Gen Chem (Molecules and Ions)
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Molecules and Ions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Monatomic Gases
Only the six noble gases in Group 8A of the periodic table exist in nature as single atoms. For this reason, they are called ______.
Molecules
an aggregate of at least two atoms in a definite arrangement, held together by chemical forces (chemical bonds). It may contain: 1. Same element atoms (e.g., H₂) 2. Different element atoms in a fixed ratio, following the law of definite proportions.
Diatomic Molecules
Molecules with two atoms. Can be same elements and can also be different elements: Examples: HCl, CO
Polyatomic Molecules
Molecules with more than two atoms. Can be: Same element: O₃ (ozone) – 3 oxygen atoms; Different elements: H₂O (water), NH₃ (ammonia)
Ions
Atoms become ___ when they gain or lose electrons. Metals, like sodium (Na), lose 1 or 2 electrons easily, so they become positive. Nonmetals, like chlorine (Cl), gain electrons, so they become negative. This way, both atoms get a stable electron arrangement, and ionic bonds can form.
Monatomic Ions
An ion that consists of only one atom.
Naming Cations
The name of the cation is the same as the element’s name.
Naming Anions
For anions, the name of the element is modified by the suffix -ide.
Polyatomic Ion
Consists of two or more atoms that are covalently bonded and have an overall charge (positive or negative).
Chemical Formulas - Composition
uses element symbols to show the composition of molecules and ionic compounds. They indicate: What elements are present; The ratios in which atoms are combined.
Molecular Formula
Shows the exact number of atoms of each element in the smallest unit of a substance. Subscripts indicate the number of atoms. No subscript = only 1 atom (e.g., O in H₂O). Oxygen (O₂) and ozone (O₃) are allotropes — different forms of the same element.
Empirical Formula
Shows the elements present and the simplest whole-number ratio of their atoms. It does not show the actual number of atoms in a molecule.
Formula of Ionic Compounds
is made up of positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) that are held together. The formula is written in its empirical form, meaning the smallest whole number ratio of cations to anions that makes the compound electrically neutral.
Binary Compounds
The first element keeps its name. The second element gets the suffix "-ide". Greek prefixes are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the molecule.
Molecules or Ions
Most matter is composed of this formed by atoms.
Choose This
Just Memorize the IONS
Common Polyatomic Ions
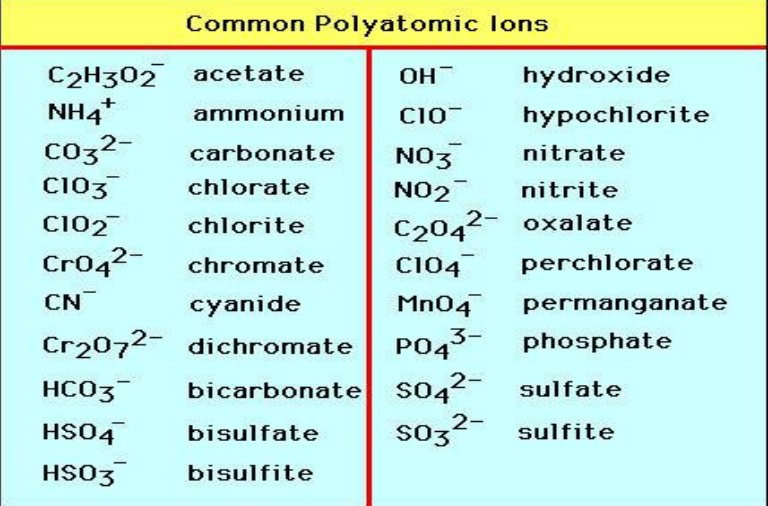
Allotropes
different forms of the same element
Subscripts
indicate the number of atoms
Cation
loss of electrons
Anion
gain of electrons
ammonium
NH₄⁺
carbonate
CO₃²⁻
hydroxide
OH⁻
nitrate
NO₃⁻
nitrite
NO₂⁻
phosphate
PO₄³⁻
sulfate
SO₄²⁻
sulfite
SO₃²⁻