CHEM MOCK COMBINED
1/247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
248 Terms
how do metals form ions?
LOSE electron, positive ion
how do non metals form ions?
GAIN electron, negative ions
valency =
charge
zinc ion
Zn2+
silver ion
Ag+
Hydrogen ion
H+
iron (II) ion
Fe2+
Iron (III) ion
Fe3+
copper (II) ion
Cu2+
sulfate ion
SO42-
carbonate ion
CO32-
hydrogencarbonate charge
HCO3-
nitrate ion
NO3-
Hydroxide ion
OH-
ammonium ion
NH4+
definition of ionic bond
an ionic bond is an electrostatic force of attraction between positive and negative ions
boiling point of ionic compounds
high
why is boiling point of ionic compounds high
strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive and negative ions throughout whole structure which takes lots of energy to overcome
how do ionic compounds conduct electricity
ions
when do ionic compounds conduct electricity
solution/molten
why don’t ionic compounds conduct in solid
ions are in a fixed posision
why do ionic compounds conduct when molten/solution
ions are free to move + carry charge
covalent bond definition
the electrostatic atraction between the shared pair of electrons and the positive nuclei of the atoms either side
covalent - metal or non metal
2 non metals
what are simple molecular structures?
molecules which are neutral particles
fixed number of atoms
strong covalent bonds
weak intermolecular forces
melting point of simple molecular
low melting + boiling point
weak forces between molecules
not much energy needed to OVERCOME them
do simple molecular structures conduct electricity?
no
no charge particles
current cannot flow
giant covalent structure
giant 3d lattice, regular arrangement of atoms
many strong covalent bonds throughout
no molecules
diamond structure
each C bonded to 4 others
many strong covalent bonds throughout
no electrons are free to move
melting point diamond
very high
many strong covalent bonds = lots of energy
conductivity of diamond
DOES NOT CONDUCT
no charged particles
all electrons involoved in bonding
are diamonds hard?
yes
rigid 3d structure
held together by strong covalent bonds
uses of diamond
jewelry
driling + cutting
graphite structure
each C bonded to 3 others
atoms in layers
many strong covalent bonds within each LAYER
electrons free to move between layers
forces betweel layers are weak
melting point of graphite
HIGH
many strong covalent bonds = lots of energy to break
conductivity of graphite
DOES CONDUCT
there is a delocalised electron per carbon
free to move + carry charge
why is graphite soft/slippery
arranged in layers
weak attraction
slide over each other
uses of graphite
pencils
electrical componens
lubricant in industry
sporting equipment
metallic bond definition
electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and negative sea of delocalised electron
how to draw bonding
at least 3 rows positive ions (+ in circle)
delocalised electrons (- in circle)
labelled
melting point metallic
high
strong attraction between positive ions and electrons
lots of energy to overcome
electrical conductivity metallic
conducts
delocalised electrons free to move + carry current
strength of metallic
strong but malleable
bonds strong
layers of ions can slide
metallic solubility?
insoluble
what is an alloy
mixture of a metal with small amounts of other elements
why are alloys harder than pure metals?
layers cannot slide over eaxh other so easly as atoms are different sizes
why are noble gases inert
they have a complete outer shell, so don’t need to react
why is argon used for food packaging
unreactive, not toxic
why is argon used for welding
unreactive and not flammable
properties unique to alkali metlas
very reactive with oxygen and water- stored in oil
shiny when cut, quickly dulls
low density (some float on water)
low melting point for a metal
mainly form white compounds which are soluble in water
why do alkali metals have similar properties
they all have 1 outer shell electron, and react by losing it
observation of lithium and water
fizzes, floats on surface, gently moves, disappears (universal indicator turns purple)
sodium and water is same as lithium but…
melts into a ball, moves faster
potassium same as sodium but…
moves faster, lilac flame and sparks (H igniting)
why do alkali metals get more reactive as you go down group
react by losing outer electron
as you go down, atoms get larger
this means electron is further away from nucleus
there is less attraction
electron is lost more easily
halogen are __ non metals and are all _
reactive
toxic/harmful
fluorine state + colour
gas , pale yellow
chlorine state + colour
toxic gas, pale green
bromine state + colour
volatile liquid, red-brown
iodine state + colour
brittle solid, dark grey
astatine state + colour
solid black
halogen ions are
halides
hydrogen chloride state , solubility, what happens in water?
gas, soluble, dissociates in water to form hydrochloric acid
how to halogens react?
gain an electron
why do halogens get less reactive going down group
atoms get bigger
outer electron further from nucleus
attraction is weaker
extra electron is less easily gained
group no.
number of electrons in outer shell
period no
number of shells
water
formula
%
properties
uses
H2O
varies
polar molecule
required by living creatures
uses of carbon dioxide + why (property)
fizzy drinks - soluble in water
fire extinguisher - denser than air, doesn't support combustion
refridgerant - dry ice, solid co2, sublimes so no wet cardboard
Unburned fuels
how formed
problems
solutions
incomplete combustion
breathing problems, less efficient
ensure correct fuel:air mixture when fuel is burned
test for CO2
bubble through limewater
solution will go from colourless to cloudy
sulfur + oxygen
word equation
basic or acidic
what do you see
sulfur + oxygen ---> sulfur dioxide
acidic
glows blue
sodium+ oxygen
word equation
basic or acidic
what do you see
sodium + oxygen ----> sodium oxide
basic
yellow flame + white smoke
SO4 sulfur dioxide
how formed
problems
solutions
sulfur impurity burns with fossil fuels
acidic rain: damages plants, kills fish, corrodes limestone
remove SO4 by flue gas desulfurisation
phosphorous to find percentage of oxygen in air
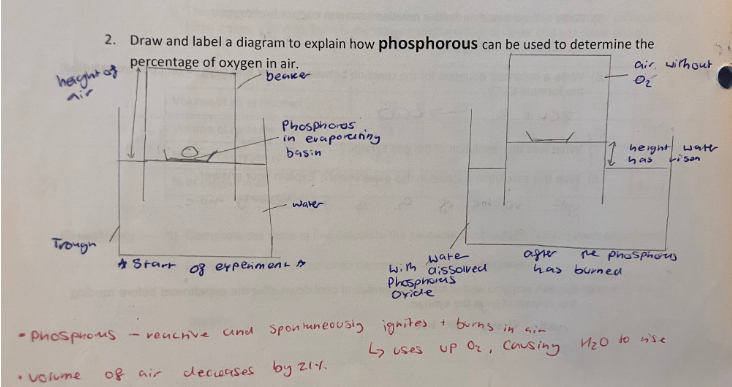

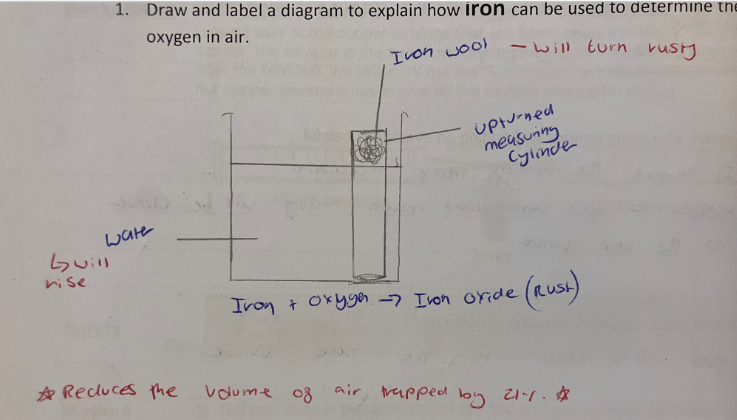
percentage of oxygen in the air using iron
oxygen
formula
%
properties
uses
O2
20%
very reactive, required for respiration
hospitals - patient breathing
NO/NO2 Nitrogen oxides
how formed
problems
solutions
car engines - N2 in air is reacting at high temos
acid rain
catalytic converters
Nitrogen
formula
%
properties
uses
N2
78%
unreactive
food packets
melting point of CO2 and explanation
low - weak intermolecular forces between molecules
co2 is simple molecular bonding
Magnesium + oxygen
word equation
basic or acidic
what do you see
magnesium + oxygen ----> magnesium oxide
basic
bright white light + white powder
is co2 soluble in water?
yes
in general, metal oxides are _____ and non-metal oxides are ____
basic, acidic
CO2 - carbon dioxide
how formed
problems
solutions
complete combustion of c in fuel
greenhouse gas causing global warming
burn less fossil fuels
CO - Carbon monoxide
how formed
problems
solutions
incomplete combustion of C in fuel
TOXIC
ensure good supply of air/oxygen when burned
carbon dioxide
formula
%
properties
uses
CO2
0.03%
unreactive
fire extinguishers
carbon + oxygen
word equation
basic or acidic
what do you see
carbon + oxygen -----> carbon dioxide
acidic
glows red
C soot/particulates
how formed
problems
solutions
incomplete combustion of C in fuel
blackens buildings, global dimming, breathing issues
ensure there is a good supply of oxygen/air when burned
Argon
formula
%
properties
uses
Ar
0.9%
very unreactive
inside filament lightbulbs
appearance of carbon dioxide
colourless gas
alkenes test/result
-reacts with Br2(aq) immediately (addition reaction)
alkenes go colourless in bromine water
addition of halogens=test for double bonds
crude oil
a mixture of hydrocarbons
alkanes test/reactions
alkanes react with Br2 (aq) in presence of uv light (goes colourless)
undergoes substitution reaction
functional group
part of an organic molecle responsible for it’s chemical reaction
alkene general formular and functional group
CnH2n
C=C
molecular formular
exact number of atoms
empirical formula
simplest ratio
displayed formula
shows all atoms and all bonds