ch8 food safety (microorganisms, characteristics, foodborne)
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
define foodborne pathogen
Virus, microorganism, or other substances that cause disease.
what is the pulsenet system
a national network of public health laboratories that per form a “fingerprinting” on bacteria that may be foodborne
safety of food is impacted by both ___________ and _________-
spoilage and contamination
define spoilage
Denotes unfitness for human consumption due to chemical or biological causes
define contamination
presence of harmful substances in food
typically is categorized as biological, physical, or chemical
Not always visible
what are the 4 criteria to ensure food is fit to eat
The desired stage of development or maturity of the food
Freedom from pollution at any stage in production and subsequent handling
Freedom from objectionable chemical and physical changes resulting from action of food enzymes; activity of microbes, insects, and rodents; invasion of parasites; and damage from pressure, freezing, heating, or drying
Freedom from microorganisms and parasites causing foodborne illnesses
define microorganisms
organisms too small to see so require microscope
-not all are harmful
define pathogens
Harmful microorganism that can cause illness or death.
categorized as bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi, and natural toxins
when does biological contamination occur
when harmful microorganisms contaminate food and cause foodborne illness
what are the most common foodborne agents (5)
Salmonella, Toxoplasma gondii, Listeria monoytogenes, Norovirus, and Campylobacter
F in FAT TOM (what it stands for and details)
Food- specifically carbohydrates and proteins
A in FAT TOM (what it stands for and details)
Acidity- a pH of 4.6 to 7.5 is ideal
T in FAT TOM (what it stands for and details)
Time- food should be in the temperature danger zone for limited amounts of time
T in FAT TOM (what it stands for and details)
Temperature- growth is best between 41°F and 135°F (5°C and 57°C)
O in FAT TOM (what it stands for and details)
Oxygen- some need oxygen, others do not
M in FAT TOM (what it stands for and details)
Moisture- water activity (Aw) of 0.85 or higher is ideal for growth
what is foodborne illness
disease transmitted to people through food
-2 or more people with same symptoms after eating same foods
who is highest risk for foodborne illness (3)
elderly, preschool ages children, people with compromised immune system
define bacteria
Bacteria are microscopic, unicellular organisms of varying size and shape, including spherical, rod, and spiral
what are the most common bacteria to cause foodborne infections (4)
Campylobacter, Nontyphoidal Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli O157:H7
what is the growth log of bacteria and its stages
lag phase, log phase, stationary phase, and death phase
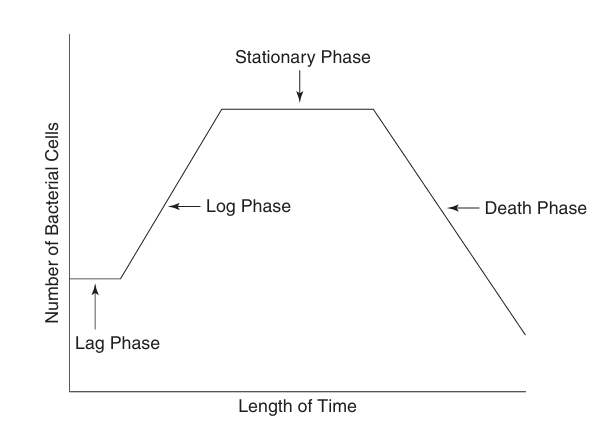
lag phase
Lag phase- initial stage where, although bacterial cells exist, little to no growth occurs
log phase
Log phase- a period of rapid growth in a relatively short period of time
stationary phase
Stationary phase- the rate of growth is slowed and eventually stops as bacterial cells begin to die
death phase
Death phase - bacterial cells die more rapidly, new cells are created due to lack of nutrients and the excess waste the cells create
what types of foods are most supportive of bacterial growth
high protein or carbs foods
what are the 6 things that affect bacterial growth
temp
time
pH
respiration
moisture
natural inhibitors
define pH value
degree of foods acidity or alkalinity
best pH for growth
near neutral (slightly acidic, neutral, and slightly alkaline food materials)
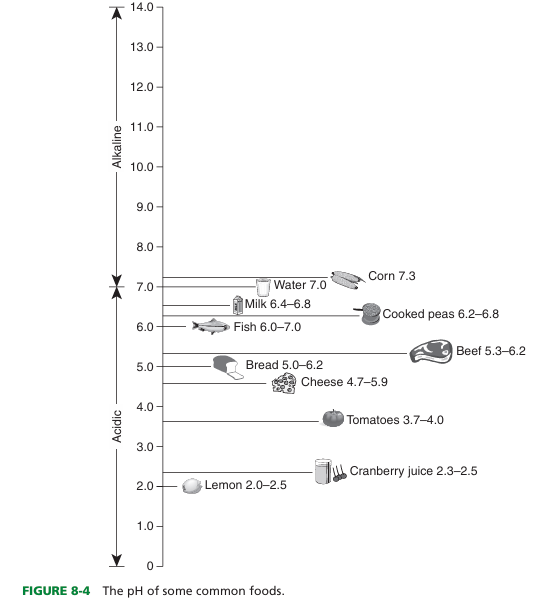
define time/temperature control for safety food (TCS)
Food items that require temperature control because they are capable of supporting growth of pathogenic microorganisms or toxin formation
food that require TCS usually have what characteristics (4)
high protein, moisture, neutral or slight acidic, and require time and temperature controls to prevent growth of microorganisms
- include products such as milk and dairy products, meat, poultry, pork, lamb, fish and shellfish, eggs, raw sprouts, baked potatoes, tofu, and sliced melons.
spores are what (what characteristics)
more resistant to high heat, low humidity, and other adverse conditions than are vegetative bacterial cells
They may remain dormant for long periods of time and germinate when conditions are favorable into new, sensitive, vegetative cells
define thermal death time
Time required at a specific temperature to kill a specified number of vegetative cells or spores
time and bacterial growth
need only a few hours to generate more than 4 million cells
-usually illness occurs in 4 hours
define aerobic and anaerobic bacteria
Aerobic bacteria- Bacteria that need oxygen to grow.
Anaerobic bacteria- Bacteria that reproduce without oxygen
what moisture do bacteria need to grow and reproduce
at least as of 0.85
define foodborne infection
Caused by activity of large numbers of bacterial cells carried by the food into the gastrointestinal tract.
define foodborne intoxication
caused by toxins formed in the food prior to consumption
Consumption of the toxins causes the illness
Quick onset (as little as 2 hrs)
what are the bacteria (11)
Salmonella
Shigella
Listeria monocytogenes
Staphylococcus aureus
Clostridium perfringens
Bacillus cereus
Clostridium botulinum
Campylobacter jejuni
Escherichia coli
Vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio vulnificus
Yersinia enterocolitica, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
salmonella
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 6-48 hours
duration: 2-3 days
symptoms: abdominal, pain, headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, diarrhea
source: water, soil, domestic and wild animals, also humans, specially as carriers
associated food: poultry and poultry salads, meat and meat products, milk, shell eggs egg custard and sauces, and other protein foods
is it spore former: no
prevention: avoids cross contamination, cook poultry to 165, cool cooked meats and poultry quickly, avoid fecal contamination from food handlers
shigella
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 12-50 hours
duration: undefined; depends on if treatment
symptoms: abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, chills, dehydration, vomiting
source: human feces, flies
associated food: potato, tuna, shrimp, turkey, macaroni salad, lettuce, moist and mixed foods, milk and milk products
is it spore former: no
prevention: avoid cross contamination, fecal contamination from handlers by having personal hygiene, use sanitary food and water sources, control flies, rapidly cool foods
listerila
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 3-70 days
duration: indefined; depends on treatmeant but has high fatality with immunocompromised
symptoms: nausea, vomiting, headache, fever, chills, backacke, meningitis
source: humans, domestic and wild animals, fowl, soil, water, mud
associated food: unpasteruized milk and cheese, veggies, poultry and meat, seafood, prepared, chilled, RTE foods
is it spore former: no
prevention: use only pasteurized milk and dairy, cook to correct temp, avoid contamination, clean and sanitize surfaces
staphylococcus aureus
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 1-6 hours
duration: 1-2 days
symptoms: nausea, diarrhea, vomit, dehydration
source: humans, also animals
associated food: reheated foods, ham and other meats, dairy products, custard, meat, egg, potato salad, cream filled pastries, other protein foods
is it spore former: YES
prevention: avoid contamination from bare hands, exclude sick food handlers, practice sanitary habits, proper heating, cooking, and refrigeration
clostridium perfringens
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 8-22 hours
duration: 24 hours, symptoms can last 2 weeks
symptoms: abdominal pain and diarrhea
source: humans (intestinal tract), animals and soil
associated food: cooked poultry and meat that is improperly cooked, held, or cooled
is it spore former: yes
prevention: careful time and temp control in cooling and reheating
bacillus cereus
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 1.2-5 hours, or 8-16 hours
duration: 6-24 hours
symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdomial cramps
source: soil, cereal crops
associated food: rice and rice dishes, custards, seasoning, dry food mixes, spices, pudding, cereal products, sauces, veg dishes and meatloaf
is it spore former: yes
prevention: use careful time and temp control and quick chilling; proper reheating
clostridium botulinum
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 12-36 hours
duration: several days or a year
symptoms: vertigo, visual disturbance, inability to swallow, respiratory paralysis
source: soil and water
associated food: improperly processed canned goods of low acid foods, garlic in oil products, grilled onions, stews, meat/poultry loafs
is it spore former: yes
prevention: do not use home canned products; use temp and time control; keep sous vide refrigerated; purchase garlic in oil in small quantities, cook red onion only on request, rapidly cool leftovers
campylobacter jejuni
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 3-5 days
duration: 1-4 days
symptoms: diarrhea, fever, nausea, abdominal pain, headache
source: domestic and wild animals
associated food: raw veg, unpasteurized milk and dairy products, polutry, beef. pork, and lamb
is it spore former: no
preventionL avoid cross contamination and cook properly
Escherichia coli
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 12-72 hours
duration: 1-3 days
symptoms: bloody diahrrea, severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diahrrhea, and ocassional fever
source: humans, animals, particularly cattle
associated food: raw and undercooked beef and other red meats, imported cheeses, unpasteurized milk, raw fin fish, cream pies, mashed potatoes, and other prepared foods
is it spore former: no
prevention: cook beef properly, avoid cross contamination, use food and water supplies, avoid fecal contamination from handlers
vibrio (parahaemolyticus and vulnificus)
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 4-96 hours
duration: 1-8 days
symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal cramp, vomit, headache, fever chills
source: fish and shell fish (mainly from gulf of Mexico)
associated food: raw or improperly cooked oysters or shellfish from contaminated waters
is it spore former: no
prevention: avoid raw or undercooked seafood, purchase seafood from approved sources
Yersinia enterocolitica, pseudotuberculosis
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 24-48 hours
duration: days to weeks
symptoms: abdomial pain, vomit, diahrrhea, headache
source: soil, water, pigs, wild rodents
associated food: raw and partially cooked meat (lamb, pork, beef), oysters, fish, raw milk
is it spore former: no
prevention: thoroughly cook foods, minimize cross contamination, properly clean and sanitize facilities
define virus
small pathogens that are not a complete cell
viruses cannot grow where
outside of host (so not cooked food)
types of viruses (3)
norovirus
hepatitis A
rotavirus
norovirus
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 24-48 hours
duration: 1-3 days
symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, and low grade fever
source: humans, contaminated water
associated food: raw veg, prepared salads, raw shellfish, water contaminated human feces
is it spore former: no
prevention: use safe water and water supplies, avoid fecal contamination from food handlers, cook foods well, purchase shellfish from reputable supplier
hepatitis A
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 10-50 days
duration: 1-2 weeks
symptoms: sudden onset of fever, fatigue, nausea, headache, abdominal pain, jaundice
source: humans, contaminated water and food
associated food: water and shellfish, salads, ice, cold, cuts, fruits and juices, veg, milk and milk products
is it spore former: no
prevention: obtain shellfish from reputable source, prevent cross contamination with proper handwashing, use sanitary water, exclude food handlers who have Hepatitis A
rotavirus
onset time
duration
symptoms
source
associated food
is it spore former
prevention
onset time: 1-3 days
duration: 4-8 days
symptoms: abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, mild fever
source: humans, contaminated water
associated food: water, ice, foods that do not have further cooking after handling such as salads, fruits, and raw veg
is it spore former: no
prevention: use sanitary water sources, prevent contamination by prper handwashing
define parasites
are living organisms that need a host to survive
types of parasites (6)
richinae, Anisakis simplex, Cryptosporidium parvum, Cyclospora cayetanensis, Giardia duodenalis, Cyclospora cayetanensis.
trichinae
-effects of body
-foods
-prevention
affects the muscles of the body and is caused by the Trichinae parasite
undercooked meat from infected animals
Wild animal meat is the primary sources of trichinella
Pork should be cooked to an end temperature of 160°F to prevent
Anisakis simplex
-food
-illness name
-destroyed how
raw seafood dishes, like sushi, sashimi, and ceviche, and undercooked fin fish
results in an illness termed anisakiasis.
destroyed by cooking or freezing
Cyclospora cayetanensis, Cryptosporidium parvum, Giardia duodenalis
-source
-spreadability
feces of contaminated individuals or contaminated water
Infected individuals can transmit the parasite to others
Cyclospora cayetanensis.
-common place where found
microscopic parasite composed of a single cell
often is found in people who live or travel in developing countries and consume contaminated water or fresh produce washed in contaminated water
what are fungi (the 3 types)
single and multicellular organisms such as molds, yeasts, and mushroom
define molds
multicellular fungi
mold
-size
-grow where (environment characteristics)
-temp
larger than bacteria and more complex in structure
grow on a wide range of substrates—moist or dry, acid or nonacid, high or low in salt or sugar.
grow over a wide range of temperatures (optimum temperature is between 77°F and 86°F)
yeast is what
unicellular form of fungi
yeast
-causes what
-found in/ used for
not known to cause foodborne illnesses, but may cause spoilage of sugar-containing foods
n important role in the food industry, particularly in the fermentation or leavening of beer, wine, and bread
mushrooms
-safety
Type of fungi
Many forms are safe to eat, some are toxic and can cause foodborne illness if eaten
natural toxins define
biological contamination can occur from the microorganisms themselves or by the toxins produced from these microorganisms
natural toxins resistance
toxins cannot be killed by freezing, cooking, or curing--> PASSED TO HUMANS WHEN CONSUMED
histamine
-food
-causes what
Scombroid poisoning occurs when persons consume scombroid and related species of fish (tuna, mackerel, mahi mahi) that have been time/temperature abused and bacteria on the fish have produced high levels of histamine
Ciguatoxin, Saxitoxin, Brevetoxin, and Domoic Acid
-found in what, cause issue how
Many species of marine algae contain toxins--> enter fish and shellfish--> passed on to humans who consume the fish
Ciguatoxin
-food
Ciguatera fish poisoning occurs with the consumption of Ciguatoxin and is found in predatory tropical reef fish such as barracuda, grouper, jacks, and snapper who eat smaller fish who have consumed the algae toxin.
saxotoxin
-cause what
which causes paralytic shellfish poisoning
brevetoxin
-cause what
which causes neurotoxic shellfish poisoning
domoic acid
-causes what
amnesic shellfish poisoning, can be in shell fish (clams, mussels, oysters, scallops) from contaminated waters
mushroom toxin
-categories
-produced by
-destroyal
-symptoms
four categories of mushroom toxins: protoplasmic poisons (amanitin, gyromitrin, orellanine), neurotoxins (ibotenic acid, muscimol, psilocybin), gastrointestinal irritants, and disulfiram-like toxins
produced naturally by a variety of types of mushrooms.
cannot be destroyed by cooking or freezing
can cause gastrointestinal distress, neurological impairment, organ failure, and even death
define prions
(PROteinaceous INfectious particle)
small glycosylated protein molecules found in brain cell membrane
Prion diseases, often termed transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE), are infectious diseases of the brain that can occur in both animals and humans
prions and heat
Prions are extremely resistant to heat!!
effects of prions in body
the disease course in humans includes behavioral changes, ataxia, progressive dementia, and death