1.01 - Understand Types of Body Tissues
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
5 Questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
-ac
pertaining to
bio-
life
cyt-
cell
epi-
above
-ologist
specialist
-ous
pertaining to
pariet-
wall
ser-
watery
viscer-
guts or internal organs
anatomy
study of a structure of an organism
calcify
to deposit mineral salts
cutaneous
pertaing to skin
cytology
study of cells
elastin
elastic-like fibers found in connective tissue
fascia
bond or sheet of fibrous membranes covering, binding, and supporting muscle
graft
transplant tissue into a body part to replace damaged tissue
granulation
tiny red granules that are visible in base of healing wound
histology
microscopic study of small tissues, organs, and cells not seen with the naked eye
mucosa
mucuous membrane
mucous membrane
type of tissue that lines the surface and spaces that lead to the outside of the body
parietal membrane
lining of body cavity
what are tissues composed of?
cells grouped by size, shape, and function
what are the four types of tissues?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
what is epithelial tissue?
protects by covering internal and external surfaces, and produces secretions (digestive juices, sweat, hormones)
what is connective tissue?
supports and connects organs and tissues
what is muscle tissue?
contracts and moves a body part (ex. movement of digestive tarct, pupil eye) 3 types: cardiac (the heart, striated, involuntary), skeletal (attached to skeleton striated, voluntary), smooth (prvement, unstriated, involuntary)
what is nervous tissue?
reacts to stimulation and conducts an impulse (brain, spinal cords, nerves)
what is anatomical position?
standing straight up, palms out
what is the difference between posterior and anterior?
posterior- above
anterior- below
how does the coronial plane cut?
cuts the body into front and back
what is the difference betweend medial and lateral?
medial- towards the midline
lateral- away from midline
how does the midsagittal plane cut?
cuts the body into left and right
what is the difference between superior and inferior?
superior- above
inferior- below
how does the transverse plane cut?
cuts the body into top and bottom
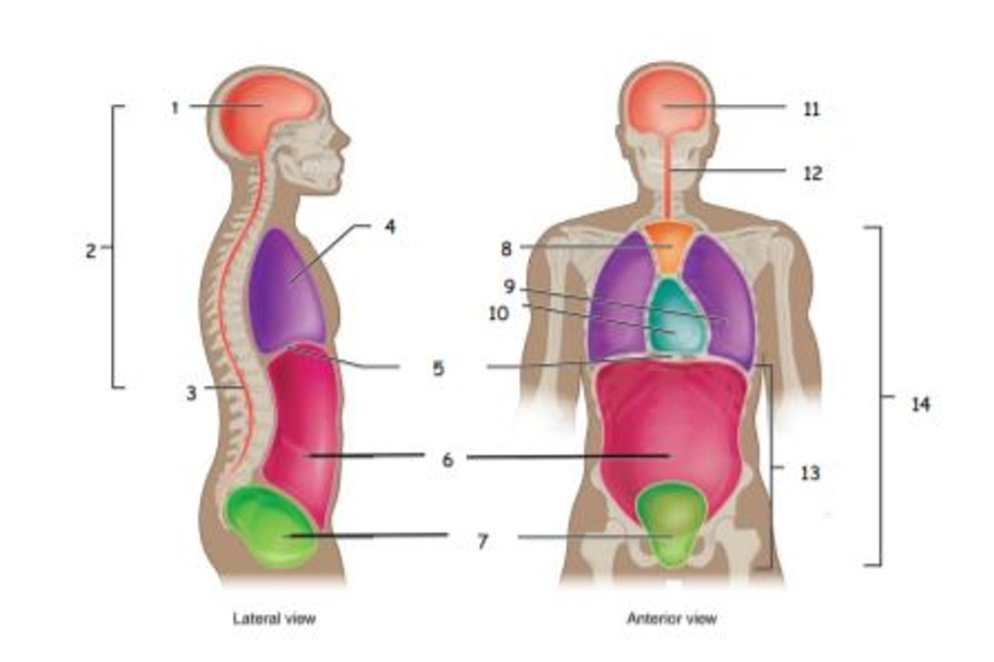
name the body cavities
cranial 2. dorsal 3. spinal 4. thoracic 5. diaphragm 6. abdominal 7. pelvic 8-12. blank 13. abdominopelvic 14. ventral
what are the 4 abdominal quadrants?
left upper quadrant (luq), right upper quadrant (ruq), left lower quadrant (llq), right lower quadrant (rlq)
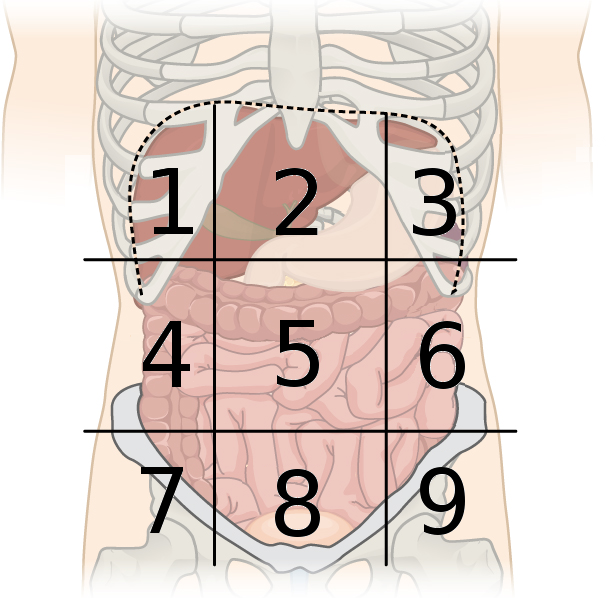
what are the abdominal regions?
right hypochondriac 2. epigastric 3. left hypochondriac 4. right lumbar 5. umbilical 7. left lumbar 8. right inguinal 9. hypogastric 10. left inguinal