6- Survival and response, RP10, Receptors, Control of heart rate
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is a stimulus?
a change in an organism’s internal or external environment
Why is it important that organisms can respond to stimuli?
organisms increase their chance of survival by responding to stimuli
What is a tropism?
growth of a plant in response to a directional stimulus
> positive tropism= towards a stimulus
> negative tropism= away from stimulus
Summarise the role of growth factors in flowering plants
specific growth factors (hormone-like growth substances) e.g. auxin (such as IAA) move (via phloem or diffusion) from growing regions e.g. shoot/ root tips where they’re produced
to other tissues where they regulate growth in response to directional stimuli(tropisms)
Describe how indoleacetic acid (IAA) affects cells in roots and shoots
In shoots, high concentrations of IAA stimulates cell elongation
In roots, high concentrations of IAA inhibits cell elongation
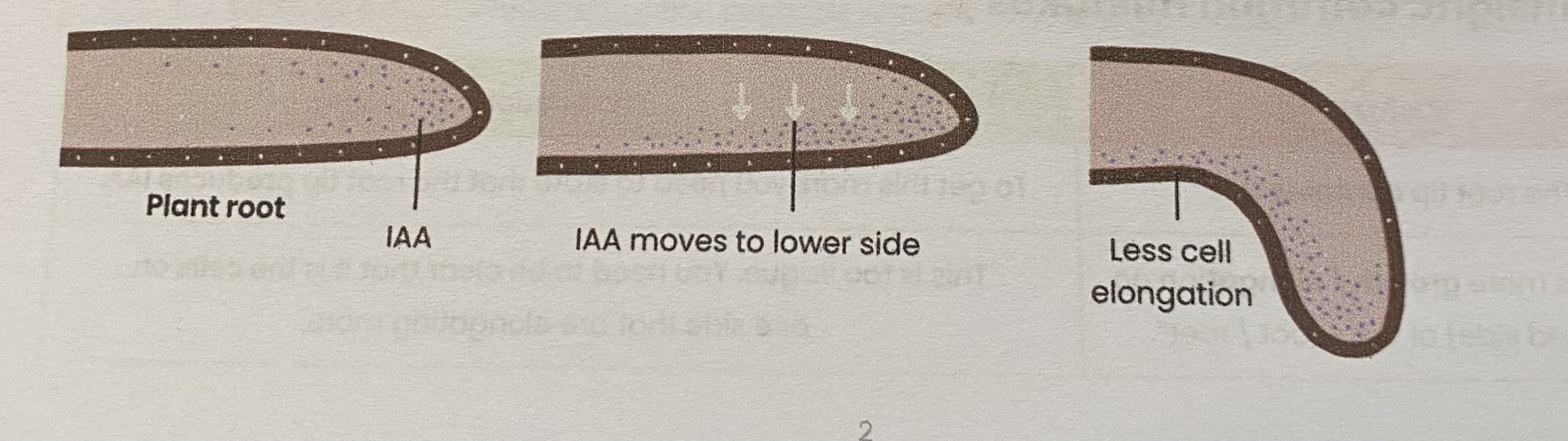
Explain gravitropism in flowering plants
Cells in tip of shoot/ root produce IAA
IAA diffuses down shoot/ root (evenly initially)
IAA moves to lower side of shoot/ root (so concentration increases)
In shoots this stimulates cell elongation whereas in roots this inhibits cell elongation
so shoots bend away from gravity whereas root bend towards gravity
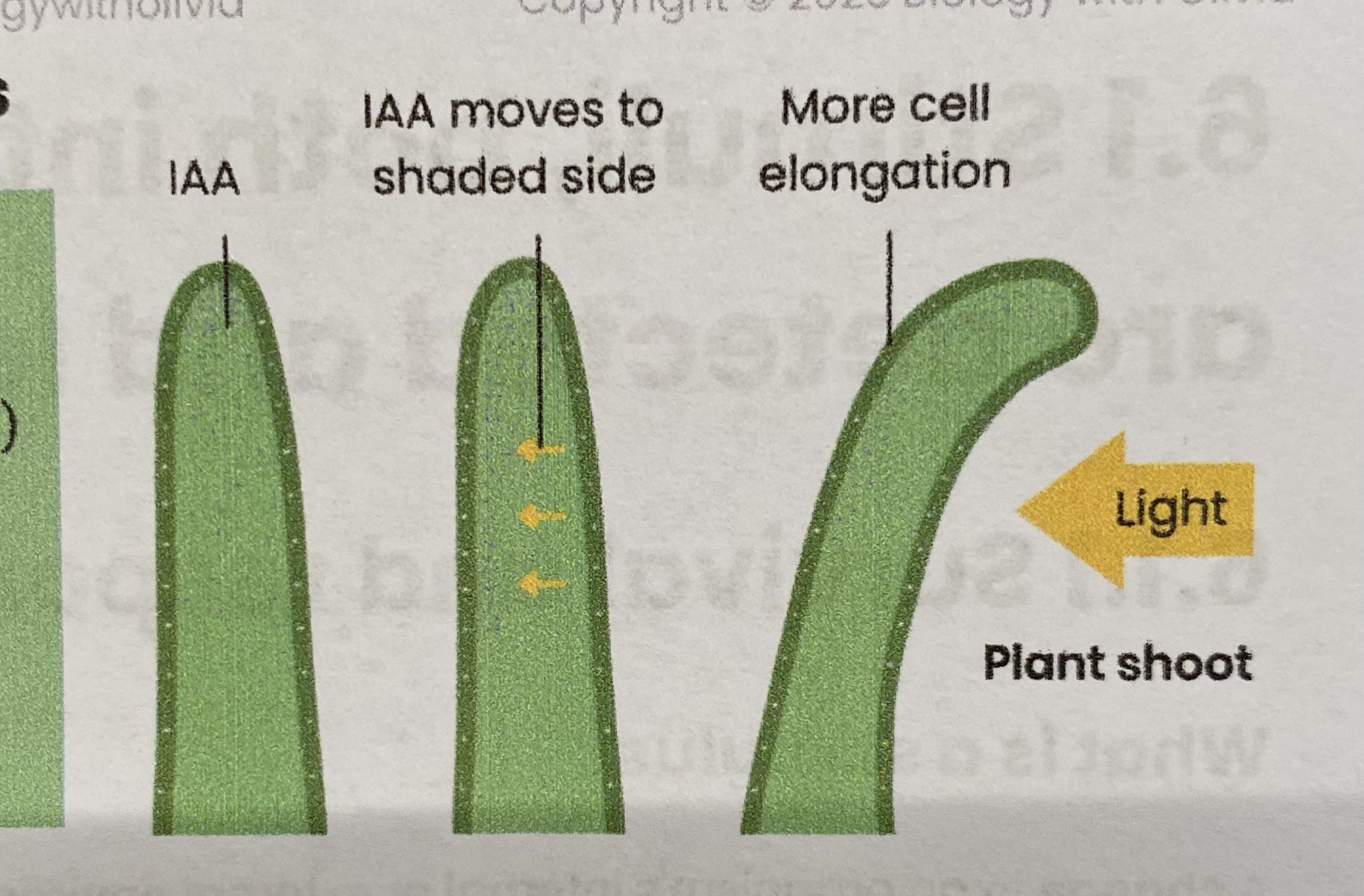
Explain phototropism in flowering plants
Cells in tip of shoot/ root produce IAA
IAA diffuses down shoot/ root (evenly initially)
IAA moves to shaded side of shoot/ root (so conc increases)
In shoots this stimulates cell elongation whereas in roots this inhibits cell elongation
so shoots bend towards light whereas roots bend away from light
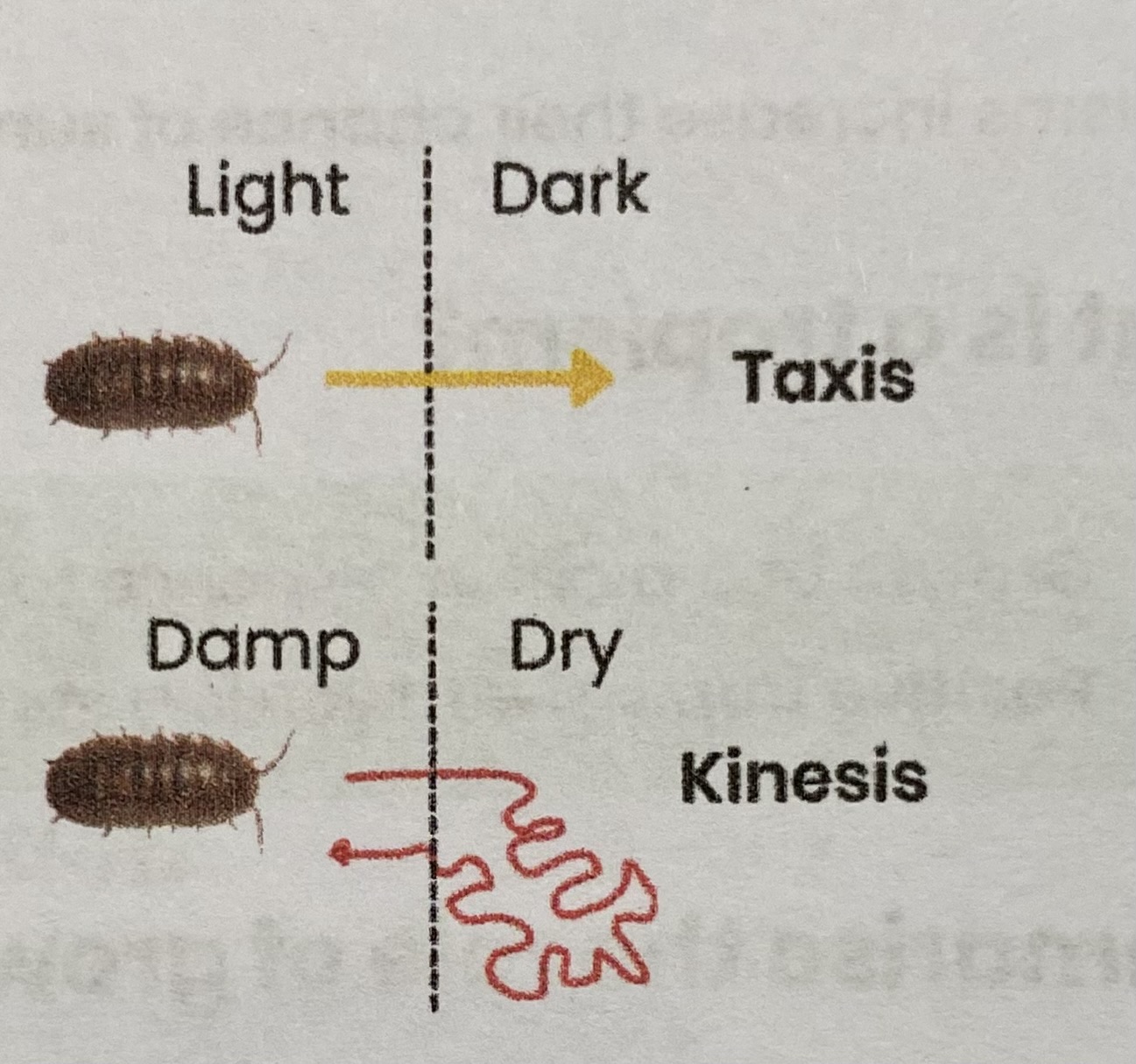
Describe the simple responses that can maintain a mobile organism in a favourable environment
Taxes (tactic response)
directional movement
movement towards or away from a direction stimulus
Kinesis (kinetic response)
non-direction response
speed of movement or rate of direction change changes in response to a non-directional stimulus
depending on intensity of stimulus
Examples:
> taxis= woodlice moving away from light to avoid predators
> kinesis= woodlice moving faster in drier environments to increase their chance of moving to an area with higher humidity to prevent drying out
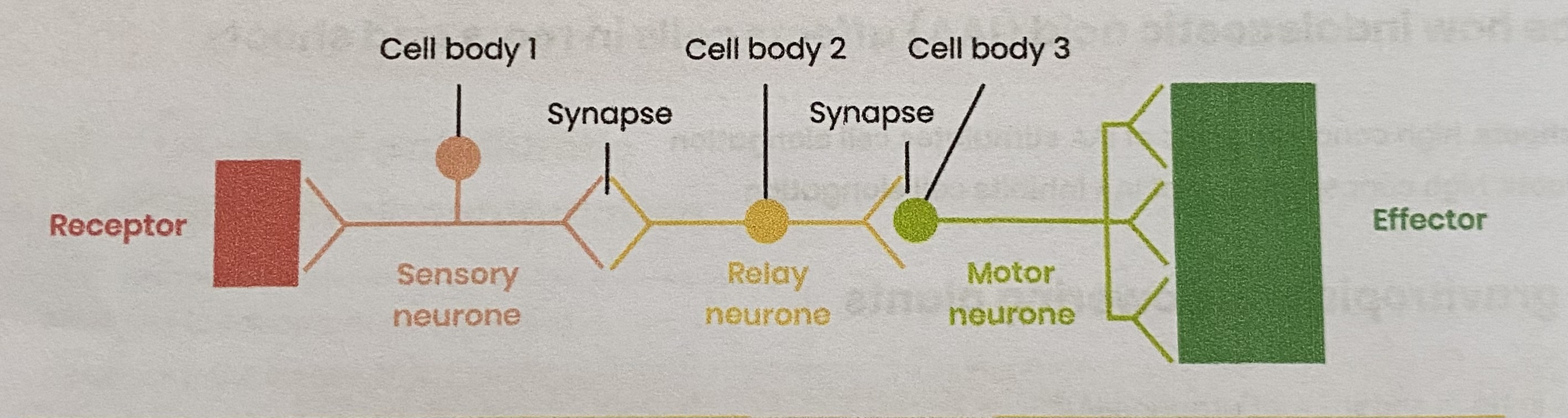
Explain the protective effect of a simple (e.g. 3 neurone) reflex
Rapid as only 3 neurones and few synapses (synaptic transmission is slow)
Autonomic (doesn’t involve conscious regions of brain) so doesn’t have to be learnt
Protects from harmful stimuli e.g. escape predators/ prevents damage to body tissues
What is RP10?
Investigation into the effect of an environmental variable on the movement of an animal using either a choice chamber or a maze
RP10- Describe how the effect of an environmental variable on the movement of an animal (e.g. woodlice) can be investigated using a choice chamber
Set up choice chamber (different compartments) to create different environmental conditions
e.g. humidity= add a drying agent to 1 side and damp filter paper to other
e.g. light= shine a light but cover one half with black card
Control other environmental conditions
e.g. if investigating humidity control light intensity with a dim even light above
Use a teaspoon to place a set number of animals e.g. 12 woodlice on centre of mesh platform and cover with lid
After a set amount of time e.g. 10 mins record the number of animals in each section
Repeat after gently moving woodlice back to centre
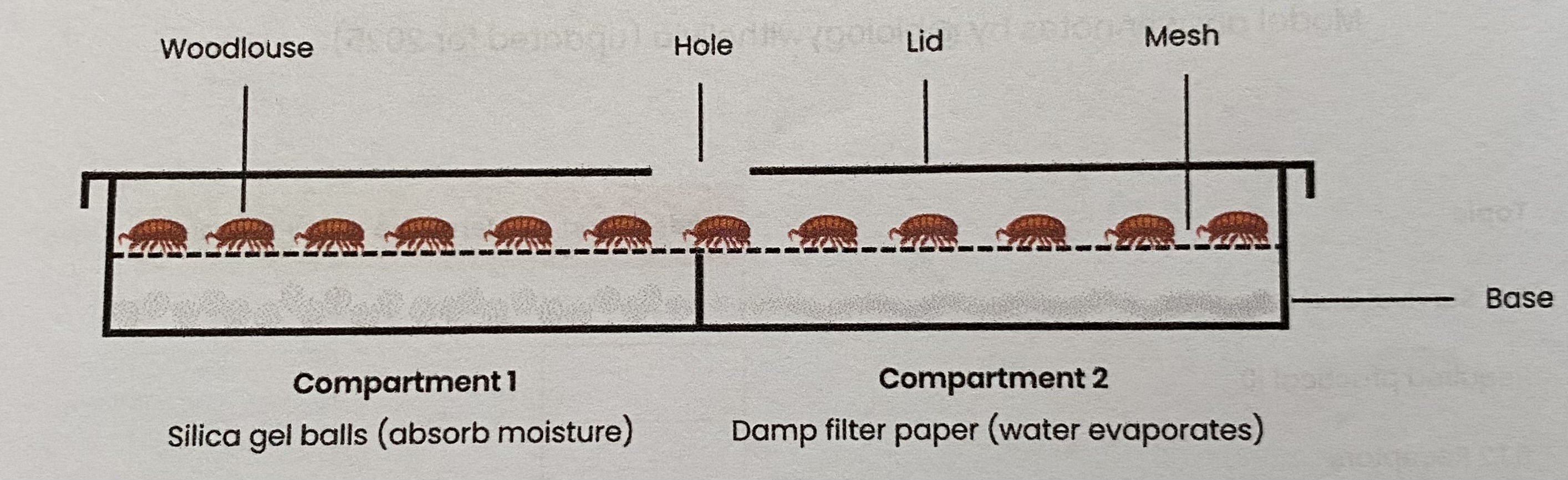
RP10- The woodlice were left for 15 mins before their movement was recorded when investigating the effect of humidity. Explain why (2 marks)
time to establish humidity/ for substance to absorb water/ water from paper to evaporate
woodlice no longer affected by handling
so that behaviour is typical of that humidity
RP10- Explain how you would ensure the safe and ethical handling of animals (2 marks)
safely- cover open wounds/ wash hands with soap after
to minimise risk of infection
ethical- handle carefully/ return to habitat ASAP
RP10- Explain why a mesh platform is used when investigating the effect of humidity (1 mark)
to keep woodlice a safe distance from drying agent
RP10- Describe how the effect of an environmental variable on the movement of an animal (e.g. maggots) can be investigated using a maze
Mazes are used to investigate turning behaviour in response to different environmental conditions:
Change environment at one end of T shape e.g. add food source
Place animal e.g. maggot in stem of T
Record whether animal turns towards or away from food source
Repeat with a large number of maggots
wipe/ clean maze between trials
Repeat with food on other size of T
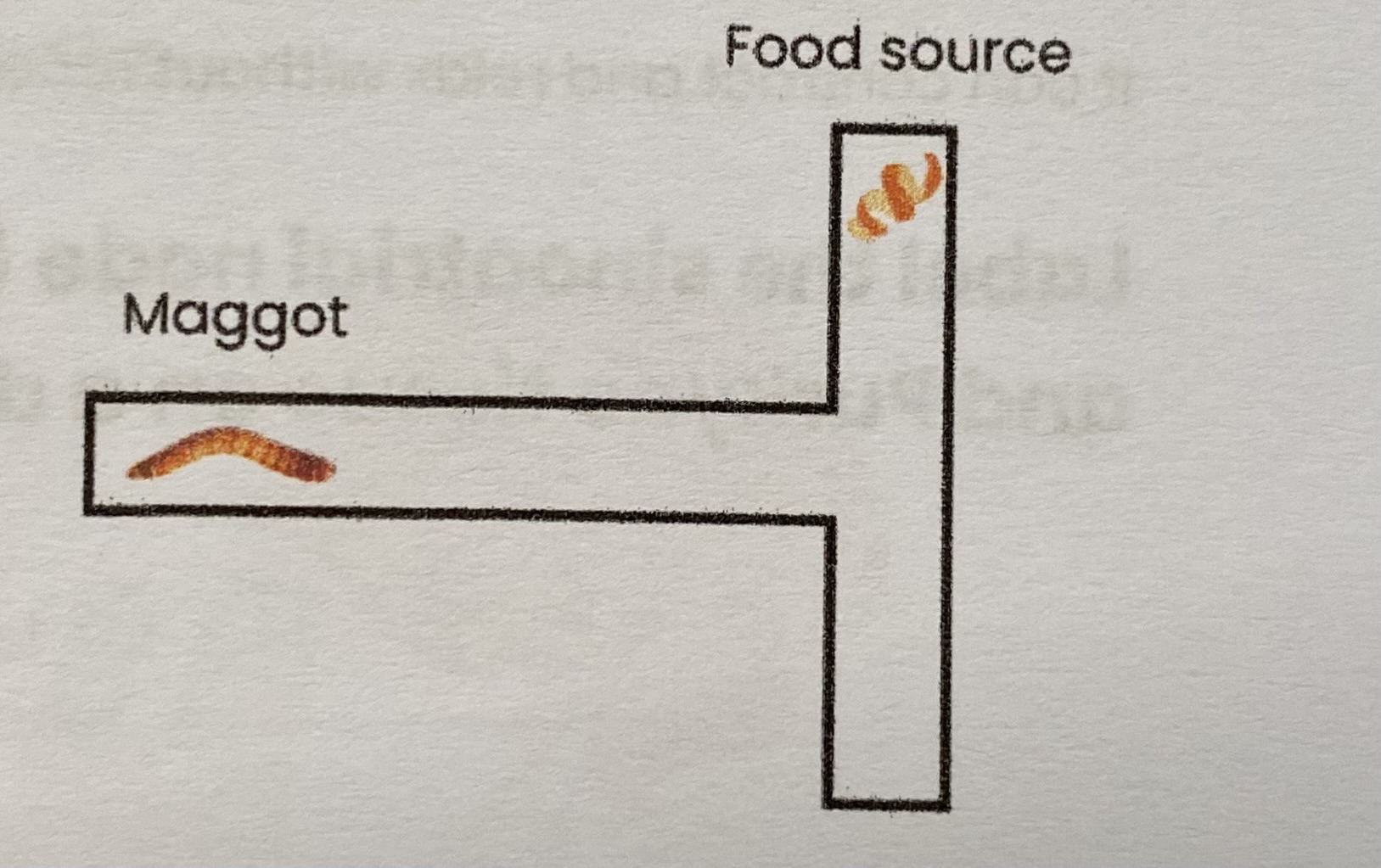
RP10- Explain why the same organism is not used more than once (2 marks)
reduces stress on maggots
prevents chance of learned behaviours
RP10- Explain why a clean petri dish/ maze is used each time (2 marks)
animals may leave chemicals/ scents
which influence behaviour of other animals
RP10- Explain which statistical test should be used to analyse results
chi-squared
as data are categorical and comparing frequencies
to see if there is a significant difference between observed and expected frequencies
expected= equal numbers each side
Describe the basic structure of a Pacinian corpuscle
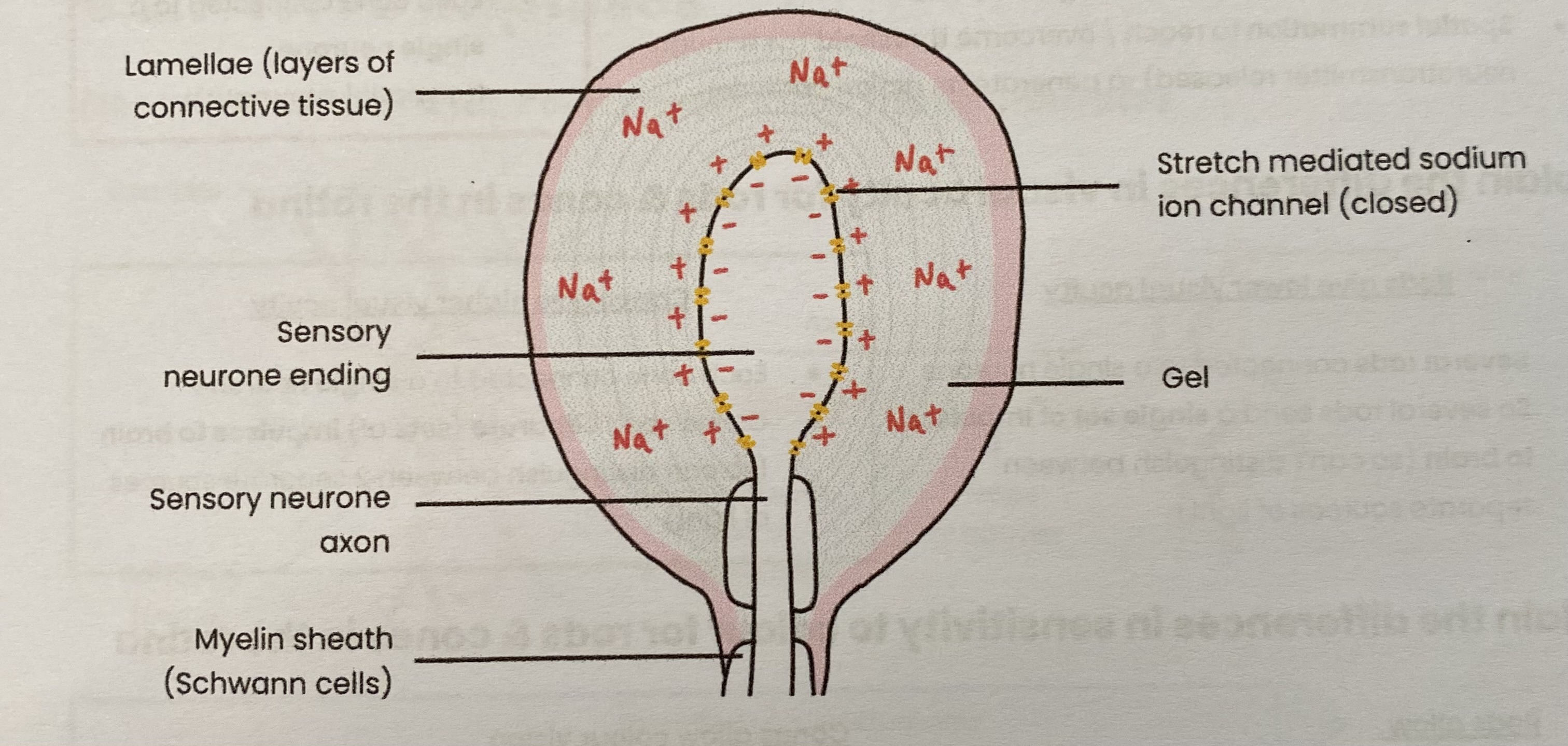
Describe how a generator potential is established in a Pacinian corpuscle
Mechanical stimulus e.g. pressure deforms lamellae and stretch- mediated sodium ion (Na+) channels
So Na+ channels in membrane open and Na+ diffuse into sensory neurone
greater pressure causes more Na+ channels to open and more Na+ to enter
This causes depolarisation, leading to a generator potential
if generator potential reaches threshold it triggers an action potential
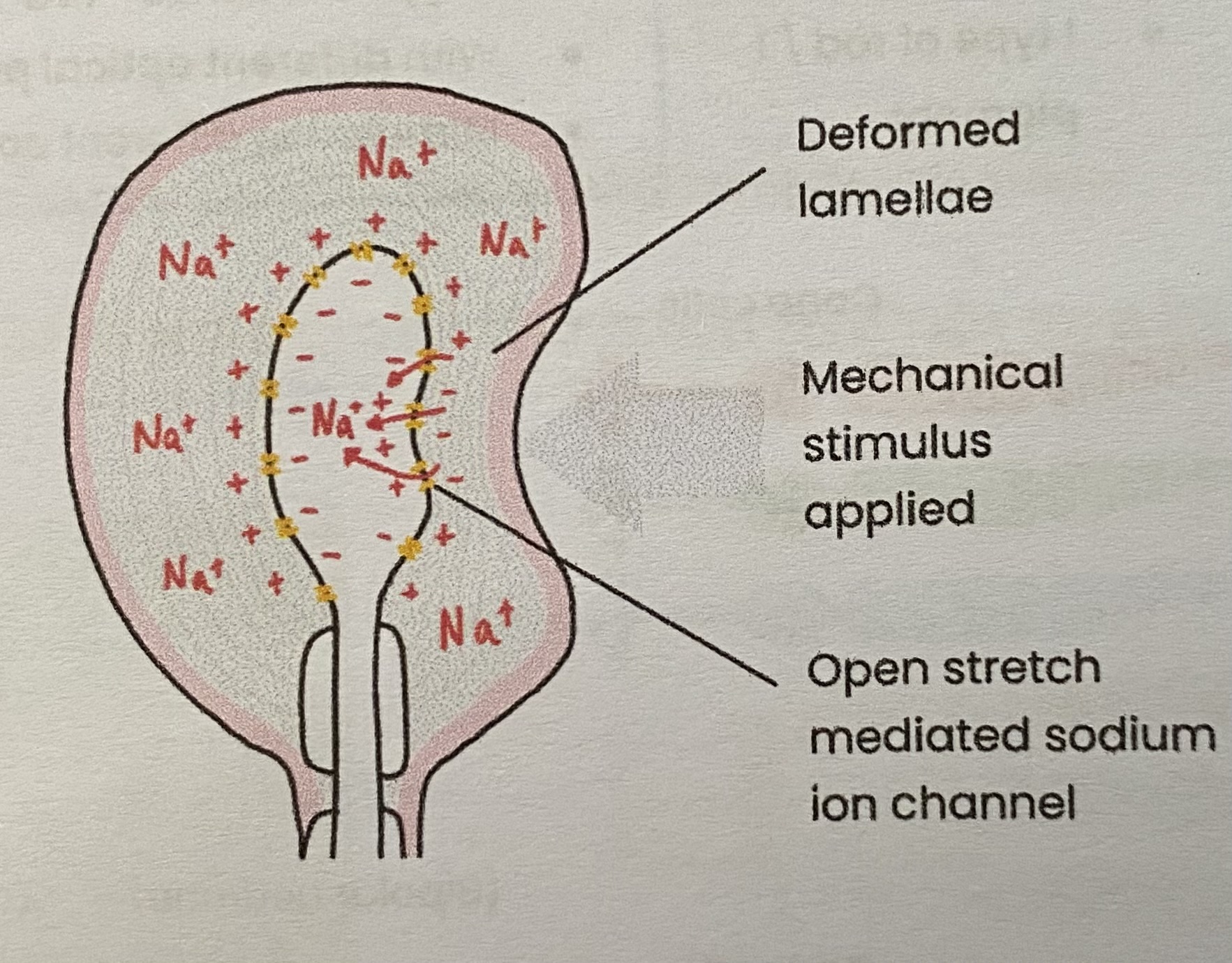
Explain what the Pacinian corpuscle illustrates
Receptors respond only to specific stimuli
Pacinian corpuscle only responds to mechanical pressure
Stimulation of a receptor leads to the establishment of a generator potential
when threshold is reached, action potential sent (all-or-nothing principle)
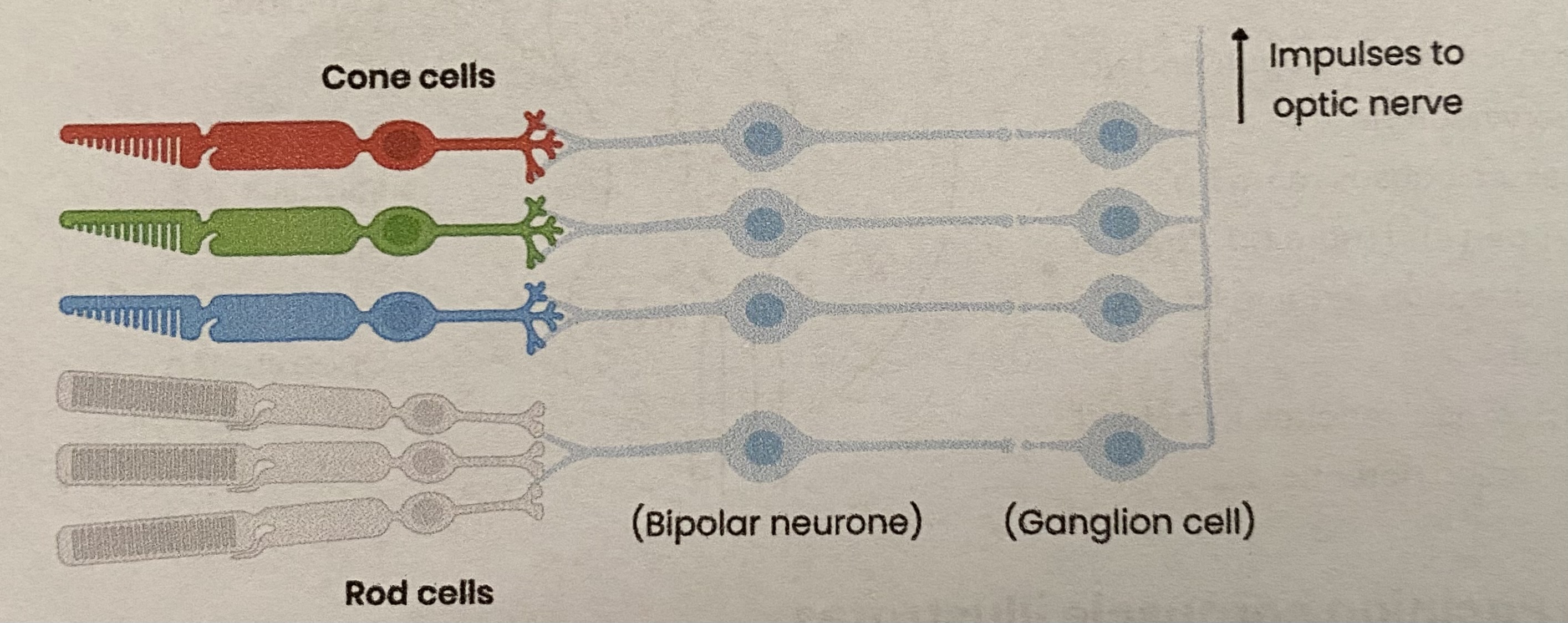
Explain the differences in sensitivity to light for rods & cones in the retina
RODS are more sensitive to light:
several rods connected to a single neurone
spatial summation to reach/ overcome threshold (as enough neurotransmitter released) to generate an action potential
CONES are less sensitive to light:
each cone connected to a single neurone
no spatial summation
Explain the differences in visual acuity for rods & cones in the retina
RODS give lower visual acuity:
several rods connected to a single neurone
so several rods send a single set of impulses to brain (so can’t distinguish between separate source of light)
CONES give higher visual acuity:
each cone connected to a single neurone
cones send separate (sets of) impulses to brain (so can distinguish between 2 separate sources of light)
Explain the differences in sensitivity to colour for rods & cones in the retina
RODS allow monochromatic vision:
1 type of rod/ 1 pigment
CONES allow colour vision:
3 types of cones- red- green- and blue- sensitive
with different optical pigments= absorb different wavelengths
stimulating different combinations of cones gives range of colour perception
Cardiac muscle is myogenic. What does this mean?
it can contract and relax without receiving electrical impulses from nerves
Label the sinoatrial node (SAN), atrioventricular node (AVN), Bundle of His and Purkyne tissue on a diagram of the heart
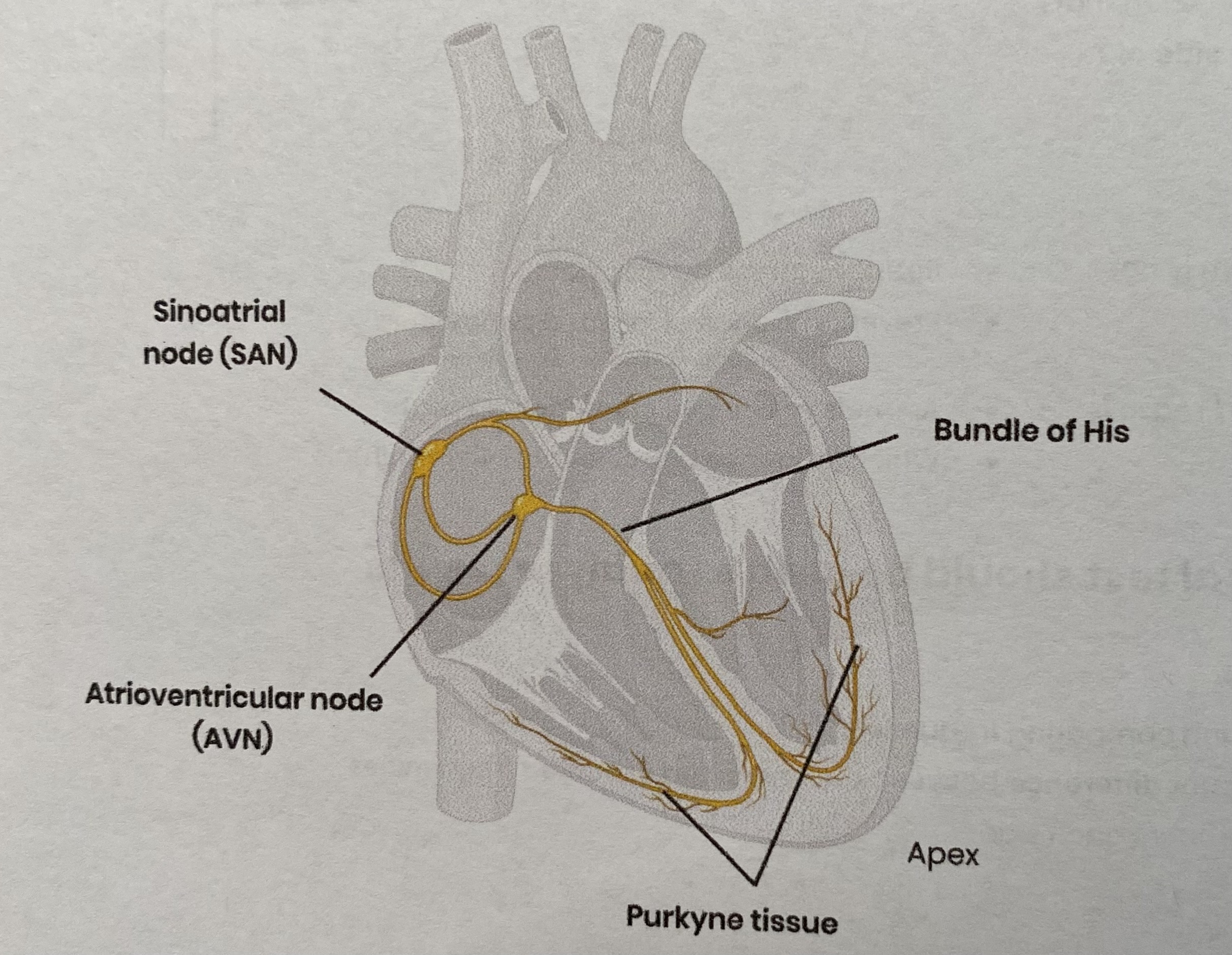
Describe the myogenic stimulation of the heart and transmission of a subsequent wave of electrical activity
Sinoatrial node (SAN) acts as pacemaker= releases regular waves of electrical activity across atria
causing atria to contract simultaneously
Non-conducting tissue between atria/ ventricles prevents impulse passing directly to ventricles
preventing immediate contraction of ventricles
Waves of electrical activity reach atrioventricular node (AVN) which delays impulse
allowing atria to fully contract and empty before ventricles contract
AVN sends wave of electrical activity down bundle of His, conducting wave between ventricles to apex where it branches into Purkyne tissue
casuing ventricles to contract simultaneously from the base up
Where are chemoreceptors and pressure receptors located?
chemoreceptors and pressure receptors are located in the aorta and carotid arteries
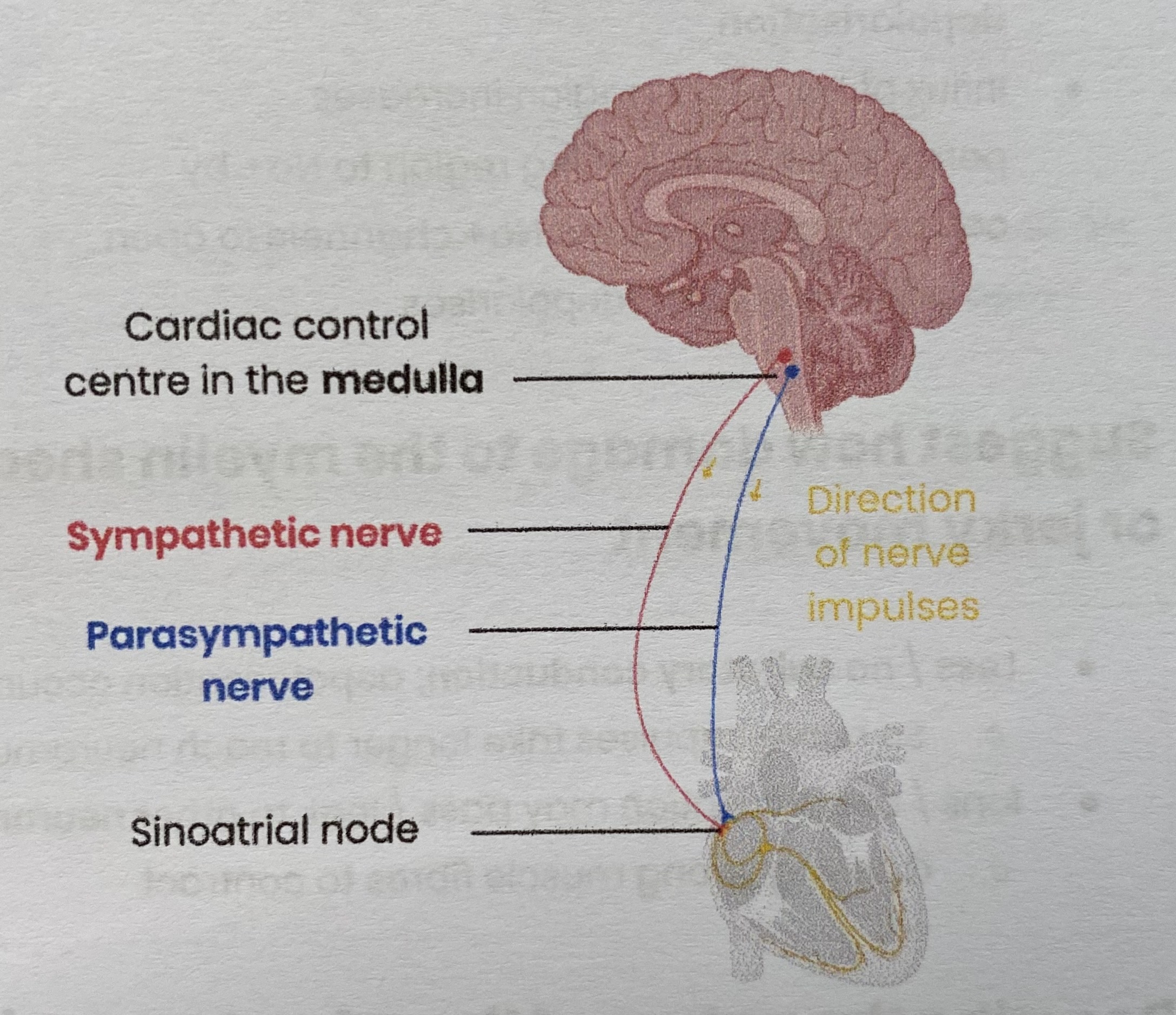
Describe the roles of chemoreceptors, pressure receptors, the autonomic nervous system and effectors in controlling heart rate
Baroreceptors detect (fall/ rise) in blood pressure and/ or chemoreceptors detect blood (rise/ fall) in blood CO2 conc or (fall/ rise) in blood pH
Send impulses to medulla/ cardiac control centre
Which send more frequent impulses to SAN along (sympathetic/ parasympathetic) neurones
So (more/less) frequent impulses sent from SAN and to/ from AVN
So cardiac muscle contracts (more/ less) frequently
So heart rate (increases/ decreases)
Pink= for a fall in blood pressure OR rise in blood CO2 conc/ fall in blood pH
Blue= for a rise in blood pressure OR fall in blood CO2 conc/ rise in blood pH