Respiratory Medicine Study Materials: Emphysema, COPD, and Related Definitions
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
interstitial lung disease
umbrella term referring to a group of ~200 d/o's that cause inflammation leading to fibrosis & scarring of the lungs
*often called "pulmonary fibrosis"
*rare (compared to COPD, which is much more common)
What are the 2 hallmark symptoms of interstitial lung disease?
1. dry, hacking cough
2. dyspnea (at rest or on exertion)
What are 6 causes of interstitial lung disease?
1. connective tissue dysfunction
2. autoimmune disease (e.g. lupus, sarcoidosis)
3. Side effects of medications: Amiodarone (Have you ever had an arrhythmia?), Nitrofurantoin (Do you have a hx of UTI?)
4. occupational exposure to lung irritants
5. radiation exposure (e.g. from cancer tx)
6. idiopathic (~25% of cases)
What 2 treatments of interstitial lung disease?
- anti-fibrotic agents
- cough suppressants
*NOT curable!
Define Restrictive lung disease
condition in which ↓ lung compliance leads to ↓ inspiratory capacity
Decreased inspiratory capacity
includes: interstitial lung disease (pulmonary fibrosis)
Define obstructive lung disease?
type of lung disease that occurs due to blockages or obstructions in the airways, which causes narrowing that leads to difficulty breathing.
Increased residual volume = air trapping
includes: COPD + emphysema & asthma
Define COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
umbrella term referring to the combo of chronic bronchitis + emphysema
*common in smokers
A client is scheduled to have a series of pulmonary function tests (PFTs). For which medication should the nurse anticipate an order to withhold six hours prior to the test?
a. Azithromycin
b. Robitussin
c. Albuterol
d. Cefaclor
c. Albuterol
Bronchodilator so we hold because it would improve the results
A client with COPD is being discharged from the hospital. Which statement by the client indicates further teaching is necessary?
a. "I will eat six small meals a day"
b. "I will get a flu shot every winter"
c. "I will walk every morning before breakfast"
d. "I will call my healthcare provider if I get cold symptoms"
c. I will walk every morning before breakfast
Morning is the best time to get sputum production
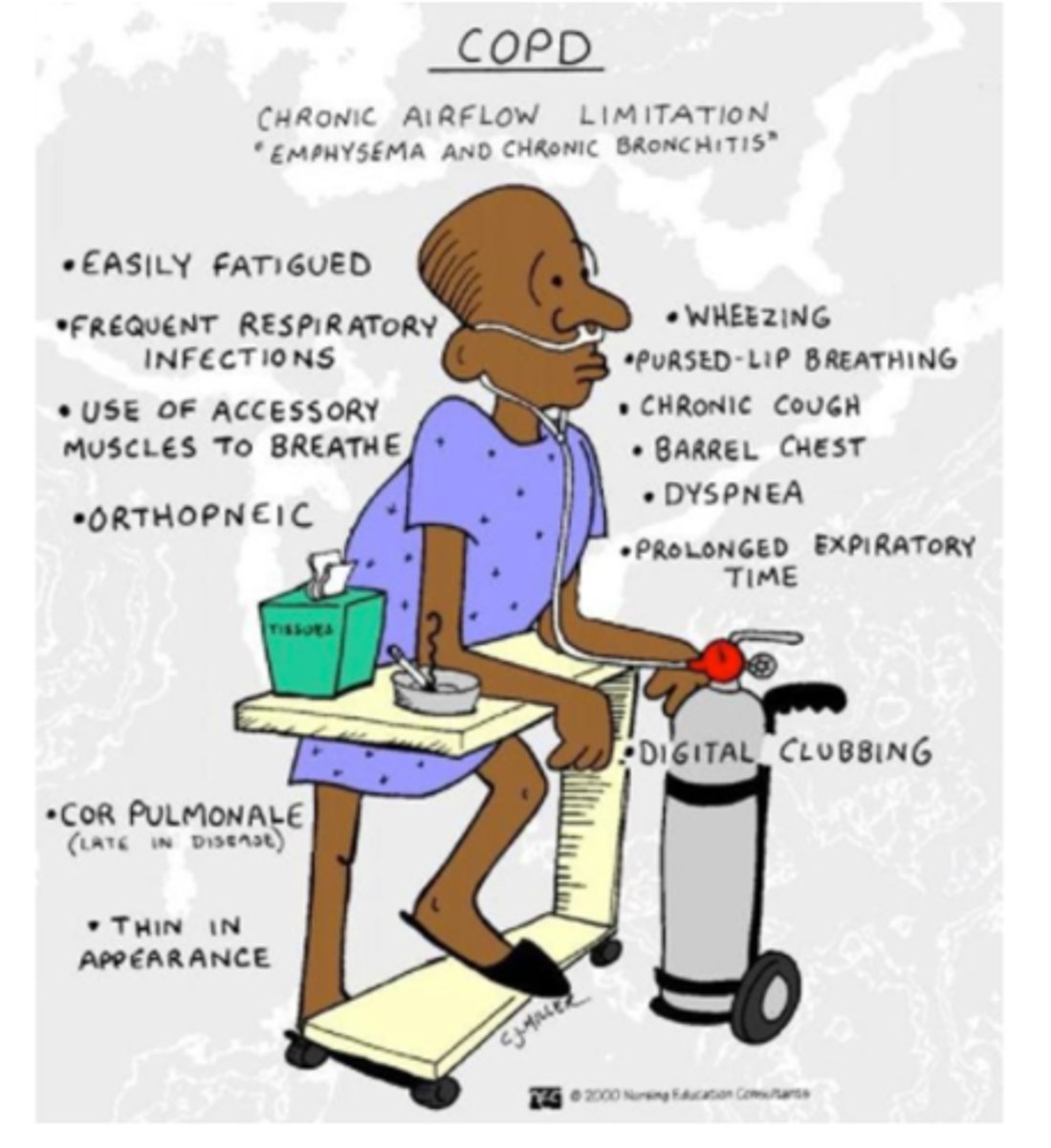
What are the 12 manifestations of COPD
- fatigue
- weight loss
- frequent respiratory infections
- dyspnea
- orthopnea
- wheezing
- chronic cough*
- barrel chest
- prolonged expiratory time
- clubbing**
- cor pulmonale
-using accessory muscles
*tends to be productive bc of bronchitis
**more common in interstitial lung disease, but still possible!
**sign of late-stage chronic lung disease
Define emphysema
condition in which the alveoli are damaged & enlarged, causing air trapping & breathlessness
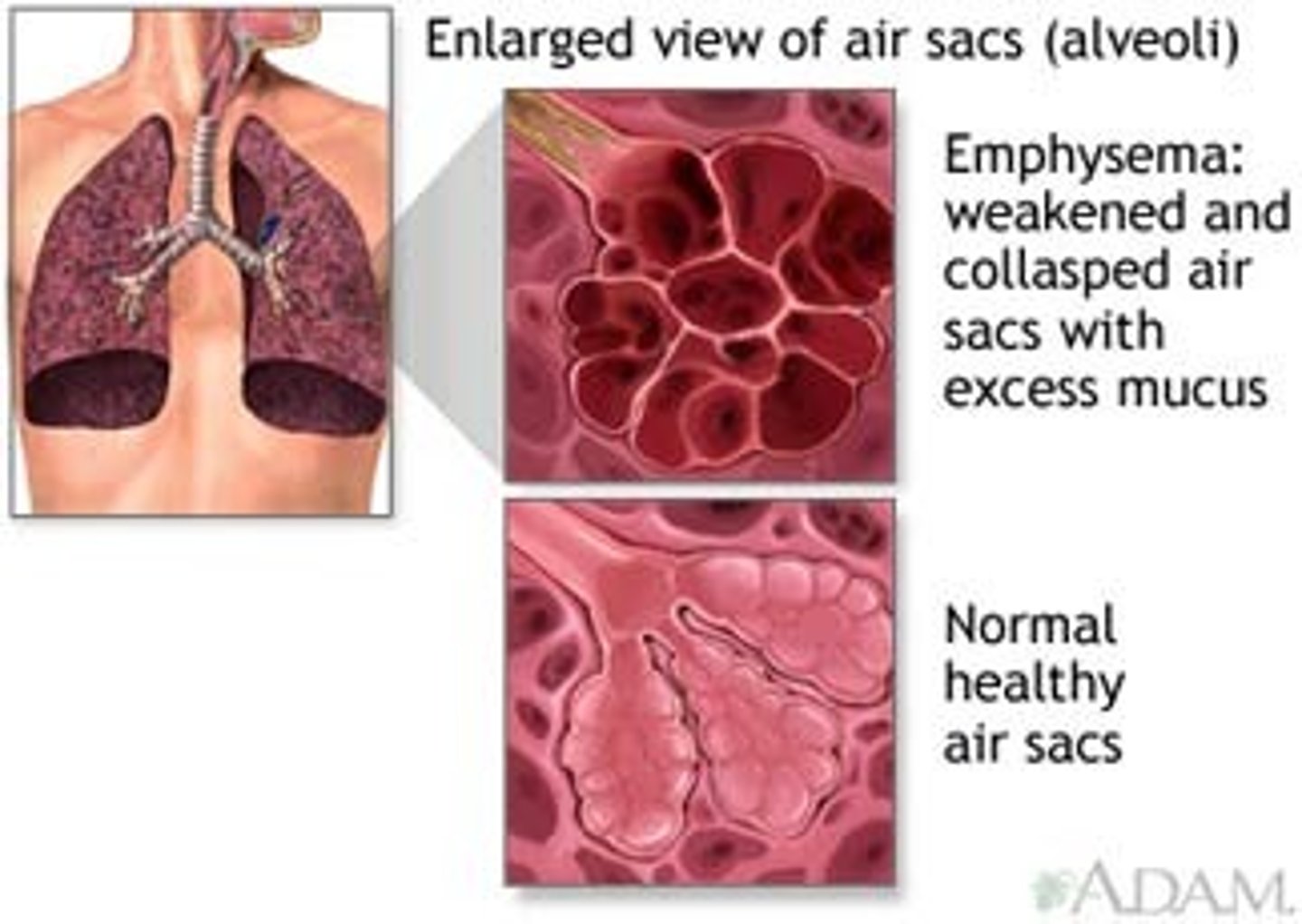
What lung volume is increased in emphysema?
RV (what leads to air trapping!)
What is cor pulmonale?
R-sided heart failure arising from chronic lung disease that causes pulmonary HTN
*sign of late-stage chronic lung disease
What are the 12 interventions for COPD?
1. alternate activity with rest, but encourage activity as tolerated
2. stress reduction techniques
3. cough and deep breath as ordered (NOT incentive spirometry!)
4. maintain SpO2 ~92 - 93% (recognize hypercapnia and hypoxemia)
5. clear airways before eating
6. eat 5 - 6 small, high-calorie meals throughout day
7. maintain adequate hydration (to thin out secretions)
8. nasotracheal suction if pt unable to expectorate own mucus
9. pursed lip breathing
10. diaphragmatic breathing or other accessory muscles
11. upright positioning (high-Fowler’s, tripod)
12. prevent infection (e.g. annual flu shot, call HCP if they have cold sx)
Why must we avoid over-oxygenating patients with COPD?
COPD causes air trapping leading to chronic hypercapnia, which is usually the body's trigger to breath; in patients with COPD, the body becomes desensitized to this mechanism, so hypoxemia becomes the trigger to breath
→ always give low-flow O2 via NC or Venturi mask (for those who need closer SpO2 monitoring)
What is hypercapnia?
abnormally high CO2 in the blood
What is hypoxemia?
abnormally low O2 in the blood
Why is it common for COPD patients to be underweight?
↑ WOB → ↑ metabolic demands & breakdown of tissues
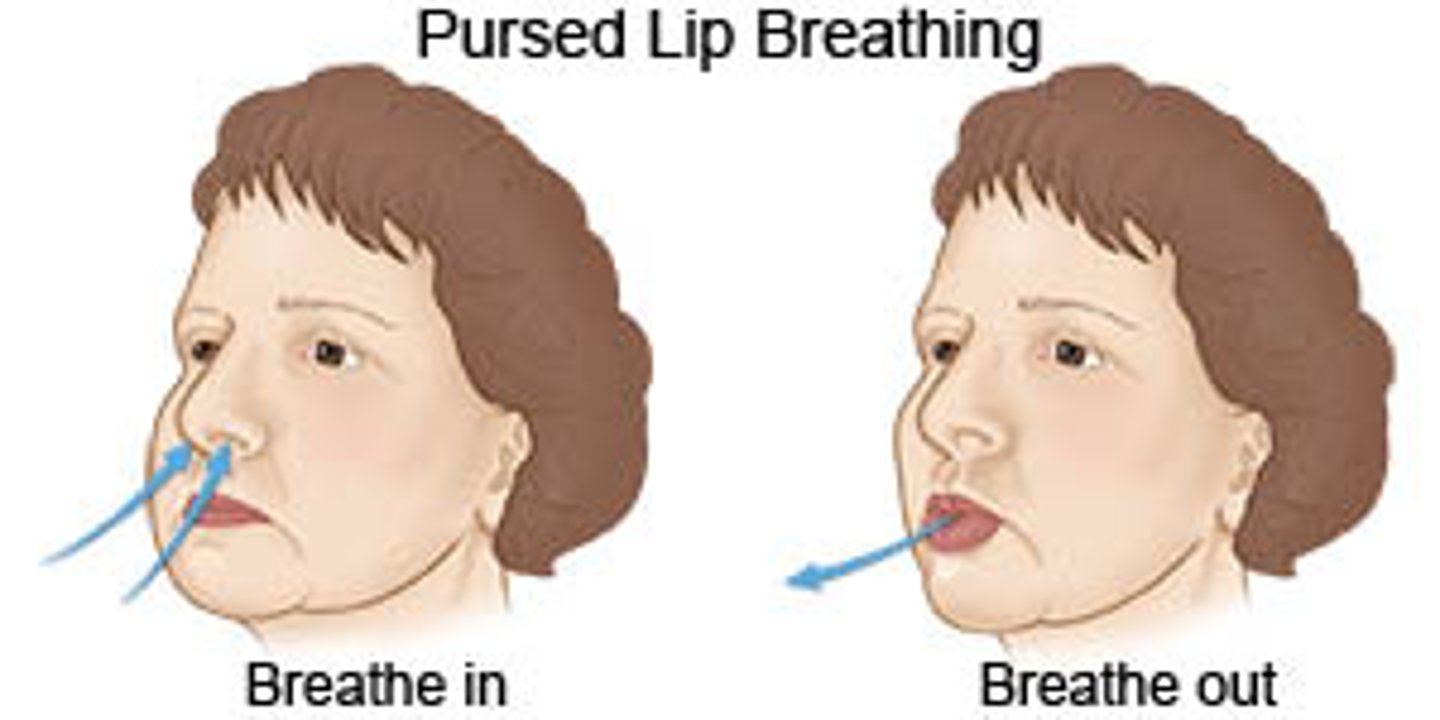
What is pursed lip breathing? How is it helpful?
breathing technique to prolong exhalation (2:1 ratio with inhalation)
TE: ↑ airway pressure to open airway during exhalation & ↓ air trapping
*keeps the airway open longer
*pt teaching should NOT occur during an exacerbation!
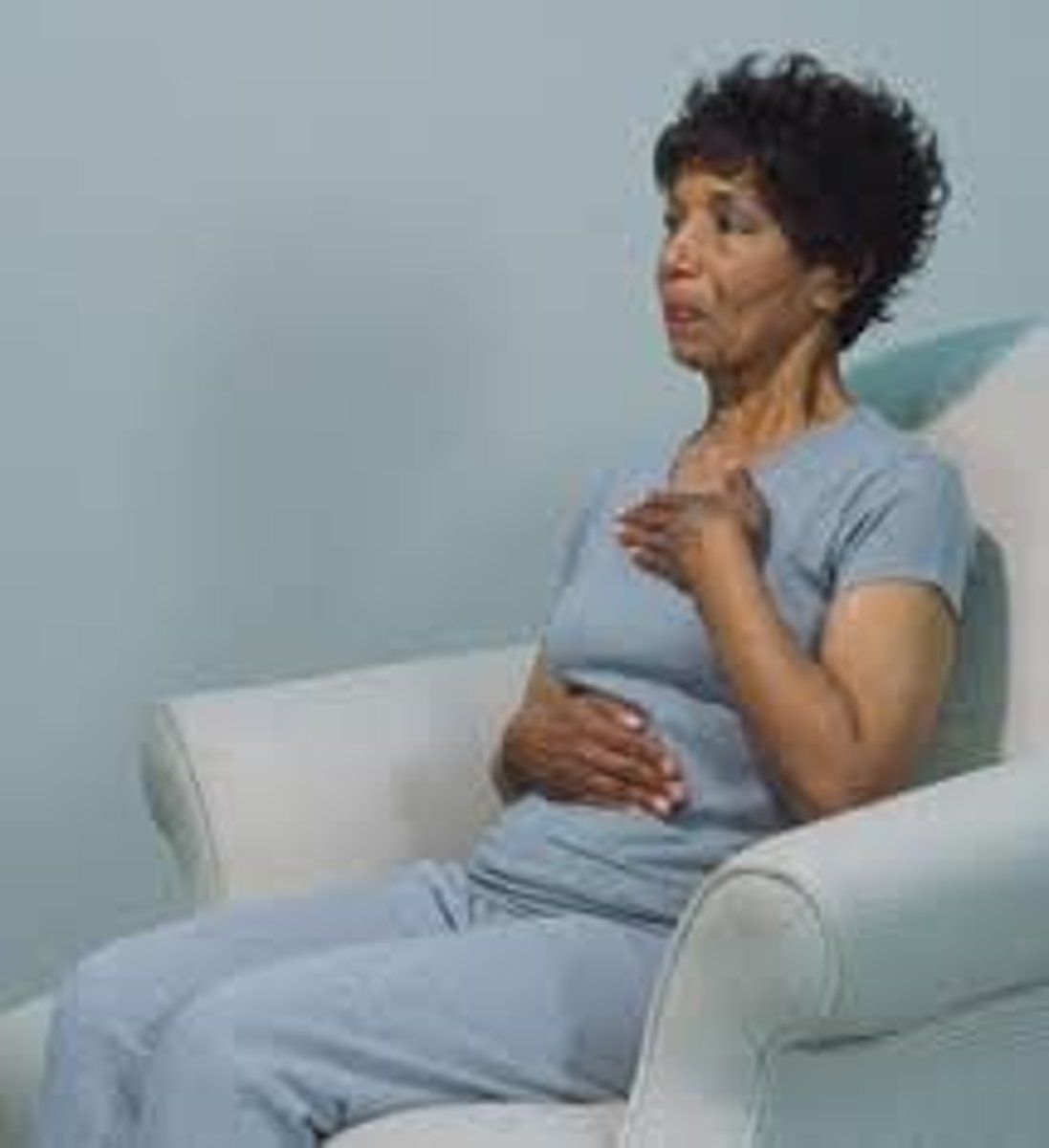
Define diaphragmatic breathing
breathing technique that involves fully engaging the stomach, abdominal muscles, & diaphragm
TE: achieve max inhalation & slow RR
*also called "belly breathing"
*pt teaching should NOT occur during an exacerbation!

A nurse is caring for a client with emphysema. Which nursing interventions are appropriate? Select all that apply
a. Reduce fluid intake to less than 2500 mL/day
b. Teach diaphragmatic & and pursed-lip breathing
c. Administer low-flow oxygen
d. Keep the client in a supine position as much as possible
e. Encourage alternating activity with rest periodically
f. Encourage increased protein & and caloric intake
b. c. e. f.
What are the 2 signs of chronic respiratory disease?
1. Barrel chest (1:1 ratio) due to air trapping
2. Clubbing due to hypoxia the growth of endothelial cells. Early on it can be reversed.
What are the 2 cardinal features of asthma?
1. airway inflammation
2. bronchial hyper-responsiveness → bronchospasm
What are the three manifestations of asthma?
- SOB
- cough
- wheezing (can be both inspiratory & expiratory)
What 4 types of medications are used to treat asthma?
1. bronchodilators
2. corticosteroids (for long-term relief)
3. mucolytics
4. abx (for 2° only)
What 3 subtypes of bronchodilators are used to treat asthma?
1. beta-2 adrenergic agonists
2. anticholinergic agents
3. methylxanthines
Albuterol [Ventolin, Proventil]
beta-2 adrenergic agonist
TE: bronchodilation
SE: tachycardia & related anxiety
*quick relief inhaler
Ipratropium Bromide [Atrovent]
anticholinergic agent
TE: bronchodilation
*often admin'd with Albuterol [Ventolin, Proventil]
Theophylline [Theo-Dur]
methylxanthine
TE: bronchodilation
SE: tachycardia
Aminophylline
methylxanthine
TE: bronchodilation
SE: tachycardia
Corticosteroids
Use a corticosteroid inhaler for long term control of asthma
help with anti inflammatory effect
-ends in “sone”
What should patients do following administration of an inhaled corticosteroid?
rinse their mouth to prevent thrush
Guaifenesin [Robitussin, Mucinex]
mucolytic
TE: thin secretions
agent that destroys or dissolve tenacious sputum
Why are antibiotics part of medications for obstructive pulmonary disorders?
When there is a secondary infection because they are at risk for respiratory infection
Albuterol (Proventil) and beclomethasone (Vanceril) by metered dose inhaler (MDI) are ordered for a client recently diagnosed with asthma. How should the nurse instruct the client to take the medications?
a. "Take Vanceril first, followed by Proventil"
b. "Take Proventil first, wait 5 min, followed by Vanceril"
c. "Take Vanceril first, wait 5 min, followed by Proventil"
d. "Take Proventil first, followed by Vanceril "
b.
What kind of testing is used to diagnose respiratory conditions?
PFTs (spirometry)
*Albuterol [Ventolin, Proventil] would need to be held 6 hrs prior to testing
What are the 2 pre and 3 post procedures of bronchoscopy & laryngoscopy
pre-procedure:
- conscious sedation
- topical anesthesia
post-procedure:
- risk for aspiration → wait a few hrs to eat / drink, start with ice cubes
- hoarseness
- bleeding (pinkish)
*same considerations, bronchoscopy will just extend farther into airways
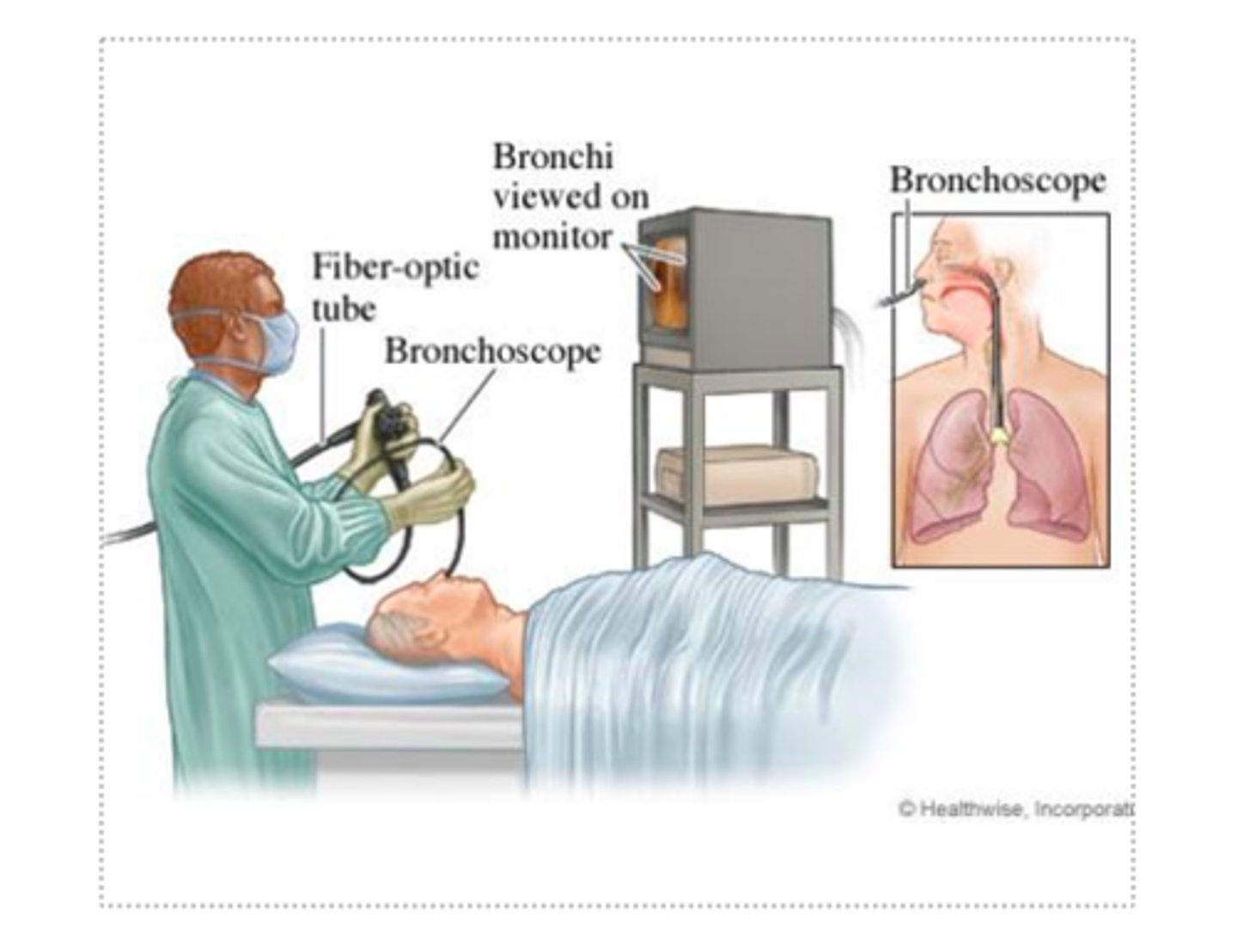
A client returns to the nursing unit after a bronchoscopy and is expectorating pink-tinged sputum. What is the most appropriate nursing action?
a. Notify provider as soon as possible
b. Take client's VS & notify provider
c. Auscultate client's lung fields for possible pulmonary edema
d. Educate client this is expected and continue to monitor
d.
Also: after any procedure that goes through throat, what is another consideration?
Note: “pink frothy sputum” is code word for acute pulmonary edema on NCLEX, but not
common in real practice
Two hours after sub mucous resection, a client's nostril's are packed. Which assessment would alert the nurse to active bleeding at the surgical site?
a. Frequent swallowing
b. Dry mucous membranes
c. Decrease in urinary output (UO)
d. Elevated temperature
a.
Also: (1) careful blowing nose, (2) position correctly post-op, & (3) check throat
What is a hallmark sign of active bleeding following a throat procedure?
frequent swallowing
What ventilator settings are checked?
- FiO2
- PEEP
- RR
- TV (more common in weight-based dosing, such as in peds)
FiO2 (fraction of inspired oxygen)
ventilator setting for [O2] in the air being delivered to pt
common setting: 40 - 50% to start & titration based on ABG & SpO2
*increasing FiO2 → poorer prognosis
PEEP (positive end expiratory pressure)
ventilator setting for the instillation & maintenance of small amounts of air into the alveolar sacs to prevent collapse each time the pt exhales
common setting: 5 - 10 mmH2O, but can be as high as 20
*increasing PEEP → poorer prognosis
Why might a patient's RR be adjusted when on a ventilator?
to compensate for acid-base imbalances
the setting changes as they learn to breathe on their own
acidosis → hyperventilation
alkalosis → hypoventilation
Tidal volume is based on?
weight
What are the ventilator modes?
controlled (volume- or pressure-control) modes → provides pt with completely mechanical breaths with a set respiratory rate
supported / assisted (spontaneous) modes → pt may initiate breaths, but rate & volume still pre-set*
*caution with hyperventilation! (“overbreathing” the vent)
SIMV (synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation) → correlates with pt's natural breath
**pt's may go on CPAP / BiPAP before or after intubation
If pt is hypercapnic (acidotic), what change might you make to vent setting?
Increase the respiratory rate to blow off Co2 that is being trapped
What are the 7 ET Precautions/Interventions?
1. Enter the mouth with a tube and stop just before the bifurcation into the bronchi
2. Give paralyzing and sedating meds (have good communication because the diagram will immediately stop working)
3. Look for an even rise and fall of the chest, check SpO2, and listen to breath sounds bilaterally so it does not slip into the right or left bronchi
4. Chest x-ray to ensure it is in the right place
5. Document how many centimeters is at the lip during dressing change
6. Move the tube around the lip every 24 hours with sliding clips
7. Empty water from the circuit (tubing) PRN
When should paralyzing & sedating medications be administered to a patient undergoing intubation?
immediately before intubation & no sooner (risk of paralyzing respiratory muscles before tube is placed)
true or false: The nurse should never silence a ventilator alarm.
true
Rationale: If a vent alarm sounds, DO NOT silence the alarm; rather, assess the pt to determine the cause!
A high pressure ventilator alarm may indicate...
- pt is coughing (from secretions in airway)
- pt is biting tube → need to ↑ sedation
- pt is fighting ventilator → need to ↑ sedation
- there's water in circuit
- there's a kink in tubing
*more common than low pressure alarms
A low pressure ventilator alarm may indicate...
- disconnection of system (circuit or airway leaks)
- disconnection from pt (extubation)
*more dangerous situation than high pressure alarms!
A client is admitted to the hospital with respiratory failure. He is intubated in the ED, placed on 100% FiO2, and is coughing up copious secretions. What is the nurse's most appropriate action?
a. Request a chest X-ray
b. Infuse the ordered antibiotic
c. Suction the client
d. Obtain the ordered arterial blood gas (ABG)
c. Suction the client
What should always be kept at the bedside of a patient who has an ET tube or is on a ventilator?
Ambu bag (in case of extubation)
Define VAP
ventilator-associated pneumonia
*hospital aquired
What are 5 interventions: preventing VAP
- HOB 30 - 45 degrees
- oral care (usually 2X/shift or q2 - 8h)
- prevent PUD (give PPI)
- perform daily "sedation vacations" (interruption)
What is the purpose of providing ventilated patients a "sedation vacation"?
provides pt with trial periods where their sedation level & vent settings are dropped in order to assess their ability to breath on their own
*helps prevent VAP by ensuring pt taken off ventilator ASAP
*this is done daily
Recent research shows using what antimicrobial agent when performing oral care for ventilated patients increases mortality rate?
chlorhexidine
A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of acute right upper pneumonia. The patient has a history of chronic bronchitis and type 1 DM. Which symptom would you expect to see?
a. Moist, cool skin
b. Rust-colored sputum
c. Bradycardia
d. Decreased respiratory rate
b. Rust-colored sputum
What s/sx would you expect for elderly client?
A change in mentation (increased confusion or change in LOC)
What are manifestations of pneumonia?
- rust-colored sputum
- tachycardia
- tachypnea
- AMS (sign of infection in elderly pt's)
What are the interventions of a tracheostomy? Awake vs Restrained
if awake (common):
- teach pt how to communicate needs, including suctioning PRN
- provide writing tablet
if restrained:
- provide appropriate call light (versions available that don’t require hands)
- hyperoxygenate pt before suctioning
- clean peri-trach area a few X/shift; full trach care daily
In addition to an Ambu bag, what should always be kept at the beside of a patient with a tracheostomy?
extra inner cannula (check sizing!)
What are 10 interventions: enhance gas exchange & airway clearance
- admin bronchodilator as prescribed
- smoking cessation
- educate re: & encourage CDB
- monitor ABGs & other indicators of hypoxia, note trends
- balance pain management with judicious use of analgesics
- maintain adequate hydration (2 - 3 L/day)
- auscultate lung sounds at least q2 - 4h
- measures to physically clear airway: suctioning, Chest physiotherapy, position changes, promote mobility
- admin O2 (caution in COPD) & humidification (starting at 4 L NC)
- educate re: reporting early s/sx of infection
What are the 3 indications for a chest tube?
1. pneumothorax
2. pleural effusion*
3. s/p mediastinal cardiac surgery
*NOT the same as pleural edema!
What are 3 nursing priorities for a chest tube?
1. mark on the actual Atrium as you monitor I&O
2. Keep below level of the chest
3. suction
*MUST use closure to clamp tube before changing chamber (also keep upright & below the level of the chest)
*use orange dial to set suction pressure, if using

What kind of drainage is expected in a chest tube following thoracic surgery?
serosanguineous
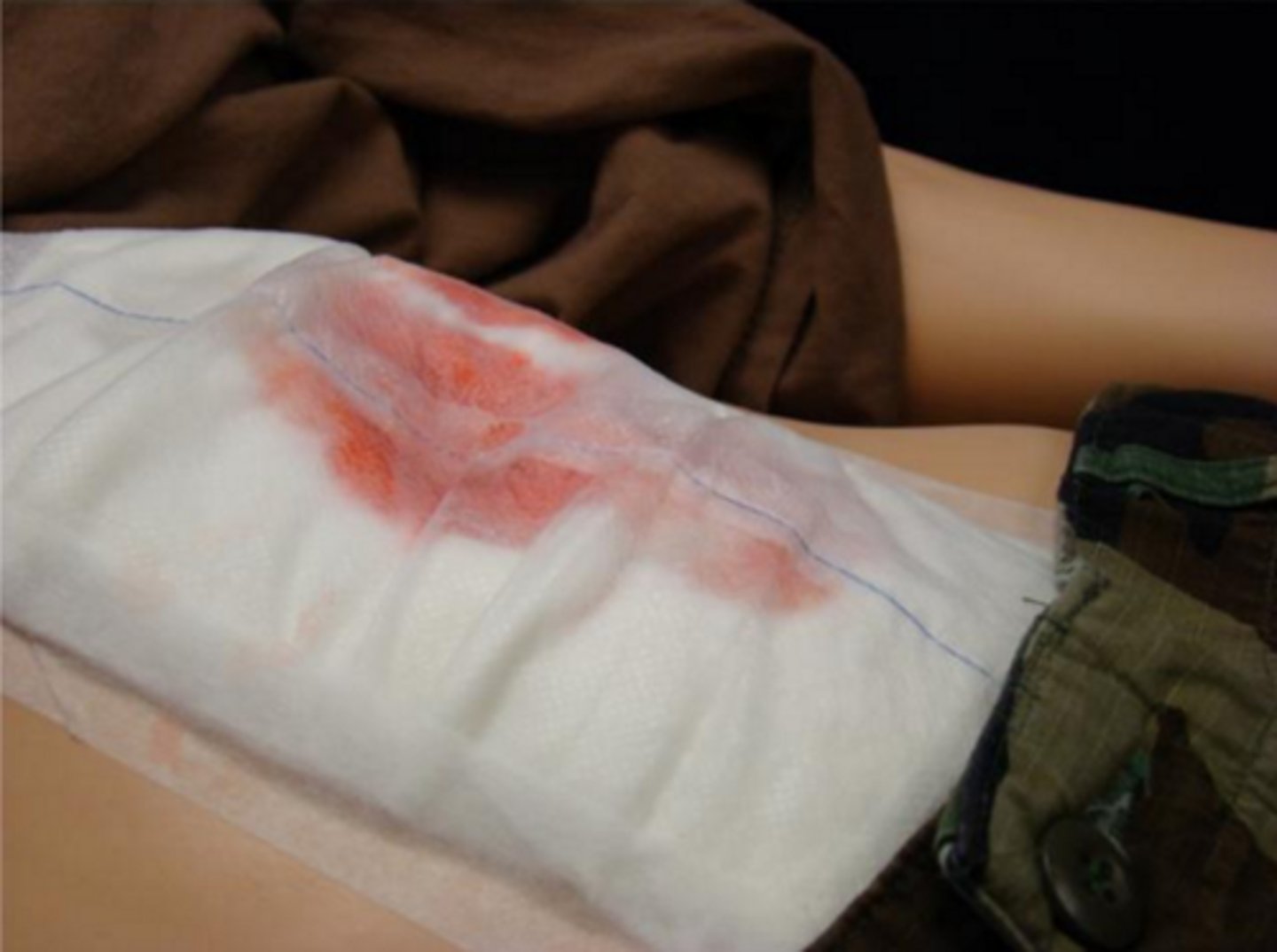
What 2 chest tube output changes would cause the RN concern?
1. any sudden change in quantity of output (↑ or ↓)
2. any change in quality of output (sanguineous = sign of active bleeding, bubbles = air leak in H2O chamber)
What should the RN do if a patient's chest tube falls out?
put petroleum gauze on top of hole in chest → call HCP
What indicates a patient is ready to have their chest tube removed?
when there is little / no output
What is subq emphysema?
accumulation of air in the skin
causes: chest tube, thoracentesis, injury to trachea during intubation, bag mask ventilation during CPR...
*feels like popping bubble wrap or Rice Krispies when the skin is pressed
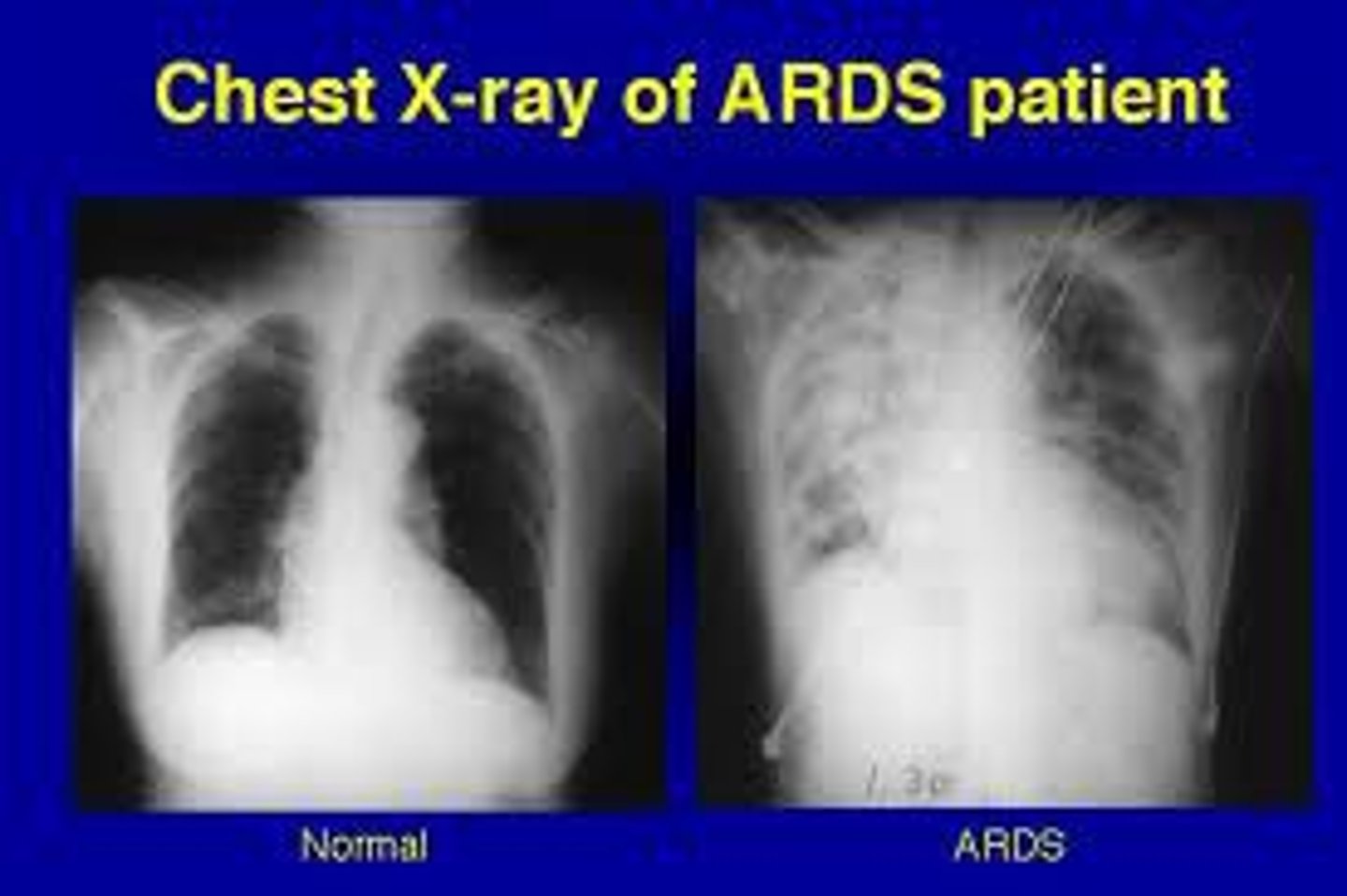
Define ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome)
nonspecific pulmonary response to a variety of pulmonary & non-pulmonary insults to the lungs that is characterized by refractory hypoxemia, interstitial infiltrates, alveolar hemorrhage, atelectasis, & ↓ lung compliance
*often called "white lung" or "stiff lung"
*mortality rate ~40%
Define refractory hypoxemia
hypoxemia that does NOT respond to O2 tx
Whats causes of ARDS?
indirect: septic shock (most common)
direct (delayed): inhalation injury, near drowning, O2 toxicity (rare), covid
What is the treatment of ARDS?
NC (↑ O2 flow) → mask (probably non-rebreather) → CPAP / BiPAP → intubation
Patients can tolerate _____ to _____ hours of 100% oxygen therapy without serious tissue damage.
24 to 48
Define thoracentesis
therapeutic removal of fluid from the pleural space via a puncture in the chest wall
*performed while pt leaning over bedside table
*patient typically has plural ed
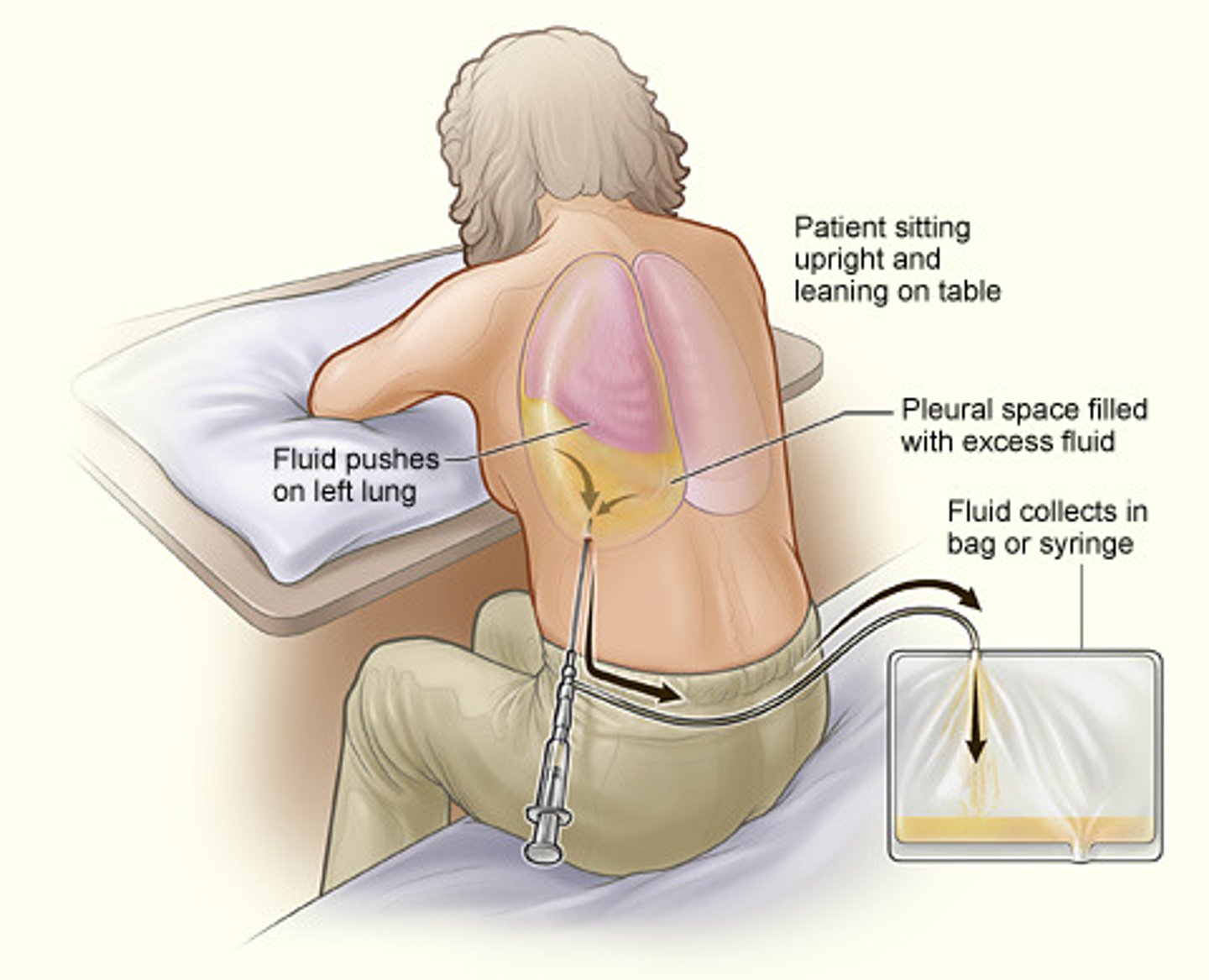
During thoracentesis, sanguineous drainage suggests the presence of __________, while purulent drainage suggests __________.
hemothorax, empyema (infection)
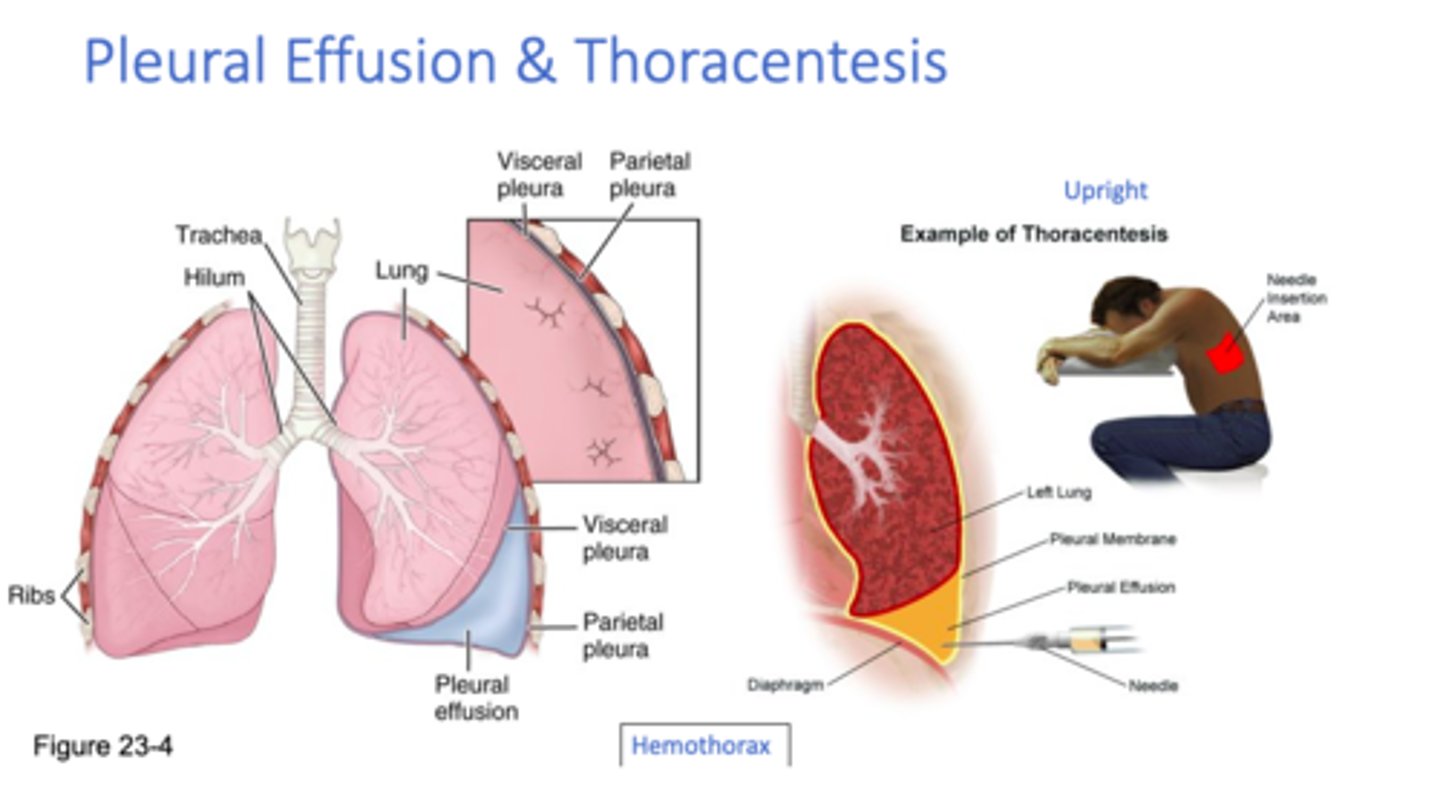
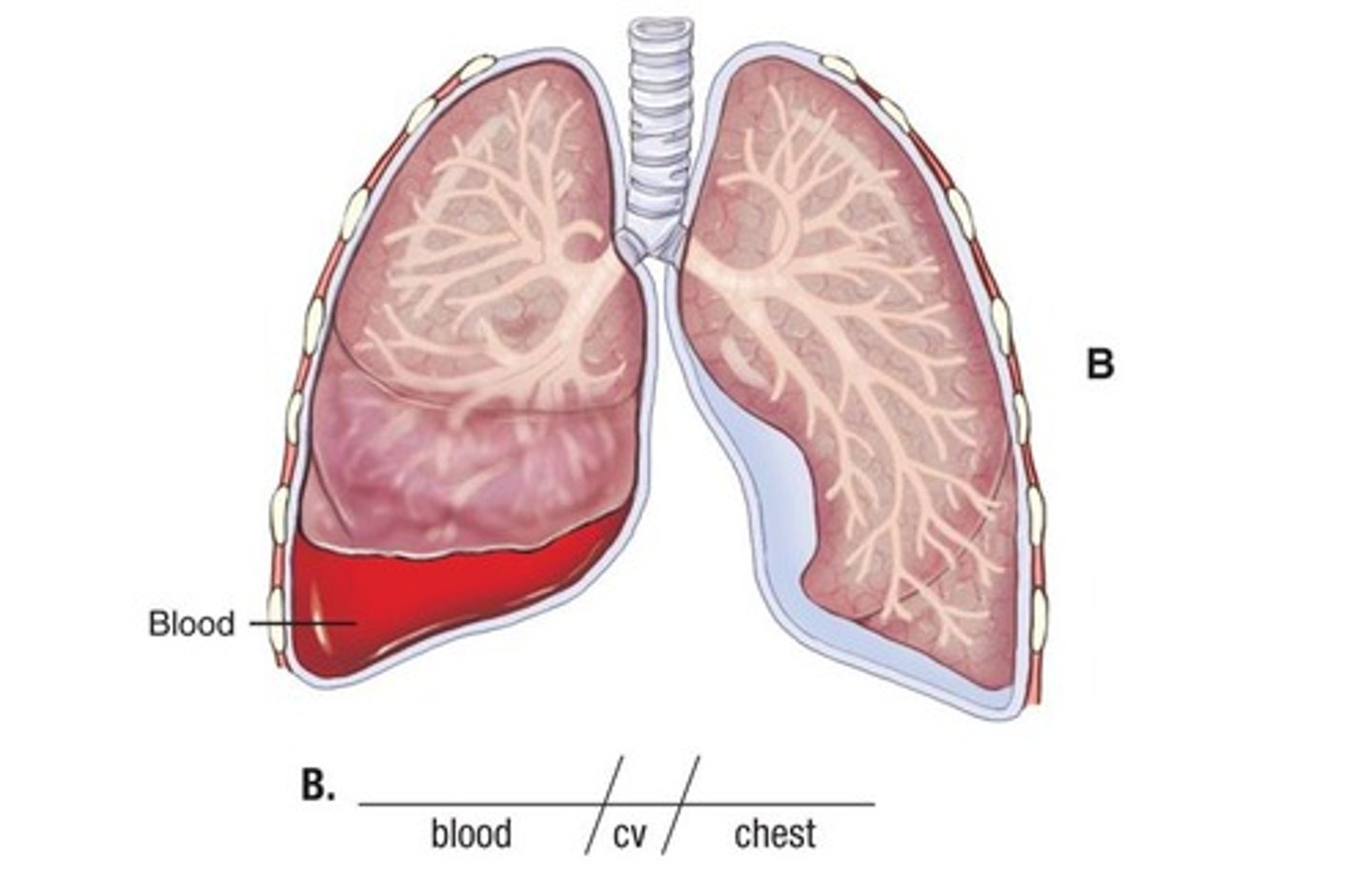
Define hemothorax
presence of blood in the pleural cavity
Define empyema
presence of pus in the pleural cavity

Define pleural edema
accumulation of fluid in the lung tissue (alveoli)
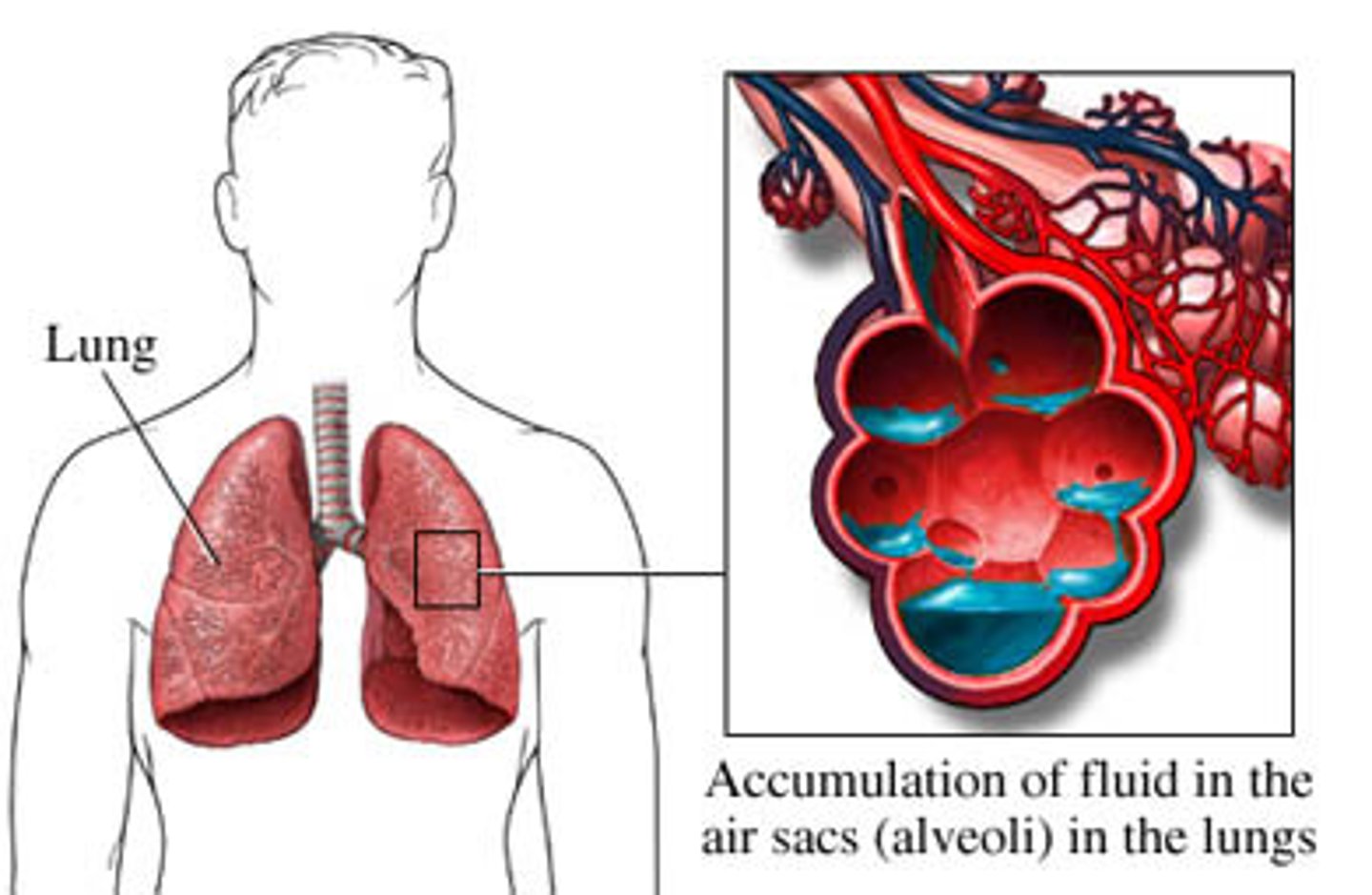
How is pleural edema treated?
diuretics
What diagnostic tests are used to diagnose pleural edema and/or effusion?
chest x-ray & CT
What is pleuritic pain
sharp, stabbing pain associated with inhalation that can be alleviated or worsened by position changes
Define closed (spontaneous) pneumothorax
pneumothorax associated with the popping of air blebs in the lungs
*pressure less than atmospheric
*adolescent skinny males more prone
Define bleb
small collection of air between the lung & visceral pleura usually found in the upper lobe of the lung
Define open pneumothorax
pneumothorax associated with a defect in the chest wall (e.g. from trauma) that allows air to enter & exit the pleural space from the outside
*also called a "sucking chest wound"
*pressure same as atmospheric pressure
Define tension pnuemothorax
pneumothorax in which air that enters the chest cavity is prevented from escaping to the outside & becomes trapped
*flap of tissue, inflammation can prevent 2-way airflow
*pressure inside lungs is greater
The presence of tracheal deviation is indicative of what kind of pneumothorax?
tension
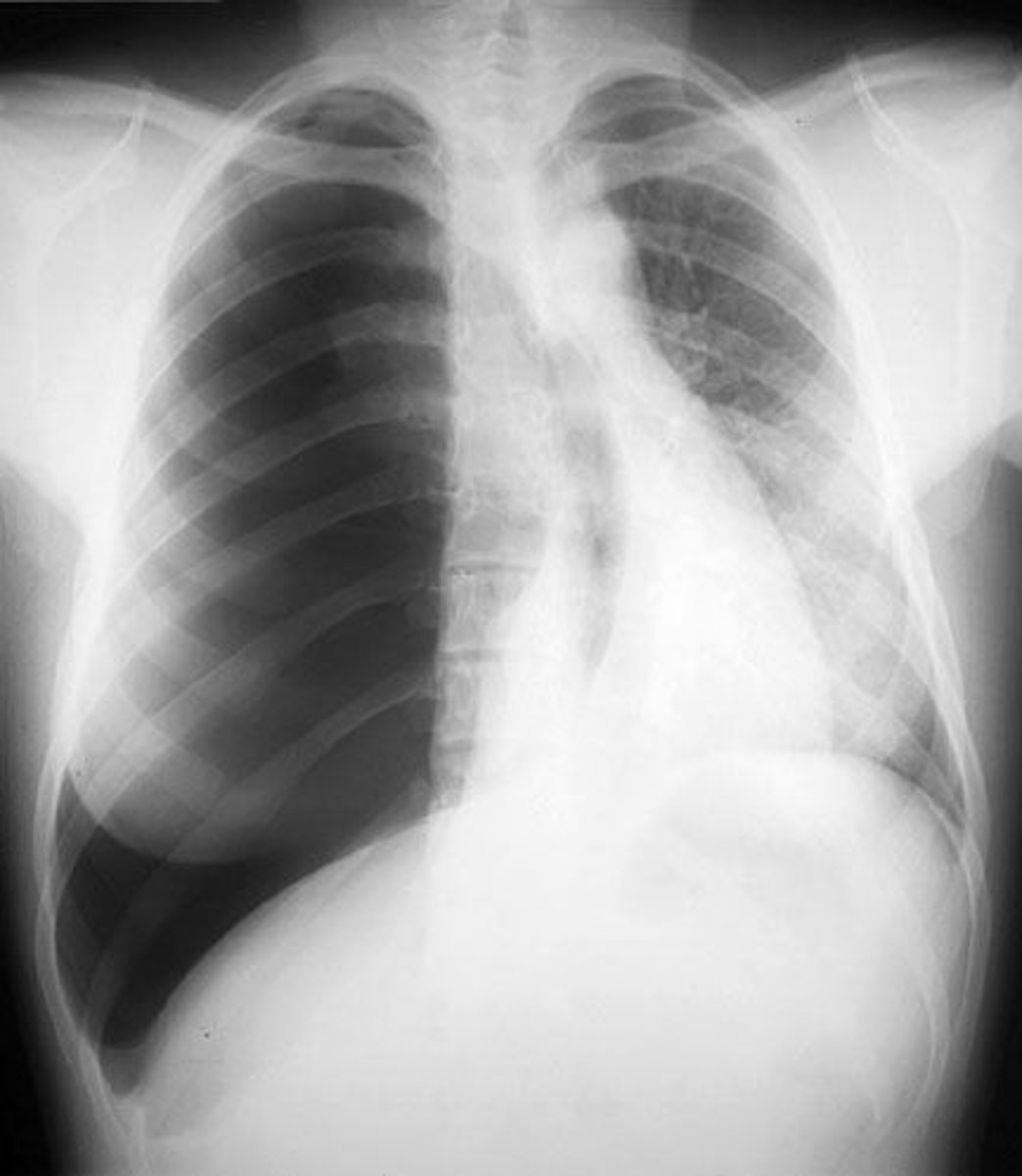
What is the 3 treatments of pneumothorax
- O2 (may be enough for minor cases)
- needle aspiration
- chest tube
Define flail chest
paradoxical chest movement cause by fracture of 3+ adjacent ribs in 2+ places, allowing for free movement of the fractured segments
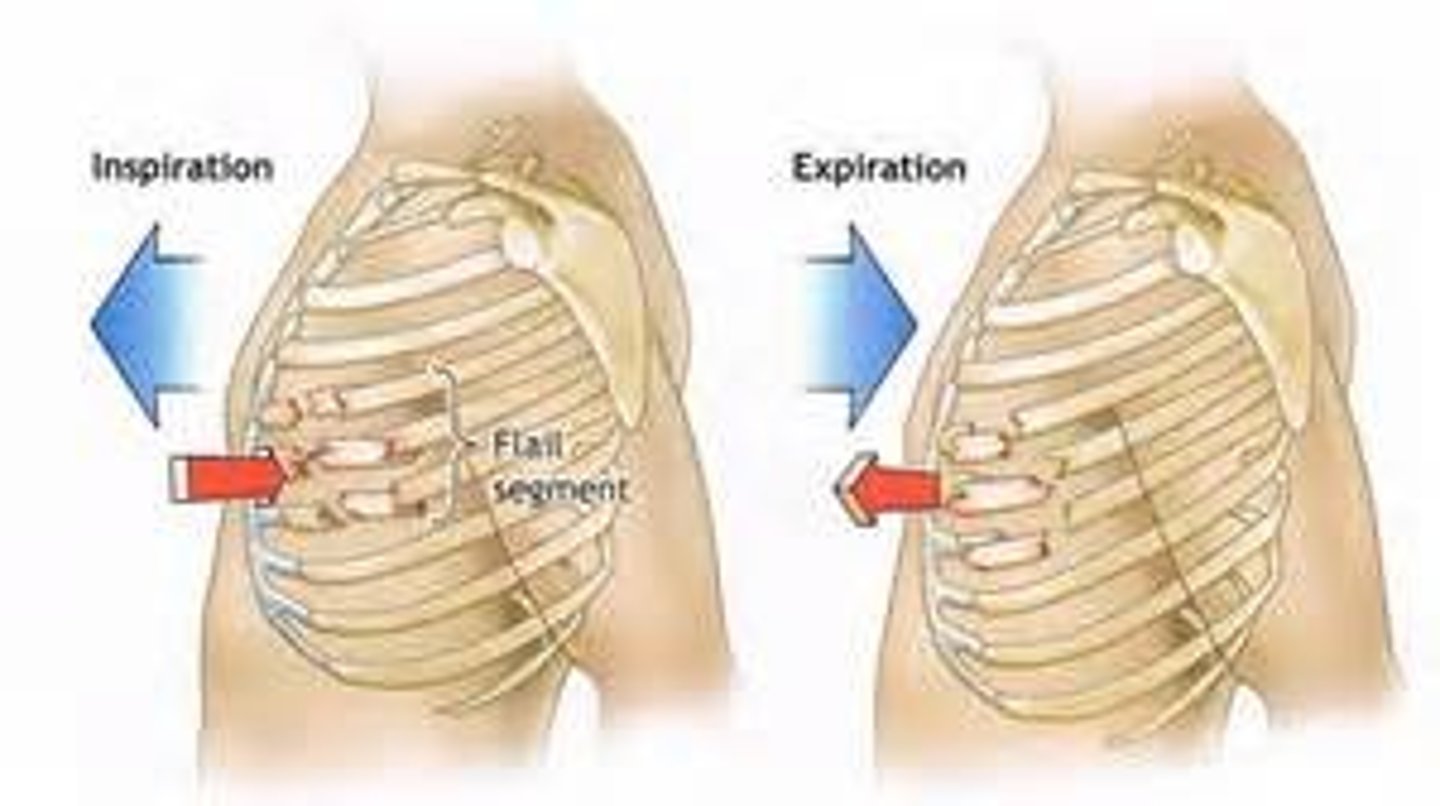
What are manifestations of pneumothorax?
- chest pain
- SOB
- diminished / absent breath sounds on affected side
- asymmetric / absent chest expansion (severe cases)
CF (cystic fibrosis)
inherited autosomal recessive d/o of the exocrine glands wherein the body makes too much mucus, affecting the digestive (pancreas), respiratory, & integumentary systems
*most lethal genetic d/o among white Americans
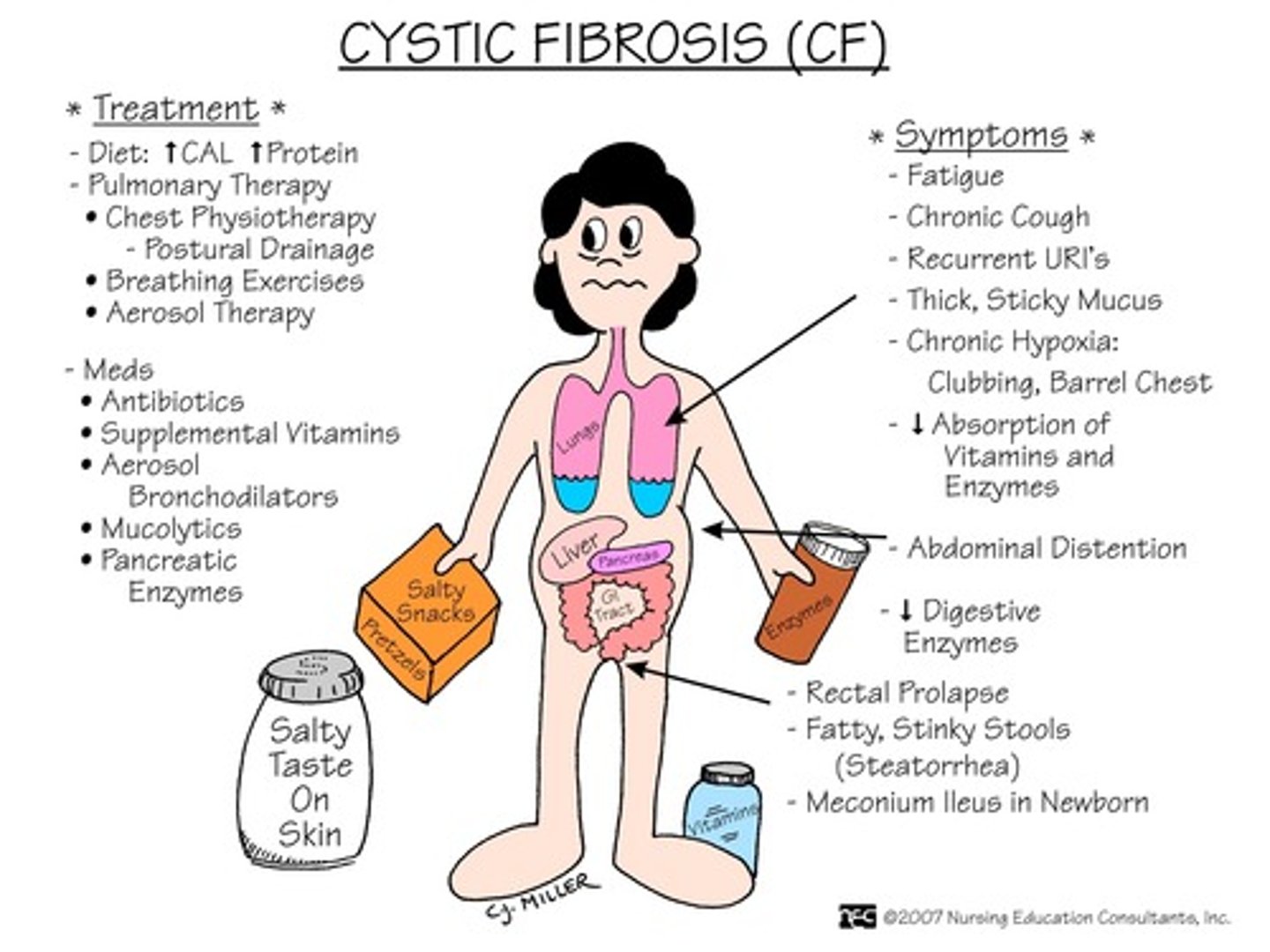
CF is caused by impaired transport of __________ ions.
chloride (which usually bind with sodium ions)
dx: sweat test (Cl- > 60 mEq/L)
What are the primary infectious organisms affecting patients with CF?
drug-resistant organisms, including:
- MDR pseudomonas
- MRSA
- NTM
MDR
multi-drug resistant
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
NTM
non-tuberculosis mycobacteria
What are the top 2 priority nursing interventions for patients with CF?
1. CPT
2. preventing infection: prophylactic abx, isolation, neutropenic precautions
Ingesting what food can cause increased & thickened secretions in patients with CF?
milk & other dairy products