Module 1 & 2: Quality Control & Quality Assurance
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Quality
Totality of characteristics or features of a product that bear on its capacity to satisfy stated or implied needs
Quality Assurance
Sum total of the organized arrangements made w/ the object of ensuring that products will be consistently of the quality required by their intended
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)
Ensure that production consistently produced & controlled according to quality standards & marketing authorization (from FDA)
Quality Control
Part of GMP concerned with sampling, specifications & testing, & with the organization, documentation & release procedures which ensures that the relevant & necessary tests are intact & in fact carried out & that materials are not released
QA Department Function
Assures policies are followed inept to economic issues associated with manufacturing & distribution of product
Cooperate with regulatory agencies & final authority for product acceptance or rejection
QA Department Function
Helps to identify & prepare necessary SOP’s relative to control of quality
Personnel
Procedure
Equipment
Premises
Environment
Package
Starting Materials
Validate Processes
Factors Affecting Quality Products (8)
Monograph
A document which specifies all the tests to be conducted on a particular material or product, the procedure and/or appropriate references containing the details of the procedure and expected results
Validated by researchers
Certificate of Analysis
A document containing the result of all tests conducted on a particular material or product to show compliance or non-compliance with established standards or specifications approved by responsible personnel
Absolute Error
Relative Error
2 Types of Error
Absolute Error
Distinction between quantities of measured value and actual value
Indeterminate (uncontrollable causes)
Determinate (identifiable systematic errors or bias)
2 Types of Absolute Error
Indeterminate
random errors
slight variations in a series of observations made by the same observer
intangible, elimination by analyst is hard
difficult to detect
difference of judgment of analyst
Determinate
Errors by analyst
methodological errors
instrumental error
Accuracy
Closeness of the data to true value
Precision
Closeness of data
Specificity
Assess unequivocally the analyte in the presence of components that may be expected to be present
Sensitivity
Refers to the ability of a test to detect very small amounts of a target analyte (the minimum detectable concentration)
Robustness
Measure of capacity to be unaffected by small but deliberate variations in method & provides indication of its reliability during normal usage
Measurability
Seriousness or Gravity
Nature
3 Category of Defects
Variable Defect
Attribute Defect
2 Defects under Measurability
Variable Defect
Can be measured directly by instruments
Confiable
Attribute Defect
Cannot be measured directly by instruments
Non confiable
Critical Defect
Major Defect
Minor Defect
3 Defects under Seriousness and Gravity
Critical Defect
May endanger life or property & may render the product non-functional (Absence of Warning)
Major Defect
May affect the function of the object, & therefore, may render the product useless. (Crack in a Bottle)
Minor Defect
Does not endanger life or property but remains a defect. (Slight deviation of the color of the label from the color standards)
Ex: packaging
Ocular Defect
Internal Defect
Performance Defect
3 Defects under Nature
Ocular Defect
Visible (Foreign particulate contamination)
Internal Defect
Not seen although present (Subpotent Drug Product)
Performance Defect
Defect in function (Suppository that does not melt at body temperature)
Materials
Variation between suppliers of same substance
Variation between batches from same suppliers
Variation within a batch
Machines
Variation equipment for the same process
Difference in adjustment of equipment
Aging & improper care
Methods
Inexact procedure
Inadequate procedures
Negligence
Men
Improper working conditions
Inadequate training, & understanding
Dishonesty, fatigue & carelessness
Confidence Interval
range of value around an actual result w/ which true value is expected
Significance Test
compare individual values or set of values for significant differences.
Null Hypothesis there is no significant differences
Alternate Hypothesis
One Tailed
there is a significant difference & indicates what is the dissimilarities or variations
Two Tailed
there is a significant difference but doesn’t indicate the dissimilarities or any variations.
Quality Control Testing Of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
sum of all processes done to ensure that product possesses, ensuring its efficacy & safety.
Packaging
Identity Test
Limit Test
Potency Test
Dosage- Form Specific Test
General Test Classifications (5)
Assumptions
Sampled using an appropriate sampling plan; Representative of the lot being tested
Packaging Material type Special Properties
Example: transparent, collapsible, easy to drain Integrity
Example: tightness, leak-free
Physical Properties
Gross physical appearance
Example: color, occurrence, odor, consistency, dimensions
Potency Test
determine conformance of dosage form to label claim
Instrumental Methods
Chemical Methods
Biological Methods
Methods Under Potency Test
Sampling
comprises the operations designed to select a portion of a pharmaceutical product (for definition, see glossary) for a defined purpose. The sampling procedure should be appropriate to the purpose of sampling, to the type of controls intended to be applied to the samples and to the material to be sampled. The procedure should be described in writing
n plan
p plan
r plan
Sampling Plans and Techniques for Starting Material (3)
n plan
when the material to be sampled is considered uniform and is supplied from a recognized source
Samples can be withdrawn from any part of the container (usually from the top layer)
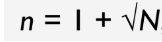
Formula of n plan
p plan
when the material to be sampled is considered uniform and is supplied from a recognized source and the main purpose is to test for identity

Formula of p plan
r plan
when the material is suspected to be nonuniform and/or is received from a source that is not well known
used for herbal medicinal products used as starting materials.

Formula of r plan
Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL)
Sampling Plans and Techniques for Finished Products
AQL
The quality level that is the worst tolerable over the course of many inspections
used to determine how many units should be inspected and how many defects are acceptable during the inspection
Statistical Quality Control
the monitoring of quality by the application of statistical methods in all stages of production
Attribute Chart
Variable Chart
Two basic Quality Control Charts
Attribute Chart
a chart when makes use of discrete data classifying the number of item conforming & the number of items failing to conform to any specified requirements
Example: P chart and C chart
Variable Chart
a chart using actual records of numerical measurement on a full continuous scale such as meter, grams, liter.
Example: X and R charts
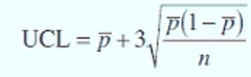
Formula of UCL
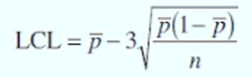
Formula of LCL
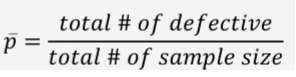
Formula of Center Line
Raw Materials Quality Control (RMQC)
In Process Quality Control
Finished Product Quality Control
3 Main Areas of Quality Control
Identity Test
Purity Test
Limit Test
Physical Test
Special Test
5 Tests Under RMQC
In Process Quality Control
These are checks that are carried out before the manufacturing process is completed
monitoring and if necessary, adaption of the manufacturing process to comply with the specifications
Primary Moisture Content 31-35%
Adequacy of Wetness
Shape
Final Moisture Content : 0.5-1%
Angle of Repose
Porosity (Pores)
Bulk Density
Tapped Density
Carr’s Index
Hausner’s Ratio
Particle Size Distribution
Thickness
Hardness
Tests Under In Process Quality Control (13)
Picking & Sticking
Capping, Chipping, and Lamination
High moisture: & ; Low moisture: , ,
Angle of Repose
A constant 3D angle assumed by a cone-like pile of material
Porosity (Pores)
measurement of the void or empty spaces of a material and is defined as the ratio between the volume of voids and the total volume
Bulk Density
the density of a large volume of porous material powder including the pore spaces within the material particles in the measurement volume
Tapped Density
an increased bulk density attained after mechanically tapping a container containing the powder sample. The tapped density is obtained by mechanically tapping a graduated measuring cylinder or vessel containing the powder sample
Carr’s Index
Index of compressibility
Indication of the compressibility of a powder
Hausner’s Ratio
measure of flowability
Stroke Monsato
test of strength
Friability Test
Hardness
Thickness
Disintegration Test
Dissolution Test
Uniformity of dosage units
6 Tests For Solid Dosage Forms
Bacterial Endotoxin Test
Particulate Matter
Pyrogen Test
Clarity Test
Safety Test
Sterility Test
Leaker’s Test
7 Tests For Parenterals
Microbial content
Stability
Sedimentation value
Redispersibility
Rheological properties
Electrophoretic Analysis
Particle Size determination
7 Tests For Non-Sterile Products
Microbial content
Spreadability
Viscosity
3 Tests For Semi-solid
Stability
Capacity of drug to remain within specifications
Established to assure identity, strength, quality, & purity
Acceptable Stability
Time in storage and use in which a particular formulation in a container remains within physical, chemical, toxilogical, and bioavailability specifications.
Expiration Date
Time in which the preparation will remain stable when stored under recommended conditions
Too Early
Too Late
Type 1 Alpha Error :
Type 2 Beta Error:
Harmful Events
Decrease in therapeutic activity of preparation to below some arbitrary content
Appearance of toxic substances formed as degradation
Stability Studies
Conducted within a span of 6 months
10 tabs
18 tabs
24 tabs
50 tabs
No. of samples
Appearance, Hardness, Thickness, Weight, Moisture = tabs
Disintegration = tabs
Dissolution = tabs
Friability = tabs
2 ½ years or 13 months
Ideal Shelf Life