NURS 333 Chapter 22 Complications Occurring During Labor & Delivery
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Preterm labor
onset of labor before 37 weeks (ATI = 36.6 weeks)
Dystocia
labor with abnormally fast or slow progression
Second Stage of Labor
What?
Ineffective pushing by the mother
When?
Frequently used in women with epidurals
Maternal exhaustion
How?
Failure of the fetus to advance its station
Precipitous labor
labor that lasts 3 hours or less
Prolonged latent phase
labor lasting > 20 hours in a nulliparous women and > than 14 hours in multiparous women
Arrest of active phase
no cervical has occurred in 4 hours with adequate contractions
no cervical has occurred in 6 hours with inadequate contractions
Group B Streptococcus (GBS)
What organism colonizes the urogenital tract and is known as Group B Streptococcus (GBS)?
Benign except in pregnancy
Is Group B Streptococcus (GBS) benign in pregnancy?
Harm to the neonate
What harm can Group B Streptococcus (GBS) cause?
80%
By what percentage does treatment reduce GBS disease in neonates?
Reduces neonatal death
What effect does treatment have on neonatal death related to GBS?
Asymptomatic
What is the typical symptom presentation for Group B Streptococcus (GBS)?
35 to 37 weeks gestation (36 weeks gestation)
When does the CDC recommend GBS culture screening during pregnancy?
GBS + Urine or previously delivered GBS + infant with 1-week after birth
What are the treatment criteria for GBS?
Penicillin
What is the antibiotic of choice for treating Group B Streptococcus (GBS)?
At the onset of active labor or ROM and then every 4 hours until delivered
When should the loading dose of Penicillin be given during labor?
At least 4 hours before delivery
How long before delivery must Penicillin be started?
Ampicillin or Vancomycin
What should be given to patients allergic to Penicillin?
Antibiotic prophylaxis regardless of prior screening
What should be initiated for all preterm labor patients regarding GBS?
Five Ps of Labor
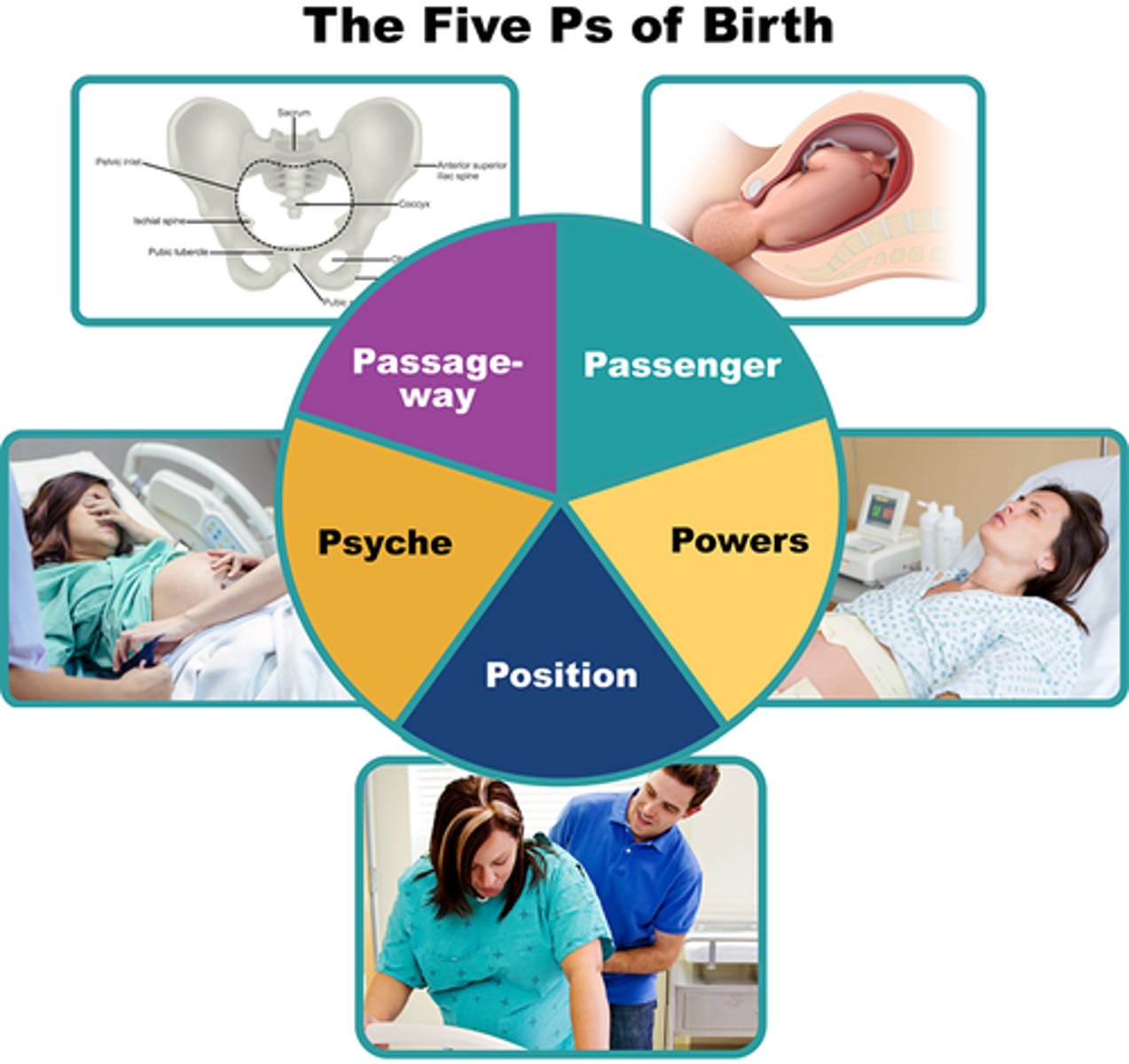
power
refers to uterine contractions and pushing efforts
Passageway
refers to the maternal bony pelvis and soft tissues.
Passenger
refers to fetal factors.
Psyche
refers to maternal state of mind
Anxiety can have a negative impact on normal labor progress and fetal outcomes.
The nurse may play a role in labor support.
Position
refers to maternal position.
Upright positions such as sitting, kneeling, squatting, or standing can shorten the first stage of labor by 90 minutes
Hypotonic Uterine Dysfunction
A condition where uterine contractions are either too uncoordinated or too weak to effectively dilate the cervix.
Occurs in the active phase of labor and is related to polyhydramnios, macrosomia, or multiple pregnancy.
Abdomen is soft when palpated during a contraction
Contractions: less than 3 to 4 every 10 minutes period and last < than 50
Risk factors for Hypotonic Uterine Dysfunction
premature rupture of membranes, fetopelvic disproportion, fetal malposition, overstretching of the uterus caused by a large newborn, multifetal gestation, or excessive maternal anxiety
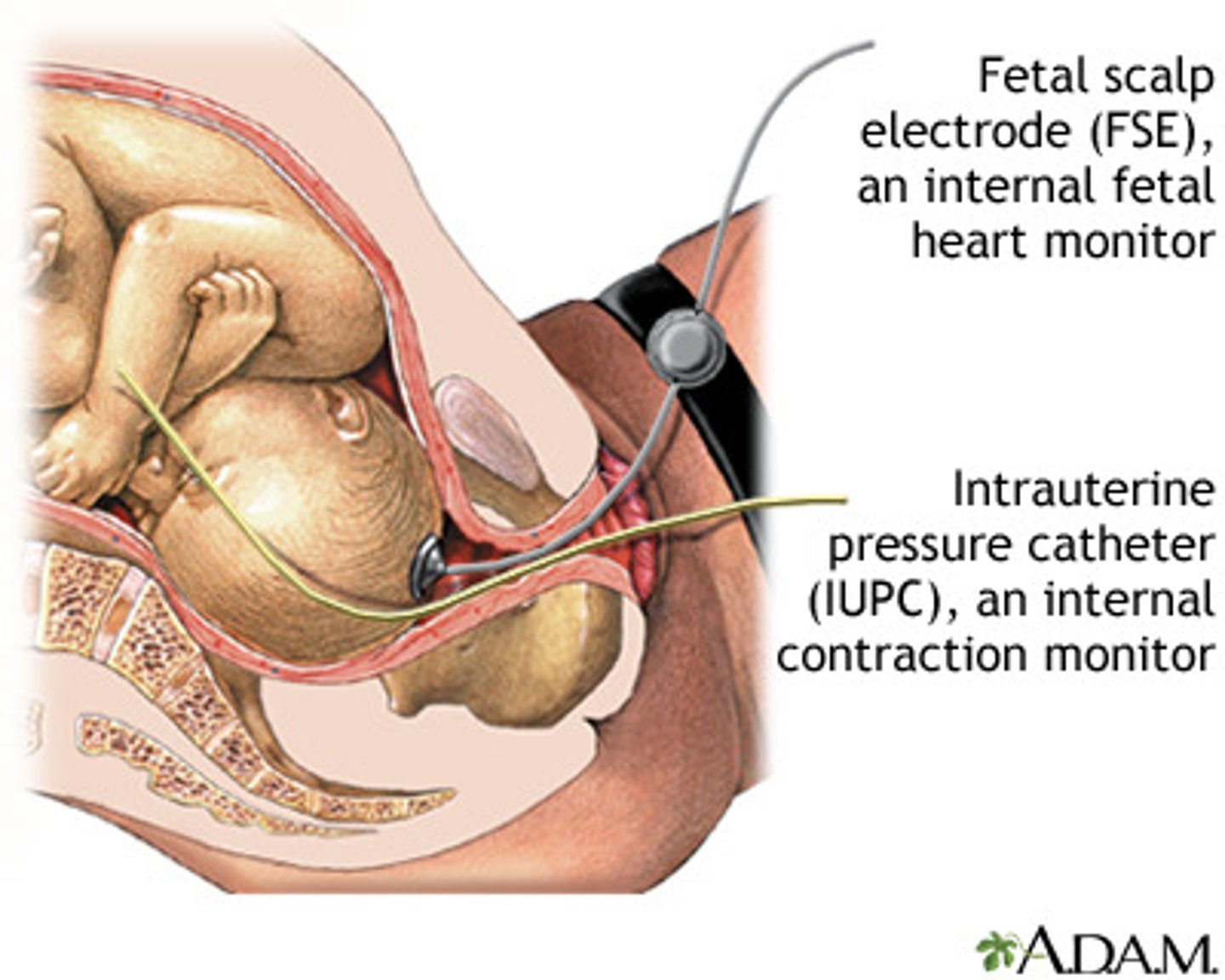
IUPC
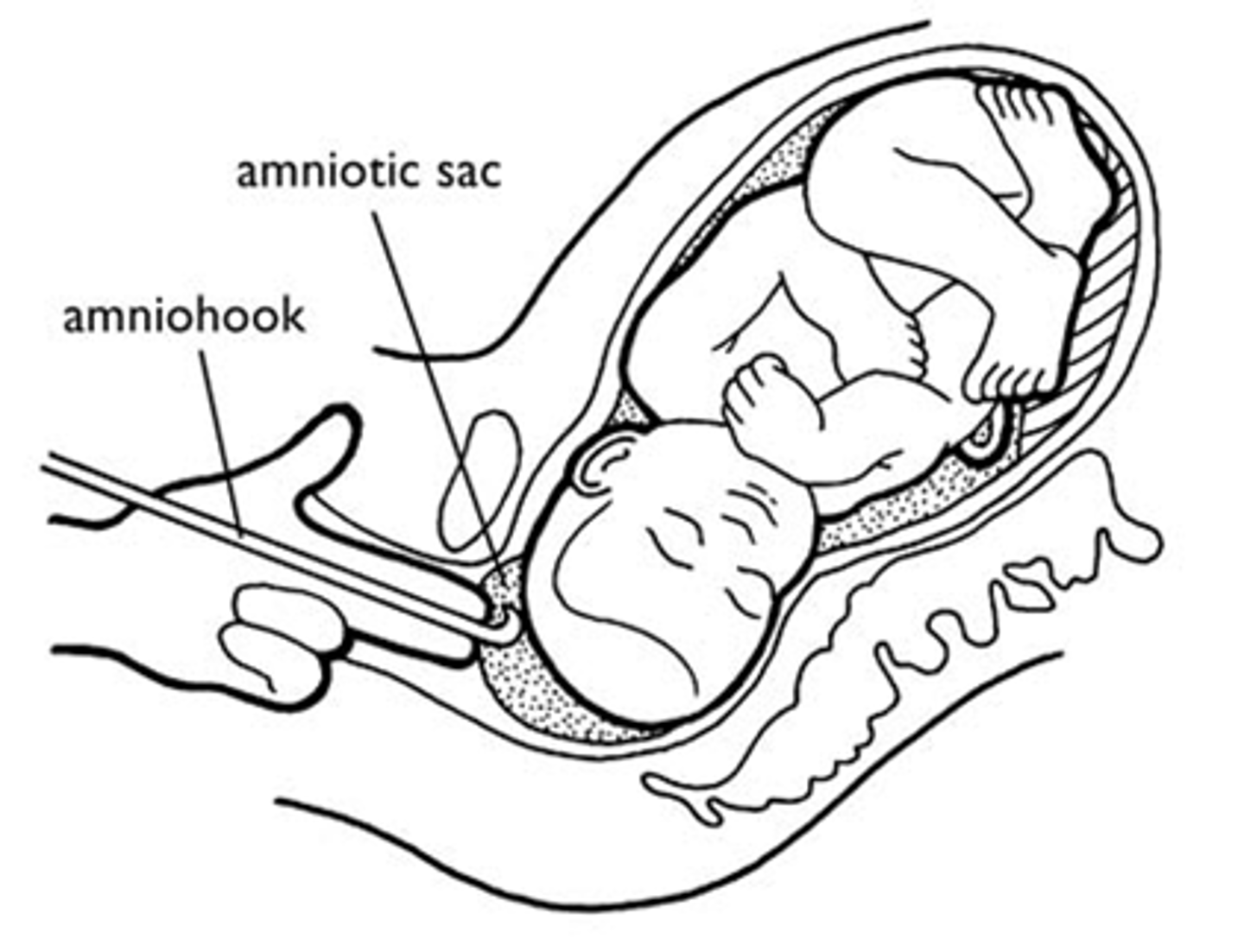
Amniotomy/AROM
Hypotonic Uterine Dysfunction Nursing Considerations
Continue to Monitor for Changes in the patient
Assess pain level
IUPC
Analyze contraction pattern (frequency, duration, and intensity)
Intensity: Montevideo Units > 200 MVUs +adequate contractions
AROM/Amniotomy
Check for prolapsed cord
Assess FHR***
Nursing Considerations/Interventions for Dystocia
Laboring down: a process of allowing the primary powers to facilitate fetal descent in the second stage.
Pushing resumes when the woman feels the urge to bear down.
Consult with OB or anesthesia to turn down or off the epidural
Bandl's ring
Cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD)
Mismatch between the size of the fetal head and the size of the maternal pelvis.
Malpresentation
Fetal position in relation to the maternal pelvis can impact labor progress is not optimal
(OP) Occiput Posterior
Most common
OP position often causes low back pain for women in labor
Longer duration of labor
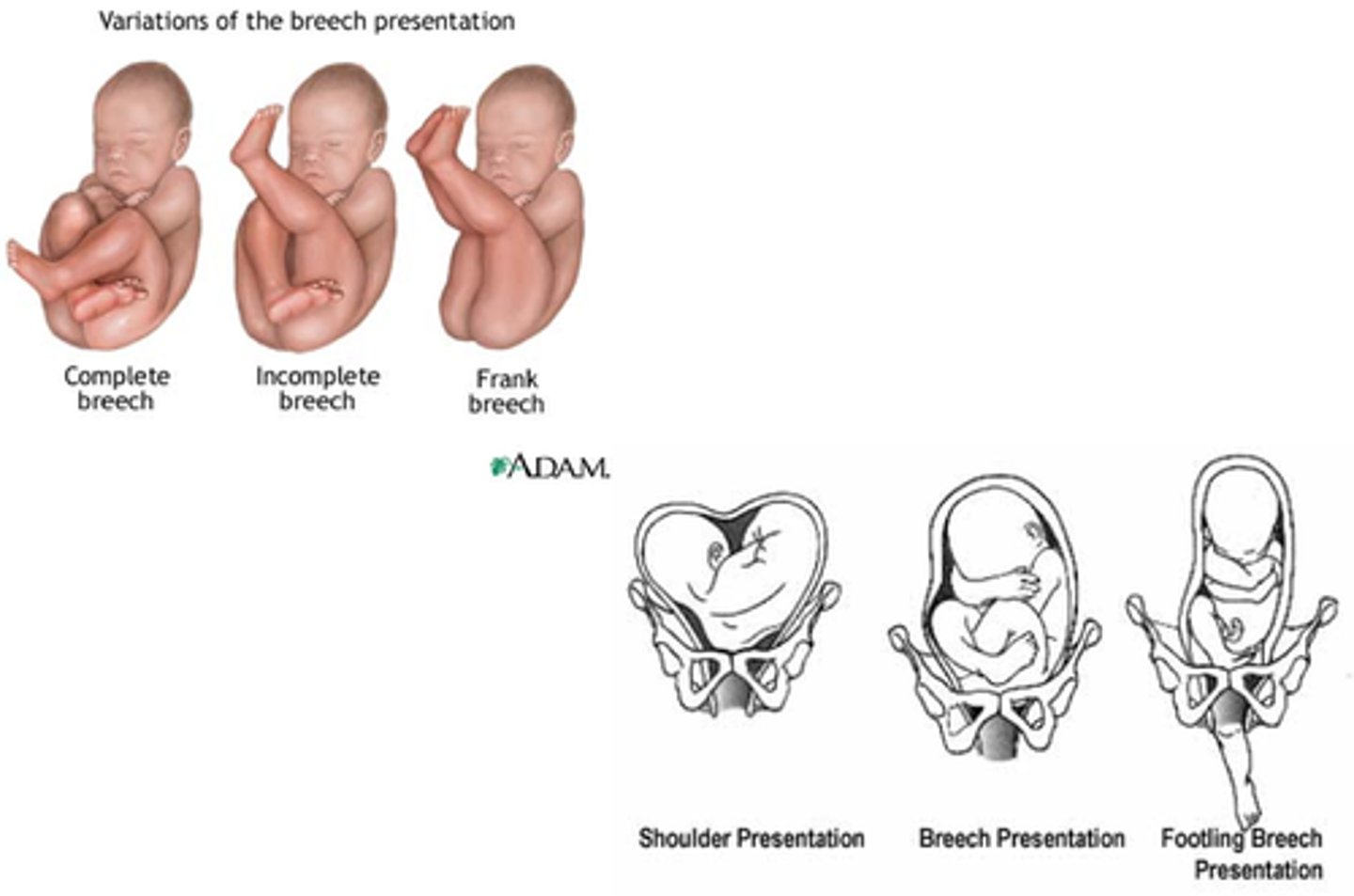
Breech presentation
Occurs in 1 of 33 births.
Various types of breech presentations
are often diagnosed by Leopold's maneuvers and confirmed by ultrasound visualization.
Why are we concerned?
Asphyxia
Birth trauma
Increased risk for delivery by cesarean.
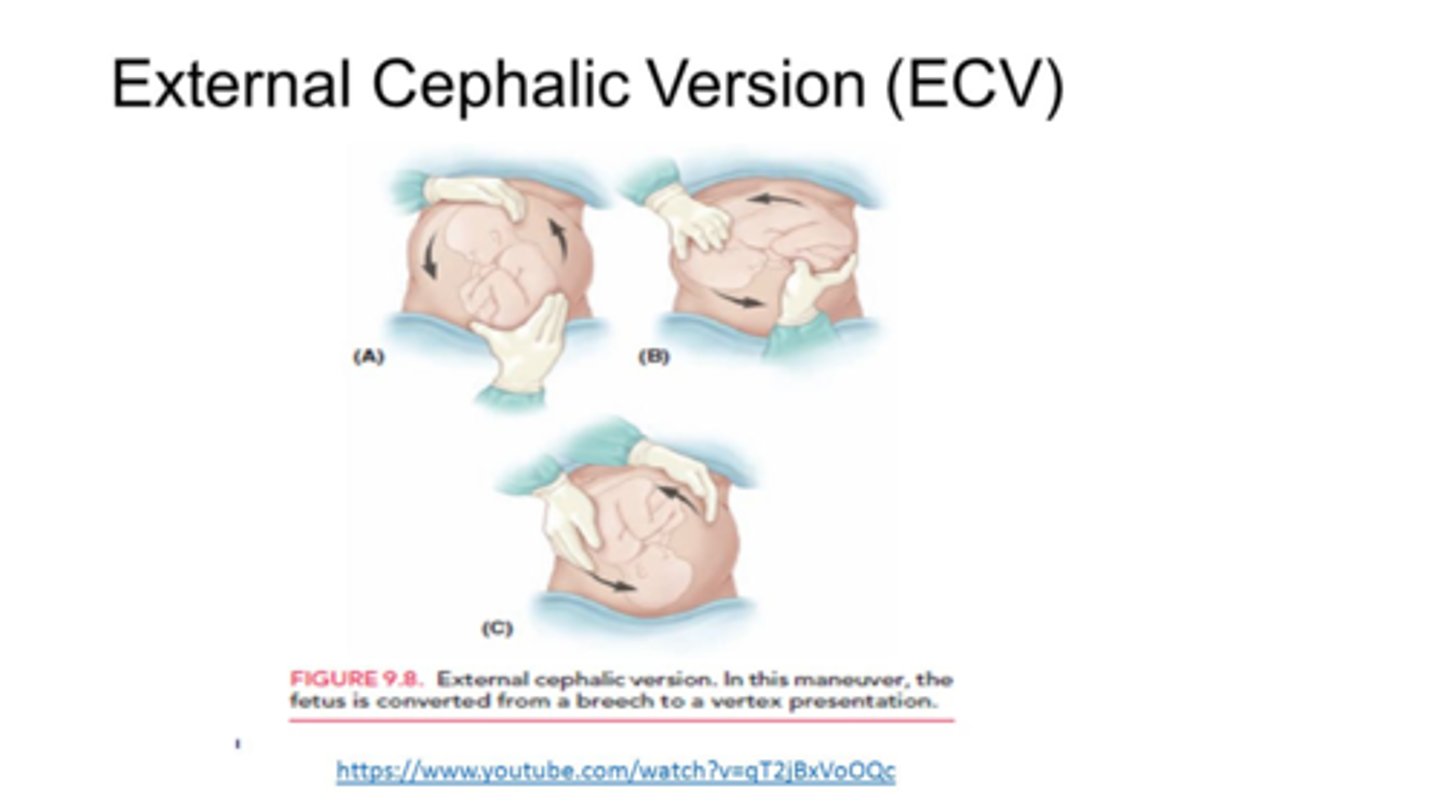
External cephalic version (ECV)
External rotation of the fetus to the head down (cephalic) position
Attempted after 36 weeks
Done under ultrasound guidance
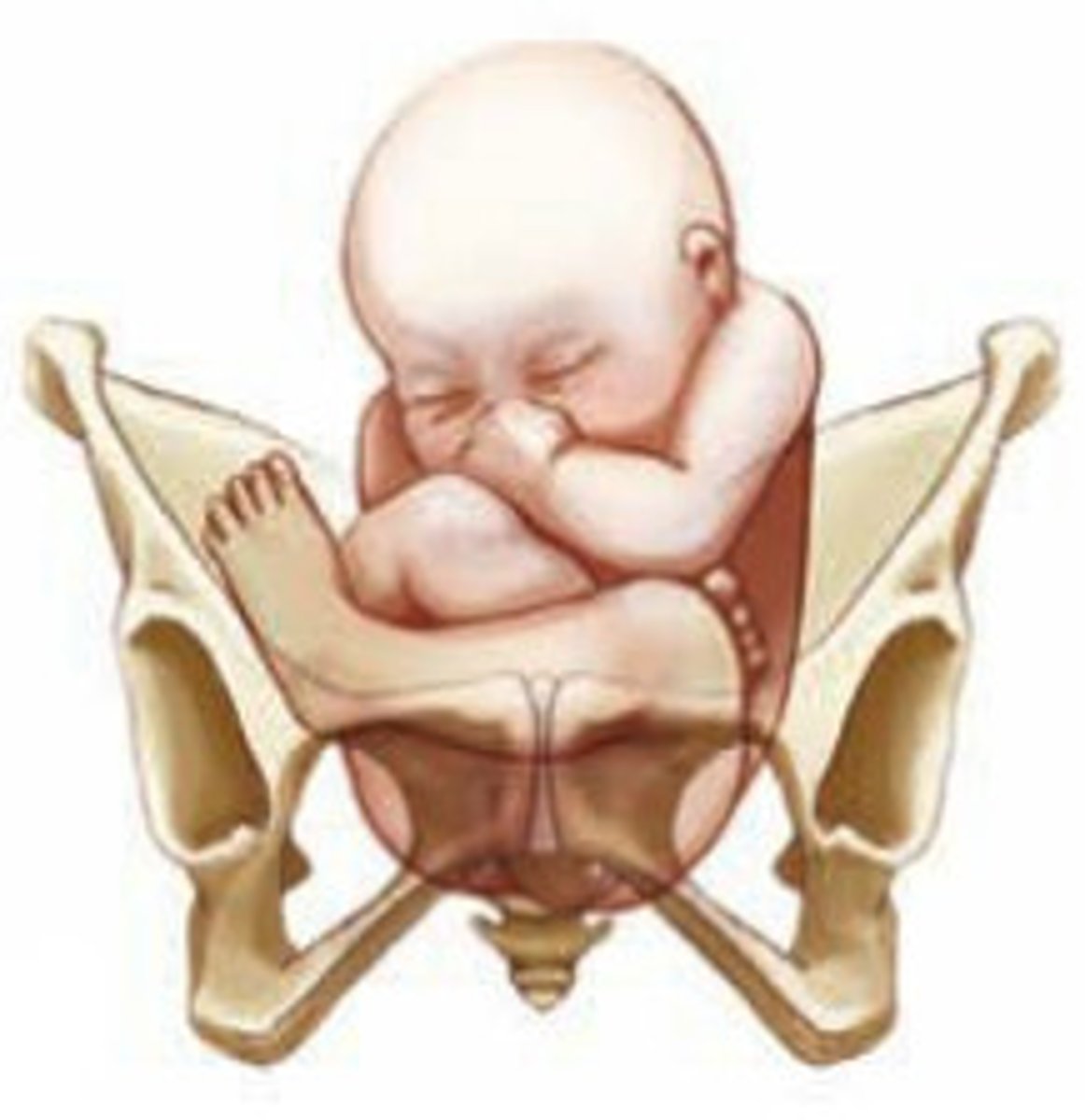
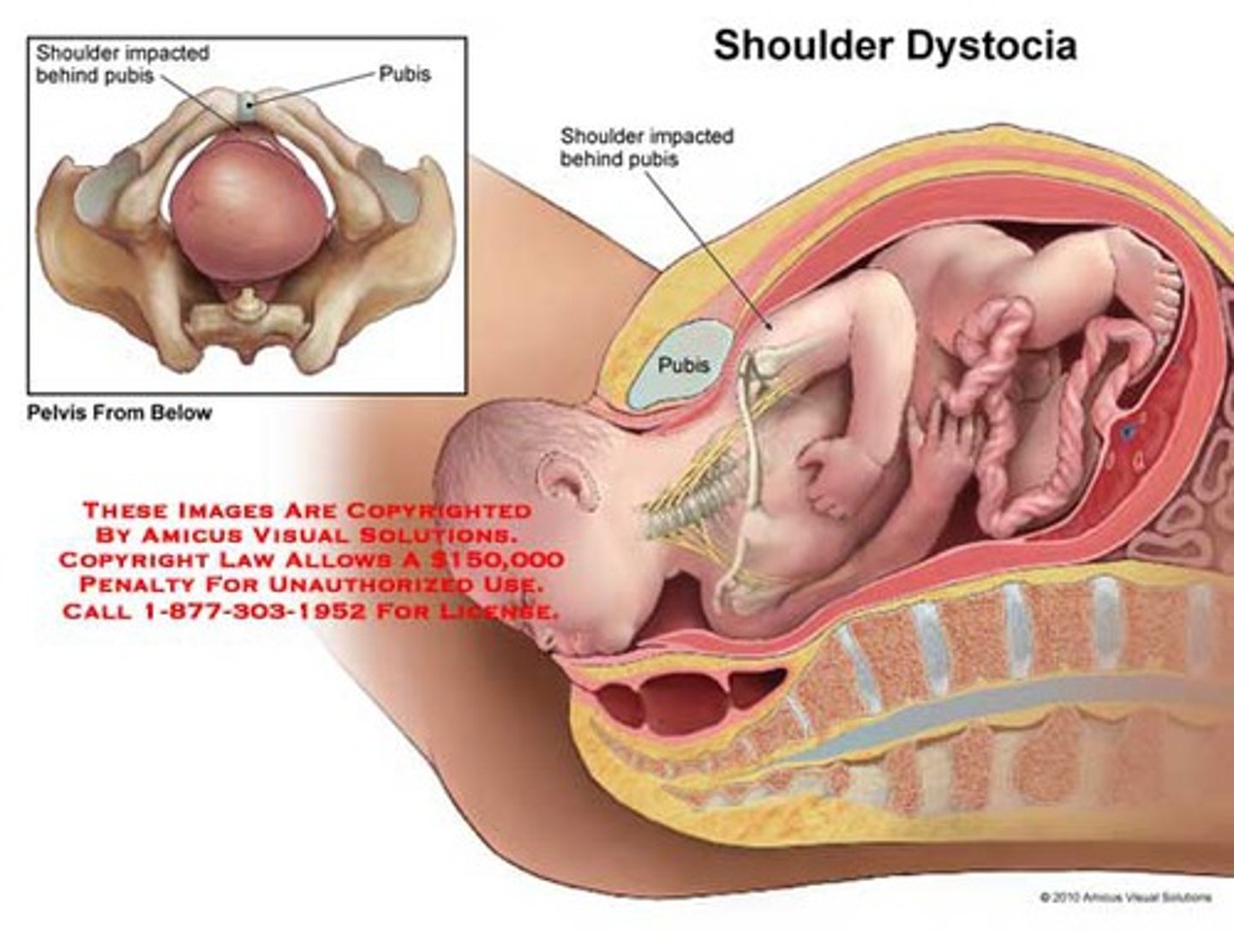
Shoulder Dystocia
Impacted shoulder above or behind the symphysis pubis
Occurs more often in large fetuses
Turtle sign
Nursing Considerations
Call for help
Lower the HOB
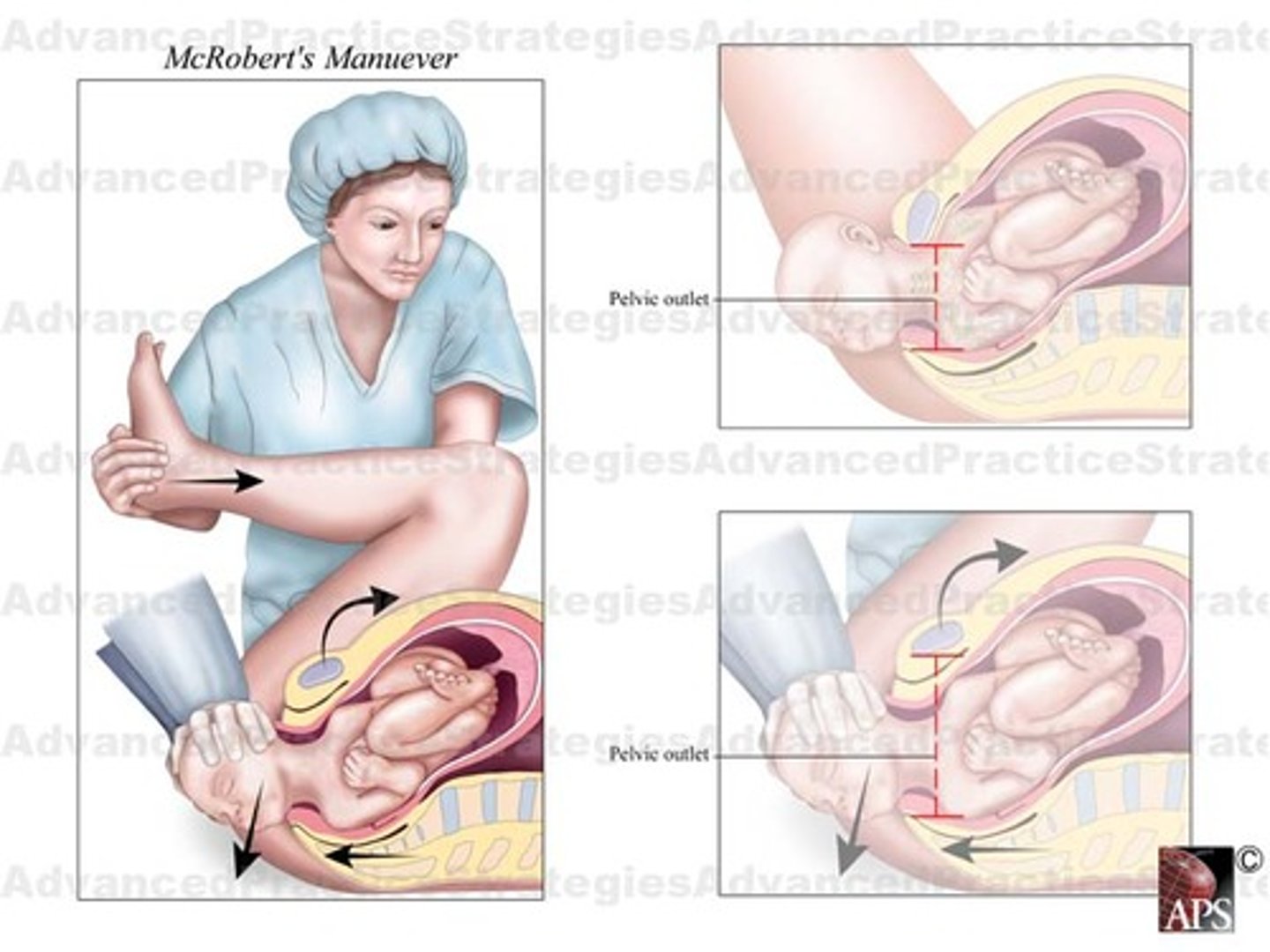
McRobert's maneuver
Suprapubic pressure
Documentation
Other maneuvers to consider:
Gaskins maneuver
Zavenelli maneuver
Turtle sign
first sign of a shoulder dystocia

McRoberts maneuver
Pull knees to head to open up pelvis.
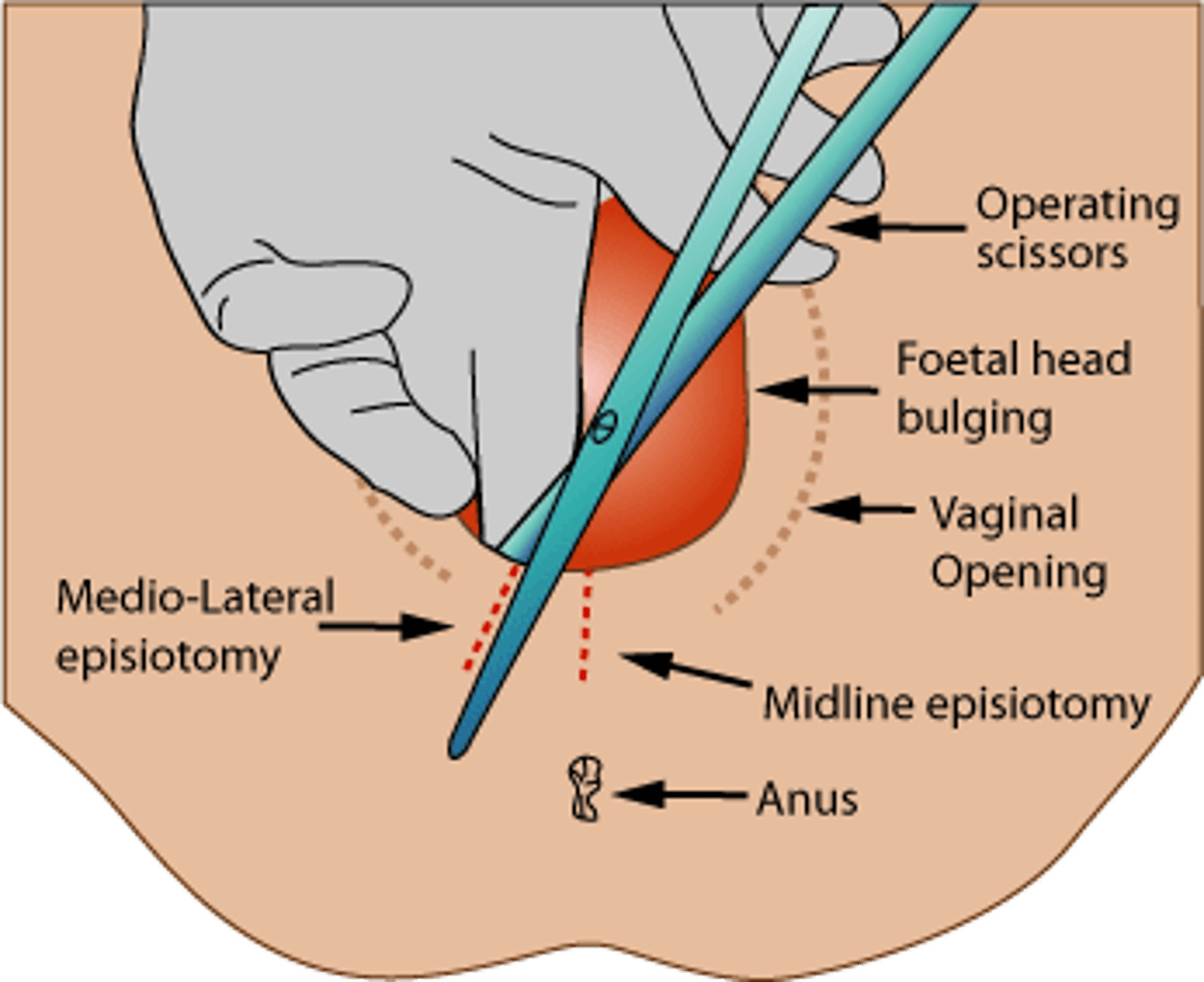
Episiotomy
is a surgical incision of the posterior aspect of the vulva made during the second stage of labor
is used if the patient is at high risk for a third- or fourth-degree perineal tear or if an expedited delivery is needed because of fetal compromise.
Risks include infection, bleeding, and pain.
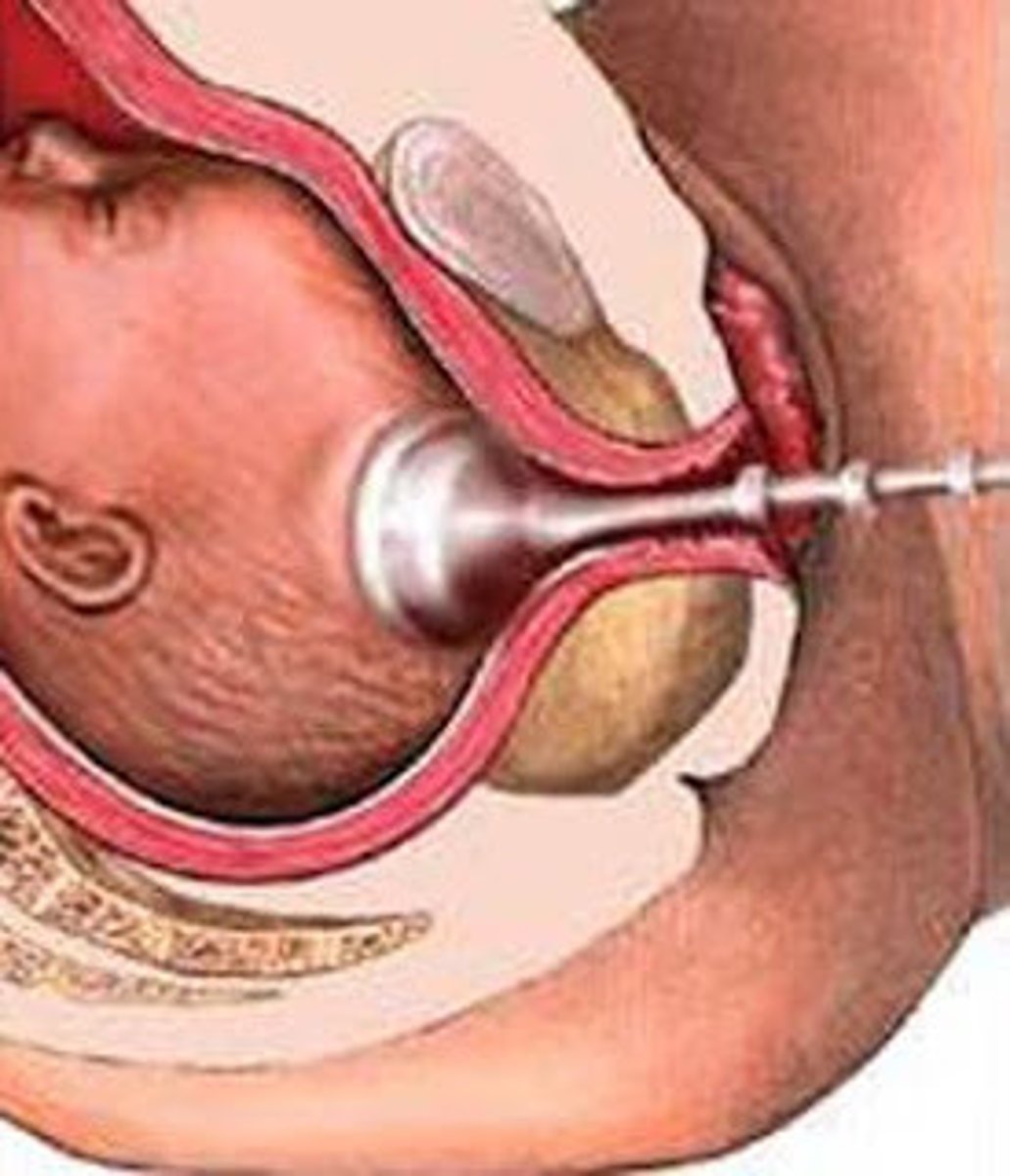
Vacuum-assisted birth
is a device that applies suction to the fetal head to aid in extraction.
Cesarean deliveries are performed after three sets of pulls (traction) or a total application time of 15 to 30 minutes.
Forceps-assisted birth
are applied to either side of the fetal head to allow the provider to pull with contractions.
Cesarean deliveries are performed if it is difficult to apply forceps safely or delivery does not occur within 15 to 20 minutes.
False
Is the following statement true or false?
After an unsuccessful delivery using forceps, the provider will likely attempt a vacuum-assisted delivery.
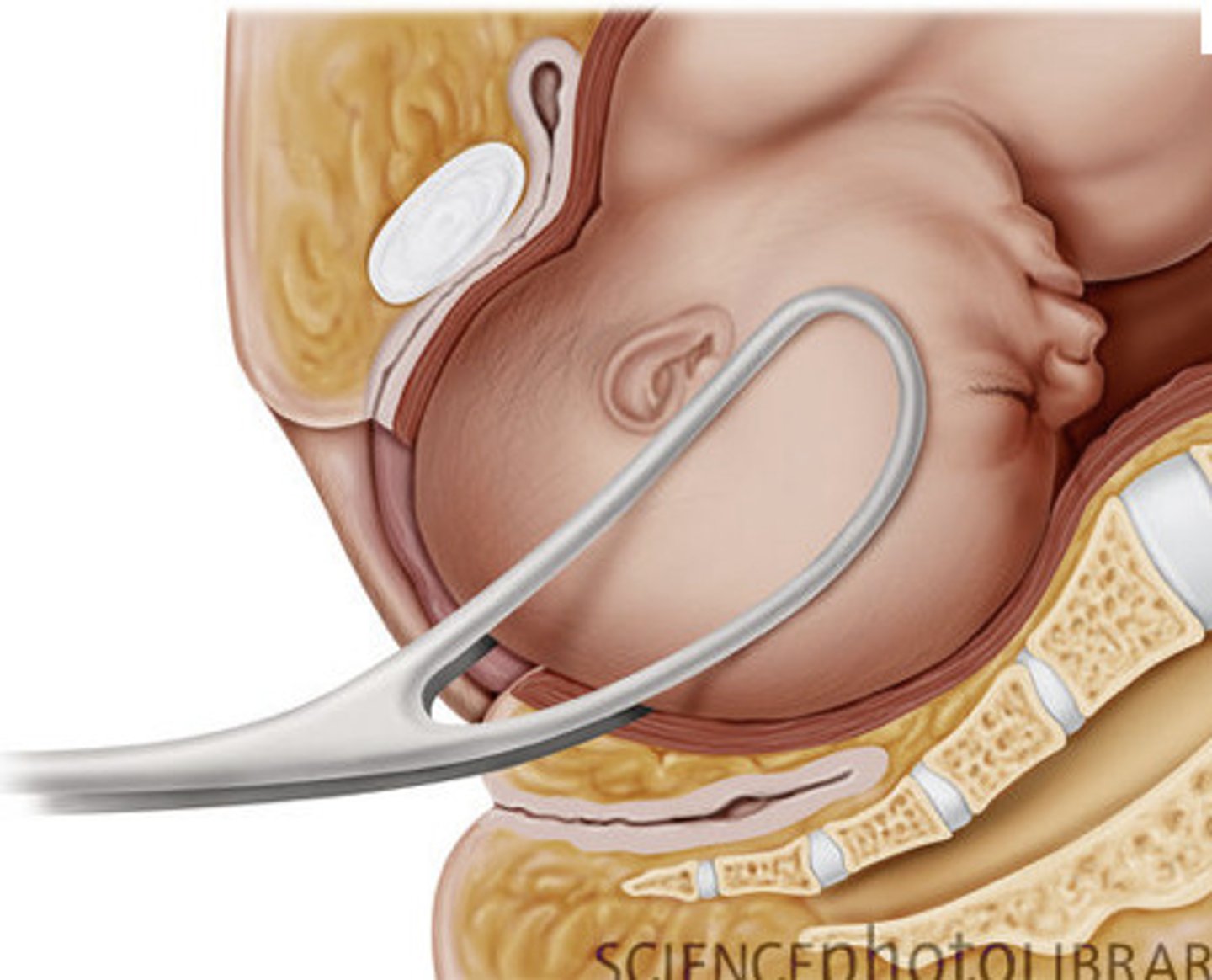
Cord prolapse
Condition where umbilical cord precedes fetal head in the birth canal.
Obstetric emergency
How?
FHR tracing/pattern
Severe Bradycardia
Variable deceleration
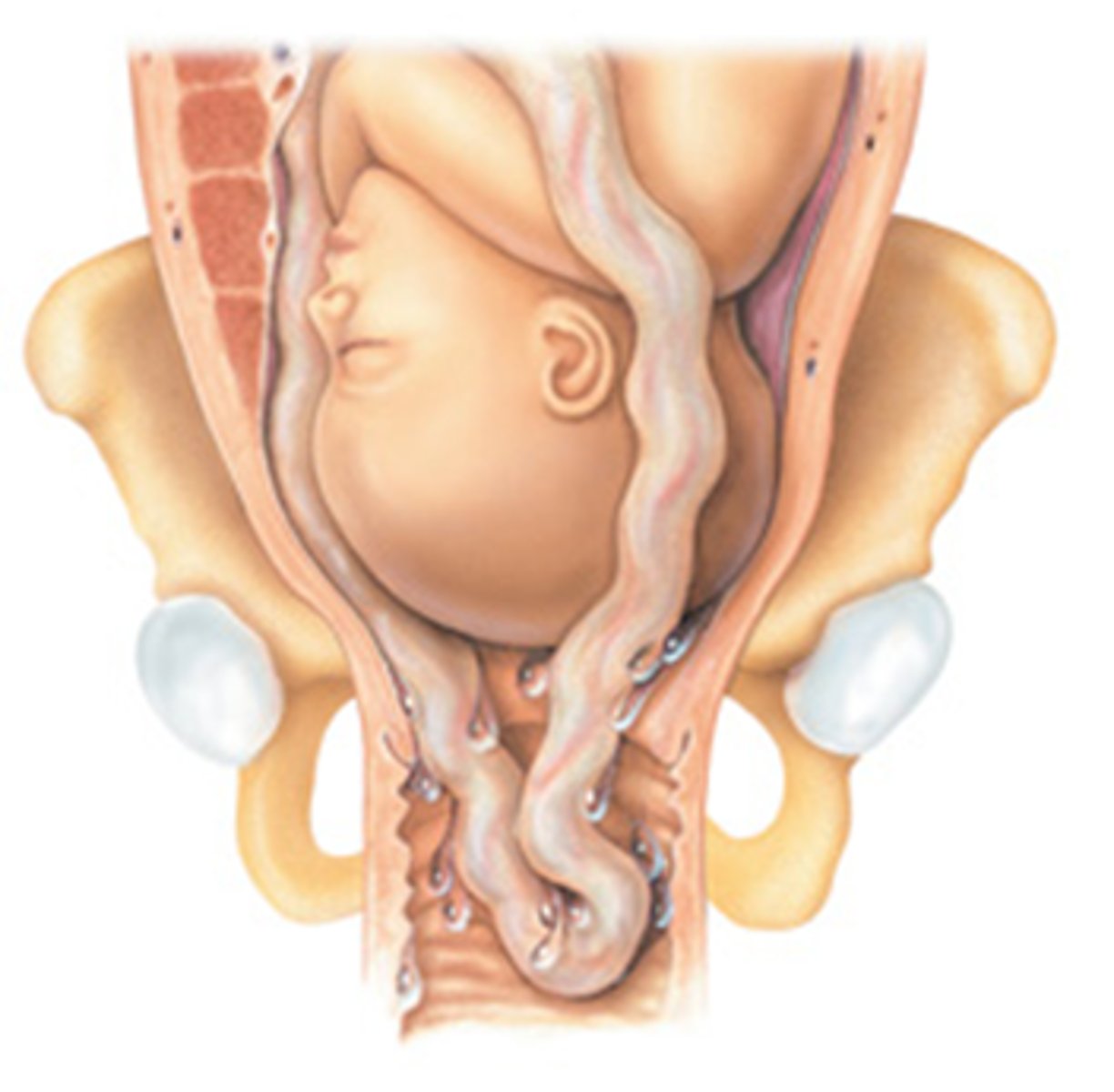
Causes of cord prolapse
High station
Small or preterm fetus
Malposition of the fetus
Polyhydraminios
The cord should be handled as little as possible to prevent spasm of the umbilical artery.
What do I do as the nurse for cord prolapse?
Cesarean Birth
Cesarean section rate 32% in the United States
Maternal Complications
Bowel and bladder injury during surgery,
Hemorrhage,
Amniotic fluid embolism
Infection
Neonatal complication
Respiratory distress
Indications for cesarean delivery
Failure to progress
Nonreassuring fetal heart rate
Fetal malpresentation
Umbilical cord prolapse
Fetal macrosomia
C. Previous cesarean birth with a vertical uterine incision.
After reviewing a patient's prenatal record, the nurse determines which of the following is a contraindication for vaginal birth after cesarean?
A. Nonreassuring fetal heart rate
B. Previous cesarean birth due to a breech presentation
C. Previous cesarean birth with a vertical uterine incision
D. Occiput anterior fetal presentation
Unplanned cesarean deliveries
may cause women a sense of frustration, disappointment, even failure.
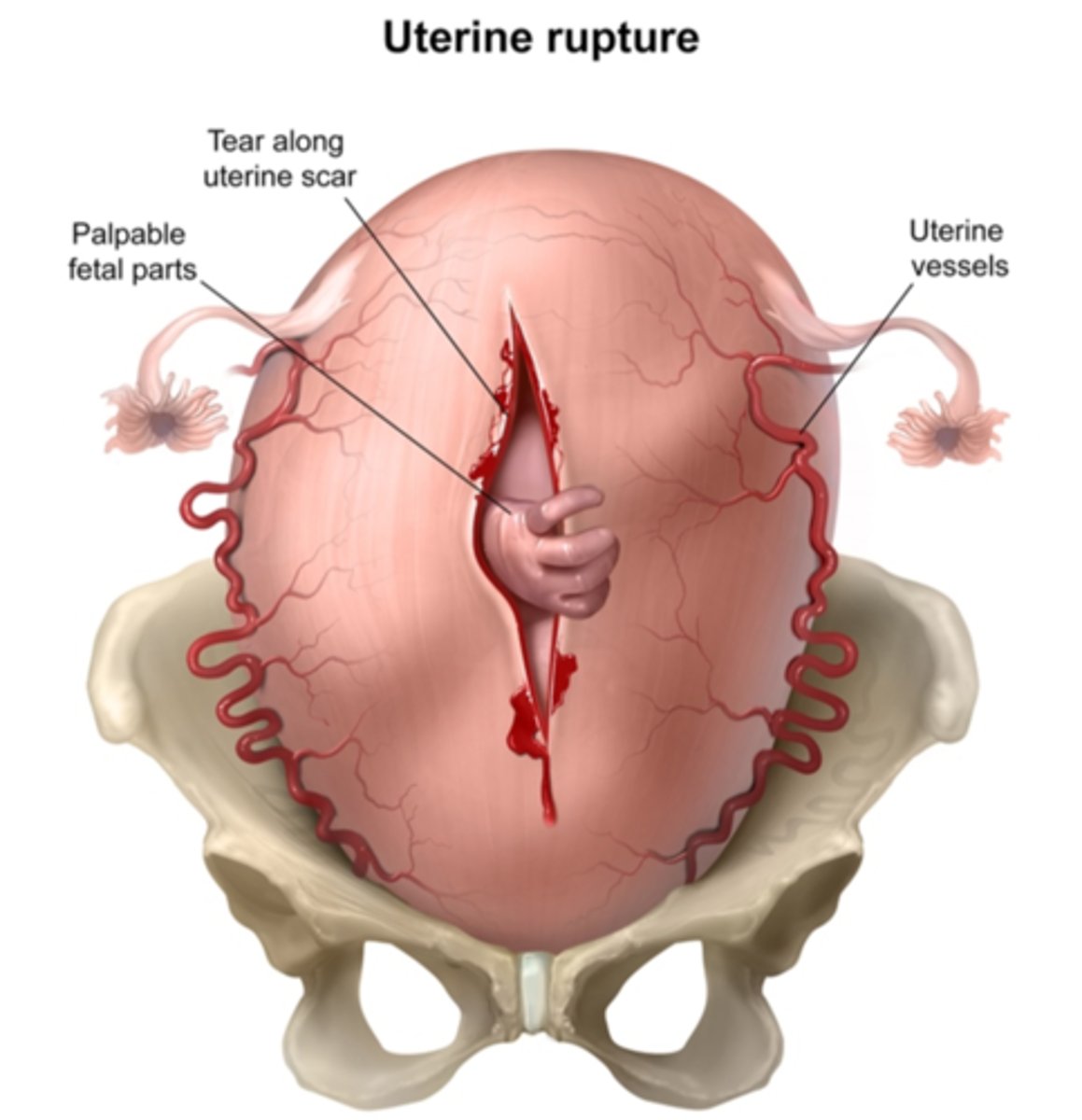
uterine rupture
tear in the uterine lining secondary to increased pressure
Risk factors
Prior uterine surgery
More common in C sections
Trial of labor after cesarean (TOLAC).
Signs
Sudden development of a category II or category III fetal heart rate pattern
Weakening contraction
Symptom
Abdominal pain
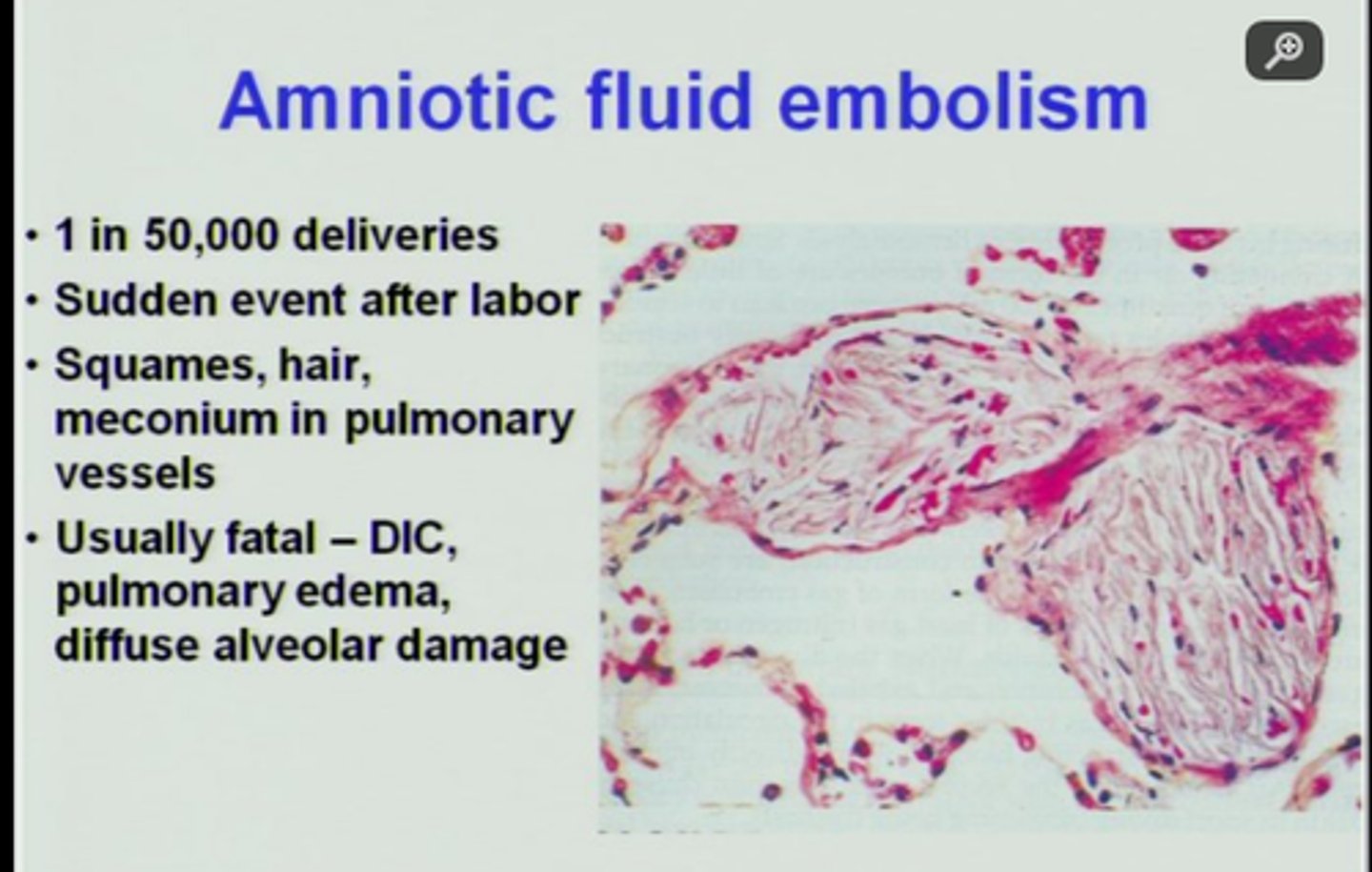
Amniotic embolism
referred to as anaphylactoid syndrome of pregnancy, may occur in pregnancy, labor, delivery, and the immediate postpartum period.
is caused when amniotic fluid enters maternal circulation and is associated with a maternal mortality rate of 32%.
Initial symptoms include respiratory failure and cardiac arrest.
If the patient survives an amniotic fluid embolism, she is at risk for hemorrhagic shock with disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Perinatal Loss
Stillbirth occurs in approximately 6 of 1,000 pregnancies that reach 20 weeks of gestation.
Risk is higher for adolescents, women over 35 years old, women of African descent, multifetal gestations, congenital anomalies, and maternal disease.
Prevention of perinatal loss may include:
Taking folic acid before and during pregnancy.
Routine syphilis screening and treatment.
Screening for and treating hypertensive disorders and maternal diabetes.
Access to emergency obstetric care.
Families who experience perinatal loss may experience anxiety, depression, or posttraumatic stress disorder.
D. All of the above.
Ms. Smith delivered 1 hour ago and suddenly experiences cardiac arrest. What should the nurse do next?
A. Call for help.
B. Open airway and assess breathing.
C. Initiate CPR.
D. All of the above.
treatment for uterine rupture
Cesarean delivery
Hysterectomy
A. Call for help.
Ms. Smith delivered 1 hour ago and suddenly experiences cardiac arrest. What is the priority action for the nurse?
A. Call for help.
B. Open airway and assess breathing.
C. Initiate CPR.
D. All of the above.
1. Frequency of contractions, how long, when the contractions started, pain assessment
2. Get fetal heart rate, cervical exam, take vitals, ask to empty bladder
Mary Smith is a 36yo G2P0010. Her LMP was April 25, 2021. Her EDC is _______. Ms. Smith is 39 weeks twin gestation. She presents to the triage complaining of contractions. Both fetuses are vertex/vertex.
What information would you want to find out from the patient?
What would be you next nursing action?
Ms. Smith most likely ruptured her membrane
Ms. Smith reports her pain is an 8 out 10 with each contraction. Her breathing is becoming more labored. She is profusely sweating. She is unable to talk through the contractions. But she also states she fells like she wet herself.