Chapter 5
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Surface that is sensitive to stimuli
Long extensions
Nerve cells
Elongated, threadlike
Contain tiny fibers that slide together forcefully
Muscle cells
Contain hemoglobin, a red pigment that attracts, then releases, oxygen
Red Blood cells
Contain sacs that release a secretion to the outside of the cell
Gland cells
Some have outer membranes able to engulf other cells
Some have systems that manufacture antibodies
Some are able to destroy other cells
immune cells
Recognize and destroy “nonself” cells such as cancer cells and invading bacteria
Immune cells
Release substances such as hormones, enzymes, mucus, and sweat
Gland cells
Transport oxygen in the bloodstream (from lungs to other parts of the body)
Red blood cells
Contract (shorten) to allow movement of body parts
muscle cells
Detect changes in internal or external environment
Transmit nerve impulses from one part of the body to another
Nerve cells
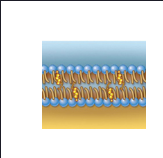
Phospholipid bilayer reinforced with cholesterol and embedded with proteins and other organic molecules
Plasma membrane
Serves as the boundary of the cell, maintains its integrity; protein molecules embedded in plasma membrane perform various functions
Plasma membrane
Network of canals and sacs extending from the nuclear envelope; may have ribosomes attached
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Functions of the Endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes attached to rough ER synthesize polypeptides that enter rough ER for folding and finishing, then move on to smooth ER; ER synthesizes integral membrane proteins (IMPs) and membrane lipids incorporated in cell membranes, steroid hormones, detoxification enzymes, glycogen-regulating enzymes, and carbohydrates used to form glycoproteins; also removes and stores Ca++ from the cell’s interior
Stack of flattened sacs (cisternae) surrounded by vesicles
Golgi apparatus
Synthesizes carbohydrate, combines it with protein, and packages the product as globules of glycoprotein
Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus functions?
Synthesizes carbohydrate, combines it with protein, and packages the product as globules of glycoprotein
Tiny membranous bags
Vesicles
Temporarily contain molecules for transport or later use
Vesicles
Tiny membranous bags containing enzymes
Lysosomes
Functions of Lysosomes
Digestive enzymes break down defective cell parts (autophagy) and ingested particles; a cell’s “digestive system”; some lysosomes involved in membrane repair or secretion
Tiny membranous bags containing enzymes (not Lysosomes)
Peroxisomes
Functions of Peroxisomes
Enzymes detoxify harmful substances in the cell
Tiny membranous capsule surrounding an inner, highly folded membrane embedded with enzymes; has small, ringlike chromosome (DNA)
Mitochondria
Catabolism; adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis; a cell’s “power plants”
Mitochondria
A usually central, spherical double-membrane container of chromatin (DNA); has large pores
Nucleus
Houses the genetic code, which in turn dictates protein synthesis, thereby playing an essential role in other cell activities, namely, cell transport, metabolism, and growth
Nucleus
Small particles assembled from two tiny subunits of rRNA and protein
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis; a cell’s “protein factories”
Ribosomes
Hollow protein cylinders with embedded enzymes
Proteasomes
Destroys misfolded or otherwise abnormal proteins manufactured by the cell; a “quality control” mechanism for protein synthesis
Proteasomes
; a “quality control” mechanism for protein synthesis
Proteasomes
Network of interconnecting flexible filaments, stiff tubules, and molecular motors within the cell
Cytoskeleton
Supporting framework of the cell and its organelles; functions in cell movement (using molecular motors); forms cell extensions (microvilli, cilia, flagella)
Cytoskeleton
Region of cytoskeleton that includes two cylindrical groupings of microtubules called centrioles
Centrosome
Acts as the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) of the cell; centrioles assist in forming and organizing microtubules
Centrosome
Short, fingerlike extensions of plasma membrane; supported internally by microfilaments
Microvilli
Tiny, fingerlike extensions that increase a cell’s absorptive surface area
Microvilli
Moderate (cilia) to long (flagella) hairlike extensions of plasma membrane; supported internally by cylindrical formation of microtubules, sometimes with attached molecular motors
Cilia and flagella
Functions of Cilia and flagella
Cilia move substances over the cell surface or detect changes outside the cell;
flagella propel sperm cells
Dense area of chromatin and related molecules within nucleus
Nucleolus
Site of formation of ribosome subunits
Nucleolus
The inside of the cell is composed largely of a gel-like substance called _______________(literally, “cell substance”). The _________________ is made of various ___________ and molecules suspended in a watery fluid called cytosol, or sometimes intracellular fluid.
The inside of the cell is composed largely of a gel-like substance called cytoplasm (literally, “cell substance”). The cytoplasm is made of various organelles and molecules suspended in a watery fluid called cytosol, or sometimes intracellular fluid.
This dense crowding of molecules and organelles actually helps improve the efficiency of chemical reactions in the cell.
the cytoplasm is crowded with large and small molecules—and various organelles. This dense crowding of molecules and organelles actually helps improve the efficiency of chemical reactions in the cell.
the main cell structures are?
the main cell structures are
(1) the plasma membrane;
(2) cytoplasm, including the organelles; and
(3) the nucleus
This membrane material is a very thin sheet—averaging only about _____________________________—made of lipid, protein, and other molecules
This membrane material is a very thin sheet—averaging only about 75 angstroms (Å) or 0.0000003 inch thick—made of lipid, protein, and other molecules
__________________is a steroid lipid that mixes with phospholipid molecules to form a blend of lipids that stays just fluid enough to function properly at body temperature. Without _________________, cell membranes would break far too easily.
Cholesterol is a steroid lipid that mixes with phospholipid molecules to form a blend of lipids that stays just fluid enough to function properly at body temperature. Without cholesterol, cell membranes would break far too easily.
The different molecular interactions within the membrane allow the formation of lipid rafts, which are stiff groupings of membrane molecules (often very rich in cholesterol) that travel together like a log raft on the surface of a lake… What do rafts do?
Rafts help organize the various components of a membrane.
Rafts play an important role in the pinching of a parent cell into two daughter cells during cell division.
Rafts may also sometimes allow the cell to form depressions that pouch inward and then pinch off as a means of carrying substances into the cell
Proteins that have some functional regions or _______________ that are hydrophilic and other domains that are hydrophobic can be integrated into a phospholipid bilayer and remain stable.
Proteins that have some functional regions or domains that are hydrophilic and other domains that are hydrophobic can be integrated into a phospholipid bilayer and remain stable.
Some IMPs have carbohydrates attached to their outer surface—forming glycoprotein molecules—that act as ____________________ markers.
Some IMPs have carbohydrates attached to their outer surface—forming glycoprotein molecules—that act as identification markers.
Other IMPs are ________________ that can react to the presence of hormones or other regulatory chemicals and thereby trigger metabolic changes in the cell.
Other IMPs are receptors that can react to the presence of hormones or other regulatory chemicals and thereby trigger metabolic changes in the cell.
The process by which cells translate the signal received by a membrane receptor into a specific chemical change in the cell is called ________________ ________________.
The process by which cells translate the signal received by a membrane receptor into a specific chemical change in the cell is called signal transduction.
Structure and fucntion
Structure: Sheet (bilayer) of phospholipids stabilized by cholesterol
Function: Maintains boundary (integrity) of a cell or membranous organelle
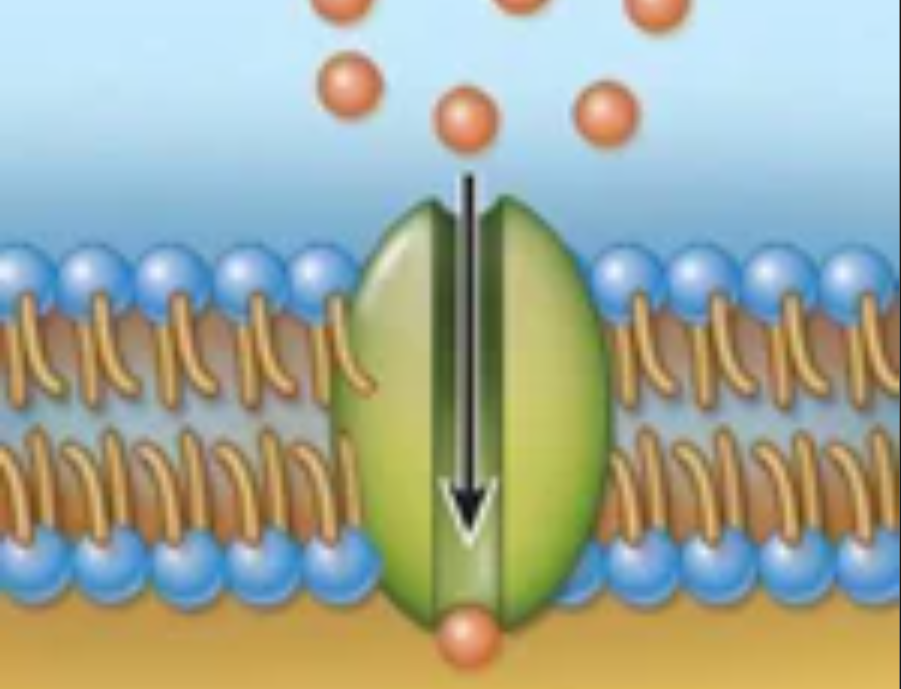
Structures and function
Structure: Integral membrane proteins that act as channels or carriers of molecules
Function: Controlled transport of water-soluble molecules from one compartment to another
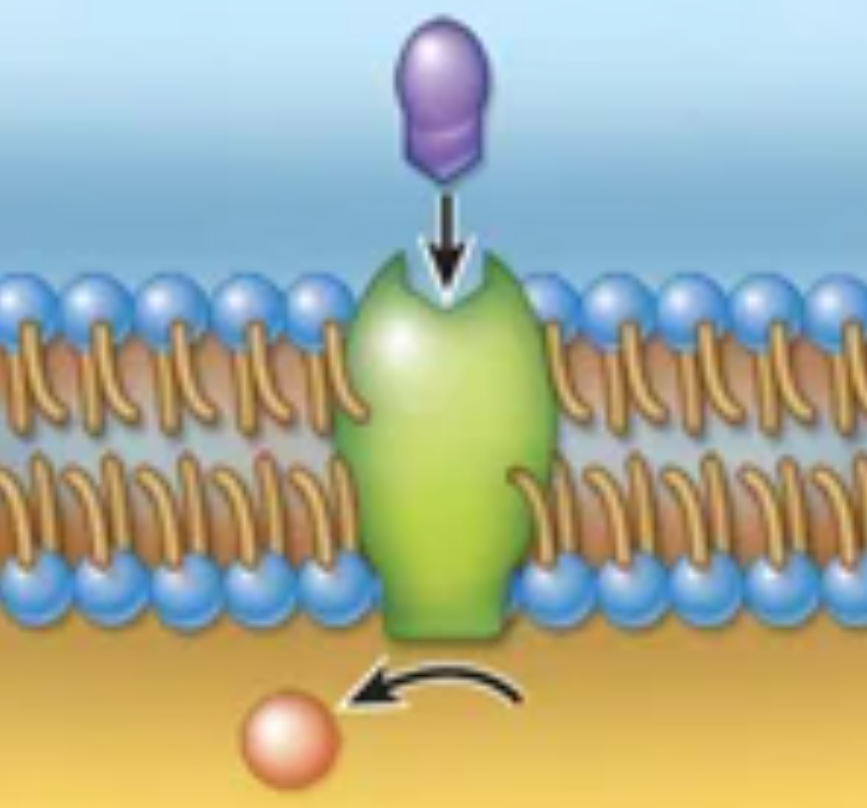
Structure and function
Structure: Receptor molecules that trigger metabolic changes in membrane (or on other side of membrane)
Function: Sensitivity to hormones and other regulatory chemicals; involved in signal transduction
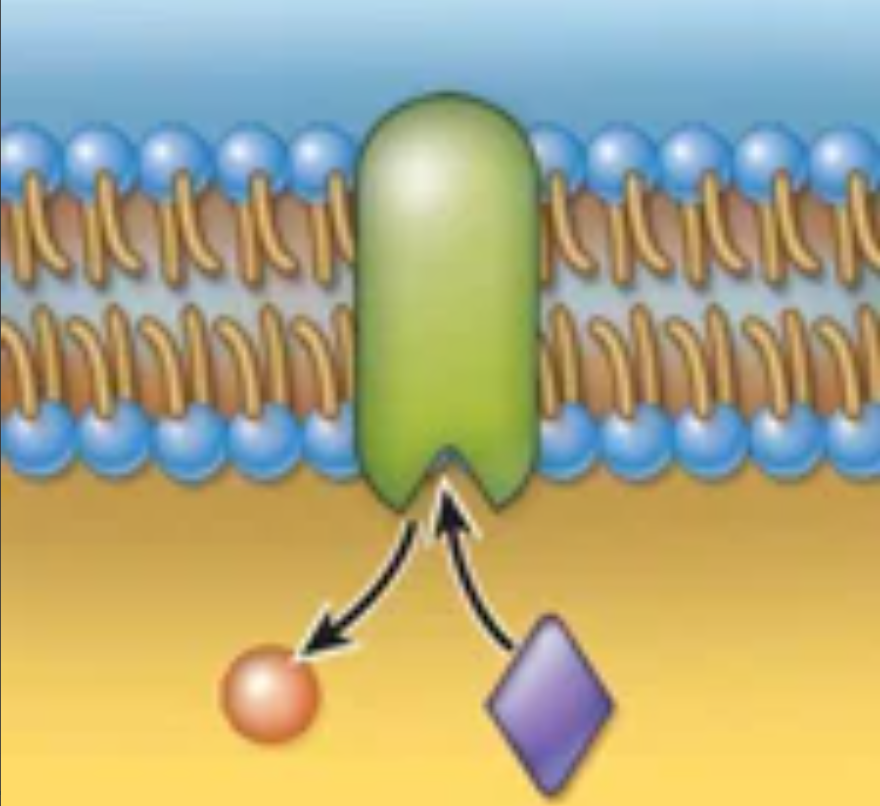
Structure and function
Structure: Enzyme molecules that catalyze specific chemical reactions
Function: Regulation of metabolic reactions
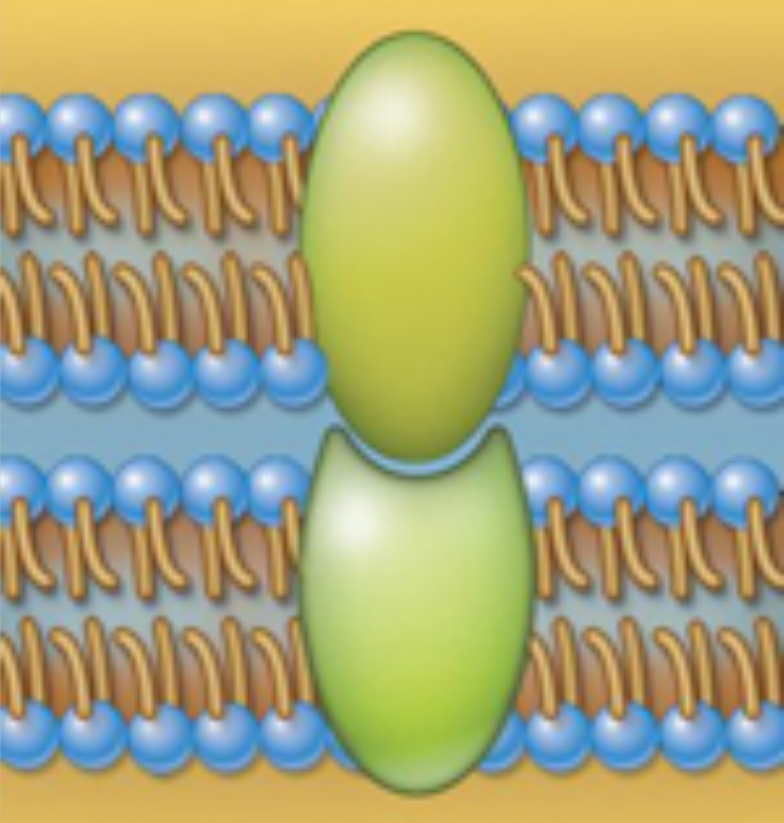
Structure and function
Structure: Integral membrane proteins that bind to molecules outside the cell
Function: Form connections between one cell and another
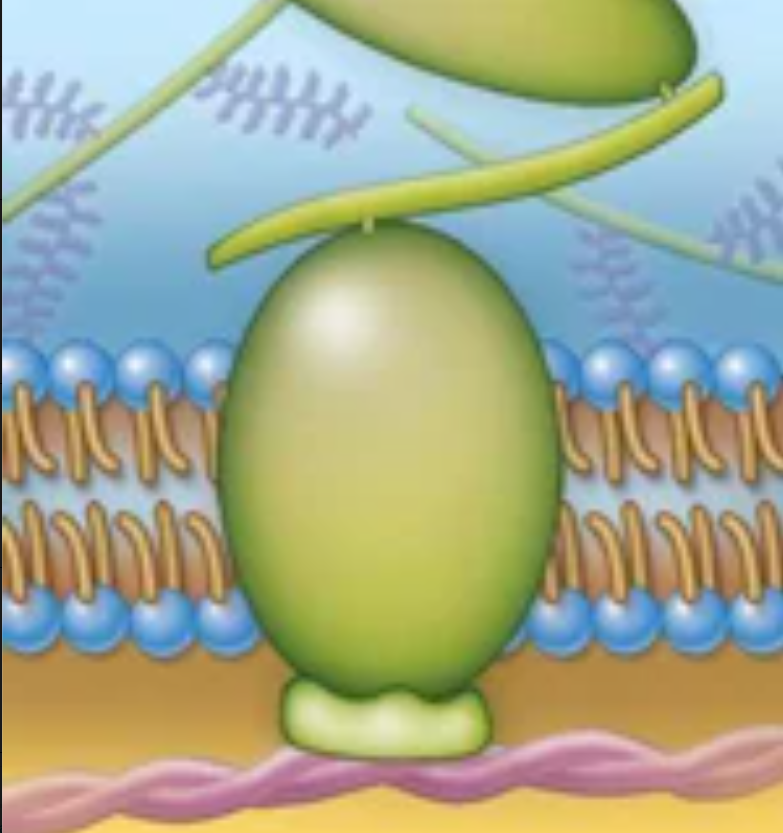
Structure and function
Structure: Integral membrane proteins that bind to support structures
Function: Support and maintain the shape of a cell or membranous organelle; participate in cell movement; bind to fibers of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
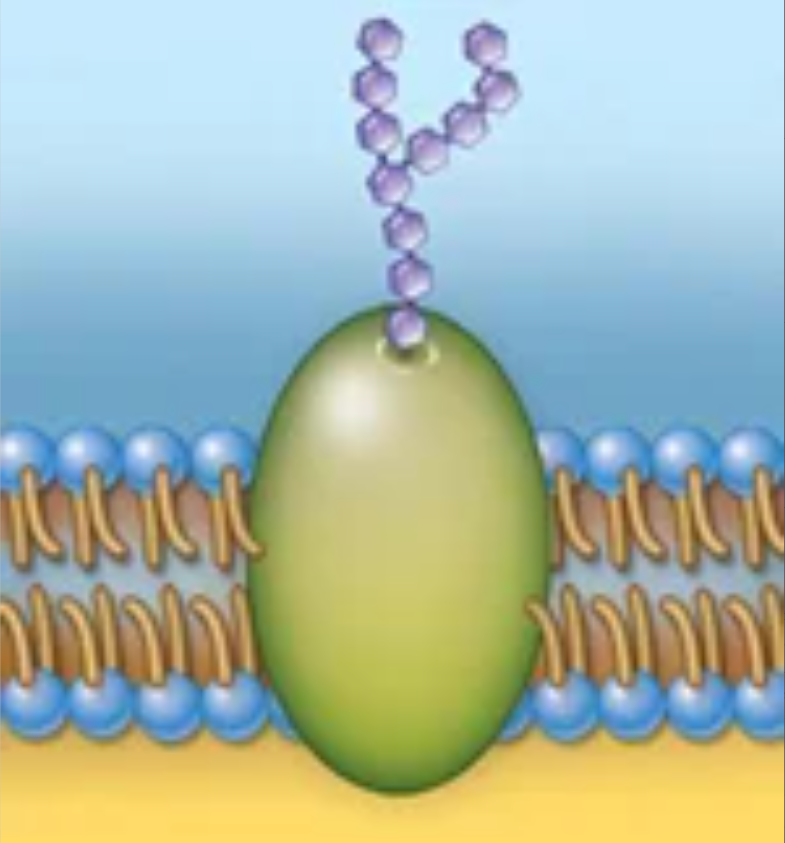
Structure and function
Structure: Glycoproteins or proteins in the membrane that act as markers
Function: Recognition of cells or organelles
_______________ organelles are not made of membrane; they are made of microscopic filaments or other particles.
Nonmembranous organelles are not made of membrane; they are made of microscopic filaments or other particles.
the ER is in constant motion within the cell, often contacting other organelles in the cell to form temporary functional “__________________.”
the ER is in constant motion within the cell, often contacting other organelles in the cell to form temporary functional “partnerships.”
RER is made up of broad, flattened sacs that extend outward from the boundary of the nucleus. RER sacs are dotted with innumerable small granules called _______________. The granules give RER the “rough” appearance of sandpaper
RER is made up of broad, flattened sacs that extend outward from the boundary of the nucleus. RER sacs are dotted with innumerable small granules called ribosomes. The granules give RER the “rough” appearance of sandpaper
Although started in the ______, most of the phospholipids and cholesterol molecules that form cell membranes are synthesized in the ___________.
Although started in the RER, most of the phospholipids and cholesterol molecules that form cell membranes are synthesized in the SER.
The function of ribosomes is _____________ synthesis.
The function of ribosomes is protein synthesis.
______________ are the molecular machines that translate the genetic code to make proteins, or to use a popular term, they are the cell’s “protein factories.” They make both its structural and its functional proteins (enzymes).
Ribosomes are the molecular machines that translate the genetic code to make proteins, or to use a popular term, they are the cell’s “protein factories.” They make both its structural and its functional proteins (enzymes).
Working ribosomes usually function in groups called _____________or _____________. ______________________ form when more than one ribosome begins translating the same long, threadlike mRNA molecule. Under the electron microscope, _________________ look like short strings of beads.
Working ribosomes usually function in groups called polyribosomes or polysomes. Polyribosomes form when more than one ribosome begins translating the same long, threadlike mRNA molecule. Under the electron microscope, polyribosomes look like short strings of beads.
The ________ ______________ is a membranous organelle consisting of separate tiny sacs, or cisternae, stacked on one another and located near the nucleus
The Golgi apparatus is a membranous organelle consisting of separate tiny sacs, or cisternae, stacked on one another and located near the nucleus
___________ form when small portions of the plasma membrane pinch inward and separate into a vesicle or sac
Lysosomes form when small portions of the plasma membrane pinch inward and separate into a vesicle or sac
Lysosomal enzymes have several important functions in cells. Chiefly……
Lysosomal enzymes have several important functions in cells
Chiefly, they help the cell break down proteins and cytoplasm that are not needed to get them out of the way. This process of “self-eating” is called autophagy.
_____________deserve their nicknames of “digestive bags” and “cellular garbage disposals.”
lysosomes deserve their nicknames of “digestive bags” and “cellular garbage disposals.”
The _____________ is another protein-destroying organelle in the cell. , the proteasome is a hollow, cylindrical “drum” made up of protein subunits.
The proteasome is another protein-destroying organelle in the cell. , the proteasome is a hollow, cylindrical “drum” made up of protein subunits.
Found throughout the cytoplasm, the ________________ is responsible for breaking down abnormal and misfolded proteins released from the ER, as well as destroying normal regulatory proteins in the cytoplasm that are no longer needed. But unlike the lysosome, which destroys large groups of protein molecules all at once, the ____________ destroys protein molecules one at a time.
Found throughout the cytoplasm, the proteasome is responsible for breaking down abnormal and misfolded proteins released from the ER, as well as destroying normal regulatory proteins in the cytoplasm that are no longer needed. But unlike the lysosome, which destroys large groups of protein molecules all at once, the proteasome destroys protein molecules one at a time.
Before a protein enters the hollow interior of the proteasome, it must be tagged with a chain of very small proteins called _____________.
Before a protein enters the hollow interior of the proteasome, it must be tagged with a chain of very small proteins called ubiquitins
Proper functioning of proteasomes is important in prevention of healthy cell function and possibly severe disease. For example,
in Parkinson disease (PD) the proteasome system fails, and consequently, the still intact improperly folded proteins kill nerve cells in the brain that are needed to regulate muscle tension.
The ________________ is another type of vesicle containing enzymes that is present in the cytoplasm of some cells.
The peroxisome is another type of vesicle containing enzymes that is present in the cytoplasm of some cells.
Peroxisomes contain the enzymes ______________ and _____________ , which are important in detoxification reactions involving hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Hydrogen peroxide is the chemical that gives this organelle its name.
Peroxisomes contain the enzymes peroxidase and catalase, which are important in detoxification reactions involving hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Hydrogen peroxide is the chemical that gives this organelle its name.
Mitochondria membranous walls consist of not one but two delicate membranes. They form a sac within a sac. The inner membrane is contorted into folds called cristae.
Their membranous walls consist of not one but two delicate membranes. They form a sac within a sac. The inner membrane is contorted into folds called cristae.
Nuclear pores are intricate structures often called _______ _________ _________ (NPCs)
Nuclear pores are intricate structures often called nuclear pore complexes (NPCs)
The two nuclear membranes, together called the __________envelope, have essentially the same type of structure as other cell membranes. The membranous walls of the ER extend outward from the membranes of the ___________ envelope.
The two nuclear membranes, together called the nuclear envelope, have essentially the same type of structure as other cell membranes. The membranous walls of the ER extend outward from the membranes of the nuclear envelope.
In nondividing cells, the DNA molecules appear as tiny bunches of tangled threads sprinkled with granules. This material is named _____________.
In nondividing cells, the DNA molecules appear as tiny bunches of tangled threads sprinkled with granules. This material is named chromatin.
Chromatin is from the Greek chroma, “color,” so named because it readily takes the color of _______.
Chromatin is from the Greek chroma, “color,” so named because it readily takes the color of g.
When the process of cell division begins, DNA molecules become more tightly coiled. They become so compact that they look like short, rodlike structures and are then called ___________________.
When the process of cell division begins, DNA molecules become more tightly coiled. They become so compact that they look like short, rodlike structures and are then called chromosomes.
All typical human cells (except mature sex cells) contain ____ chromosomes, and each chromosome consists of one DNA molecule plus some protein molecules.
All typical human cells (except mature sex cells) contain 46 chromosomes, and each chromosome consists of one DNA molecule plus some protein molecules.
The most prominent structure visible in the nucleus is a small non-membranous body that stains densely when studied in the laboratory setting and is called the _____________.
The most prominent structure visible in the nucleus is a small nonmembranous body that stains densely when studied in the laboratory setting and is called the nucleolus
The nucleolus functions to synthesize _____________________ and combine it with protein to form the subunits that will later combine to form ribosomes, the protein factories of cells
The nucleolus functions to synthesize ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and combine it with protein to form the subunits that will later combine to form ribosomes, the protein factories of cells
Cells of the pancreas, to cite just one example, make large amounts of protein and have large ________________.
Cells of the pancreas, to cite just one example, make large amounts of protein and have large nucleoli.
As its name implies, the ______________ is the cell’s internal supporting framework. Like the bony skeleton of the body, the cytoskeleton is made up of rather rigid, rodlike pieces that not only provide support but also allow movement.
As its name implies, the cytoskeleton is the cell’s internal supporting framework. Like the bony skeleton of the body, the cytoskeleton is made up of rather rigid, rodlike pieces that not only provide support but also allow movement.
The smallest cell fibers are called _______________. ____________________often serve as part of our “cellular muscles.” They are made of thin, twisted strands of protein molecules
The smallest cell fibers are called microfilaments. Microfilaments often serve as part of our “cellular muscles.” They are made of thin, twisted strands of protein molecules
Cell fibers called ________________ filaments are twisted protein strands that are slightly thicker than microfilaments. Their twisted structure allows them to stretch without breaking.
Cell fibers called intermediate filaments are twisted protein strands that are slightly thicker than microfilaments. Their twisted structure allows them to stretch without breaking.
___________________ filaments are thought to form much of the supporting framework in many types of cells. They act as the tendons and ligaments of the cell, holding the cell together as it is pushed and pulled. For example, the protective cells in the outer layer of skin are filled with a dense arrangement of tough intermediate filaments.
Intermediate filaments are thought to form much of the supporting framework in many types of cells. They act as the tendons and ligaments of the cell, holding the cell together as it is pushed and pulled. For example, the protective cells in the outer layer of skin are filled with a dense arrangement of tough intermediate filaments.
The thickest of the cell fibers are tiny, hollow tubes called ____________.
The thickest of the cell fibers are tiny, hollow tubes called microtubules.
_______________are made of protein subunits arranged in a spiral fashion. ___________________are sometimes called the “engines” of the cell because they often move things around in the cell—or even cause movement of the entire cell.
microtubules are made of protein subunits arranged in a spiral fashion. Microtubules are sometimes called the “engines” of the cell because they often move things around in the cell—or even cause movement of the entire cell.
, this nonmembranous structure is often called the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC).
Centrisome
The boundaries of the centrosome are rather indistinct because it lacks a membranous wall. However, the general location of the centrosome is easy to find because of a pair of cylindrical structures called ____________.
The boundaries of the centrosome are rather indistinct because it lacks a membranous wall. However, the general location of the centrosome is easy to find because of a pair of cylindrical structures called centrioles.
A cloudlike mass of material surrounding the centrioles is called the _____________ __________(PCM). The PCM is active in starting the growth of new microtubules.
A cloudlike mass of material surrounding the centrioles is called the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM is active in starting the growth of new microtubules.
The microtubule organizing function of the centrosome plays an important role during cell division, when a special “spindle” of microtubules is constructed for the purpose of pulling chromosomes apart and toward each daughter cell. As this spindle forms, the centrosome is anchored by an ___________, which is a formation of microtubules radiating outward from the centrioles.
The microtubule organizing function of the centrosome plays an important role during cell division, when a special “spindle” of microtubules is constructed for the purpose of pulling chromosomes apart and toward each daughter cell. As this spindle forms, the centrosome is anchored by an aster, which is a formation of microtubules radiating outward from the centrioles.
Have you wondered as you’ve read along how all the little vesicles, organelles, and molecules always seem to be able to move on their own power to where they need to go in a cell?
The cell’s internal “feet” are actually little protein structures called molecular motors.
The tiny __________ proteins transport organelles along a microtubule or fiber as if they were railway cars being pulled along a track. This system provides rapid, orderly movement of structures and materials around the cell.
The tiny motor proteins transport organelles along a microtubule or fiber as if they were railway cars being pulled along a track. This system provides rapid, orderly movement of structures and materials around the cell.
In some cells the cytoskeleton forms projections that extend the plasma membrane outward to form tiny, fingerlike processes. Name 3
These processes, microvilli, cilia, and flagella, are present only in certain types of cells—depending, of course, on a cell’s particular functions.
______________are found in epithelial cells that line the intestines and other areas where absorption is important
Microvilli are found in epithelial cells that line the intestines and other areas where absorption is important