ib econ- 3.3: macroeconomic objectives
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/macroeconomics/3-3-macroeconomic-objectives
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
what is economic growth?
a sustained increase in a country’s real gdp over time
what is short run growth? how is it different to long term growth?
short term = actual growth in an economy
long term = potential growth in an economy
draw short and long run growth on a ppc
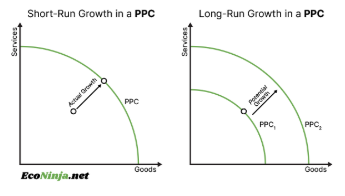
draw short and long run growth on an ad/as diagram
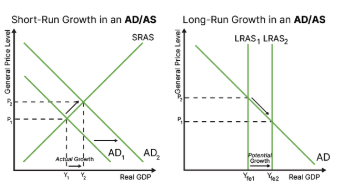
how can we measure economic growth?
comparing gdp/gni values from different times
calculating percentage change: (new gdp - old gdp)/old gdp x100
what are the three areas that economic growth can impact?
living standards
environment
income distribution
what is the consequences of economic growth on living standards?
generally an improvement
decrease poverty levels, increase spending (on merit and demerit goods), increase cost of living, risk higher inflation, and increase investment
what is the impact of economic growth on the environment?
may create negative externalities for the environment
market failure may result in issues such as climate change and overfishing as resources are consumed and produced at higher rates
current consumption of materials on earth is not sustainable in the long run
what is the impact of economic growth on income distribution?
usually creates higher gaps between the wealthy and the poor (in terms of income and wealth)
governments may generate more tax revenue which they can spend on helping the poor
what is employment?
the use of all factors of production in the process of producing a good or service
what is unemployment?
the situation in which people willing and able to work (and are actively seeking it out) are not able to find any
what is the labour force?
the amount of people employed, self-employed and unemployed within an economy
how do you calculate unemployment rate?
(number of unemployed people/labour force) x 100
what are the difficulties in measuring unemployment?
hidden unemployment (discouraged workers): many people give up looking for a job after a few months, and at this point they no longer count towards unemployment figures and become known as discouraged workers.
underemployment: some people, although working, would like to work more but can’t find extra work - this doesn’t count towards unemployment
voluntary unemployment: some people don’t want to work - they don’t count towards the figure
what are the four types of unemployment?
cyclical unemployment
structural unemployment
seasonal unemployment
frictional unemployment
what is cyclical unemployment?
unemployment as a result of a downturn in the business cycle (there is less demand for labour as the economy is in recession so consumption is down).
draw the diagram for cyclical unemployment
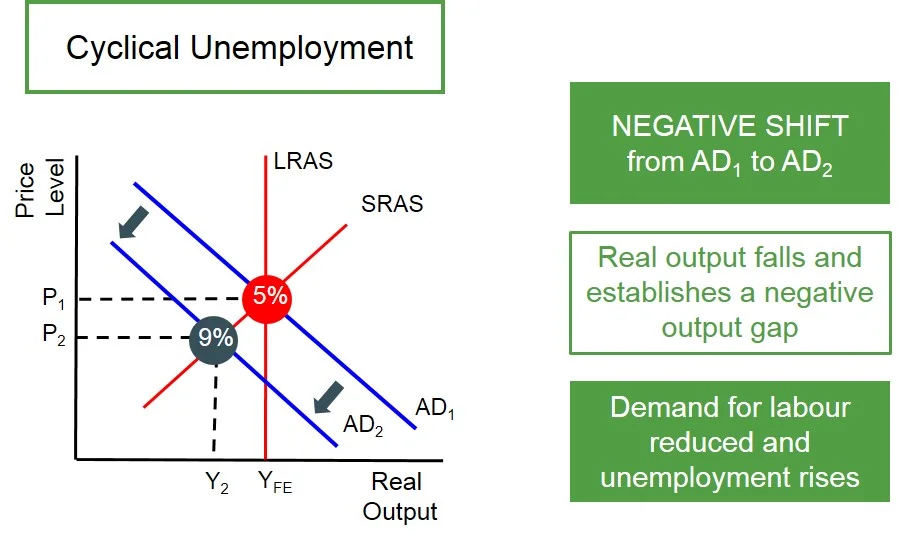
what is structural unemployment?
unemployment as a result of a skill mismatch. it takes time to learn new skills and might involve you having to move.
for example: if you are an expert welder, but all welding jobs are becoming automated and the only jobs available are in programming welding robots, you are structurally unemployed - it will take time to lean how to program welding robots
what is seasonal unemployment?
unemployment caused by seasonal changes in demand. for example, if you work as a ski instructor, you might be seasonally unemployed throughout the summer
what is frictional unemployment?
unemployment as people are transitioning to a new job. there will be a few weeks/months where people are updating their resumes, applying for jobs and attending interviews.
what is the natural rate of unemployment?
the equilibrium rate of unemployment - there will always be structural, seasonal and frictional unemployment in an economy - it is the sum of these.
how does having a minimum wage disturb the natural rate of unemployment?
more people are willing and able to work at the minimum wage than what firms will employ. it acts as a price floor, increasing quantity supplied and decreasing quantity demanded.
what are the costs of unemployment?
personal costs: stress, poverty, breakdown of familial relationships
social costs: crime, indebtedness, social deprivation
economic costs: lower gdp, lower tax revenues, more benefit claimers, more inequality
what is inflation?
the sustained rise in the general price level in an economy over time
what is price stability?
when the general price level remains constant as a result of low and stable inflation
how is inflation measured using the consumer price index (cpi)?
a base year: the price index of goods and services (usually a basket of goods) is set equal to 100 - changes in the price index can be measured by comparing them to the base year
sometimes, goods and services have different weights (as some things are purchased more than others, and inflate at different rates) - when calculating, multiply the price index by the weight before adding everything together
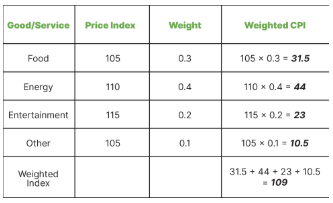
what are the limitations of measuring inflation using cpi?
not all households have the same expenditures, and cpi is an ‘average’
inflation can vary within regions of a country, and cpi only accounts for the general price level
cpi does not measure changes in product quality (i.e. phone prices increasing due to phones getting better)
consumption patterns change over time - so the basket changes, making inflation difficult to calculate over long periods of time and across countries
what are the two types of inflation?
demand pull
cost push
what is demand pull inflation?
inflation caused by higher demand for goods and services within an economy, which grows faster than supply can adapt to
considered “benign” inflation, because while general price level rises, real gdp usually does too
draw the diagram for demand pull inflation
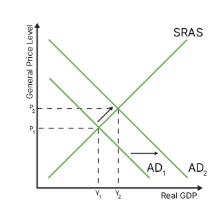
what is cost push inflation?
inflation caused by higher costs of production (supply side shocks such as natural disaster or war), shifting aggregate supply to the left
considered “malign” inflation, because general price levels rise and real gdp shrinks
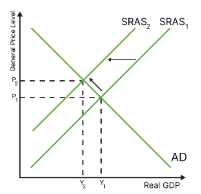
what are the costs of high inflation?
uncertainty: lower confidence in the economy (bear markets), leading to less consumption and investment
redistributive effects and effects on saving: worse for the poorest people who already struggle, also bad for savers as their savings are worse less - but good for borrowers as the money they owe is now worth less.
damage to export competitiveness: exporting goods and services becomes more expensive, and imports become cheaper (so net exports decrease)
impact on economic growth: workers are likely to want raises, increasing costs of production and decreasing as (stagflation)
inefficient resource allocation: having to update prices and look for cheaper alternatives of goods and services takes time, leading to inefficiencies
what is deflation?
the sustained fall in the general price level in an economy over time
what is benign deflation?
occurs when as shifts to the right. this is good because prices go down and real gdp increases
draw the diagram for benign deflation
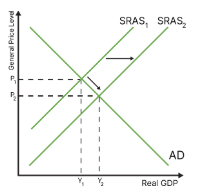
what is malign deflation?
occurs when ad shifts to the left, this is bad because both prices and real gdp go down
draw the diagram for malign deflation
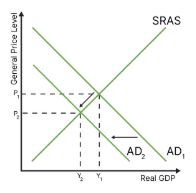
how is disinflation different to deflation?
whilst deflation is a decrease in the general price level, disinflation is a decrease in the rate of inflation (i.e. down to 5% from 10%)
what are the costs of deflation?
uncertainty: confidence levels decrease (bear market) reducing the levels of consumption and investment in an economy
redistributive effects: savers do well as their money increases in value, borrowers lose out as what they have to pay back is worth more, and lenders will win as the money they get from borrowers is worth more
deferred consumption: if things start to cost less, people will wait before they buy things, as they expect prices to continue to decline - this creates a deflationary spiral
high levels of cyclical unemployment and bankruptcies: malign deflation causes unemployment, and also bankruptcies as fewer people are consuming firms goods and services
increase in the real value of debt
inefficient resource allocation: usually due to unemployment
policy ineffectiveness
what is the conflict between low unemployment and high inflation?
when there is low unemployment, households have more money to spend, increasing aggregate demand
this may then lead to wage inflation as workers realise that their labour is scarce, using this power to lobby for higher wages - this increases firms costs of production, which could then decrease aggregate supply and cause malign inflation
what is the conflict between high economic growth and low inflation?
as the economy grows, the amount of spare capacity diminishes and costs of production increase, this increases the general price level and causes inflation.
what is the conflict between high economic growth and environmental sustainability?
increased levels of production and consumption may cause negative externalities such as pollution
what is the conflict between economic growth and equity in income distribution?
economic growth often creates a larger gap between the rich and the poor