BSCI330: Protein Shape and Structure
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
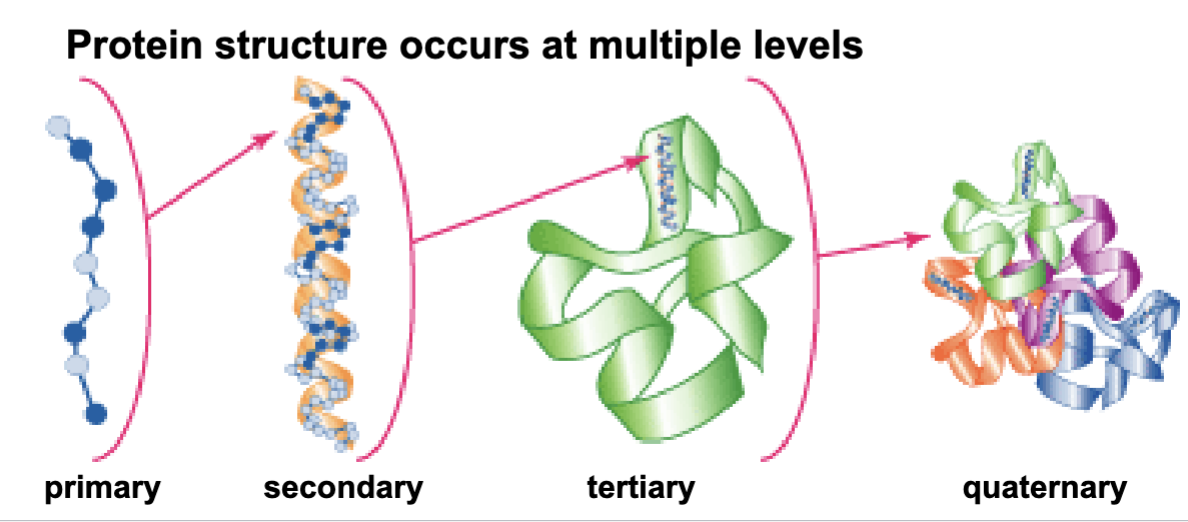
What are the 4 levels of protein structure?
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quartnernary
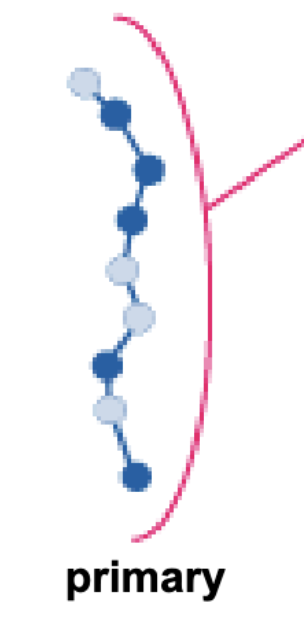
What is the primary structure?
Linear sequence of amino acids!
Determine by mRNA code; in combination with environment can determine higher level structures
Is the amino acid sequence of every protein identical to the genetically encoded primary sequence?
Yes!
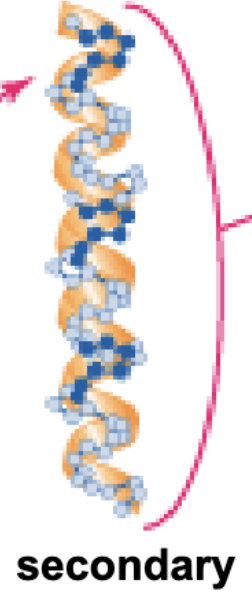
What is the secondary structure?
Folding and twisting of the peptide backbone
Held by H-bonds between carbonyl and amine groups
R-groups stick out from backbone
Alpha helices and beta sheets
What is the alpha helix?
H-bonding that occurs between carbonyl and amino groups that are 4 amino acids apart (spacing for the turn of a helix)!
Coiling in a clockwise direction!
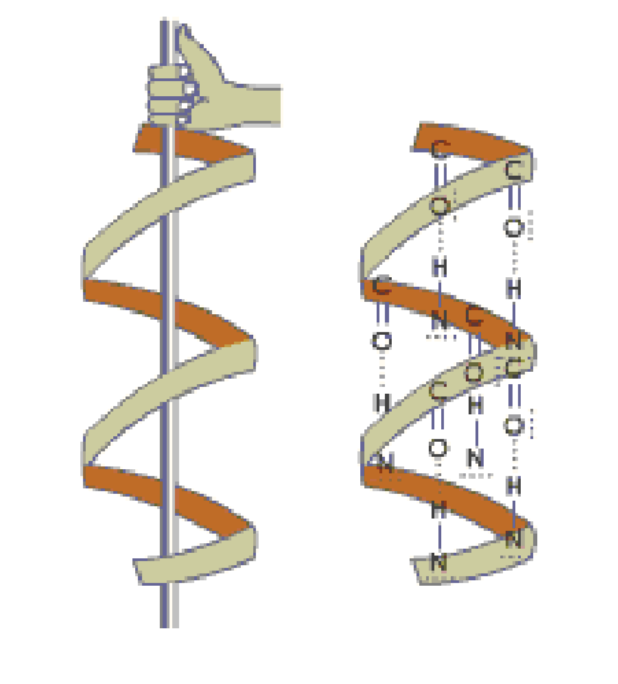
What is the beta sheet?
Pleated sheet like an accordion; H-bonding of carbonyl and amino groups on adjacent polypeptide chains
Can be parallel or anti-parallel!
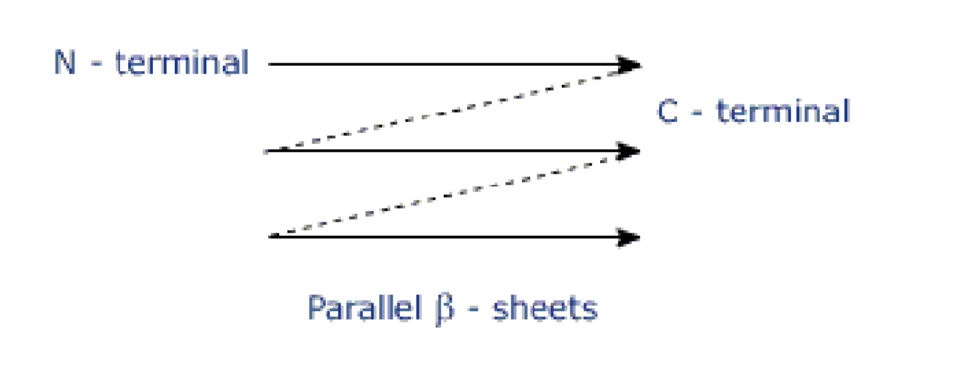
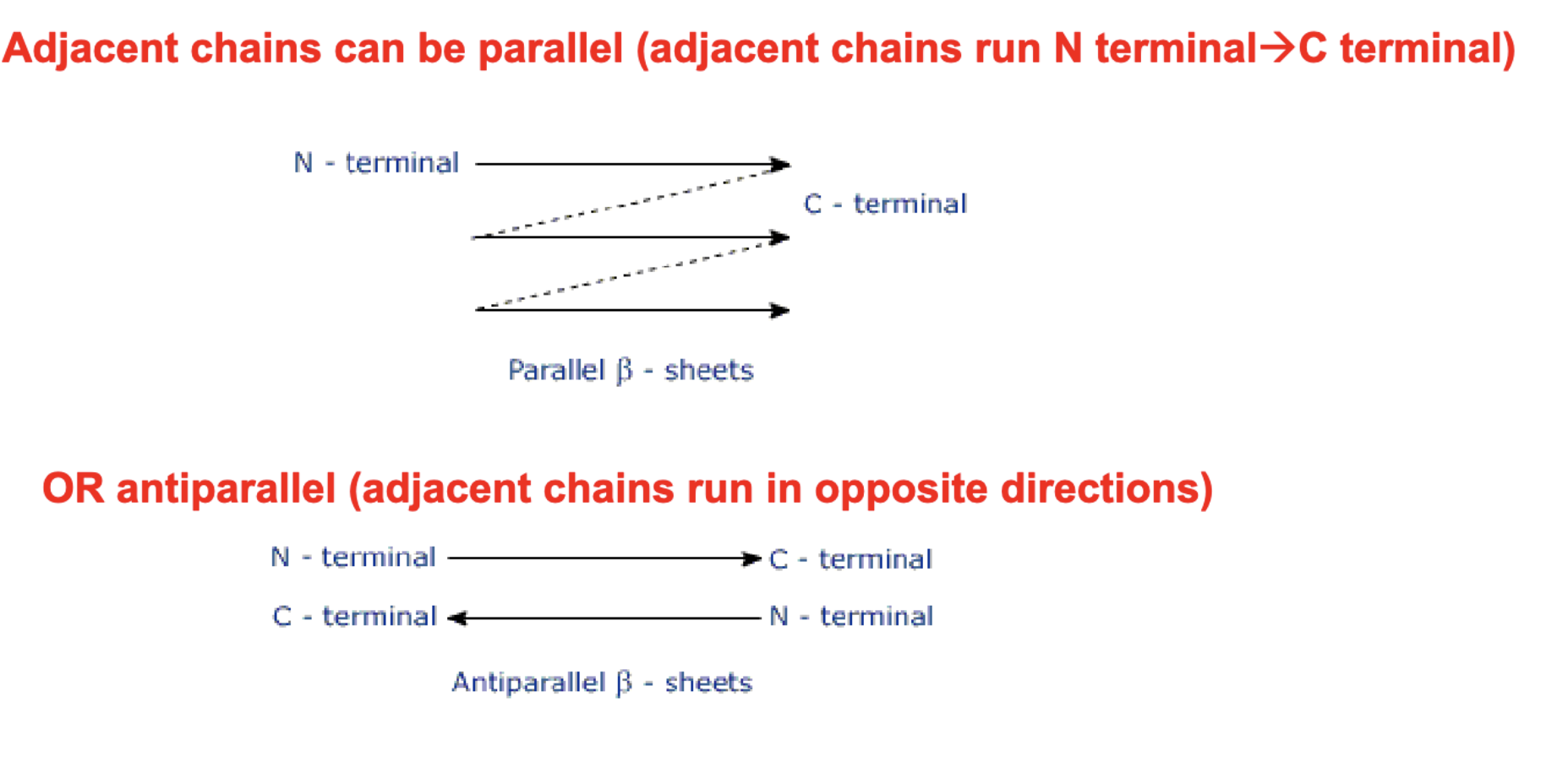
Adjacent parallel v. anti-parallel chains (beta sheets)?
Parallel - Run N-terminal to C-terminal and must loop around
Anti-Parallel - Run N to C and in opposite directions (zig-zag terminals)
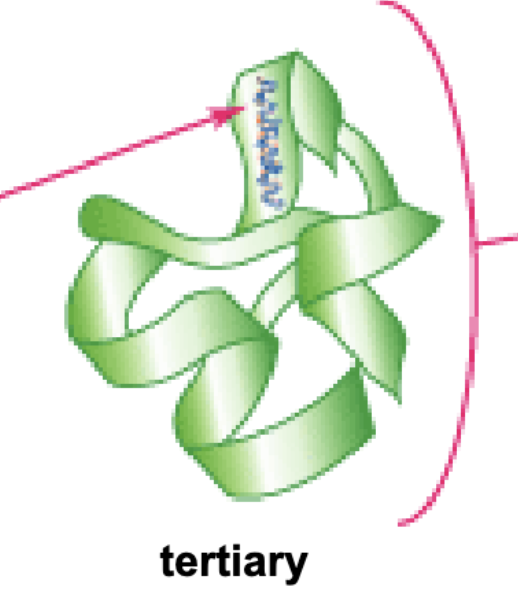
What is the tertiary structure?
Mostly held down by noncovalent attractions between R-groups and surrounding environment.
Unstructured loops (aka random coils) like the secondary structures together!
What do covalent dissulfide bonds do?
They lock tertiary structures by forming between cysteine residues to cross-link parts of the polypeptide backbone.
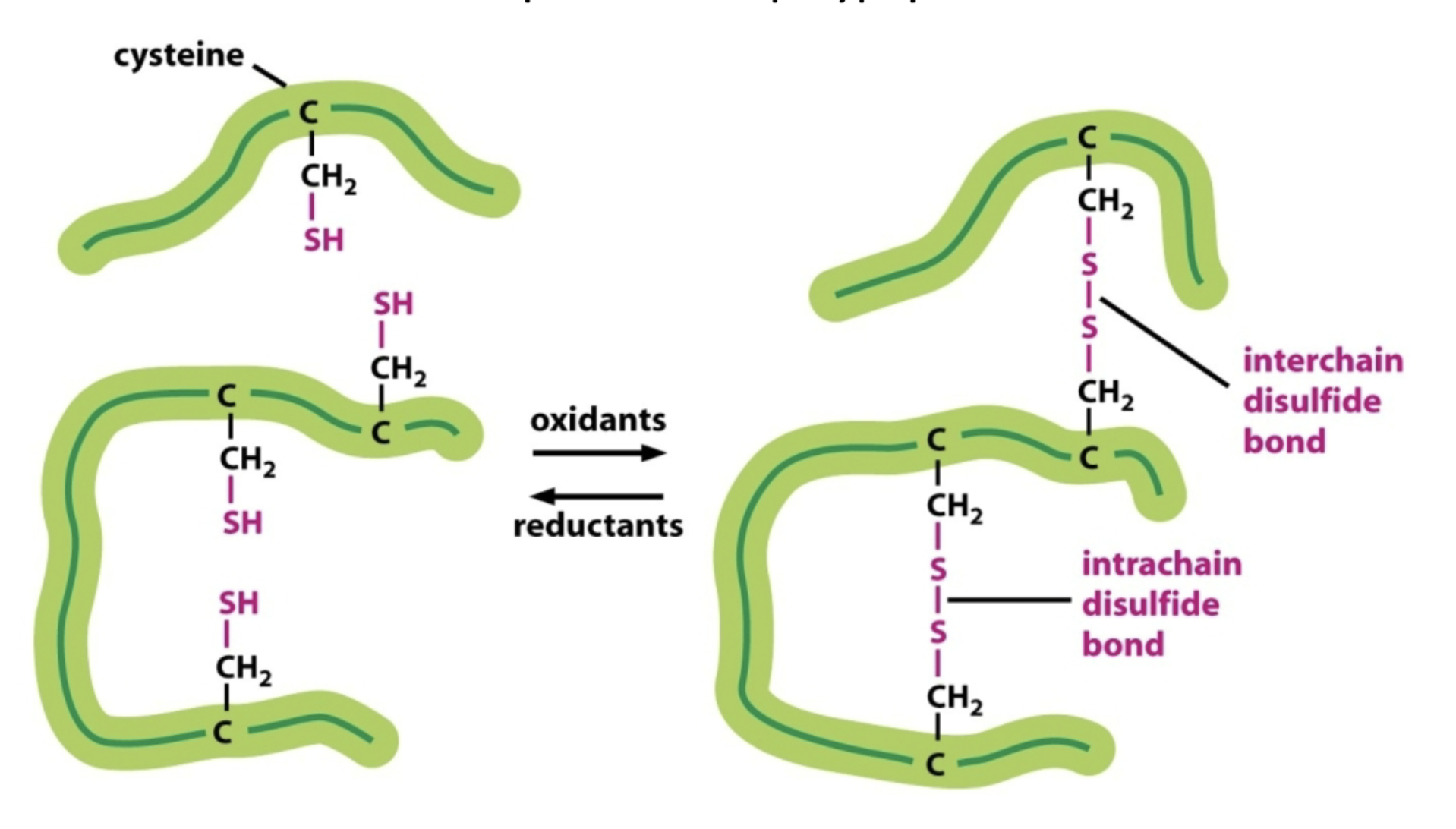
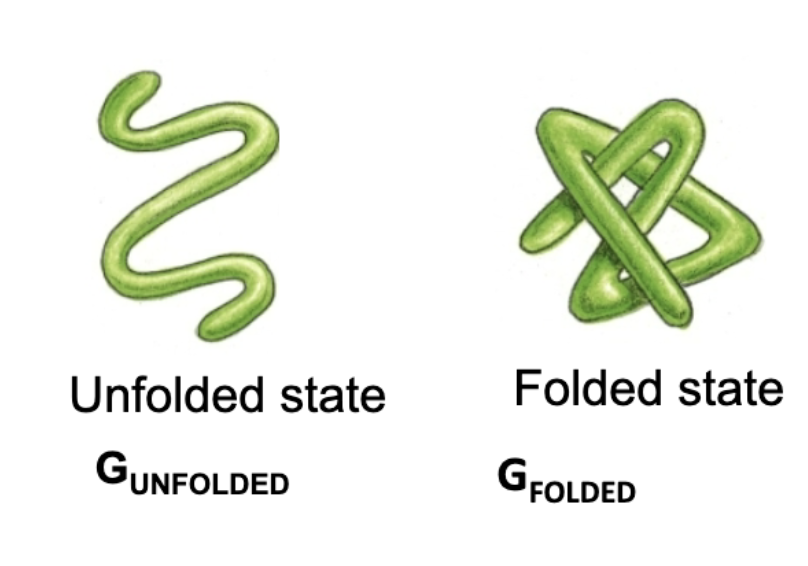
What determines 3D folding of proteins?
They will attempt to assume the lowest possible energy state! Protein stability is determined by the free energy change between folded and unfolded states!
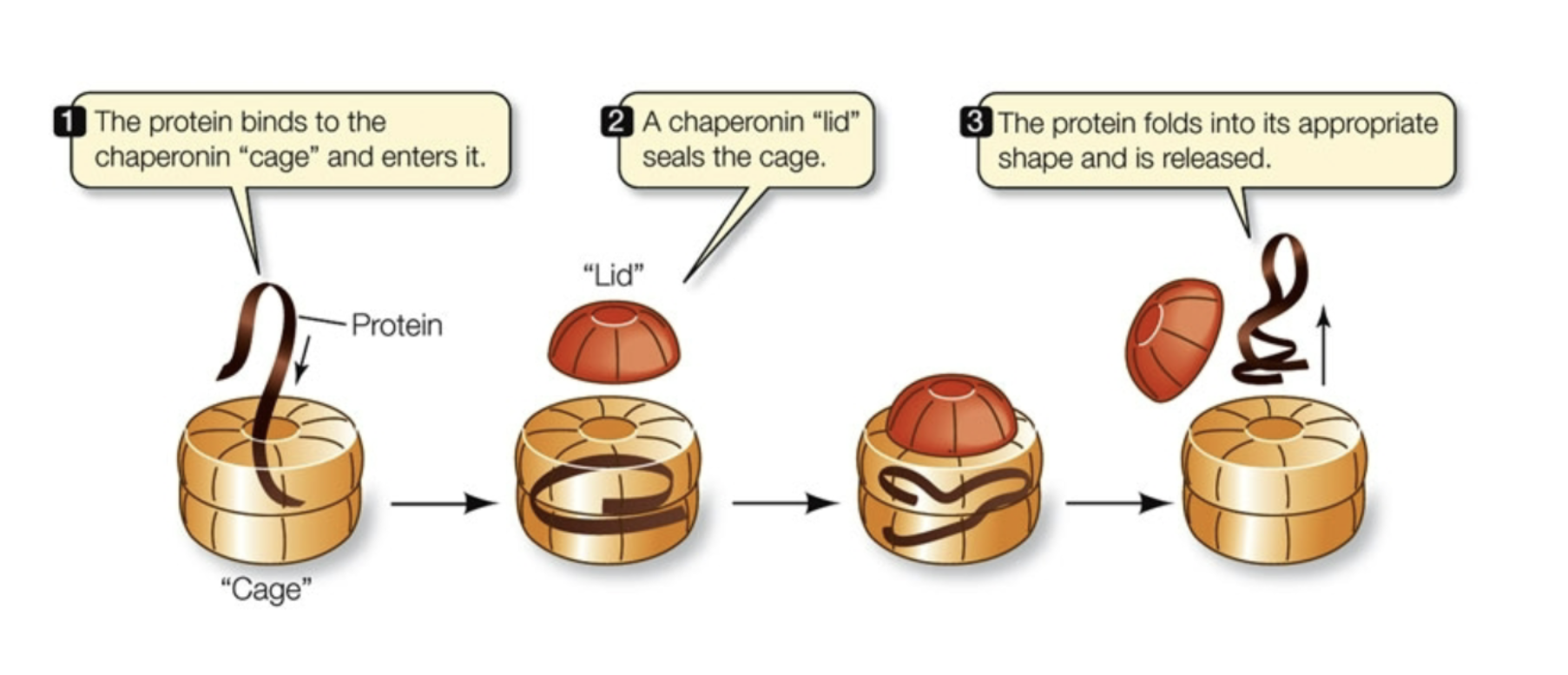
What are molecular chaperones or chaperonins?
Provide an isolated chemical environment in which proteins can fold!
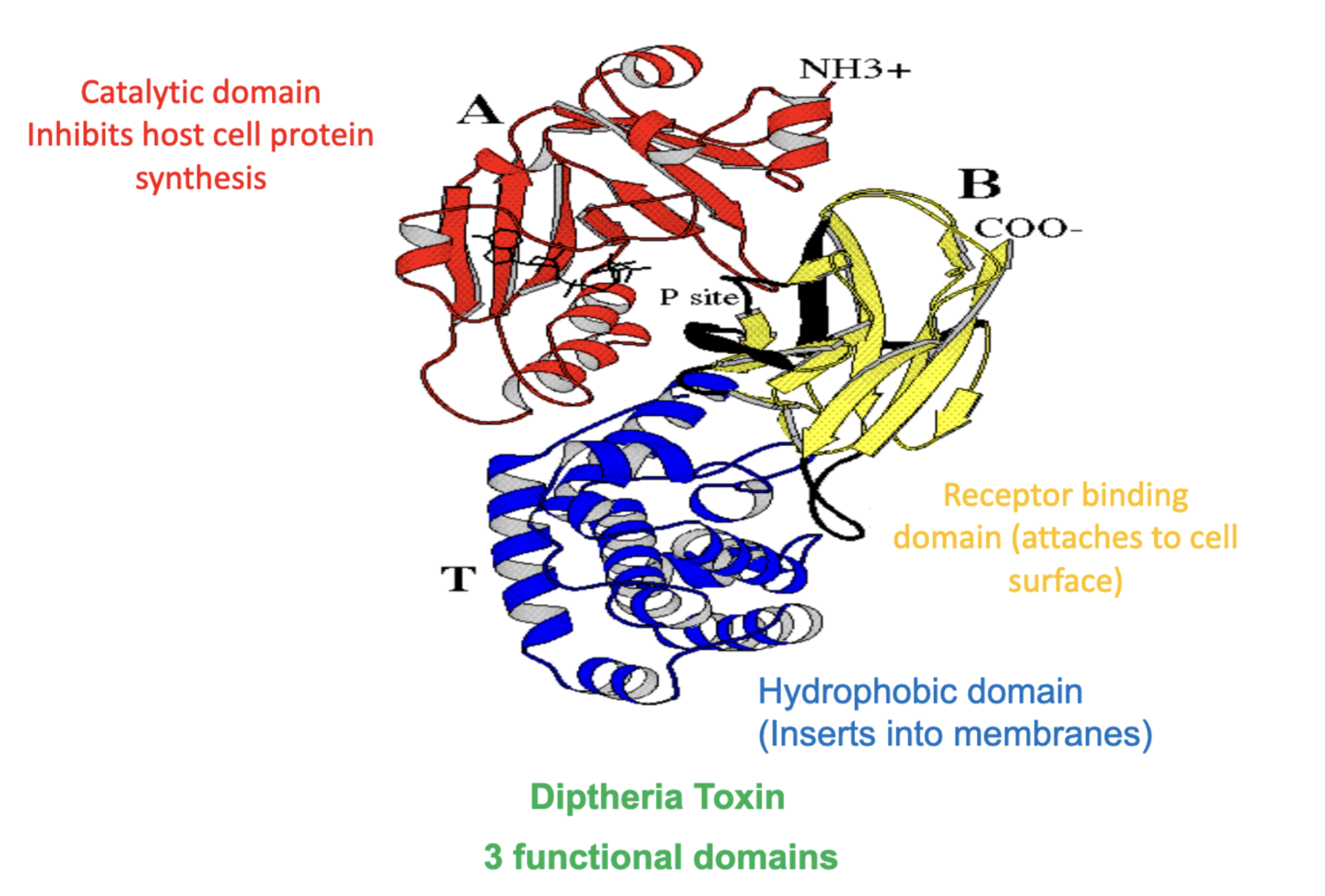
What are protein domains?
A region of the protein that folds independently of other regions! Often represents a fucntional region of the protein!
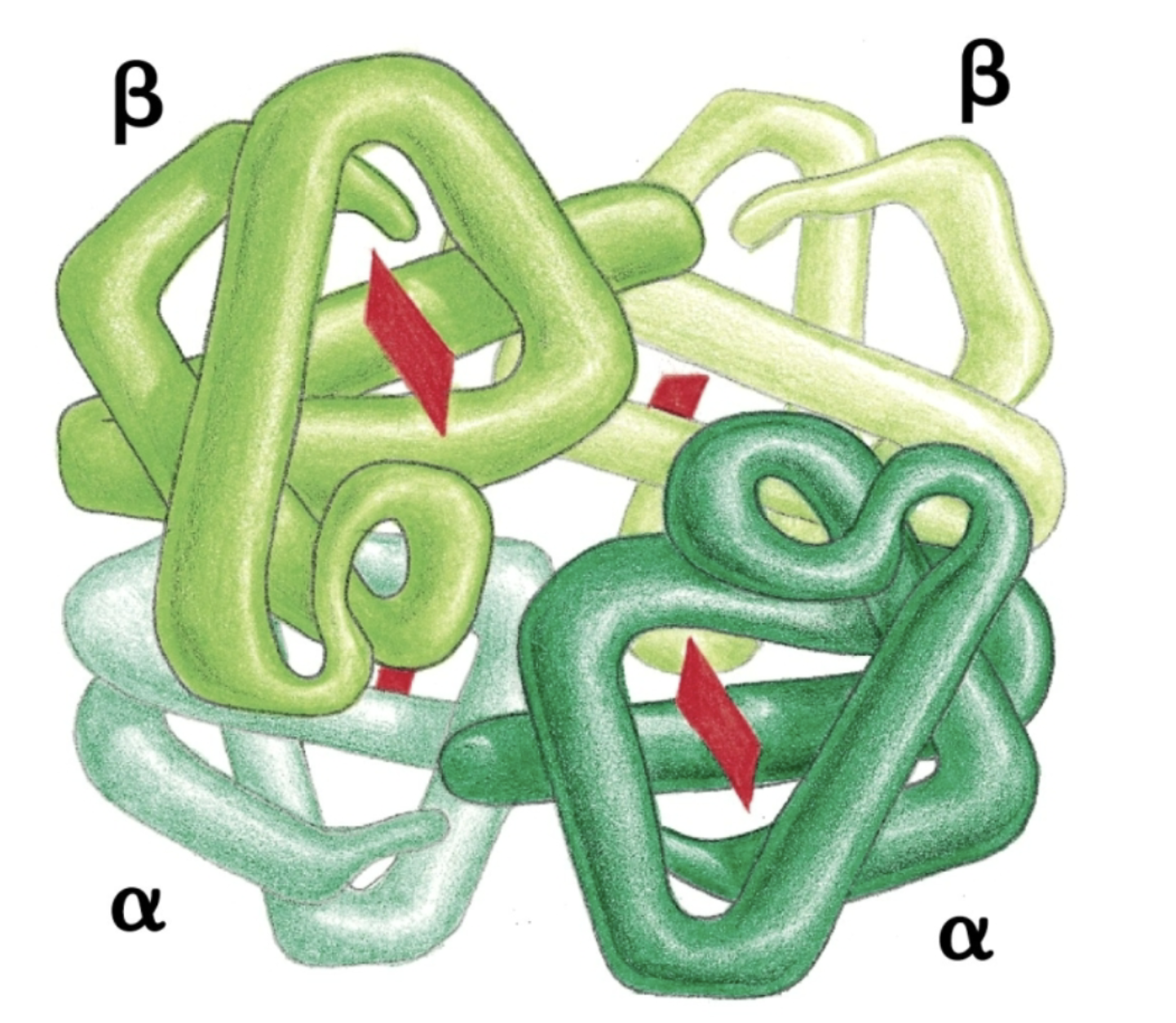
What are quaternary structures?
Arrangement of multiple tertiary stryuctures (weakly bonded, some with disulphide bonds)
What are homomers and heteromers?
Identical (homomers) and different (heteromers) subunit polypeptides!