Dioxide
-CO2 production from humans have caused pH drop from 8.25 to 8.14 (representing 30% acidification)
-When carbon dioxide reacts with water, it breaks down the coral reefs which reduces amount of calcium carbonate present