MYCOVIRO LEC 7 - Epidemiology and fungi of high priority
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
helps identify which populations are at highest risk and reveals emerging trends like the rise of resistant species.
Epidemiological knowledge
__ can develop targeted interventions, improve diagnostic strategies, and design effective treatment and prevention programs.
Public health officials and clinicians
It is slow, labor intensive, and has poor sensitivity
Traditional ‘Gold’ Standard
3 classes of antifungals
1. Azole
2. Echinocandins
3. Polyenes
These are non-competitive inhibitors of the fungal enzyme lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase, rate-limiting enzyme in the fungal biosynthetic pathway
of ergosterol.
Azole
rate-limiting enzyme in the fungal biosynthetic pathway of ergosterol.
lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase
destabilizes the fungal cell membrane, causing leakage of cellular contents, lysis, and eventual cell death.
Azole
What enzyme does azole inhibit?
lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase
These inhibit the fungal enzyme 1,3-β-glucan synthase, which is responsible for synthesizing 1,3-β-glucan
Echinocandins
key component of the fungal cell wall
1,3-β-glucan
Loss of this cell wall component leads to osmotic instability and cell death.
1,3-β-glucan
What enzyme does echinocandins inhibit?
1,3-β-glucan synthase
Polyenes antifungals bind to ergosterol, which is a sterol unique to fungi.
Polyenes
sterol unique to fungi
ergosterol
creates pores in the fungal cell membrane, ultimately leading to electrolyte leakage, cell lysis, and cell death.
polyene-ergosterol complex
Mode of action of azole
inhibitor of lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase → destabilizes the fungal cell → leakage, lysis, cell death
Mode of action of echinocandins
Inhibitor of 1,3-β-glucan synthase → osmotic instability → cell death.
Mode of action of polyenes
Binding to ergosterol → pores in the fungal cell membrane → leakage, lysis, cell death
almost always administered as combination therapy only or an adjunct to amphotericin B, which is a polyene
Flucytosine
an antimetabolite compound
flucytosine
Flucytosine characterized or classified as a ___
pyrimidine analog.
It is absorbed into fungal cells via cytosine permease.
flucytosine
Within the fungal cell, the flucytosine gets converted to
______, which interferes with fungal RNA biosynthesis.
5-FU (5-fluorouracil),
the number of identified that represent health threats because they cause severe invasive disease, and their emerging resistance to antifungal drugs
19 fungi
three priority groups:
1. Critical group
2. High group
3. Medium group
in making this pathogens priority list, WHO based it on criteria:
- Prioritization Criteria
- Corresponding Definition
- Levels
Critical group
1. Cryptococcus neoformans
2. Candida auris
3. Aspergillus fumigatus
4. Candida albicans
CCAC
High group
1. Nakaseomyces glabrata (Candida glabrata)
2. Histoplasma spp.
3. Eumycetoma causative agents
4. Mucorales
5. Fusarium
6. Candida tropicalis
7. Candida parapsilosis
NHEM FCC
Medium group
1. Scedosporium spp.
2. Lomentospora prolificans
3. Coccidiodes spp.
4. Pichia kudriavzeveii
5. Cryptococcus gattii
6. Talaromyces marnfeei
7. Pneumocystis jirovecii
8. Paracoccidiodes spp.
SLCP CTPP
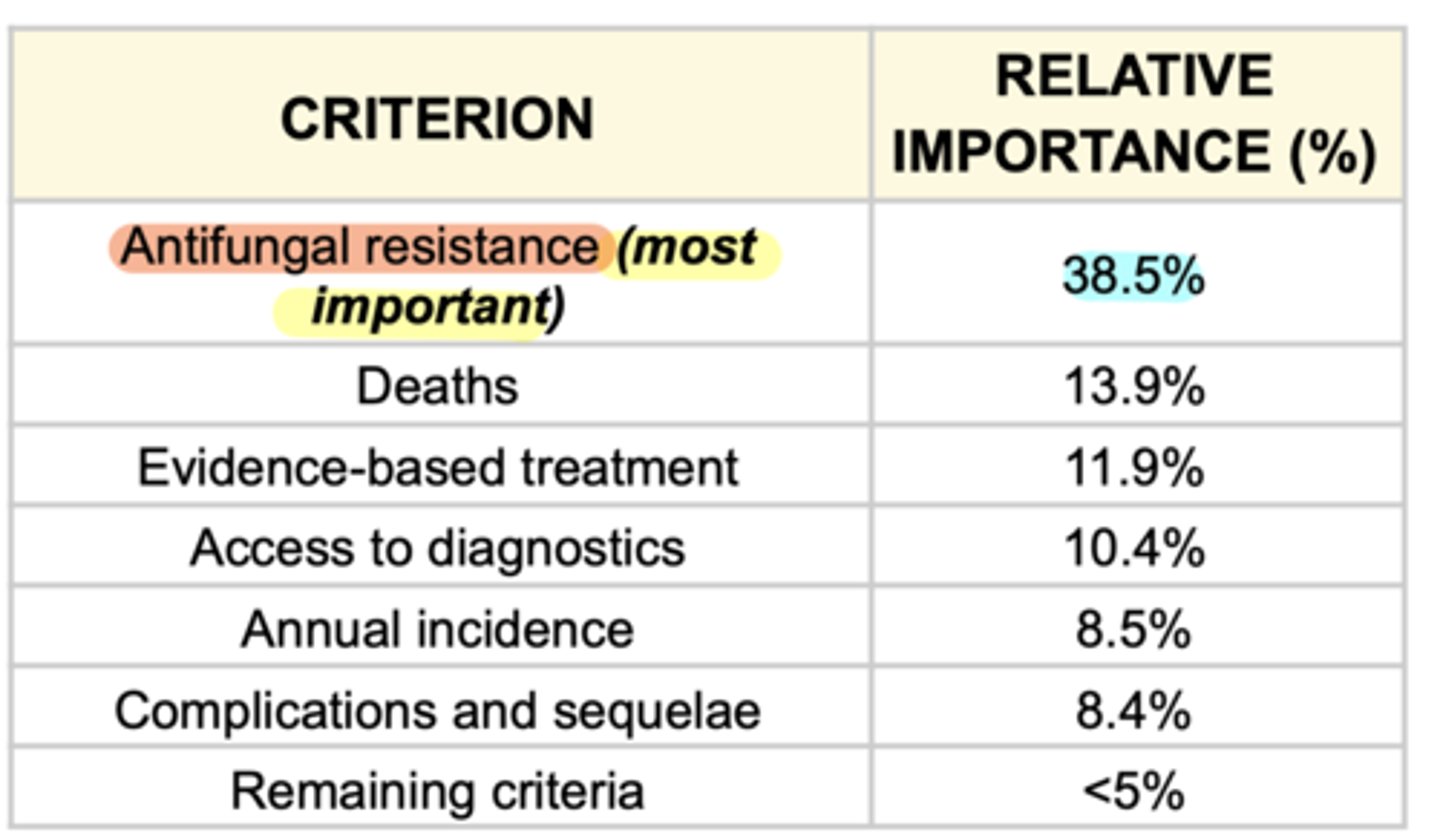
most important criterion
Antifungal resistance (38.5%)
predominantly reported for HIV-positive patients.
Cryptococcus neoformans
T/F
Cryptococcus neoformans has vaccines
F
Cryptococcus neoformans median days
18 to 39 days
reduces the incidence o cryptococcal meningiti
prophylactic and preemptive therapy
Localized cryptococcosis treatment
Fluconazole
Severe and disseminated cases of Cryptococcus neoformans treatment
Amphotericin B in combination with flucytosine
followed by step-down to fluconazole
Cryptococcus neoformans intrinsically resistant to ___
Echinocandins
Cryptococcus neoformans acquired resistance to what drugs?
● Fluconazole
● Amphotericin B (Amp B)
● 5-flucytosine (5-FC)
Candida auris median length of hospital stay:
Adults →____
Pediatric → ___
Adults → 46-68 days
Pediatric → 70-140 days
Invasive candidiasis treatment
Echinocandins
Candida auris resistance rate to
Fluconazole =
amphotericin B =
Azoles =
Fluconazole = 87-100% (high)
amphotericin B = 8-35%
Azoles = 0-8%
used for following confirmation of in-vitro susceptibility of Candida auris
azoles
Candida auris:
_____ → Isolates resistant to at least one antifungal
____ → Isolates resistant to at least two antifungal
90%
30%
- emerging multidrug-resistant yeast
- first identified in 2009 in Asia
- Often multi-drug resistant, with some strains (types)
resistant to all three available classes of antifungals.
Candida auris
Reported cases of Candida auris increased by _____% in 2018 when compared to the average number of cases reported in 2015 to 2017
318%
Azole-resistant invasive aspergillosis is a life-threatening disease
Aspergillus fumigatus
____ for high-risk groups can prevent Invasive Aspergillosis
Antifungal prophylaxis
It is recommended even in azole-naive patients and especially in high-risk patients such as:
● Cancer patients,
● Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
● Those in ICU
Screening for azole resistance
overall mortality ranges from 20% to 50% despite the availability of active antifungal treatment.
Candida albicans, Invasive candidiasis
Invasive candidiasis length of stay
24 weeks and up to 2 months
Candida albicans, invasive candidiasis treatment
Echinocandins followed by a step down to azoles when appropriate.
a very serious disease with All-cause Mortality at 30 days up to 20-50%
Nakaseomyces glabrata (Candida glabrata)
shows High minimum inhibitory concentrations (HIGH MICs) to azoles.
Nakaseomyces glabrata (Candida glabrata)
Nakaseomyces glabrata (Candida glabrata), invasive candidiasis treatment
Echinocandins, although other antifungals such as azoles might be used following confirmation of in-vitro susceptibility.
Mortality rates in HIV/AIDS patients ranged from 21% to 53%.
9-11% (lower) in:
- Immunosuppressed Patients
- Solid Organ Transplant Patient
Histplasma spp.
Histplasma, severe cases treatment
Amphotericin B followed by Itraconazole is recommended
Affected low-income patients with many complications and sequelae
Eumycetoma causative agents
60-80% report a significant impact on their daily life and Amputation rates are as high as 39%.
Eumycetoma causative agents
Risk factors of Eumycetoma causative agents
farmer, male, and 11-30 years old
Eumycetoma causative agents treatment
Long-term Antifungals and Amputation is frequently required for full resolution of infection.
Mucorales mortality ranges:
Adults → ___
Pediatric px → ____
Adults → 23% to 80%
Pediatric px → 72.7%
Affects immunocompromised patients like cancer, and transplant patients. Also seen in poorly controlled diabetes mellitus and those with trauma injuries.
Mucorales
Risk factors of mucorales
Neutropenia
Diabetes mellitus
Trauma
risk factor for Subcutaneous Mucormycosis.
trauma
MICs for azoles are generally higher for ____ species compared with others.
Mucor
Mucorales are generally susceptible to ?
Amphotericin B
Mucorales are inherently resistant to ?
Fluconazole
Voriconazole
Echinocandins
Mucormycosis gained prominence due to infections in COVID-19 patients
COVID-19 Associated Mucormycosis (CAM)
known as BLACK FUNGUS, affects weakend immunity, diabetes or cancer.
Mucormycosis
Steroids in excess causes what?
1. weakened the patient's immune system,
2. raised their blood sugar levels, and
3. made them vulnerable to fungal invasion.
affects immunocompromised patients such as those with Hematological Malignancies or Post-hemopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT)
Invasive fusariosis (fusarium)
Scedosporium spp.
Invasive fusariosis (fusarium) risk factors
acute myeloid leukemia
allogeneic HSCT
cytomegalovirus reactivation,
Presence of skin lesions
Invasive fusariosis (fusarium) mortality rates
43% and 67% for invasive fusariosis.
Based on MICs, susceptibility to azoles is generally lower than to other antifungal medicines, such as amphotericin B.
Fusarium
showed reduced susceptibility to azoles compared with non-F. Solani species.
F. solani
Candida tropicalis mortality rate:
Adults =___
Pediatric patients = ___
Adults = 55-60%
Pediatric patients = 26% - 40%
- Critical illness
- Decreased Host Immunity
- NEONATAL ICUs
Candida tropicalis risk factors
Candida tropicalis is resistant to ?
Fluconazole,
Itraconazole,
Voriconazole
Posaconazole
Invasive Candida tropicalis is empirically treated with
Echinocandins
Candida parapsilosis mortality range
20-40%
Azole Resistance Rates: Excess of 10%
Candida parapsilosis
Candida parapsilosis is resistant to ?
Echinocandins,
Flucytosine
Amphotericin (rare)
overall shows intrinsically higher MICs to Echinocandins than other Candida species.
Candida parapsilosis
Studies assessing BIOFILM MASS are concerning for higher rates of resistance to all antifungal agents in biofilm situations (such as central lines, implants and prostheses).
Candida parapsilosis
Targets Mainly: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Others: Blood, Central Nervous System, Other Organs
Invasive Scedosporiosis (Scedosporium spp.)
Invasive Scedosporiosis ( Scedosporiosis (Scedosporium spp.)) risk factors
malignancy
HSCT
severe infection
Scedosporiosis (Scedosporium spp.) moratility rate
42-46% (adults and children)
Invasive scedosporiosis treatment
VORICONAZOLE, with other antifungal medicines
the most active antifungal against scedosporium spp.
Voriconazole
scedosporium spp. has reduced susceptibility to
Amphotericin B,
Itraconazole,
Isavuconazole
Echinocandins
AIIE
- A globally distributed, opportunistic pathogenic mold
- can produce invasive infection (INVASIVE LOMENTOSPORIOSIS)
Lomenstopora prolificans
Serious Nosocomial Infection that affects cancer patients
Lomenstopora prolificans
Lomenstopora prolificans mortality raets
Adults = ___
Immunocompromised children = ___
Adults = 55% - 71%
Immunocompromised children = 50%
INVASIVE LOMENTOSPORIOSIS treatment
Toriconazole and Terbinafine
current licensed antifungals have no in vitro activity against this fungus
Lomenstopora prolificans
is a very serious disease, with Mortality ranging from 2% to 13%
Coccidiodes
Coccidiodes spp. hospitaly stay length:
- Coccidiodes spp. Infection: ___
- Coccidiodal Meningitis: ___
- Coccidiodes spp. Infection: 3 to 7 Days (median)
- Coccidiodal Meningitis: 22.7 Days (median)
could resolve without antifungal treatment; however, treatment is recommended in risk groups
Primary Pulmonary Coccidioidomycosis
Disseminated coccidioidomycosis treatment
Fluconazole,
Itraconazole
Amphotericin B
Coccidiodes MICs ?
● HIGH MICs: Fluconazole
● VARIABLE MICs: Capsofungin
● LOW MICS: Anidulafungin and Micafungin