241 Unit 2: skeletal tissue terminology
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
skeletal tissue
-includes bones, cartilages, ligaments
-bones have their own blood vessels, but ligaments and cartilages have no blood vessels or nerves (avascular)
hyaline
-cartilage taht provides support, flexibility, and resillience
-most abundant type
-present in fetal skeleton, respiratory tract, articular (joint) cartilage, and costal cartilage
elastic
-similar to hyaline cartilage, but contain elastic fibers
-provides elasticity
-found in the ear and epiglottis
fibrocartilege
-contain collagen fibers (have great tensile strength)
-found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, knee joint- meniscus
axial
-main group of bones by location
-includes the skull, thoracic cage, and vertebral column
appendicular
-main group of bones by location
-includes the limbs
bone functions
-support
-protection
-movement
-storage
-blood cell formation
-fat and triglycerides
support
-bone function
-for the body and soft organs
protection
-bone function
-for the brain, spinal cord, and vital organs
movement
-bone function
-levers for muscle action
storage
-bone function
-minerals (calcium, phosphorus, magnesium) and growth factors
blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
-bone function
-takes place in marrow cavities
fat and triglycerides
-bone function
-energy
-stored in bone cavities
long bones
-classification by shape
-longer than they are wide
short bones
-classification by shape
-cube shaped bones (in wrist adn ankle) and sesamoid bones (within tendons; e.g.: patella)
flat bones
-classification by shape
-thin, flat, and slightly curved
-ex: sternum
iregular bones
-classification by shape
-complicated shapes
-ex: vertebra
compact bone
-classification by texture
-dense outer layor
spongy (cancellous) bone
-classification by texture
-honeycomb of trabeculae
-inside compact bones
tuberosity
-rounded projection
-bone marking
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
crest
-bone marking
-narrow, prominent ridge
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
trochanter
-bone marking
-large, blunt, irregular surface
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
line
-bone marking
-narrow ridge of bone
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
tubercle
-bone marking
-small, rounded projection
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
epicondyle
-bone marking
-raised area above a condyle
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
spine
-bone marking
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
-sharp, slender projection
process
-bone marking
-site of muscle/ligament attachment
-any bony prominence
head
-bone marking
-structure that helps form joints
-bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
facet
-bone marking
-structure that helps form joints
-smooth, nearly flat articular surface
condyle
-bone marking
-structure that helps form joints
-rounded articular projection
ramus
-bone marking
-structure that helps form joints
-armlike bar
meatus
-bone marking
-depression/opening
-canal like passageway
sinus
-bone marking
-depression/opening
-cavity within a bone
fossa
-bone marking
-depression/opening
-shallow, basin like depression
groove
-bone marking
-depression/opening
-furrow
-long enough for a blood vessel
fissure
-bone marking
-depression/opening
-narrow, slitlike opening
foramen
-bone marking
-depression/opening
-round or oval opening through a bone
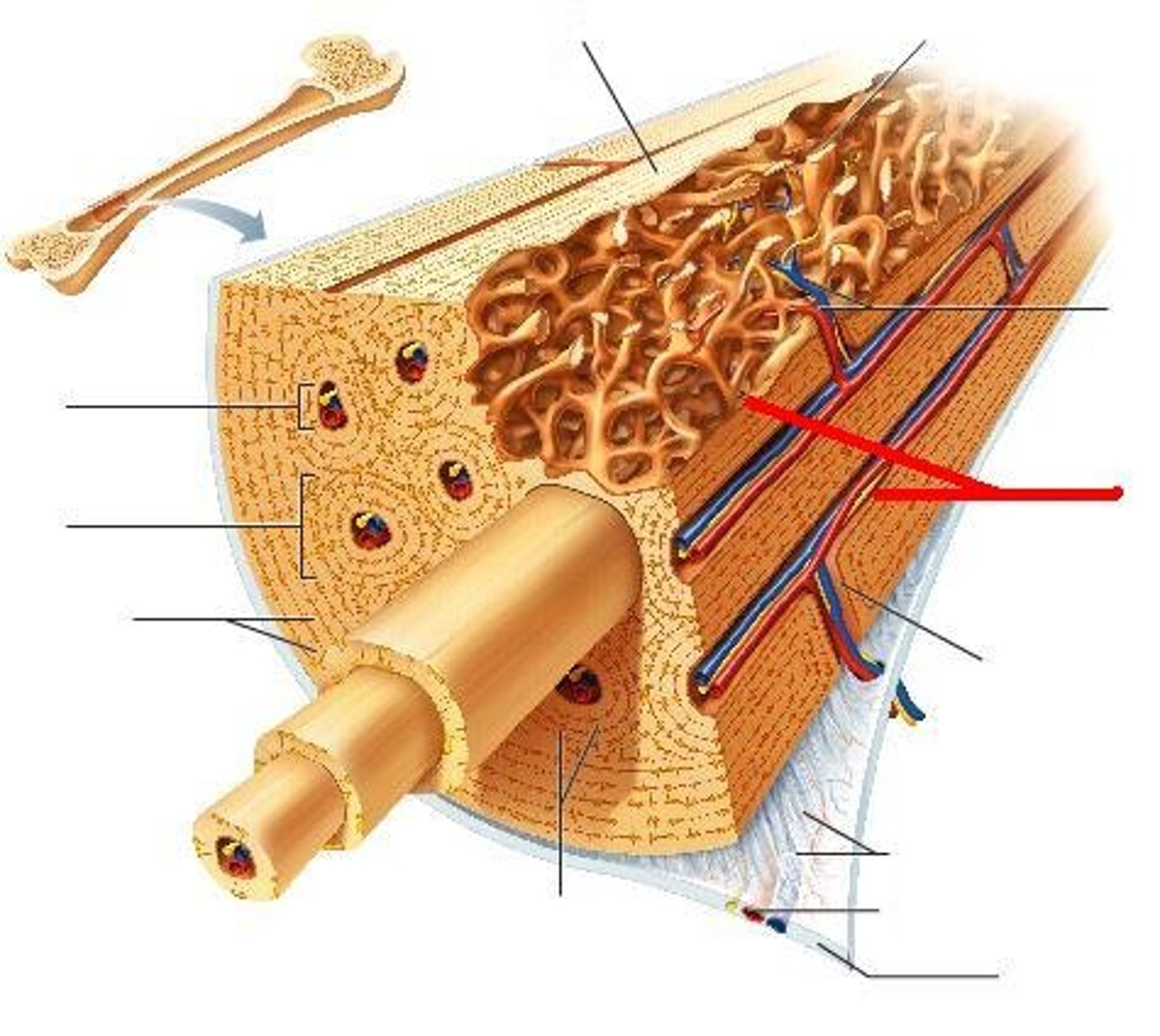
diaphysis
-shaft of bone
-compact bone collar surrounds medullary (narrow) cavity
-medullary cavity in adults contain fat (yellow marrow), early in life it contains red marrow
epiphyses
-expanded ends
-spongy bone interior
-epiphyseal line (remnant of growth plate)
-articular (hyaline) cartilege on joint surfaces
periosteum
-outer covering of bone
-two layors: fibrous and osteogenic
-nerve fibers, nutrient blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels enter the bone via nutrient foramina
fibrous layer
-outer layer of the periosteum
-very tough
osteogenic layer
-inner layer of the periosteum
-contains lots of cells: osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteogenic cells
osteogenic cell
-stem cells in the periosteum and endosteum that give rise to osteoblasts
-aka osteoprogenitor
-
osteoblasts
-in the osteogenic layer
-bone forming cells (produce bone matrix)
osteoclasts
-in osteogenic layer
-bone destroying cells (destroys matrix)
endosteum
-inner layer of bones
-delicate membrane on internal surfaces of bone
-also contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts
osteocytes
-mature bone cells
adult hematopoietic tissue
-red bone marrow
-in heads of femur and humerus
-trabecular cavities of the dipoe of flat bones
newborn hematopoietic tissue
-red bone marrow
-in the medullary cavities and all spaces in spongy bone
osteon
-aka haversian system
-compact bone
-structural unit
-includes lamellae, central (haversian) canal, and canaliculi
lamellae
-in haversian system of compact bone
-weight bearing, column-like matrix tubes
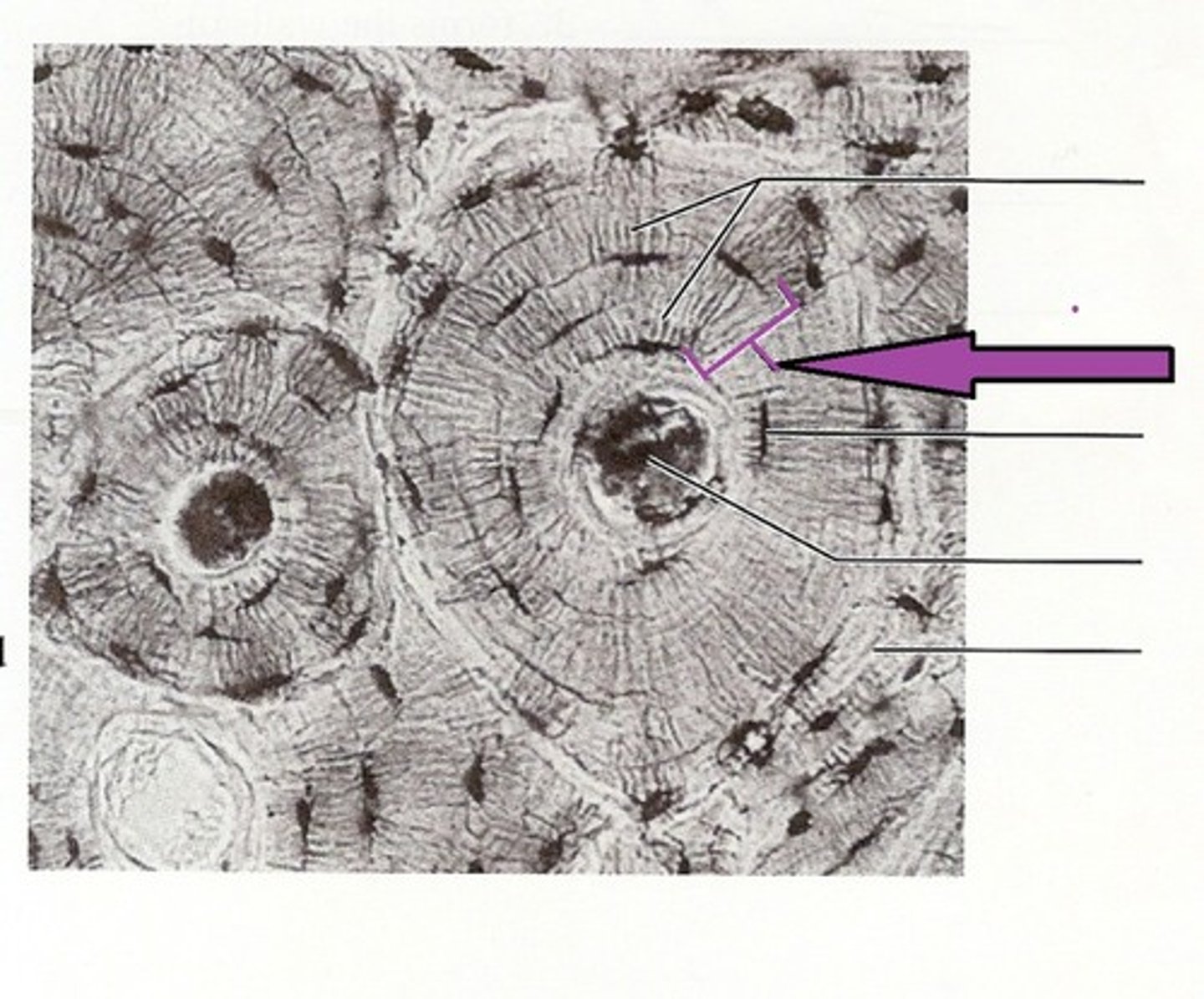
central canal
-in haversian system of compact bone
-contains blood vessels and nerves
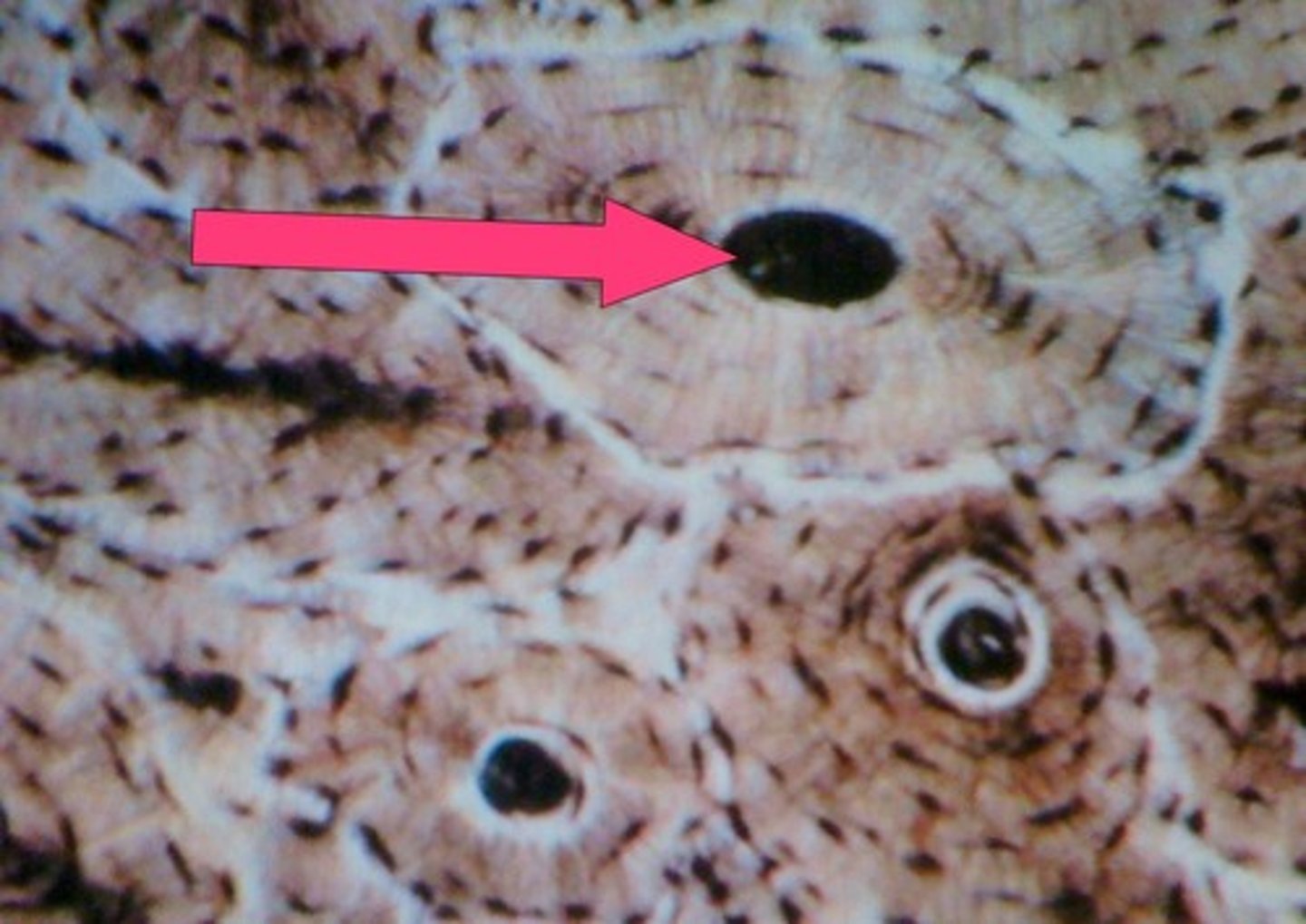
lacunae
-in haversian system of compact bones
-small cavities that contain osteocytes
-surround the central canal
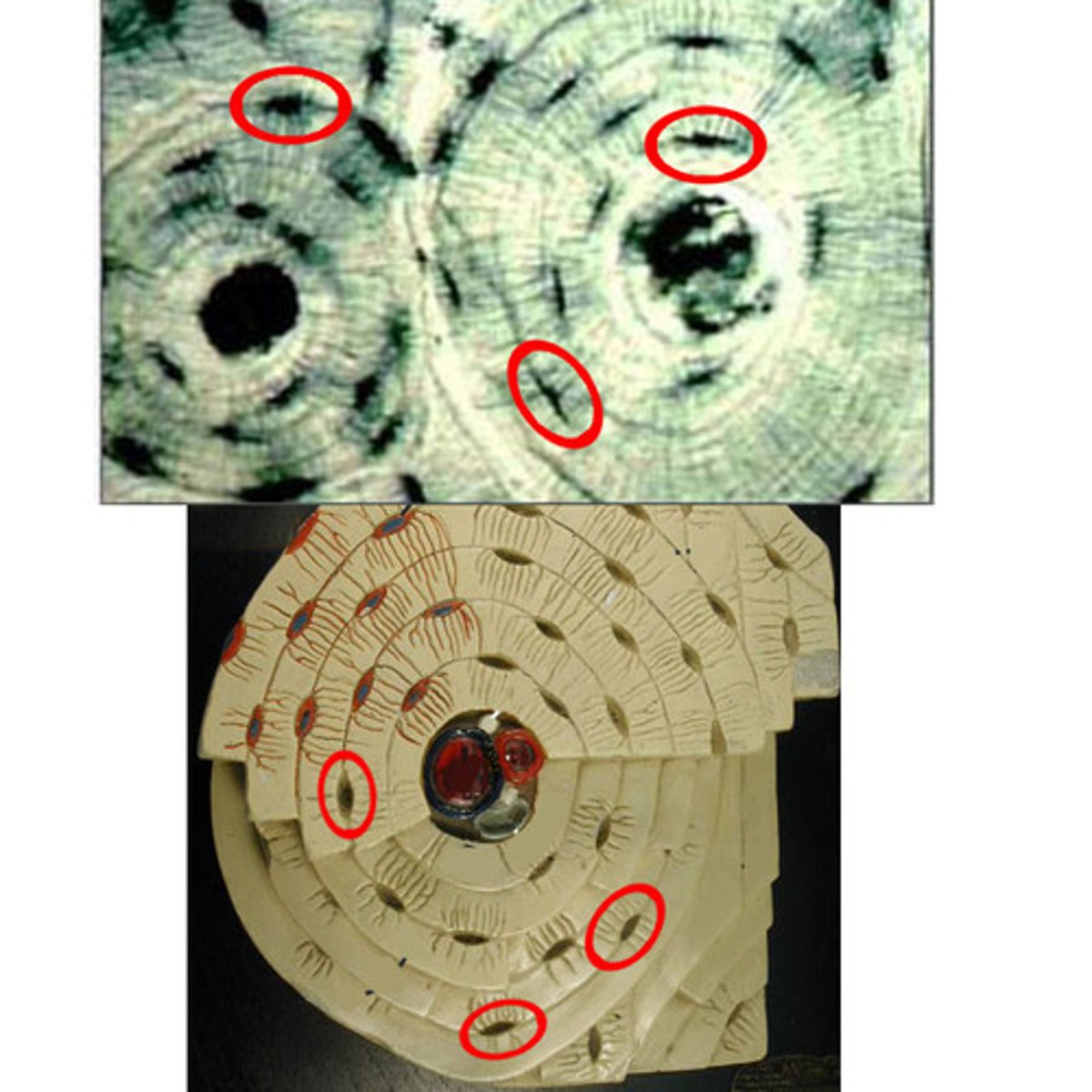
canaliculi
-in haversian system of compact bones
-hair-like canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
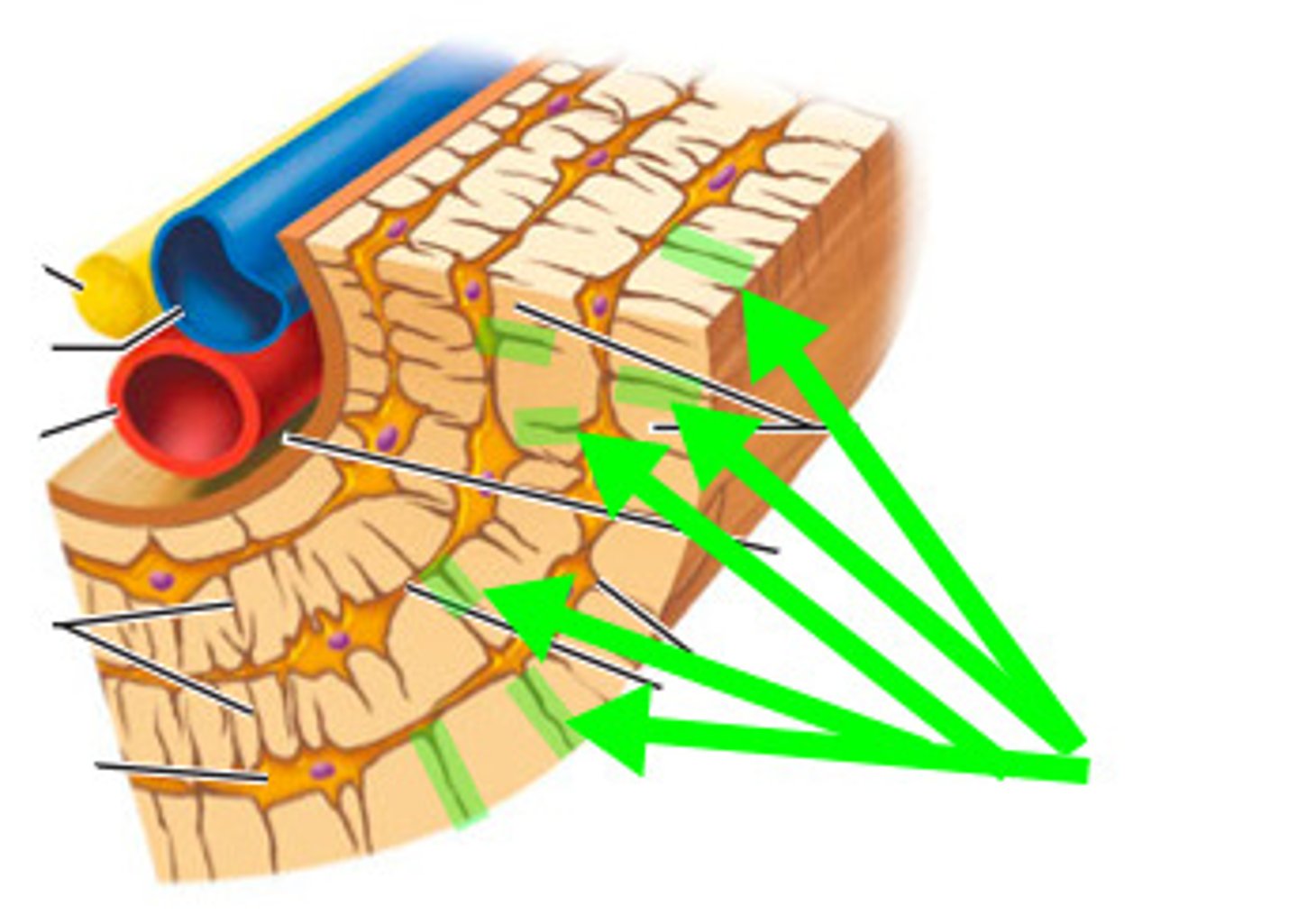
trabeculae
-spongy bone
-align along lines of stress
-no osteons
-contain irregularly arranged lamellae, osteocytes, and canaliculi
-capillaries in endostreum supply the nutrients
organic composition
-osteoid
-bone matrix secreted by osteoblasts (ground substance and collagen fibers)
-mineral salts
ground substance
-organic bone matrix
-proteoglycans and glycoproteins
collagen fibers
-organic bone matrix
-provide tensile strength and flexibility
mineral salts
-organic bone matrix
-65% of bone by mass
-mainly calcium phophate crystals
-responsible for hardness and resistance to compression
osteogenesis (ossification)
-bone tissue formation
-bone formation begins in the 2nd month of development
-can be intramembranous or endochondral
intramembraneous ossification
-type of osteogenesis
-bones develop from membrane
-forms flat bones, clavicle, and cranial bones
-selected centrally located mesenchymal cells cluster and differentiate into osteoblasts, forming an ossification center
endochondral ossification
-type of osteogenesis
-bones form by replacing hyaline cartilege
-forms most of the skeleton
-plates get thinner as bones grow
steps of endochondral ossification
-bone collar forms around hyaline cartilage model
-cartilage in center of diaphysis calcifies and develops cavities
-peristeal bud inavades internal cavities and spongy bone begins to form
-diaphysis elongates and a medullary cavity forms, secondary ossification centers appear in epiphyses
-epiphyses ossify, when completed hyaline cartilage remains only in epiphyseal plates and articular cartilages
nutrient artery and vein
-major set of blood vessels
-single pair of large blood vessels
-enter diaphysis through nutrient foramen
-femur has more than one pair
metaphyseal vessels
-major set of blood vessels
-supply epiphyseal cartilage
-where bone growth occurs
periosteal vessels
-major set of blood vessels
-provide blood to superficial osteons and secondary ossification centers
process of remodeling
-involves osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts
-bone continually remodels, recycles, and replaces
-turnover rate varies (deposition>removal=stronger, removal>deposition=weaker)
growth hormone
-hormone that helps in bone growth
-regulated by pituitary hormone
thyroid hormone
-hormone that helps in bone growth and calcium homeostasis
-modulates activity of growth hormone
-calcitonin
sex hormones
-hormones that helps in bone growth
-testosterone and estrogen
-start at puberty
-promote adolescent growth
calcitonin
-a thyroid hormone that helps calcium homeostasis
-secreted by C cells/parafollicular cells
-decreases calcium levels
PTH
-helps in calcium homeostasis
-released by parathyroid glands
-increase in serum calcium concentration (by increasing vitamin D)
-activates osteoclasts, stimulates kidney tubules to reabsorb calcium from urine
-stimulates kidney tubules to produce calcitrol from calcidiol
vitamin D
-helps in calcium homeostasis
-enters body with food
-proenzyme
-synthesized within body
-helps absorption of calcium
calcitonin effects on bone
-inhibiting activity of osteoclasts, releasing calcium and phosphorus into blood
calcitonin effects on kidney
-inhibits tubular reabsorption of calcium and phosphorus, leading to increased rates of their loss in urine
calcitrol
-most active form of vitamin D
-kidney tubules produce when PTH stimulates
calcidiol
-less active form of vitamin D
-makes the active form
calcium importance
-necessary for transmission of nerve impulses, muscle contraction, blood coagulation, secretion by glands and nerve cells, and cell division
PTH control of blood calcium
-how its primarily controlled
-low levels cause parathyroid glands to release hormone which stimulates osteoclasts to degrade bone matrix and release calcium which increases blood calcium levels
opposites
-relationship between calcitonin and PTH?
9-11
-normal range of calcium concentration in blood
hypercalcemia
-too much calcium in blood (over 11 mg/100ml)
hypocalcemia
-not enough calcium in blood (under 9 mg/100ml)
calcitonin control of blood calcium
-controls concentation of calcium
-high blood levels cause parafollicular cells of thyroid to release hormone which stimulates osteoblasts to deposit calcium salts which lower blood calcium levels
fractures
-can be described in terms of location, external appearance, or nature of break
-common types: comminuted, compression, spiral, epiphyseal, depressed, and greenstick
comminuted
-common type of fracture
-bone fragments break into three or more pieces
-particularily common in the aged, whose bones are more brittle
compression
-common type of fracture
-bone is crushed
-common in porous bones (i.e: osteoporotic bones) subjected to extreme trauma (like a fall)
spiral
-common type of fracture
-ragged break occurs when excessive twisting forces are applied to a bone
-common sports fracture
epiphyseal
-common type of fracture
-epiphysis seperates from diaphysis along the epiphyseal plate
-tends to occur where cartilage cells are dying and calcification of matrix is occuring
depressed
-common type of fracture
-broken bone portion is pressed inward
-ex: skull fracture
greenstick
-common type of fracture
-incomplete break (only one side of shaft breaks, the other side bends)
-common in children (more organic matrix and are more flexible than adults)
bone healing
-hematoma forms --> fibrocarilagenous callus forms --> bony callus forms --> bone remodeling occurs
-osteoblasts bridge gap then osteoclasts remove excess (like sandpaper)
rickets
-childhood bone disease
-causes bowed legs and other bone deformities
-calcium slats not deposited
-caused by vitamin D deficiency or insufficient dietary calcium
dwarfism
-not enough growth hormone secretion
-causes super short people
gigantism
-too much growth hormone secretion
-causes super tall people
rheumatoid arthritis
-inflammation of soft tissue structure in joints
osteoporosis
-loss of bone mass-- bone resorption
-spongy bone of spine and neck of femur become most suseptible to fracture
-risk factors: lack of estrogen (after menopause), calcium or vitamin D, low levels of TSH