1.2 Forces 🏗️
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Physics Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Motion, Force, Moments, Energy, Density, Kinetic Theory and Radioactivity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What is a force?
a push or a pull in a particular direction, either contact or non-contact
Moment of a force
turning effect produced when force(s) cause object to turn/ rotate about a pivot
Pivot (fulcrum)
The point about which moments act in a clockwise or anticlockwise direction
The equation linking moment of a force, force and distance
M = Fd
Moment = force * distance
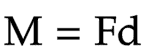
Unit for moment of a force
Newton-metre (Nm)
Unit for force
Newtons (N)
Unit for distance
Metres (m)
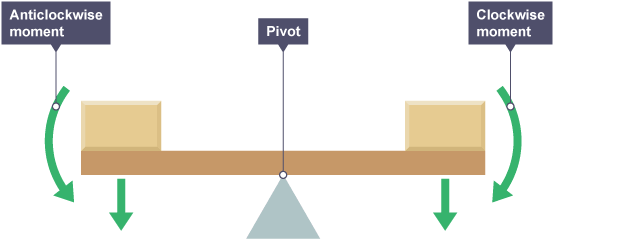
Principle of moments
the total clockwise moments about a pivot is equal to the total anticlockwise moments in equilibrium
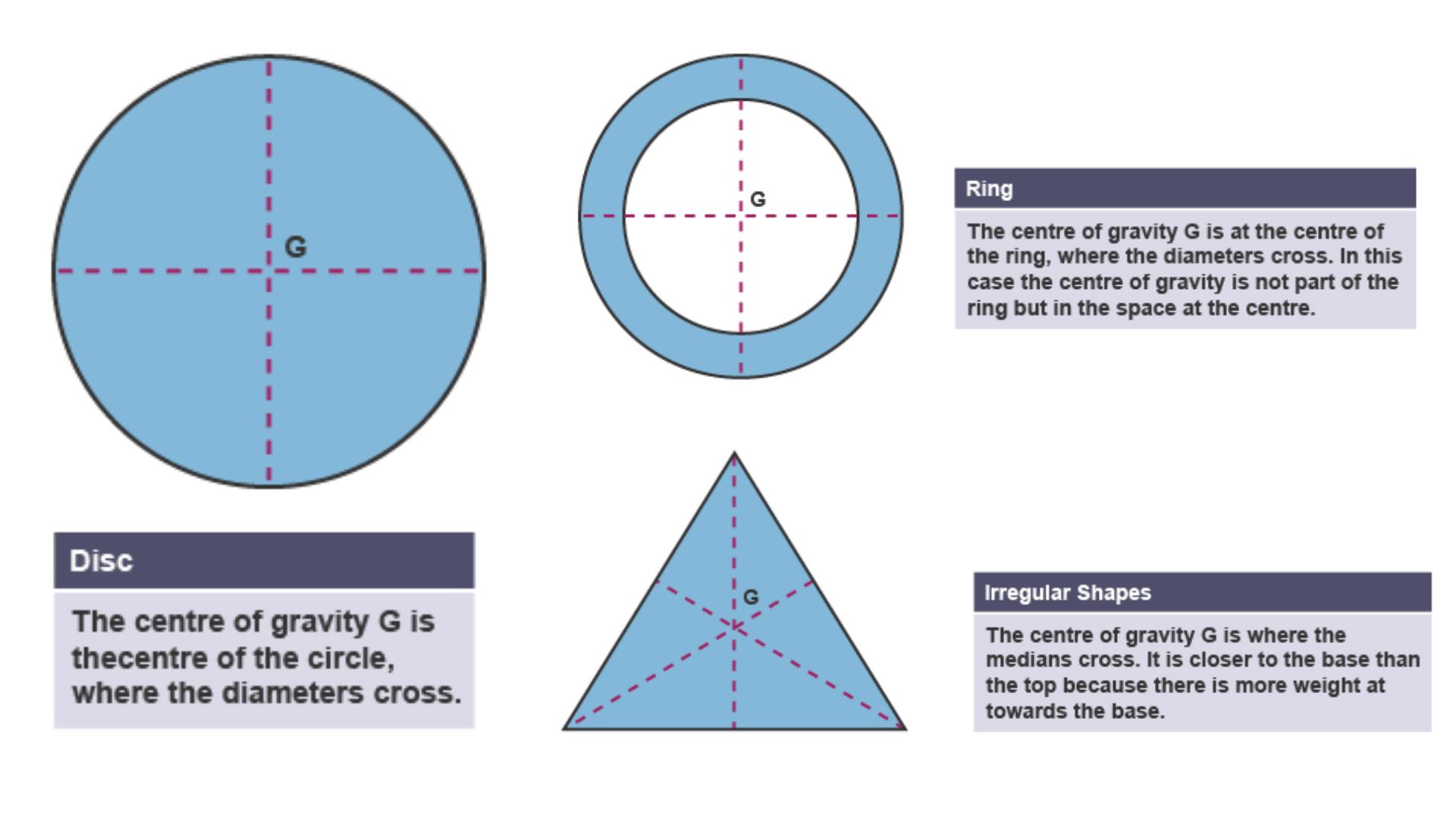
Centre of gravity
The point at which the entire weight of an object can be considered to act
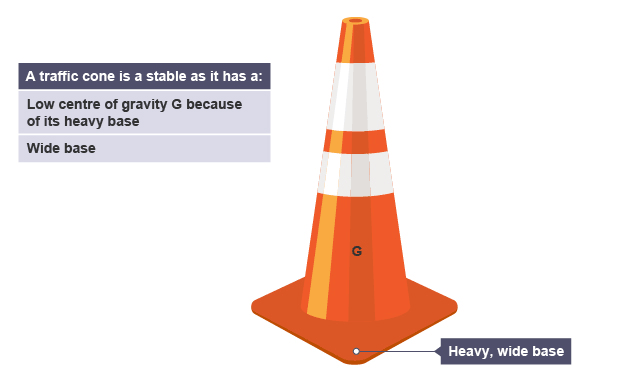
Stablility
An object resists tipping over if line of action falls within its base and it has a low centre of gravity
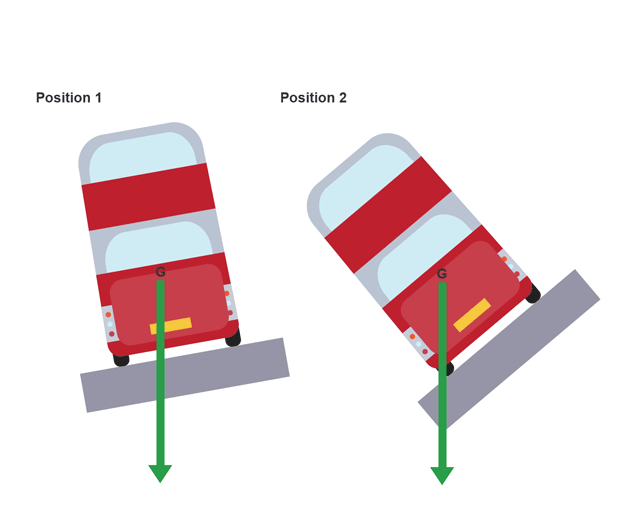
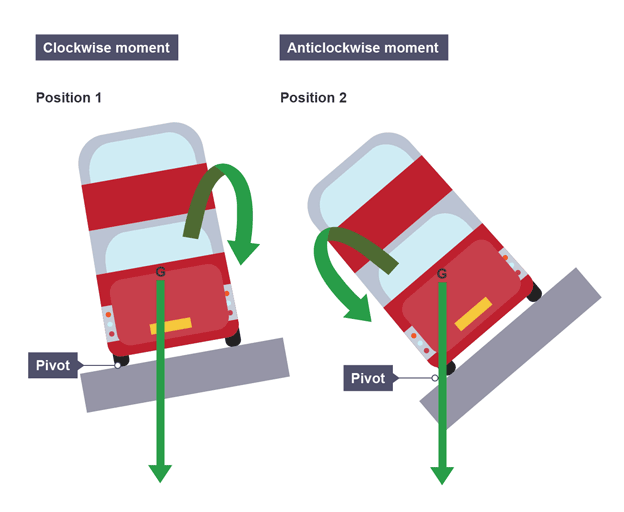
What will happen to the bus
Position 1
Does not topple over
Centre of gravity is inside the wheel base, producing a clockwise moment to pull the bus back onto its base
Position 2
Topples over
Centre of gravity is outside the wheel base, producing an anticlockwise moment to pull the bus off its base and on to its side
Newton's First Law
in the absence of unbalanced forces an object will continue to move in a straight line at constant speed
Resultant force
single force with the same effect as original forces acting together
When the resultant force is zero
object is stationary or continues to move at the same speed/direction
Newton's Second Law
acceleration is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to the mass
The equation linking resultant force, mass and acceleration
Resultant force = mass * acceleration
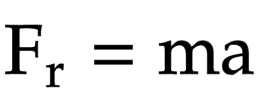
Unit for mass
Kilograms (kg)
Unit for acceleration
Metres per second squared (m/s²)
Newton's Third Law
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
Inertia
an object continues in their state of rest or in uniform motion
Inertial mass
how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object, a heavier object is harder
Deformation
change of shape/ size as a result of forces being applied
Conditions required to deform a stationary object
must be more than one force acting on the object
Extension
increase in length/ size as a result of an object being stretched
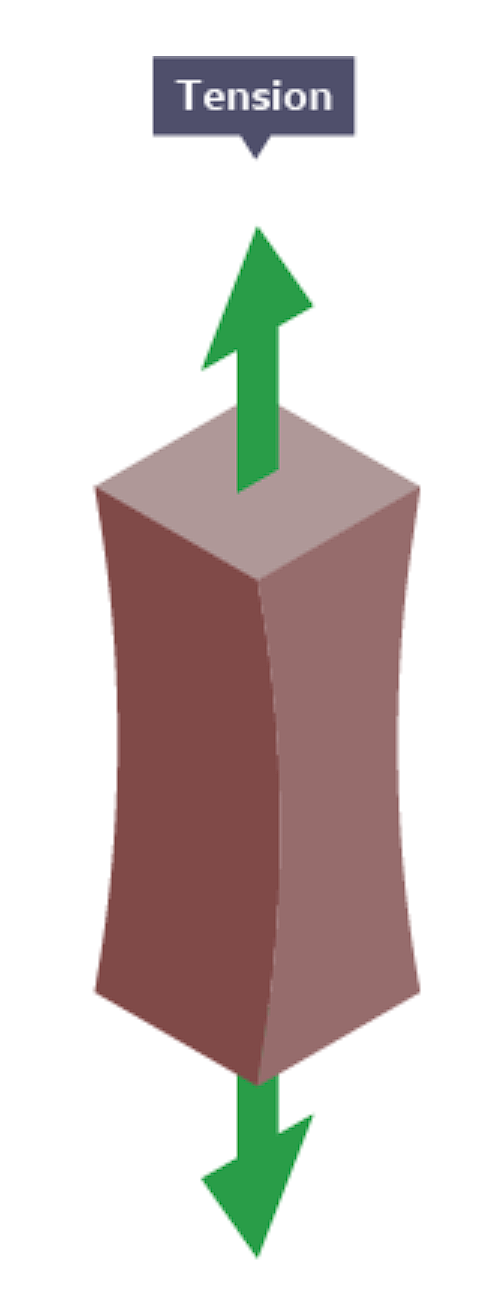
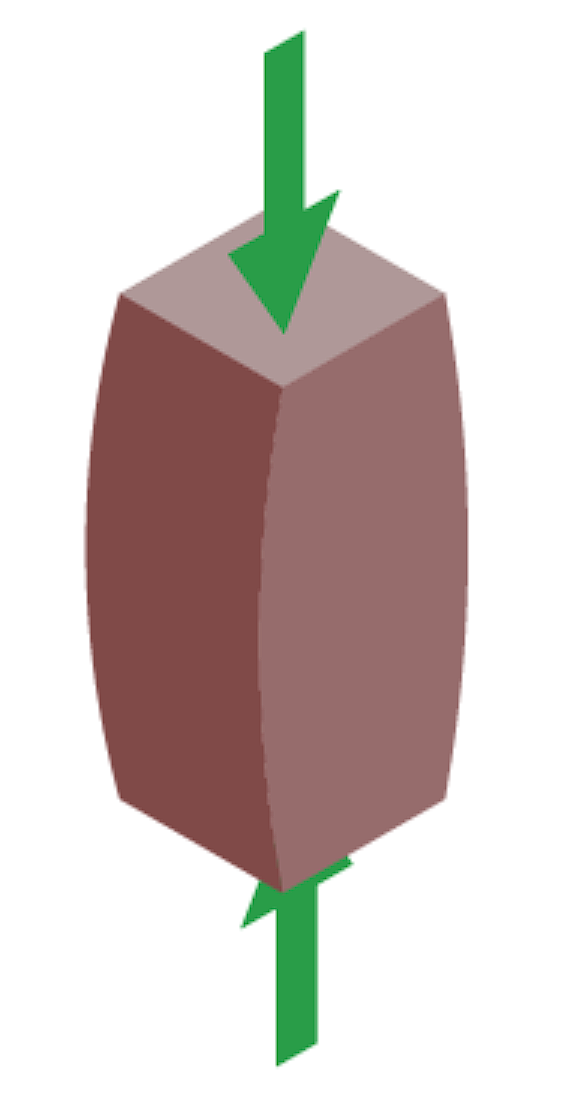
Compression
reduction in length/ size as a result of an object being squashed

Acceleration of free fall (gravity)
when ignoring air resistance, object falling freely from rest will accelerate at rate of 10 m/s2 regardless of mass
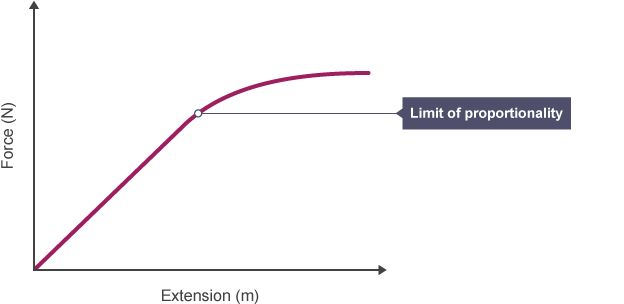
Hooke's Law
extension is directly proportional to force applied, provided limit of proportionality isn’t exceeded
Limit of proportionality
point beyond which Hooke's law is no longer obeyed
The equation linking force, spring constant and extension/compression
force = spring constant * extension
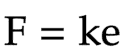
Unit for spring constant
Newtons per metre (N/m)
Unit for extension
Metres (m)
Spring constant
measure of the stiffness of a spring
Relationship between spring constant and extension
higher the spring constant, the stiffer the spring
Scalar quantity
quantity that has a magnitude (size) only
Examples of scalar quantities
Speed, temperature, mass, energy, distance, density
Vector quantity
quantity that has a magnitude and direction
Examples of vector quantities
Velocity, force, displacement, acceleration, momentum
Contact forces
Forces between two objects that are physically touching each other
Examples of contact forces
friction, air resistance, tension
Non-contact forces
Forces between two objects that are not physically touching each other
Examples of non-contact forces
gravitational force, electrostatic force, magnetic force
Free body diagram
diagram showing all the forces acting on an object
Friction
Contact force that always opposes the motion of an object
Pressure
The force per unit area
the equation linking pressure, force and area
pressure = force ÷ area
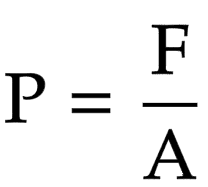
Unit for pressure
Pascals (Pa)
Unit for area
Square metres (m²)
A unit used for pressure that is equivalent to pascals (Pa)
Newtons per metre squared (N/m²)
How to increase pressure
Increase the force or decrease the area
Mass
the amount of matter in an object
Weight
force acting on an object due to gravity
Relationship between weight and mass
directly proportional to one another
The equation linking weight, mass and gravitational field strength
Weight = mass * gravity
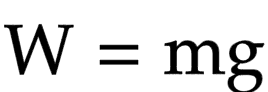
Unit for gravitational field strength
Newtons per kilograms (N/kg)
Newton meter
calibrated spring-balance used to measure an object's weight