Diffusion: simple and facilitated diffusion
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of solute particles within a gas or a liquid from a region of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
The particles keep moving until they are evenly dispersed
The difference in the concentration of the particles between the 2 areas is called a concentration gradient
The particles move down the concentration gradient, therefore don’t require any energy to move other than the kinetic energy they all ready have
Diffusion is a passive process
Fick’s Law
Rate of diffusion = (surface area x concentration difference) / Length of diffusion pathway
Plasma membranes
Permeability is affected by the polarity of molecules
Hydrophobic molecules (phospholipid tails) have an equal distribution of electrons in their molecules and therefore have no polarity
Non-polar substances that are lipid soluble can easily diffuse through the bilayer (O2 and CO2)
Hydrophilic molecules (proteins) have an unequal distribution of electrons which makes one part of them slightly negative and one part slightly positive
Facilitated diffusion
Polar substances (certain ions) and large molecules (glucose) can’t pass through the lipid bilayer
Instead they travel through polar molecules, proteins
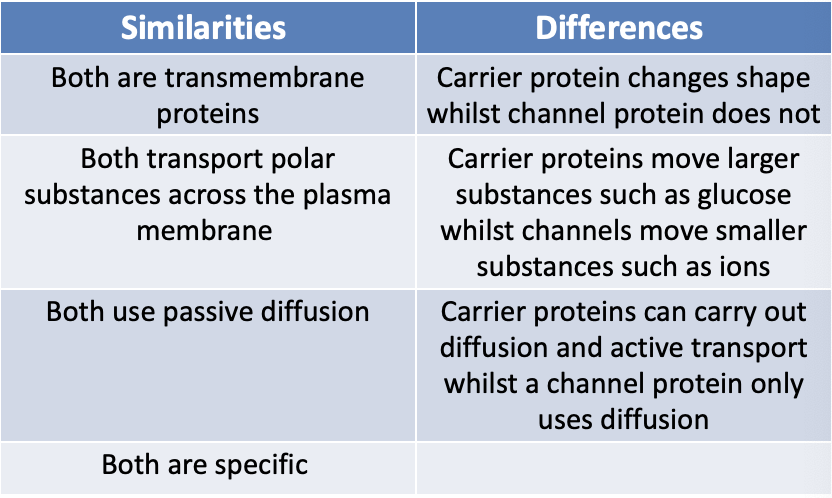
Channel Proteins: ions
Carrier Proteins: glucose
Diffusion of substances through these proteins is called facilitated diffusion
Channel Proteins
Hydrophilic channels that act as pores that allow substances to move from a high concentration to a low concentration
They allow water soluble ions such as Na+, K+, Ca+ to pass through
The protein doesn’t bind to the ions but simply allows them to pass through
They’re very selective
Gated Channels
Some channel pores are grated, which means that they can open and close
This is important to the function of the cell
E.g. nerve cells contain Na gated channels. When they’re open, Na+ enter the cell and cause the propagation of a nerve impulse. When the gates are closed the impulse stops. Constant propagation of impulses would result in permanently contacted muscles
Carrier Proteins
They’re specific (i.e. they only take in certain substances that are too large to pass through the bilayer)
As soon as diffusing molecules arrives at one side of the carrier protein a change in its shape takes place and the diffusing molecule ends up on the other side of the membrane where it’s released
The molecules are travelling down a concentration gradient and so the process is passive
Carrier proteins can also be used in active transport
Compare and Contrast Carrier Proteins and Channel Proteins