7. intra/extra oral landmarks
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
eye landmarks: lateral canthus
outer eye corner
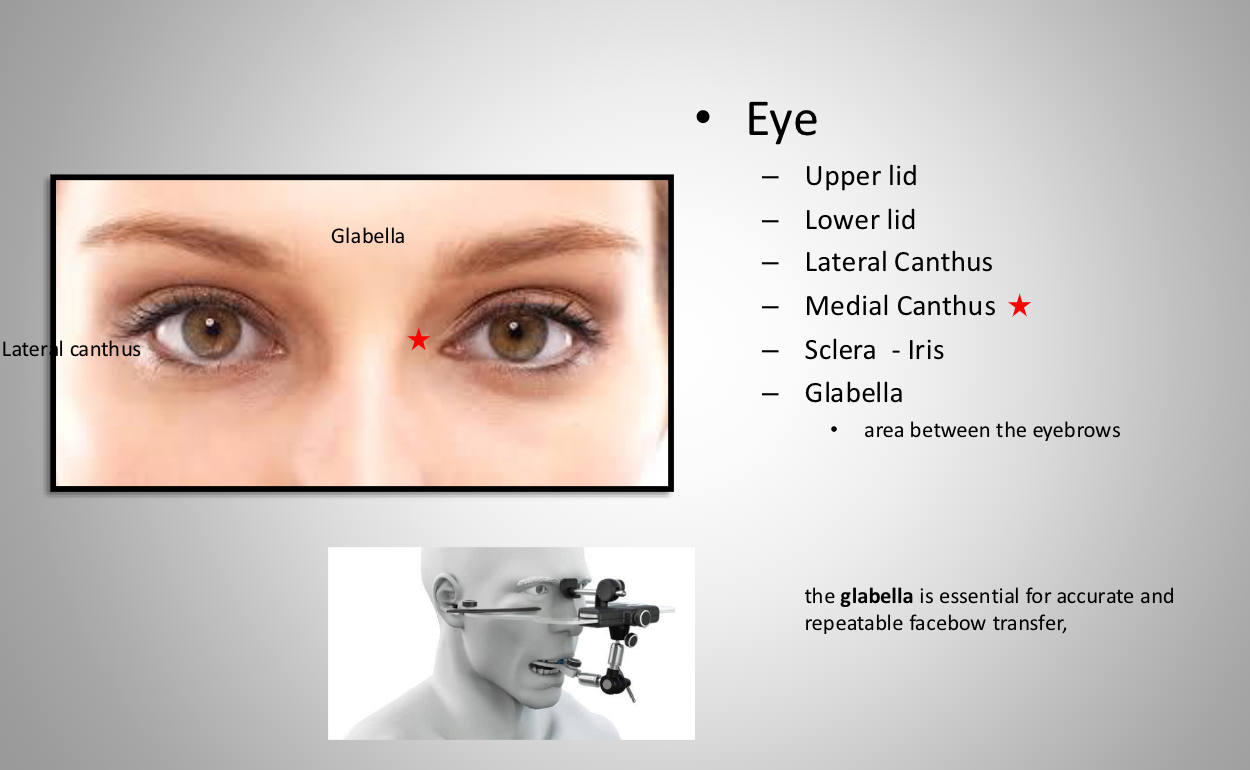
eye landmarks: medial canthus
inner eye corner (toward midline)
eye landmarks: sclera
white of eye
eye landmarks: iris
color part of eye
eye landmarks: glabella
area between eyebrows
**essential for accurate and repeatable facebow transfer
nose: ala
ala outwardmost part of the nose
nose landmarks: naris
external openings of nasal cavity
nose landmarks: nostril
orifice of the nose
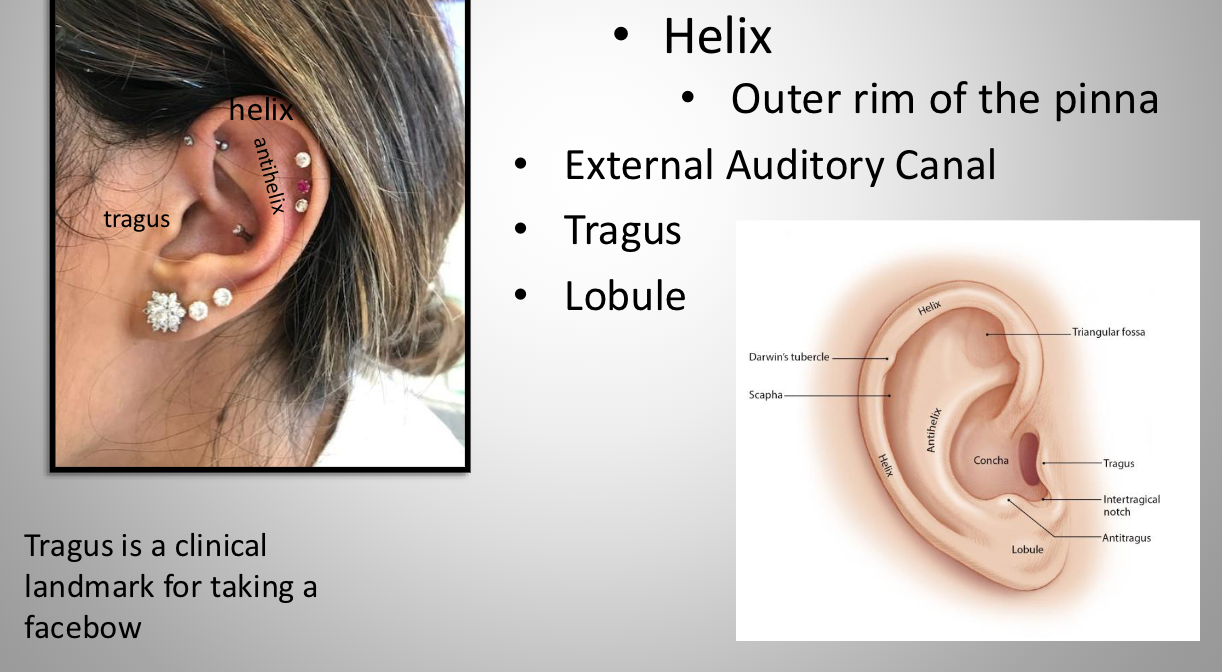
ear landmarks: Pinna (auricle)
External part of the ear
ear landmarks: helix
Outer rim of the pinna
ear landmarks: tragus
clinical landmark for taking a facebow
ear landmarks: lobule
ear lobe
ear landmarks: eternal auditory canal
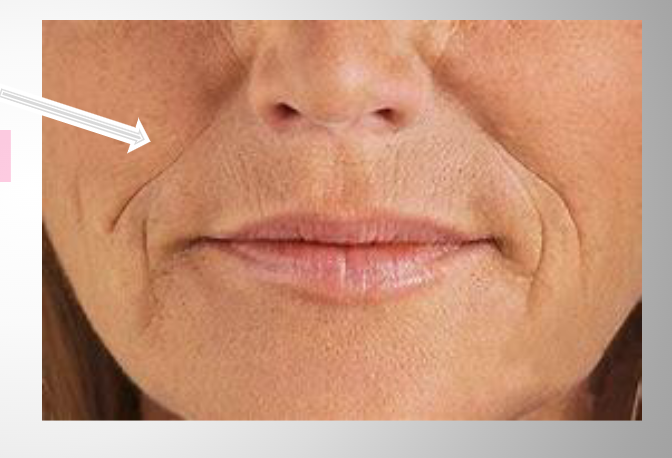
nasolabial folds
Laugh lines
Soft tissue "sagging" lines between nose and lips/chin
more prominent with age
Disappears on facial paralysis
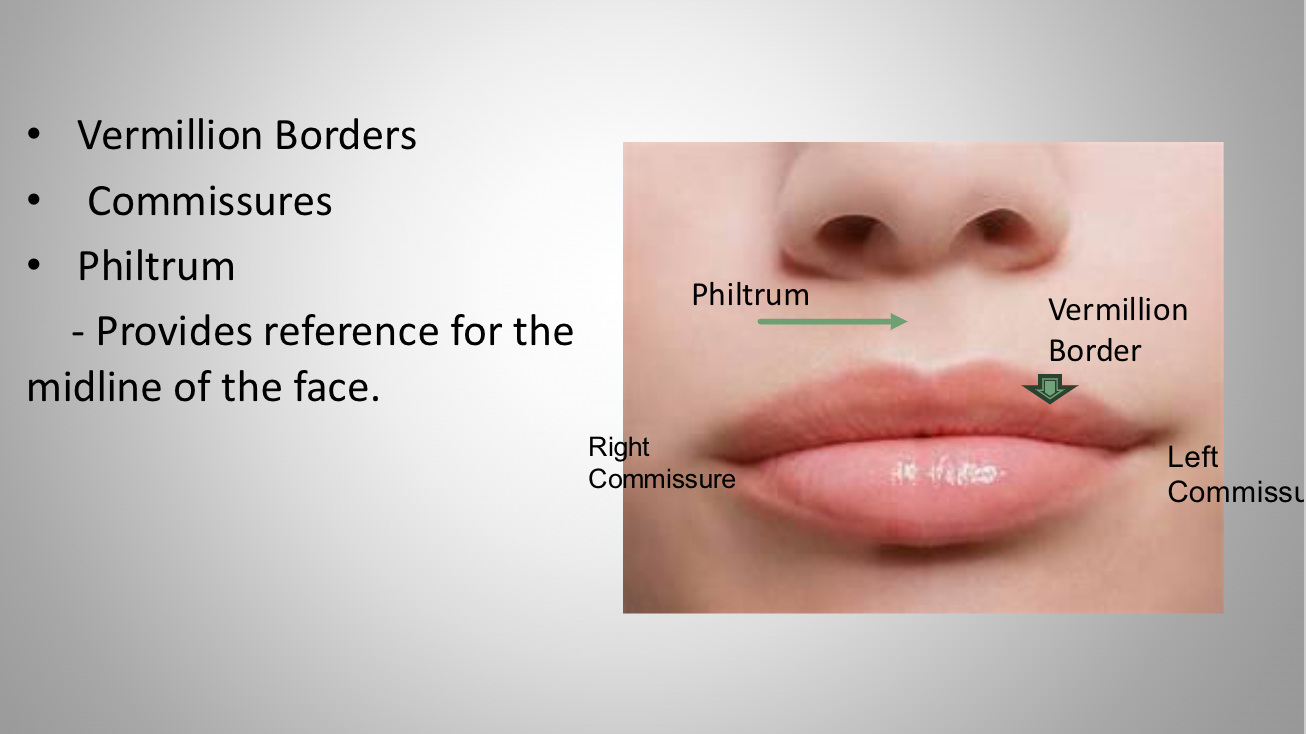
lips
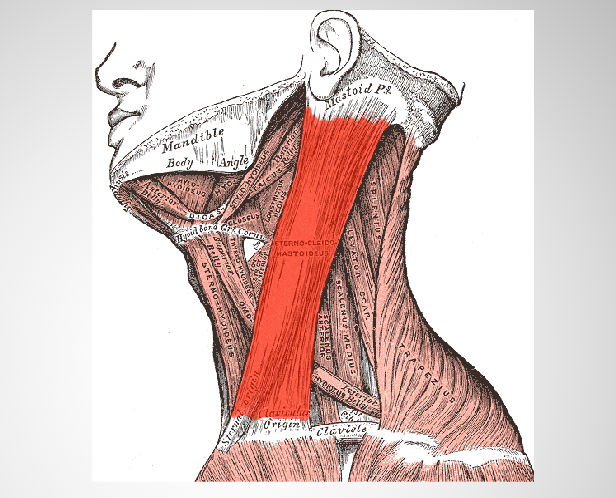
sternocleidomastoid muscle
the most superficial and largest muscle in the front portion of the neck
Originates from the manubrium of the sternum and clavicle – across the
side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull
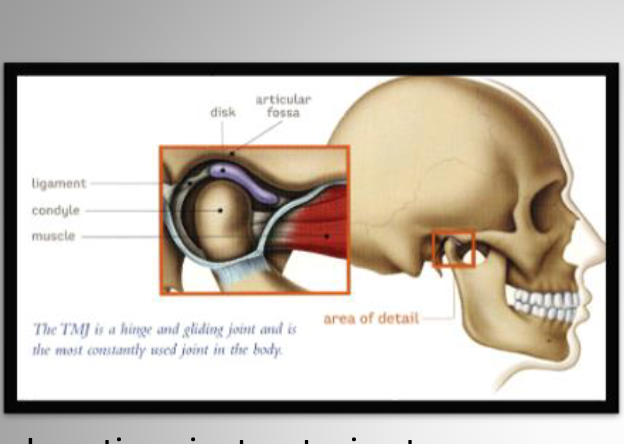
tmj
Open and feel Small indentation between ear & condyle.
This is the posterior wall of the chamber.
just anterior to ext. auditory meatus. Open and close to feel condyle moving
buccal mucosa
inner lining of the oral cavity
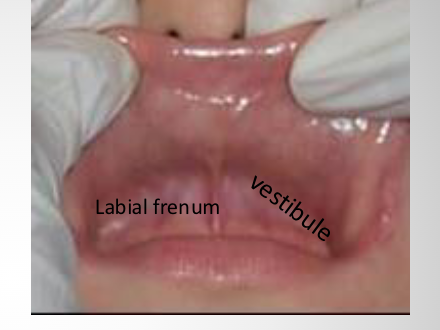
labial frenum
attachment that connects lip to gums
you make a notch on dentures for pts
vestibule
the potential space between the teeth, lips and cheeks
gingiva
tissue surrounding the teeth
alveolar ridge
the bony ridge in the upper or lower jaw that contains the tooth sockets and supports the teeth
It is covered by gum tissue and plays a critical role in dental stability and prosthetic retention, but undergoes changes after tooth loss
Found between the buccal and labial mucosa
alveolar process
the alveolar process is the entire bony structure containing the tooth sockets and undergoes remodeling and resorption after tooth loss, which affects implant placement and bone preservation strategies
the alveolar ridge refers specifically to the visible or palpable external bony margin that supports denture stability and prosthetic fit, making its preservation critical for functional and esthetic dental restorations.
Parotid Papilla
Tissue covering the opening of the Parotid Duct (Stenson's Duct)
Location: on the buccal mucosa opposite the maxillary 2nd molar
fordyce granules
Small yellow-white dots that can appear on the buccal mucosa and lip
Ectopic Sebaceous glands of the skin
Mucogingival Junction
“line" separating the lining mucosa from the gingival mucosa (attached gingiva)
Maxillary Labial Frenum
The maxillary frenum is a thin mucosal tissue that connects the upper lip mucosa to the gingiva between the upper central incisors.
dorsal tongue
Top surface of the tongue
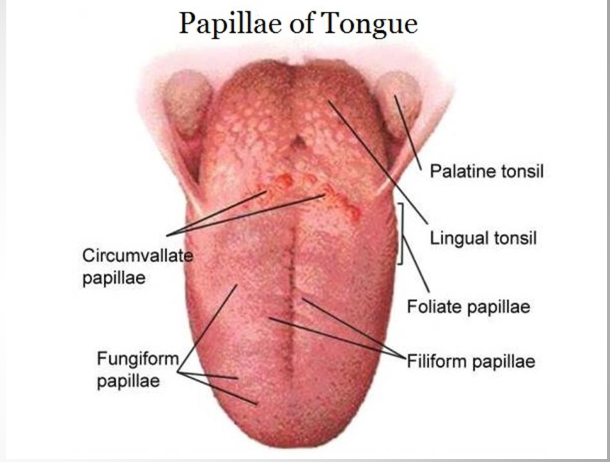
filiform papilae, fungiform, circumvallate papilae
Filiform Papillae
Long, threadlike extensions of the mucosa
Fungiform
Small mushroom shaped
Scattered among the filiform papillae
Circumvallate Papillae
mushroom shaped structures with deep furrow surrounding it
Largest papilla on the tongue
Location: back of the tongue and arranged in a "V" pattern
Medial Sulcus (in some individuals)
Shallow grove dividing the the tongue longitudinally
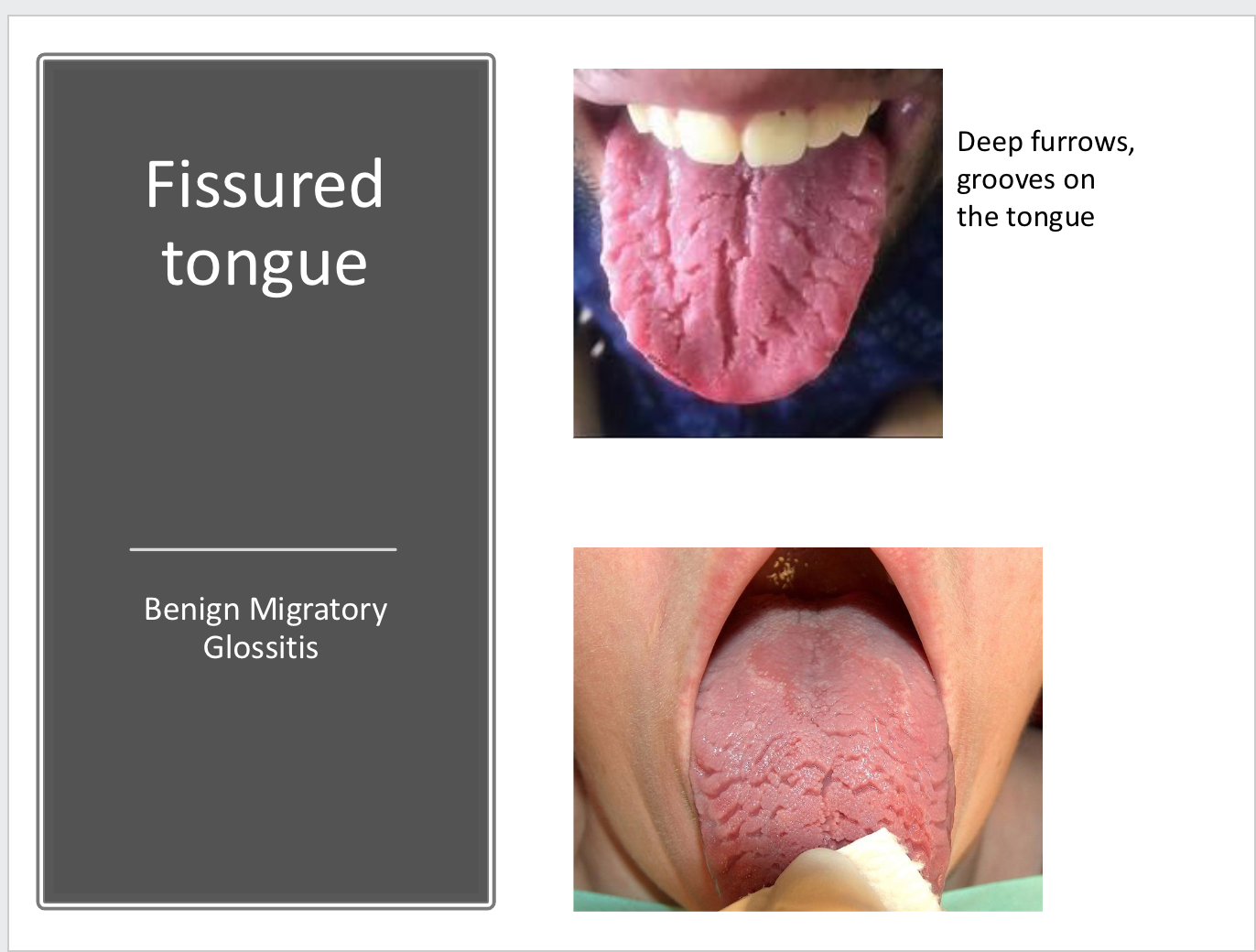
fissured tongue
Deep furrows, grooves on the tongue
lateral border
foliate papilae + lingual tonsil
lingual tonsil
Lingual tonsils are usually distal to foliate papillae and red, glistening papules and nodules on the posterolateral border of the
tongue Is the continuation of the ligual tonsil on the base of the tongue –beyond the curcumvalate papillae
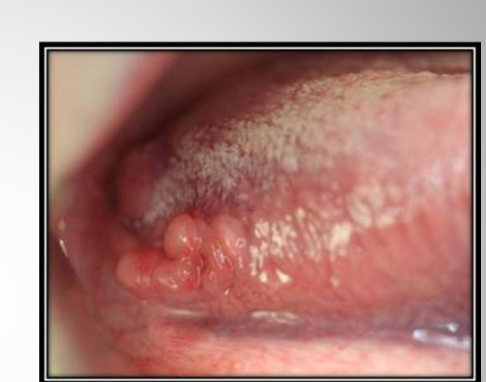
foliate papilae

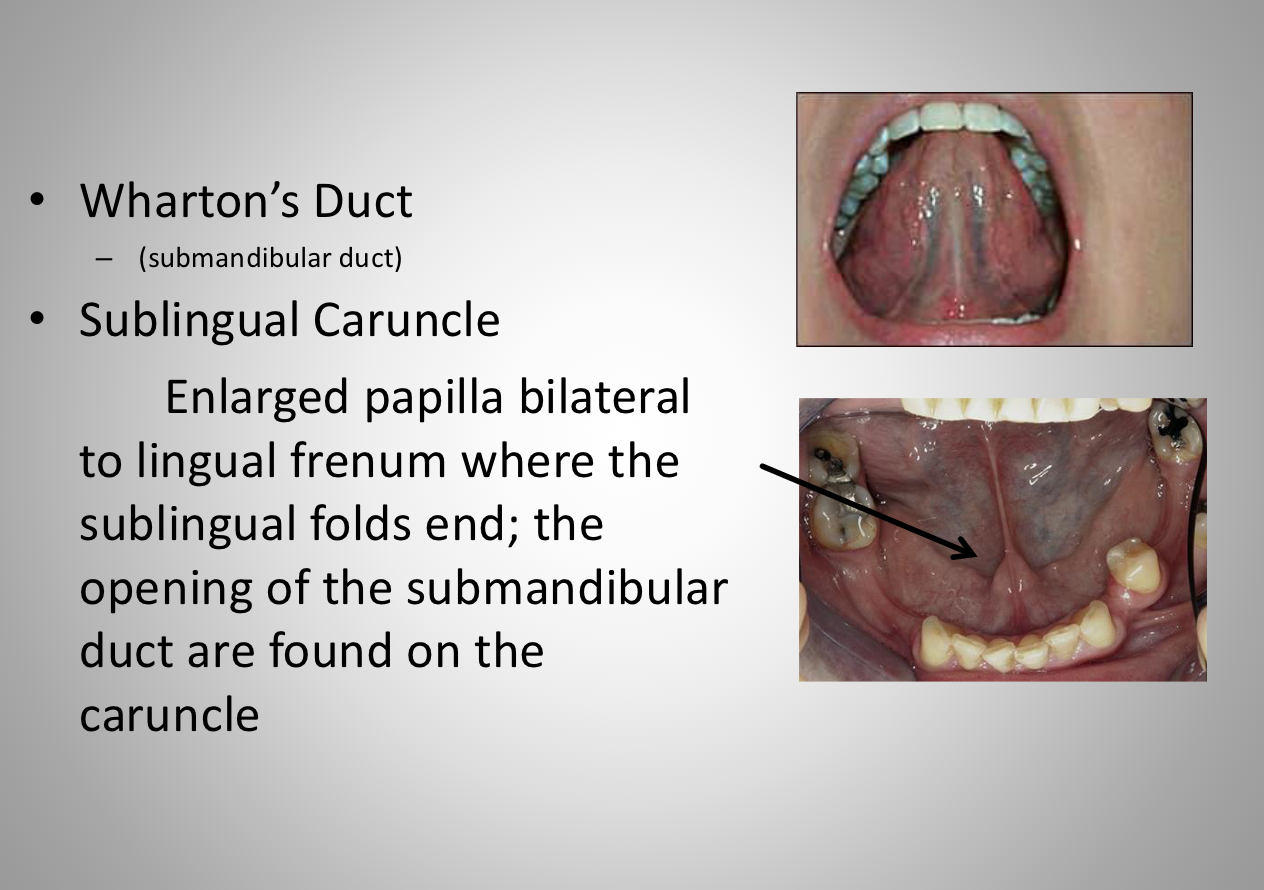
whartons duct + sublingual caruncle
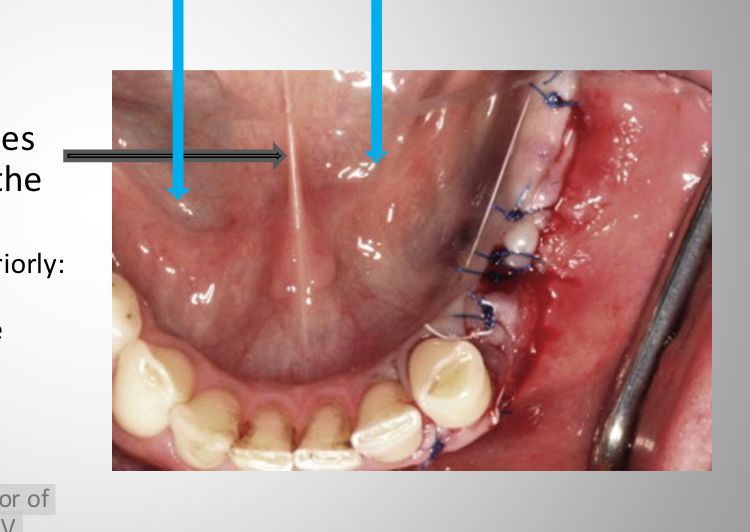
lingual frenum
a band of mucosa that attaches the ant 2/3 of the tongue to the floor of the mouth
too short or too far anterior frenum
Ankyloglossia, can affect speech due to immobility of the tongue
Correction : frenectomy
Sublingual folds
• a soft tissue ridgeon both sides of the floor of
the mouth end in the caruncle, forming a V
shape on the floor of the mouth. Contains duct
openings of the sublingual gland
a soft tissue ridgeon both sides of the floor of the mouth end in the caruncle, forming a V shape on the floor of the mouth.
Contains duct openings of the sublingual gland
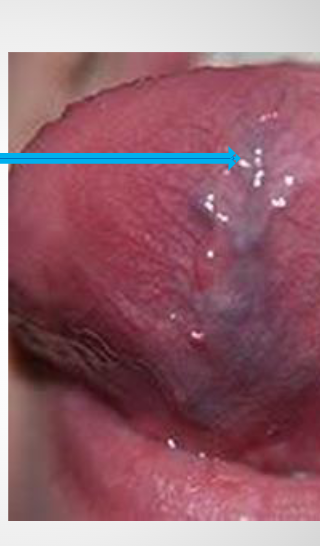
Sublingual Varices
It is mostly seen at the undersurface of the tongue
Means dilation of the veins
Varices: plural – is an abnormal dilated vessel with a tortuous course
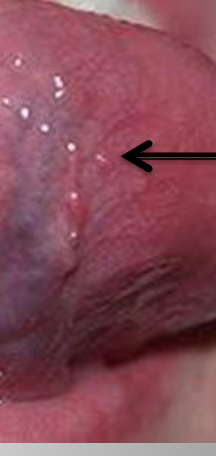
Plica Fimbriata
a fold resembling a fringe on the under surface of the tongue on either side of the frenulum
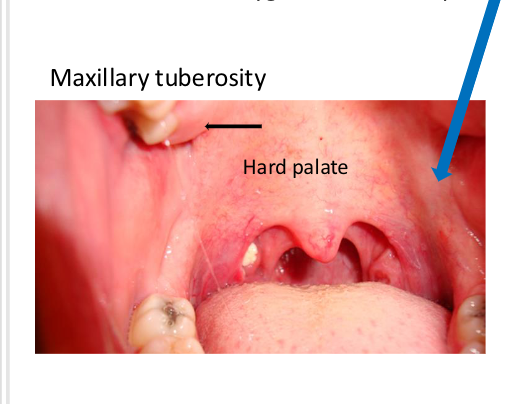
Hard Palate
Anterior portion of the palate covering bony extensions of the maxillary and palatine bones. More pink in color.
Soft Palate
Posterior portion of the palate without bony support. Demarcated by the “vibrating line” (say Ahh).
More red in color Hard palate
Maxillary tuberosity
posterior border of the maxillary alveolar ridge,
covered by tissue, rounded in shape
Palatoglossal arch vs Palatalpharygeal arch
palatoglossal = more anterior
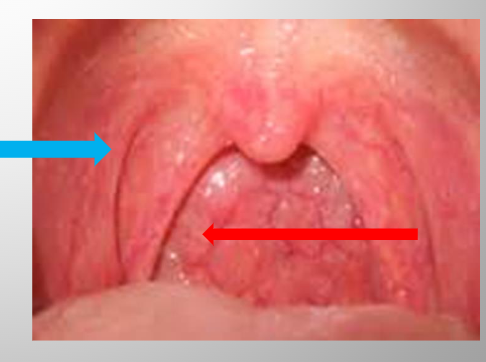
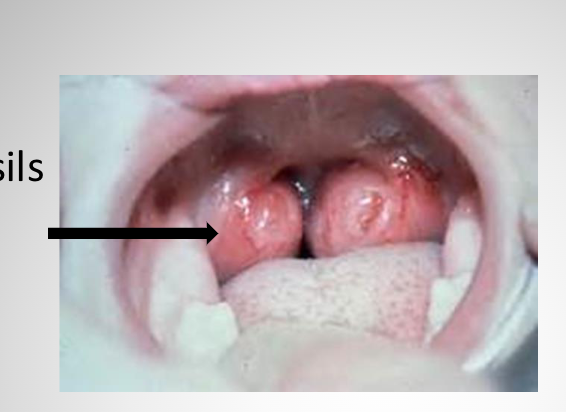
palatine tonsils
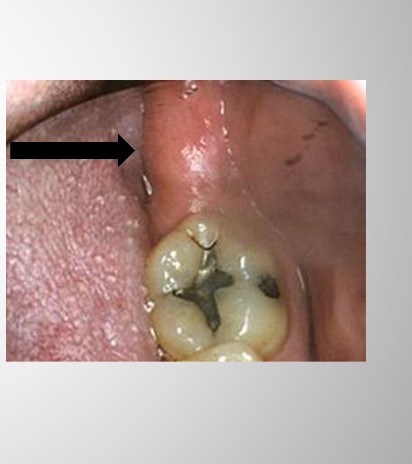
Retromolar Pad
A soft tissue mass that marks the posterior end of the mandibular alveolar ridge.
Posterior to the mandibular third molar area.
Palatal Rugae
Irregular ridges of the mucosa in the anterior of the hard palate located on each side of the median palatal raphe
Posterior to anterior teeth (#6-11)
Incisive Papilla
Smooth soft tissue directly posterior to #8,9 (central incisors)
Covers the nasopalatine foramen
Pharyngeal Fauces
Anterior (palatoglossal) and posterior (palatopharyngeal) fauces, pillars or arches;
vertical folds of tissue forming an arch, with the tonsils in the middle if they are still present
Pterygomandibular /Fold
A band of tissue from the mandibular retromolar area to the maxillary tuberosity area, when opening wide (The pterygomandibular raphe (pterygomandibular ligament) is a ligamentous band of the buccopharyngeal
fascia, attached superiorly to the pterygoid hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate, and inferiorly to the posterior end of the mylohyoid line
Fold is the tissue over the ligament (Raphe)
Mandibular Tori
Bony protuberance on the lingual surface of the mandible
Nontender usually located in the canine to premolar region above the attachment of the mylohyoid muscle
Maxillary Torus
Maxillary palatal torus is a bony protuberance on the midline of the palate.