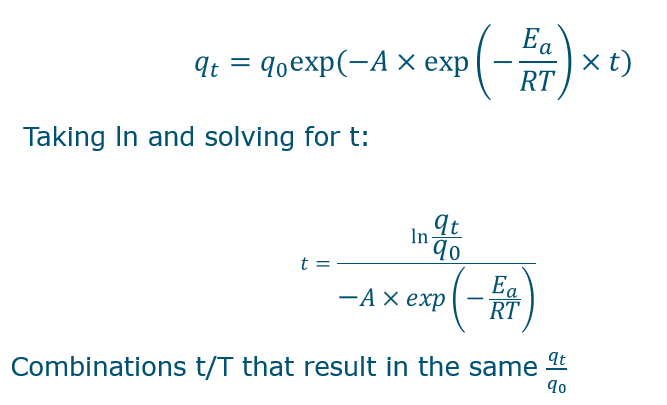C3 - Modelling the effect of temperature on kinetics
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Effect of temperature on quality
Temperature increases the kinetic energy of molecules and thus increases:
The rate of diffusion phenomena
The rate of chemical reactions
The rate of enzymatic reactions (within limits)
The numerical value of your rate parameter!!
How to model temperature relating to rate constant?
by using the Arrhenius equation
Make sure to use the right units, formula is in formularium
Temperature is in K (absolute temperature)!!
Units for R and activation energy should be the same
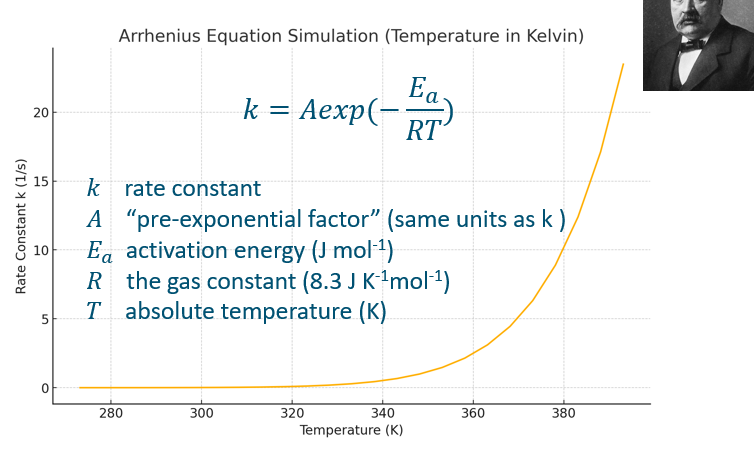
Linear version of Arrhenius equation (not in formularium), with axis.
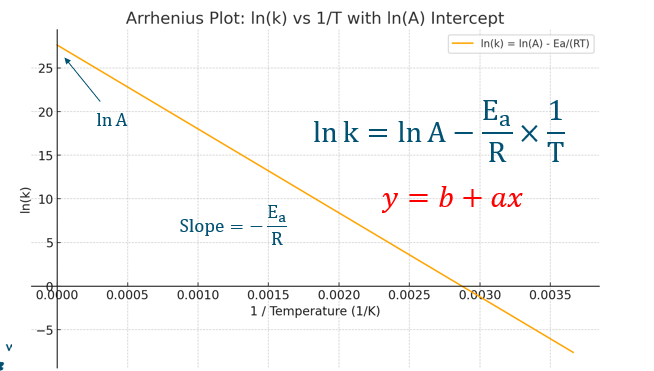
Effect of activation energy on the curve modelling Arrhenius equation.
reaction goes slower when the activation energy is increased.
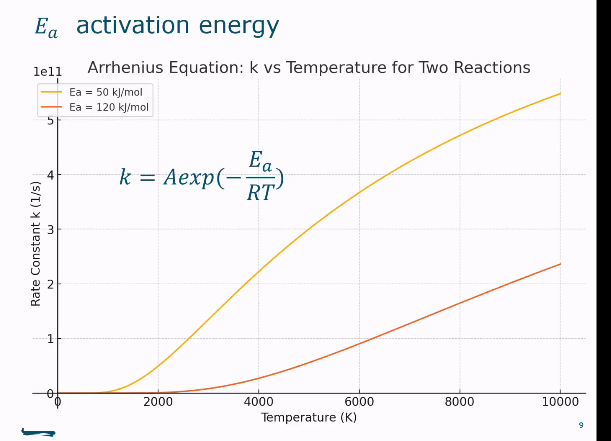
The higher the activation energy…
The higher the Ea, the faster k increases with T.
What happens if you lower activation energy
Results in increase in rate.
What does A mean in Arrhenius equation?
Factor A represents the upper limit for k, when T → infinite.
Is the rate constant always the same for the same chemicals?
No, it can be different from system to system.
How does activation energy differ?
Activation energy will differ from food to food.
which units should be the same in arrhenius equation?
R and Ea!!
Does Arrhenius equation work for non-chemical changes
No
Only if you turn it into what is seen in the picture.
The B doesn’t have any physical or chemical meaning
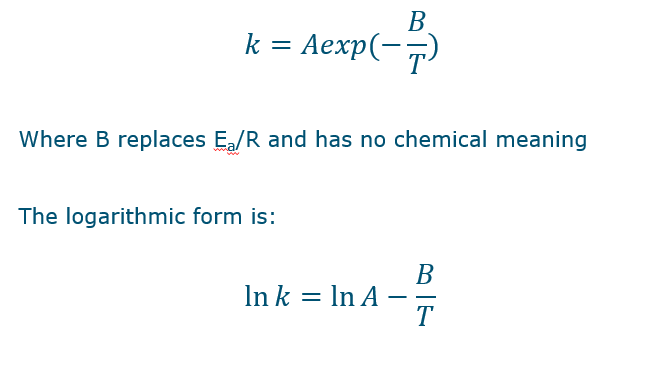
Even for chemical reactions, Arrhenius equation may not apply or may enable inter- and extrapolation for a limited temperature range.
Deviations are possible because of:
Complex (non-elementary) reactions
Changes in physical state (e.g. freezing)
Water changes with temperature
pH changes with temperature
Solubility changes with temperature
Inactivation of catalysts (e.g. enzymatic reactions)
Log logistic model
Relates rate constant to the temperature
often used to model the B parameter in the Weibull model
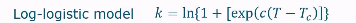
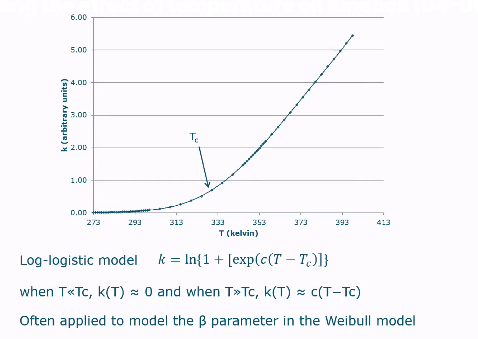
Graph log logistic model
Used as a replacement to Arrhenius model in non-chemical changes.
Tc represents the threshold temperature or critical temperature. It is the temperature at which the behavior of the function k(T) changes significantly:
When temperature « Tc, the K will be = 0
When temperature » Tc, then K will be proportional to the difference between T and Tc
Non-Arrhenius behavior or Arrhenius-like behavior
Always check whether Arrhenius equation applies: Arrhenius plot
For chemical QPI, Arrhenius equation may apply only on a limited temperature range…
Arrhenius equation may not apply for non-chemical QPI
Because of complex reactions or the effect of T on food matrix
For non-chemical QPI it is advised to use an Arrhenius-like model
Other k(T) models are possible: log-logistic model
How to incorporate effect of temperature in kinetic models
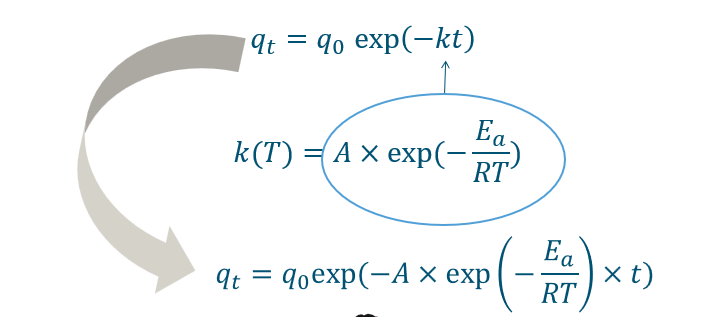
Kinetic models for optimization
This creates Iso-effect curves.
This iso-effect curve will show for example a time and a temperature for which when combined will produce a certain efficiency.