Algebra 1 Midterm Review
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
independent variable
input (typically x)
dependent variable
output (typically y)
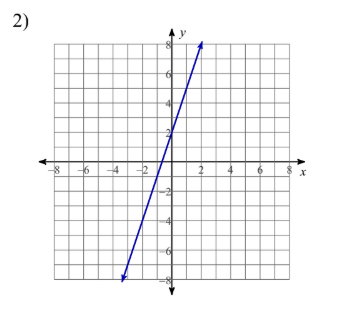
linear function
A function that graphs to a straight line, represented as y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
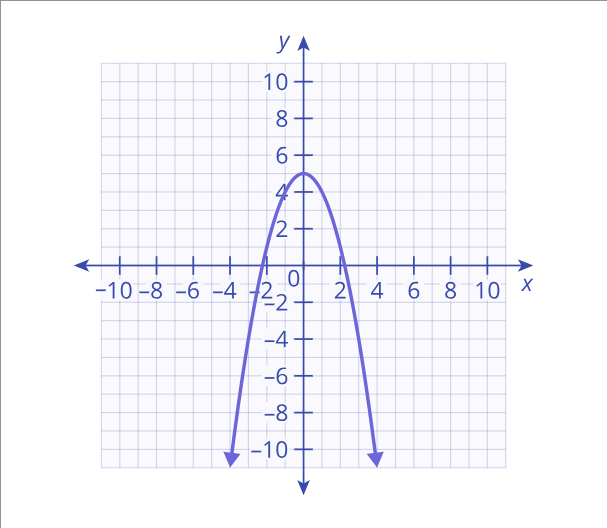
quadratic function
A function that graphs to a parabola, represented as y = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants.
continuous function
A function that has no interruptions or breaks in its graph, meaning it can be drawn without lifting a pencil. It can take any value in a given interval.
slope-intercept form
A way to express a linear function in the format y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b the y-intercept.
standard form of a linear function
A way to express a linear function in the format Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are constants.
m
represents the slope of the line in the slope-intercept form.
b
the y-intercept of a linear function in the slope-intercept form, representing the value of y when x is zero.
discrete function
A function that has specific, distinct values and does not take on all values in an interval. Discrete functions often represent countable data.
increasing function
A function that rises as the input values increase, meaning that for any two points in its domain, if one point has a smaller input, its output is less than or equal to the other.
decreasing function
A function where the value decreases as the input increases, resulting in a downward slope on its graph.
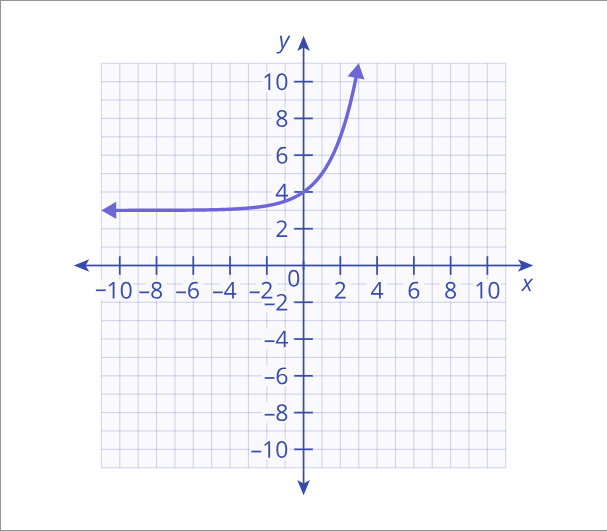
exponential function
A mathematical function of the form f(x) = a * b^x, where a is a constant, b is a positive real number, and x is the variable. Exponential functions are characterized by rapid growth or decay.
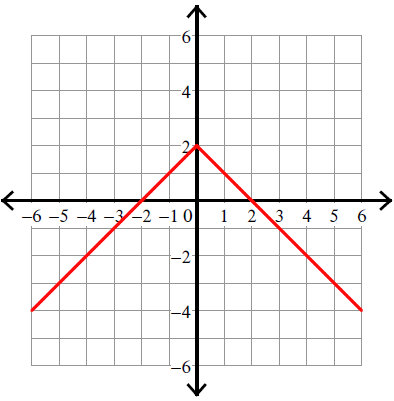
absolute value function
A function that maps any real number to its non-negative magnitude, expressed as f(x) = |x|. The graph forms a V shape, reflecting the positive and negative values around the y-axis.
vertical line test
A method to determine if a curve is a function by checking if any vertical line crosses the graph at more than one point.
transformation
A mathematical operation that alters the position, shape, or size of a graph. Common transformations include translations, reflections, stretches, and compressions.
translation
A transformation that shifts a graph horizontally and/or vertically without changing its shape. It alters the position of the graph in the coordinate plane.
dilation
A transformation that changes the size of a graph while maintaining its shape. It involves scaling the graph by a certain factor.
reflection
A transformation that flips a graph over a specified line, creating a mirror image. Common lines of reflection include the x-axis, y-axis, or any other line on the coordinate plane.
rate of change
A measure of how a quantity changes over time, typically represented as the ratio of the change in the output value to the change in the input value. (i.e. the slope)
arithmetic sequence
A sequence of numbers in which the difference between consecutive terms is constant, typically defined by a starting term and a common difference.
geometric sequence
A sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio.
an = a1 + (n - 1)d
is the formula for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence, where a1 is the first term, n is the term number, and d is the common difference.
an = a1*rn-1
is the formula for the nth term of a geometric sequence, where a1 is the first term and r is the common ratio.
get x by itself
means to isolate the variable x on one side of the equation, making it possible to solve for its value.
A = ½bh
is the formula for the area of a triangle, where b is the length of the base and h is the height.
inequality
is a mathematical statement that shows the relation between two expressions that are not equal, using symbols such as <, >, ≤, or ≥.
closed circle
is used on a number line to indicate that the endpoint is included in the solution set of an inequality. (e.g. ≤ or ≥)
open circle
is a notation used on a number line to indicate that a value is not included in the set, typically representing an inequality that is strict (e.g., < or >).
most import rule of solving inequalities
multiplication or division by a negative number flips the inequality sign.
system of equations
a set of two or more equations with the same variables that are solved together to find a common solution.
solving systems by substitution
a method for solving a system of equations by isolating one variable and substituting it into another equation.
solving systems by graphing
a method for solving a system of equations by plotting the equations on a graph and identifying the point of intersection as the solution.