Oral Path Exam 1
1/404
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
405 Terms
Neoplasm
New growth
The definitions of tumor and neoplasm are _____________
interchangable
T/F:
All cancers are neoplasms, but not all neoplasms are cancer?
True
3 multiple choice options
The suffix "oma" usually refers to..
Benign lesions
Benign lesions typically _____ the nearby structures
push
The suffix "caricnoma" or "sarcoma" usually refers to...
Malignant lesions
A failure of an extraction site to properly heal could be an indication of what?
A malignant lesion
What is the #1 route of tumor metastasis?
Lymphatic spread
What are the 3 routes of tumor metastasis?
Lymphatic spread
Hematologic spread
Seeding within body cavities
If the lesion can be seen radiographically and appears corticated, this is typically a ______ lesion
benign
Smooth root resorption and displacement of structures radiographically is indicative of a ______ lesion
benign
Spiky root resorption and a sunburst appearance are indicative of a _______ lesion
Malignant
What locations are salivary glands not present?
-Gingiva
-Attached alveolar mucosa
-Mid Palatine raphe
- Dorsum tongue anterior to CV papillae
What is the most common salivary tumor?
(video lecture question)
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Salivary gland aplasia
A rare condition where there is lost or missing of a salivary tissue, typically the gland fails to develop
Can occur in more than 1 gland
Sialorrhea
Excess salivation
Sialadenitis
Inflammation of the salivary gland
Sialadenosis
Non-inflammatory salivary gland enlargement
Xerostomia
Dry Mouth
What can cause Sialadenitis?
Infections
Recent surgery
Dehydration
Debilitation
Medication
Which endocrine disorders can cause Sialadenosis?
Diabetes
Acromegaly
Hypothyroidism
What nutritional conditions can cause sialadenosis?
Malnutrition
Alcoholism
Anorexia
Bulimia
What can cause xerostomia?
Local factors
Systemic factors
Iatrogenic factors
Water/Metabolite loss
Developmental
What causes a mucocele?
Damage or the severing of a saliva gland duct
*NOT a true cyst
What is one of the most common oral soft tissue enlargements?
Mucocele
These clinical characteristics indicate what oral pathology?
Fluctuant & fluid filled
Dome shaped mucosal swelling
Fluctuates in size
Bluish
Non-blanching
Mucocele
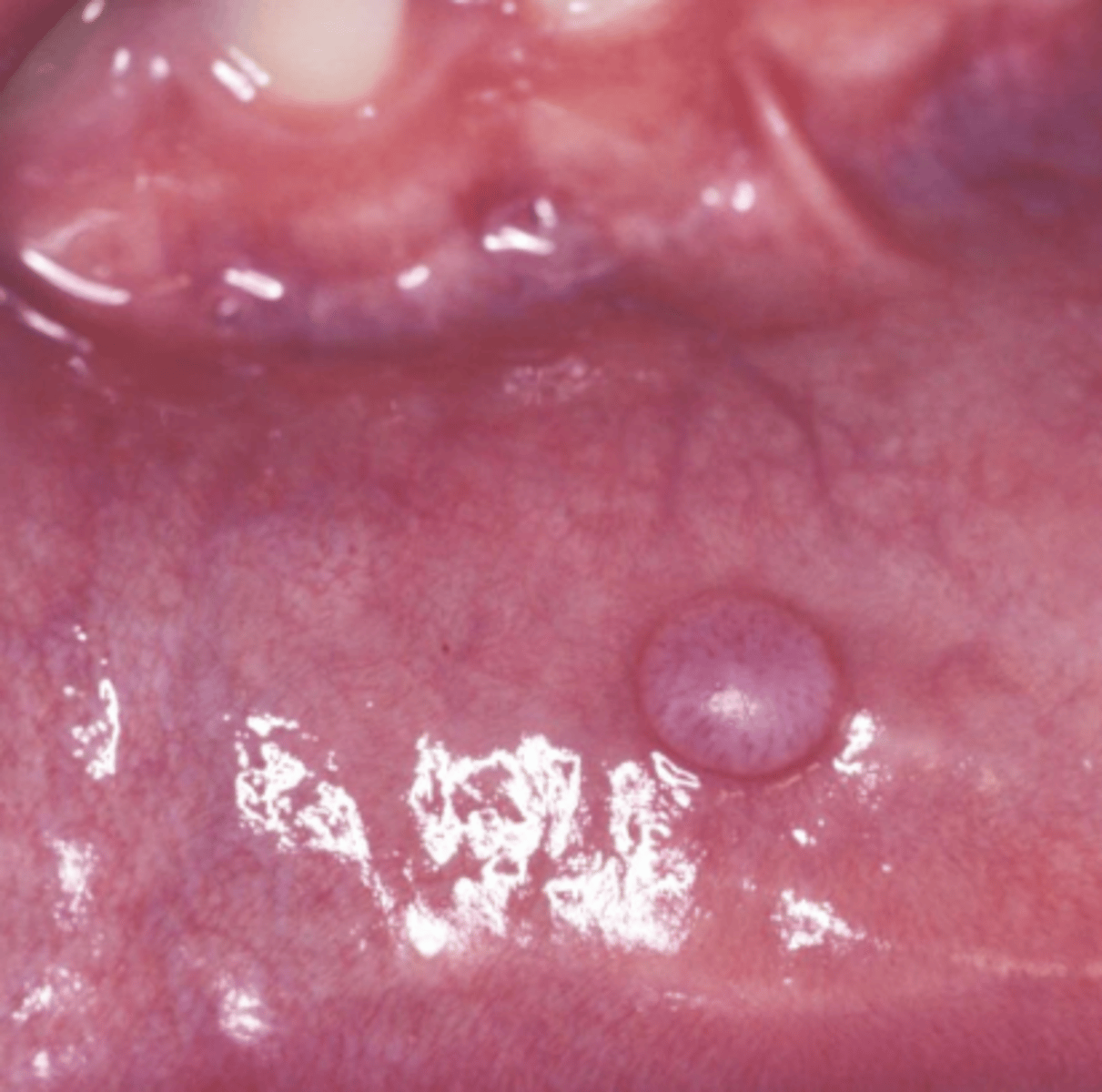
Where is a mucocele most commonly found?
Lower lip
Mucoceles typically only arise in _____ salivary glands
minor
Mucocele
These histology characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
-Granulation tissue
-Spilled mucin
-inflamed salivary gland tissue
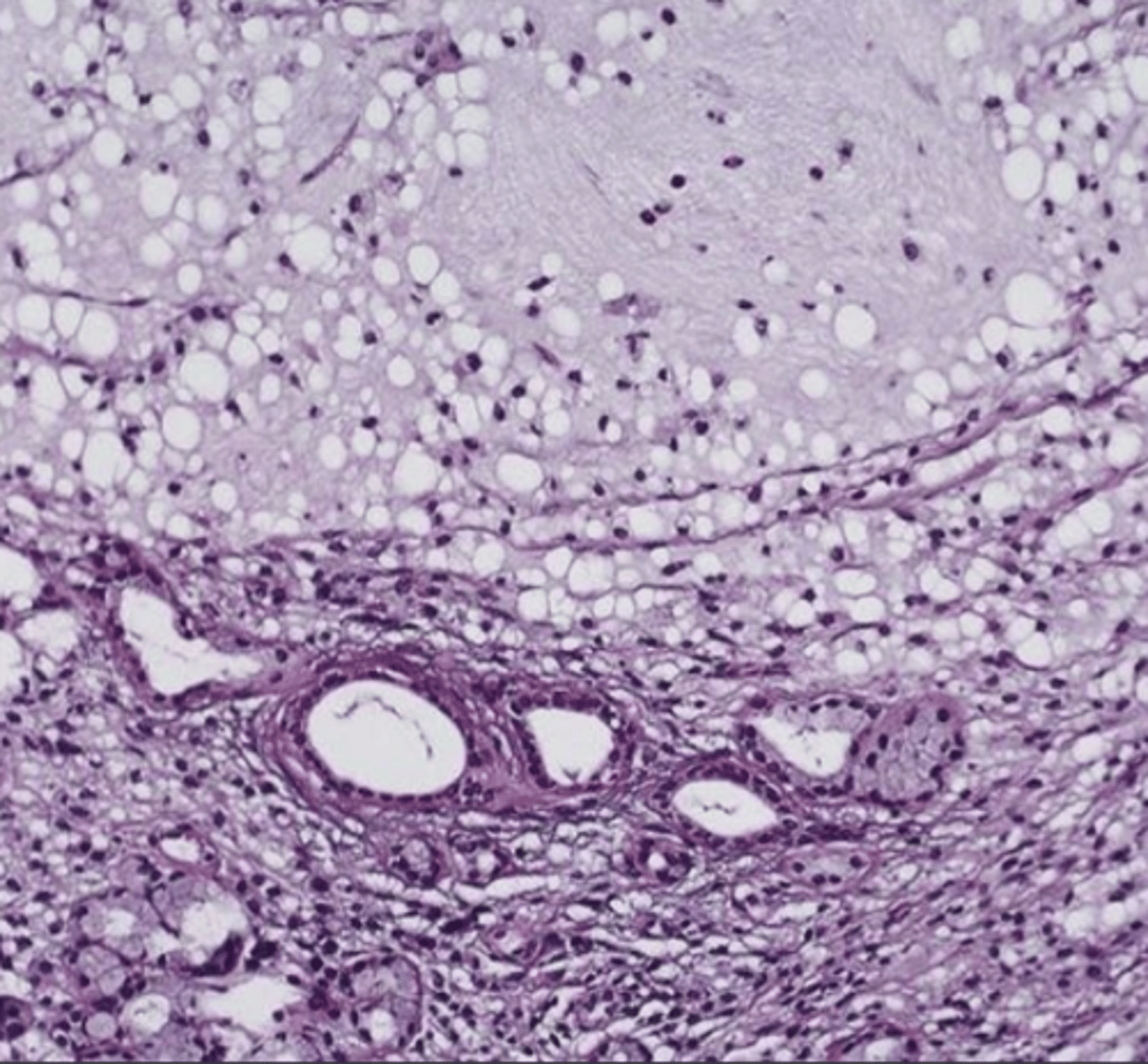
What oral pathology can mimic mucoceles in appearance?
Salivary Duct Cyst
*This is a true cyst
What sites can salivary duct cysts occur?
Major and minor salivary glands
What is the treatment for mucoceles?
Local surgical excision
Removable of adjacent salivary gland tissue to prevent recurrence
What is the most common site for Ranulas to develop?
Floor of the mouth
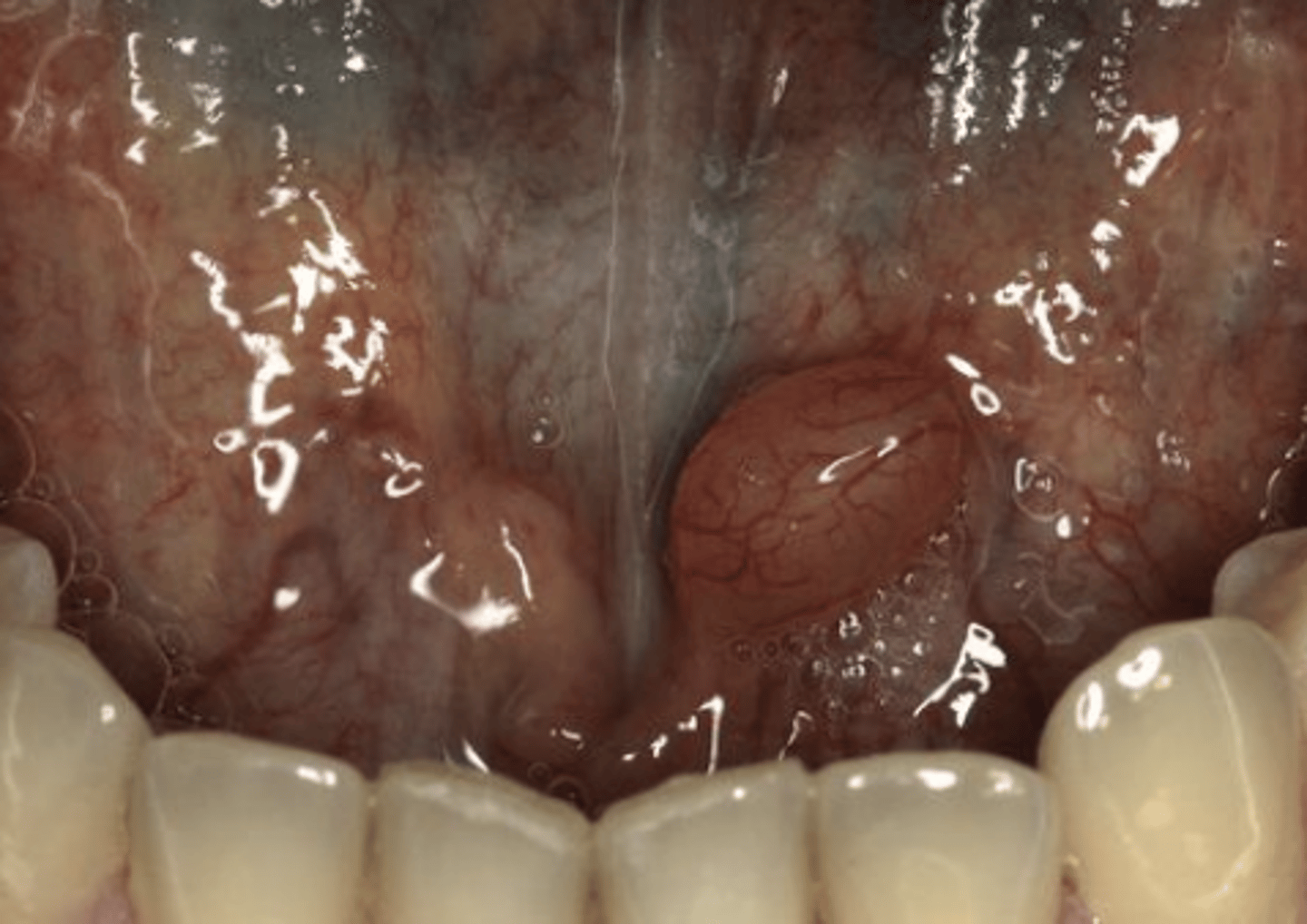
Ranulas involve what salivary gland?
Sublingual*
Can be submandibular too
What oral pathology is considered the "less common type of mucocele?"
Ranula
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
-Blue, dome-shaped mass
-May fill the floor of the mouth and elevate tongue
Lateral to midline
Ranula
What is it called when this oral pathology can dissect through the mylohyoid and cause swelling into the neck?
Plunging ranula
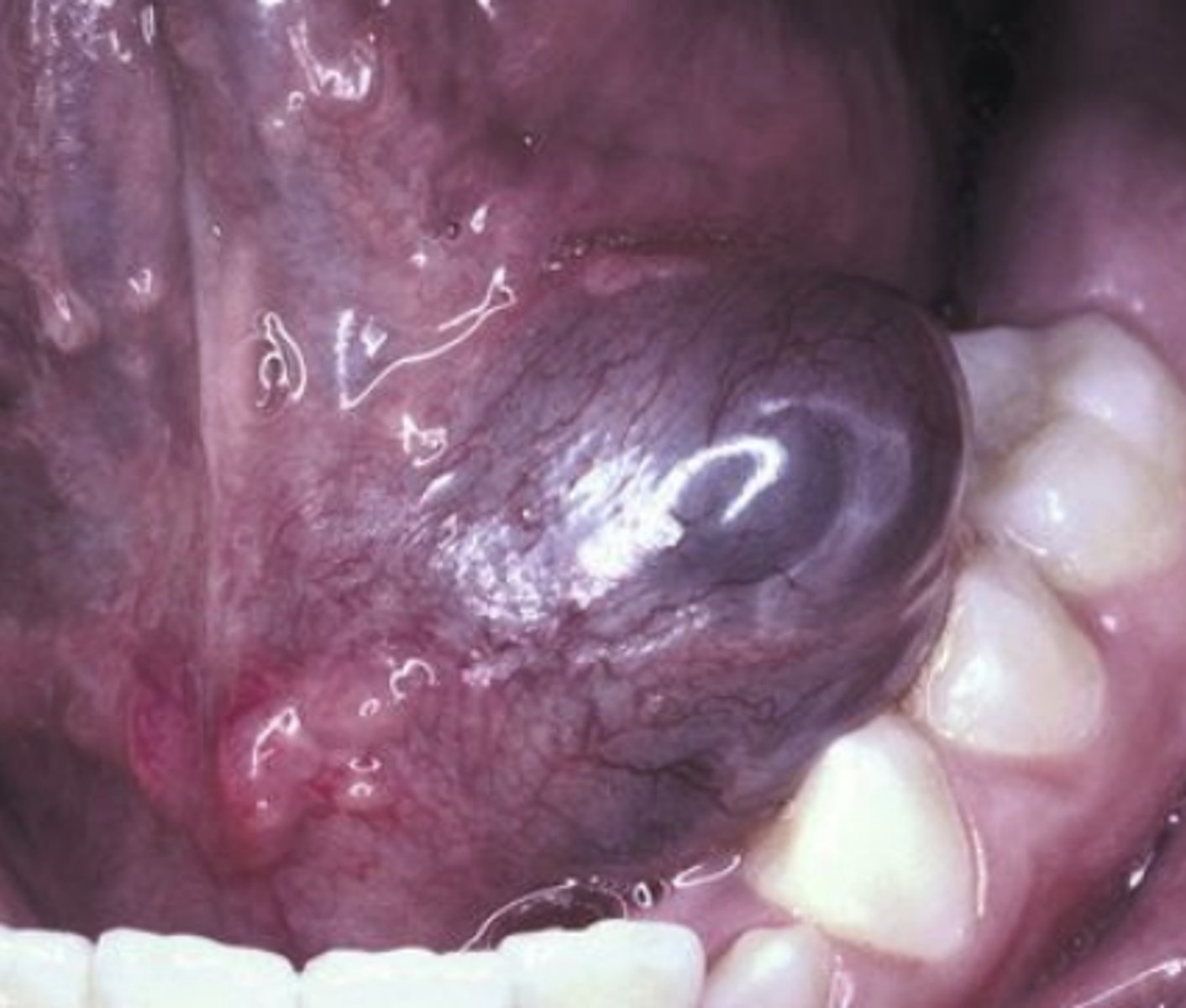
What is the treatment for a ranula?
Removal of feeder gland
Marsupialization for smaller lesions
Sialolith (Sialolithiasis)
Deposits of calcium salts in the salivary gland/duct
Decreased salivary
What can cause a Sialolith?
A decrease in salivary flow or increased viscosity of saliva
What is the least common site for a mucocele?
(video lecture question)
Upper lip
What gland is the most common location for sialoliths?
Submandibular gland/duct
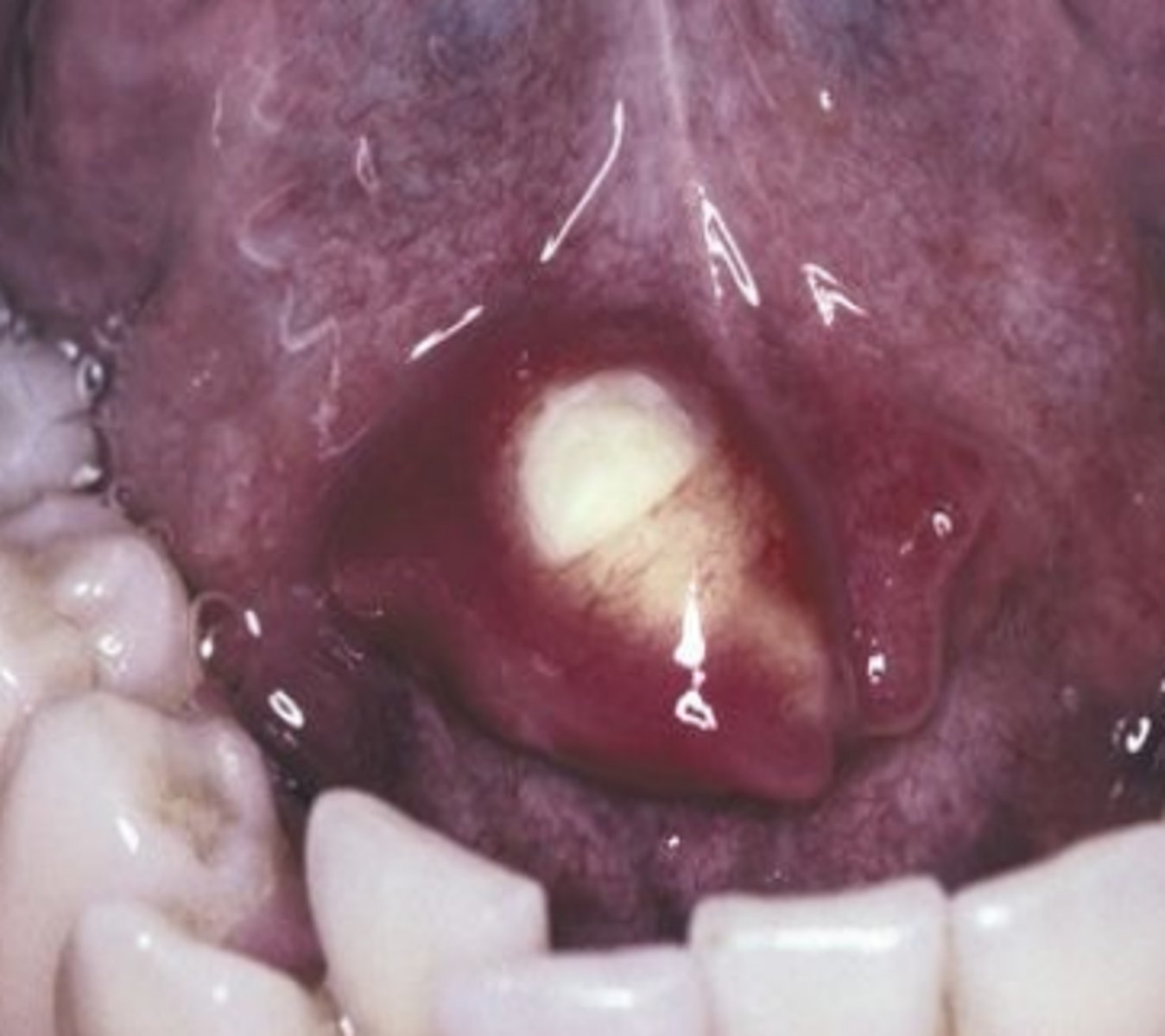
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Pain & swelling of affected gland usually with mealtime
Pus may be extruded from the gland
*Radiographic appearance is a round radiopaque mass
Sialolith
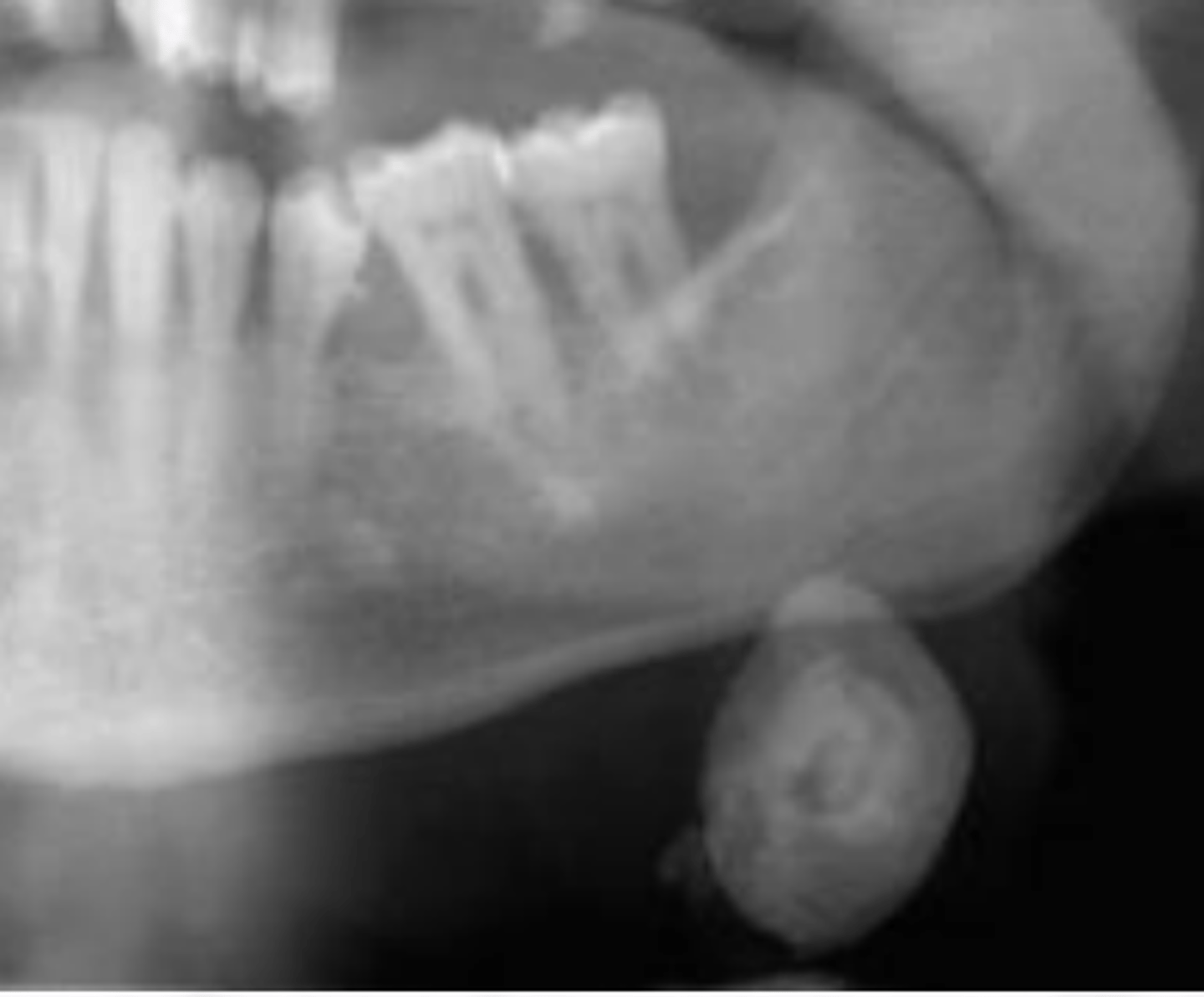
Sialolith
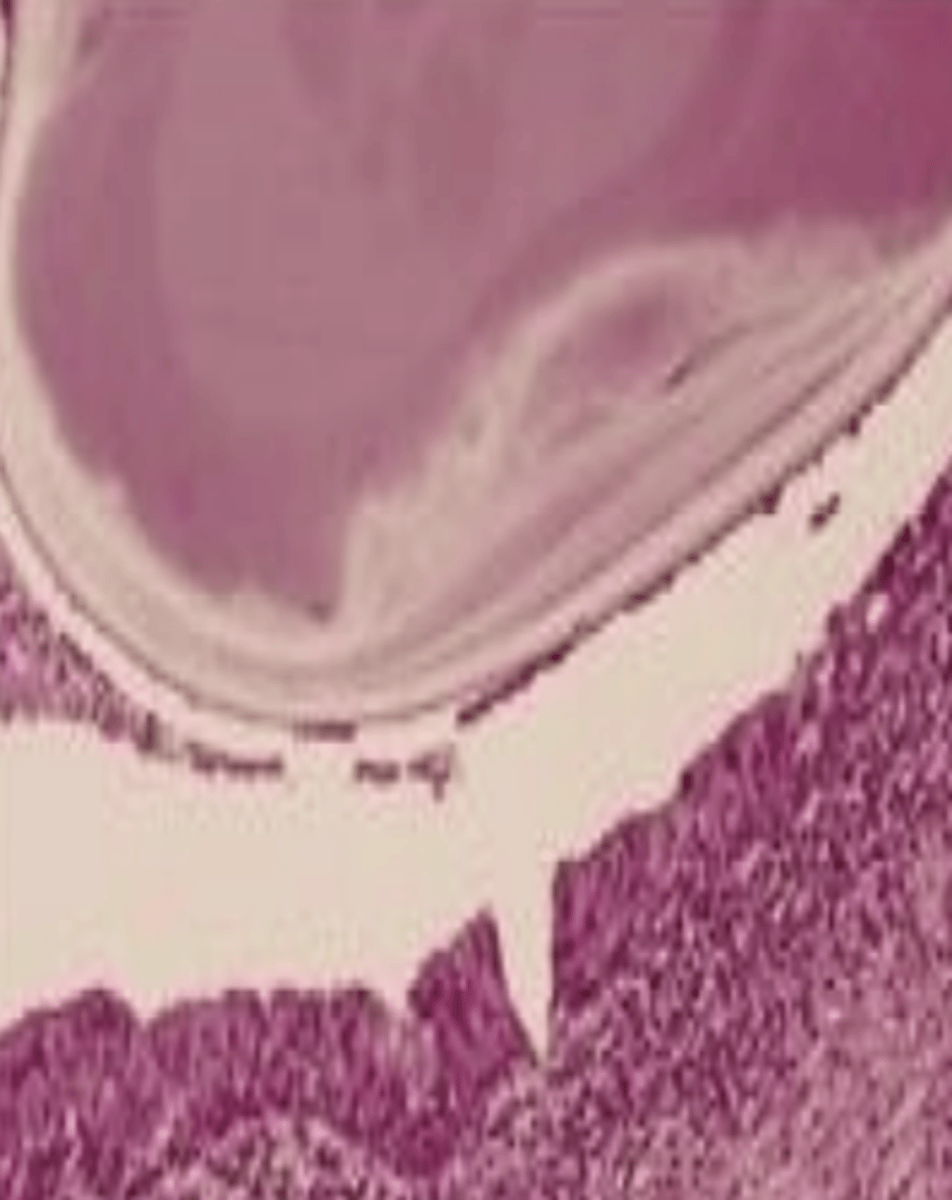
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
calcified mass surrounded by inflamed and fibrotic salivary glands
What is the treatment for sialoliths?
Gentle massage
sialogogues to increase flow
Increased fluid intake
Lithotripsy
*May need to remove gland
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Ischemia of salivary glands of hard palate
Often bilateral & symmetrical
*Can mimic squamous cell carcinoma
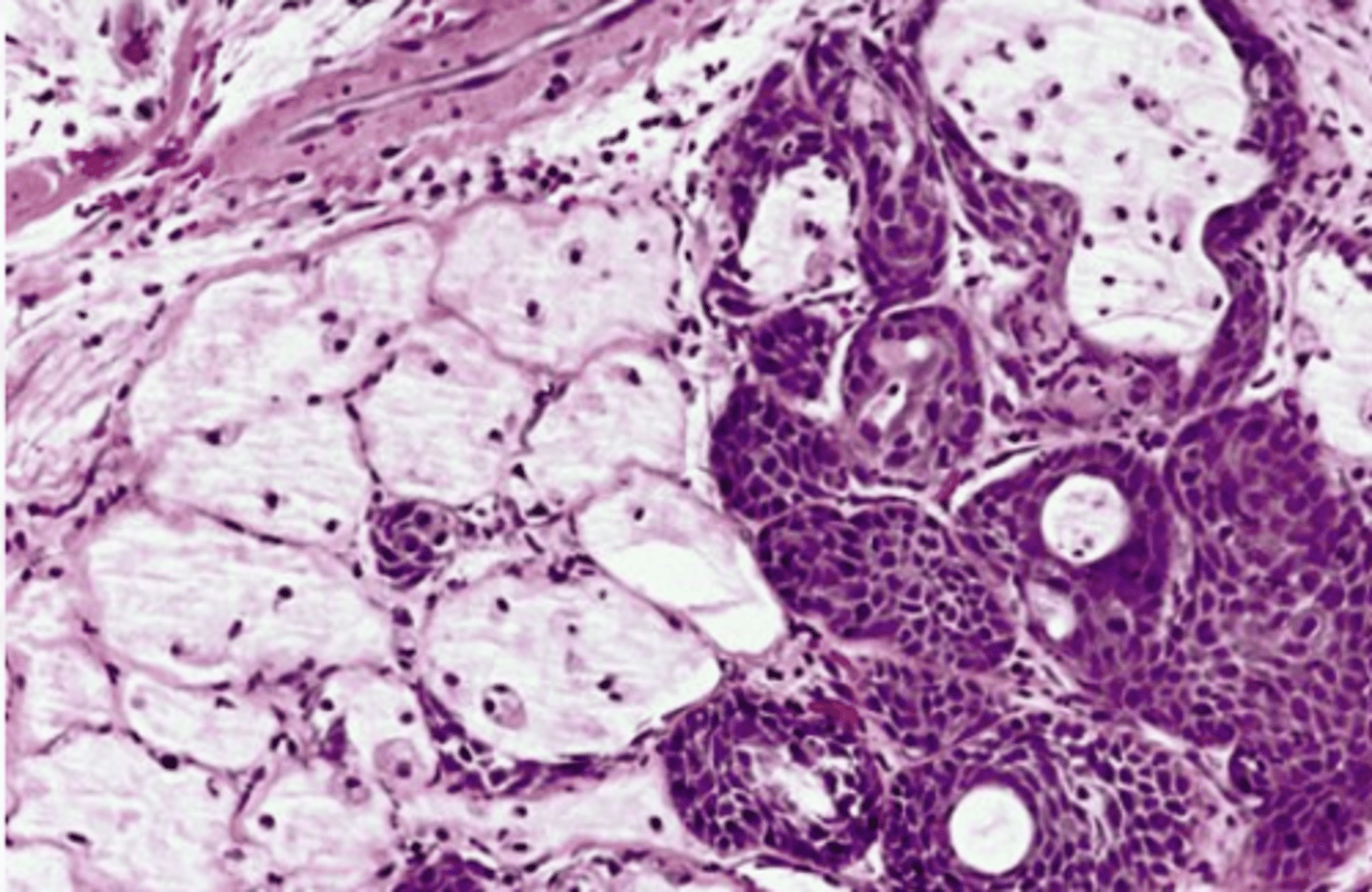
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
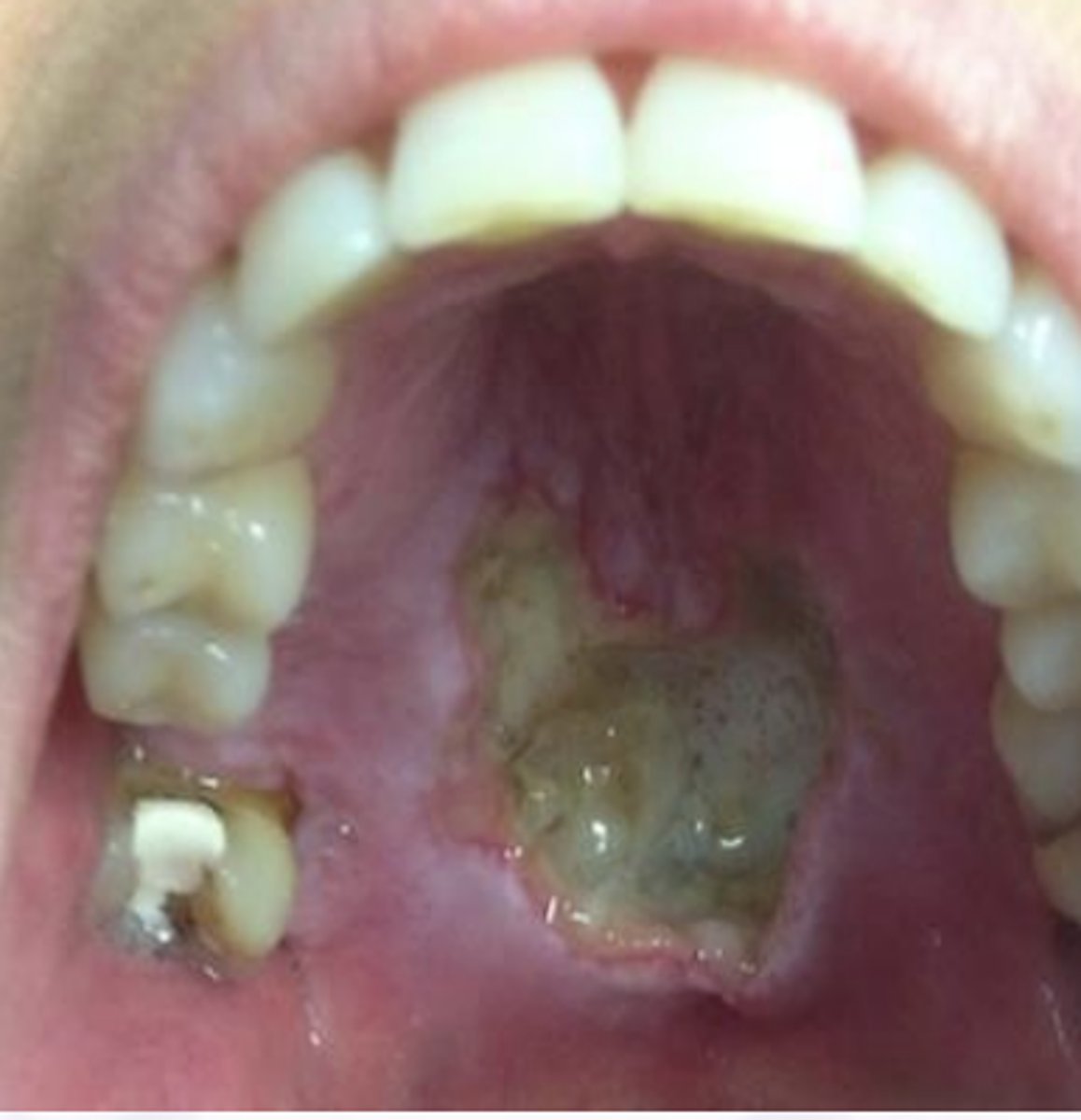
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
-Pseudoepitheliomatous Hyperplasia
-Sialometaplasia
-Coagulative necrosis of the adjacent glands
What is Sjogren syndrome (SS)?
Autoimmune disease
Enlargement of salivary glands
What are the classic signs of primary Sjogren syndrome?
Dry mouth + Dry eyes
What are the classic signs of secondary Sjogren syndrome?
Dry mouth + Dry Eyes + Some other autoimmune disorder (RA, SLE)
What are the symptoms of Sjogrens Syndrome?
Xerostomia, pain, burning
Erythematous tissues
Increased caries
Increased perio
Increased candidiasis
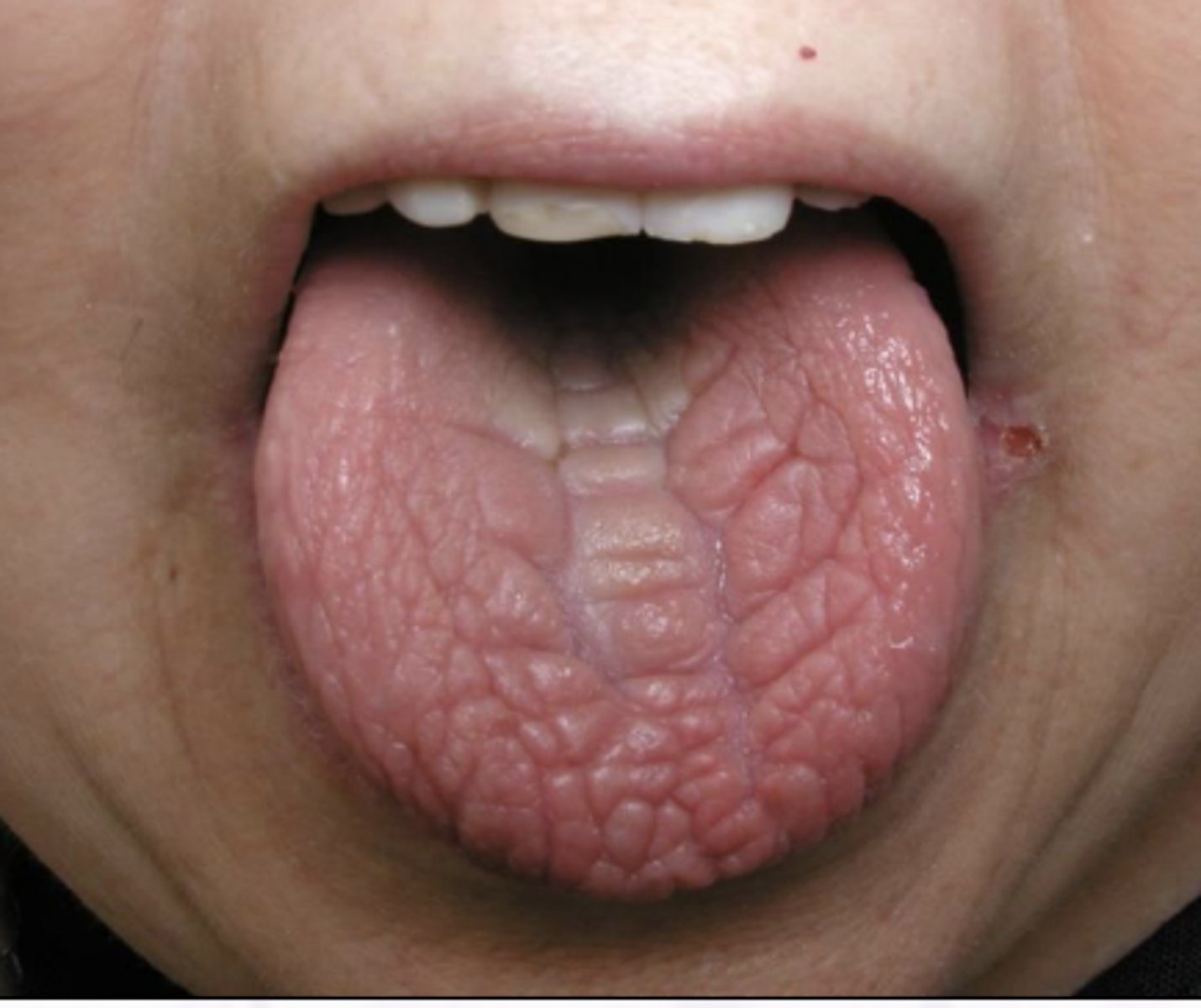
Xerophthalmia is a clinical feature of what oral pathology?
Sjogren Syndrome
Anti-SSA and Anti-SSB are lab values used to diagnose what oral pathology?
Sjogren Syndrome
T/F: You can biopsy minor salivary glands to diagnose Sjogren Syndrome
True
3 multiple choice options
Which oral pathology prognosis is considered a "chronic"?
Sjogren Syndrome
3 multiple choice options
What oral pathology puts patients at an increased risk for MALT lymphoma?
Sjogren Syndrome
3 multiple choice options
Which salivary gland do most salivary gland tumors occur?
Parotid gland
Most salivary tumors are ______ lesions
benign
Most salivary gland tumors in the Parotid gland are _______
benign
Most salivary gland tumors in the submandibular glands are _____________
50% benign - 50% malignant
Most salivary gland tumors in the Sublingual gland are ________
malignant
Minor salivary Gland tumors that occur in the palate and buccal mucosa are ______
benign
Minor salivary Gland tumors that occur in the upper lip are _______
benign
Minor salivary Gland tumors that occur in the lower lip are _______
malignant
Minor salivary Gland tumors that occur in the tongue are _______
malignant
Minor salivary Gland tumors that occur in the floor of the mouth are _______
malignant
Minor salivary Gland tumors that occur in the retromolar pad are _______
malignant
What is the most common site for a minor salivary gland tumor?
Palate
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Most common salivary gland neoplasm
Mix of epithelial and mesenchymal elements
painless, slow growing, firm mass
Seen in middle aged adults
Female predilection
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Pleomorphic Adenoma
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Various patterns within tumor
Encapsulated
Double layer ductal structures
Stroma appear myxoid, cartilaginous, & hylanized
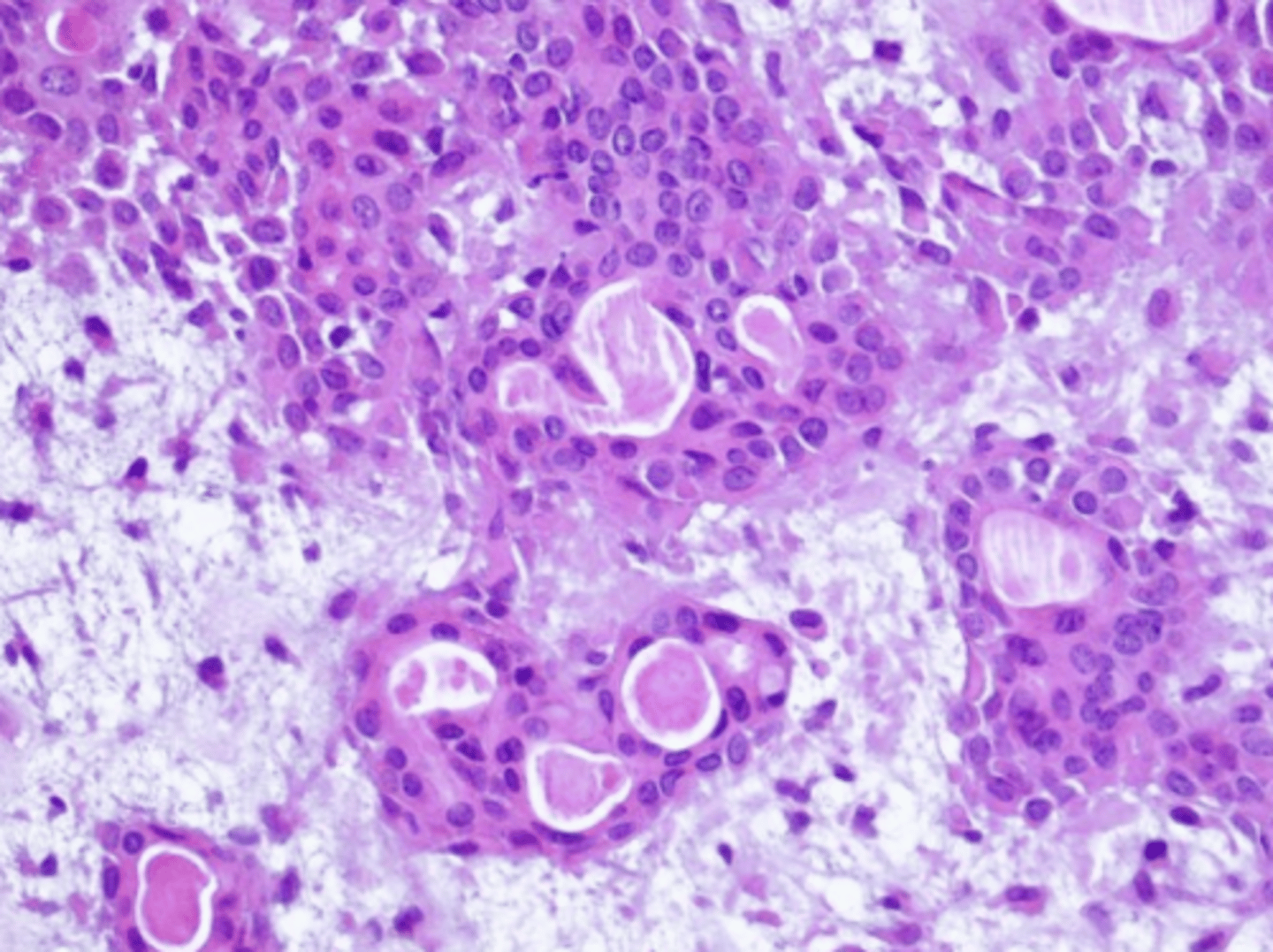
What is the most common site for Canalicular Adenoma?
Upper lip
Canalicular Adenoma
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Well encapsulated
Cells are similar in appearance
Look like canals
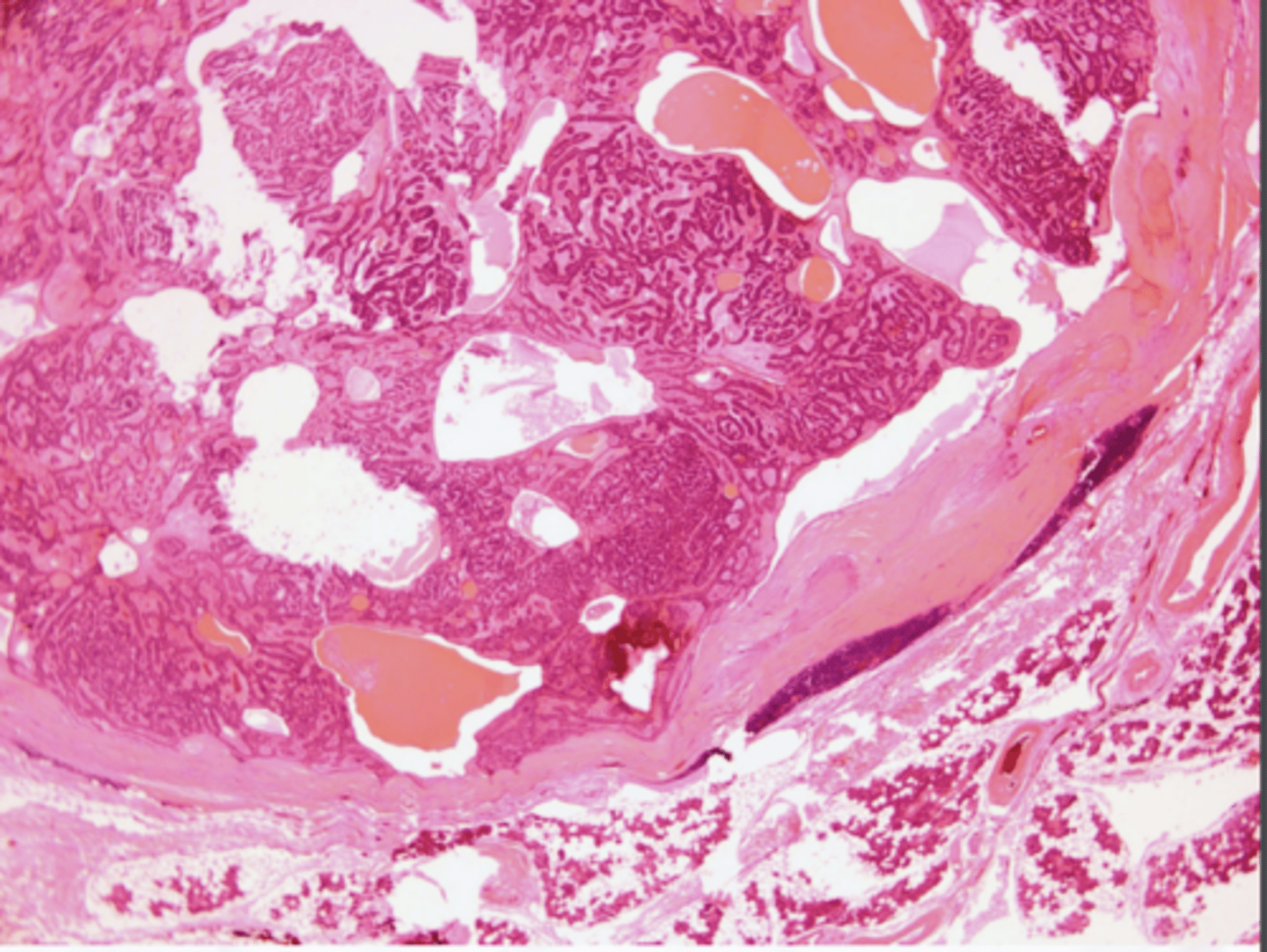
What oral pathology is an uncommon tumor found primarily in the parotid gland?
Basal cell adenoma
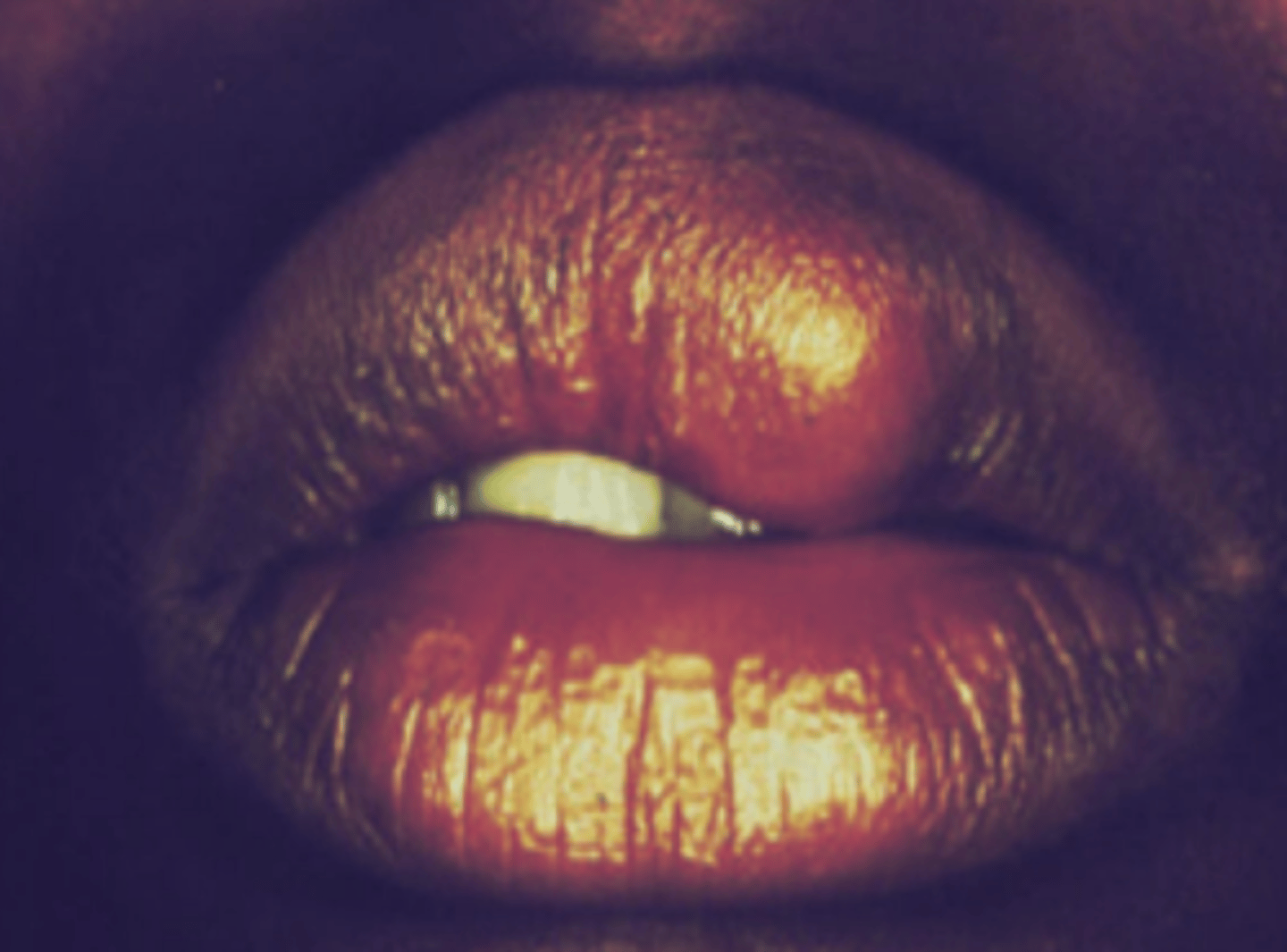
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Most common site is upper lip
Seen in middle aged females (>50 years)
Painless, slow growing
Bluish
Canalicular Adenoma

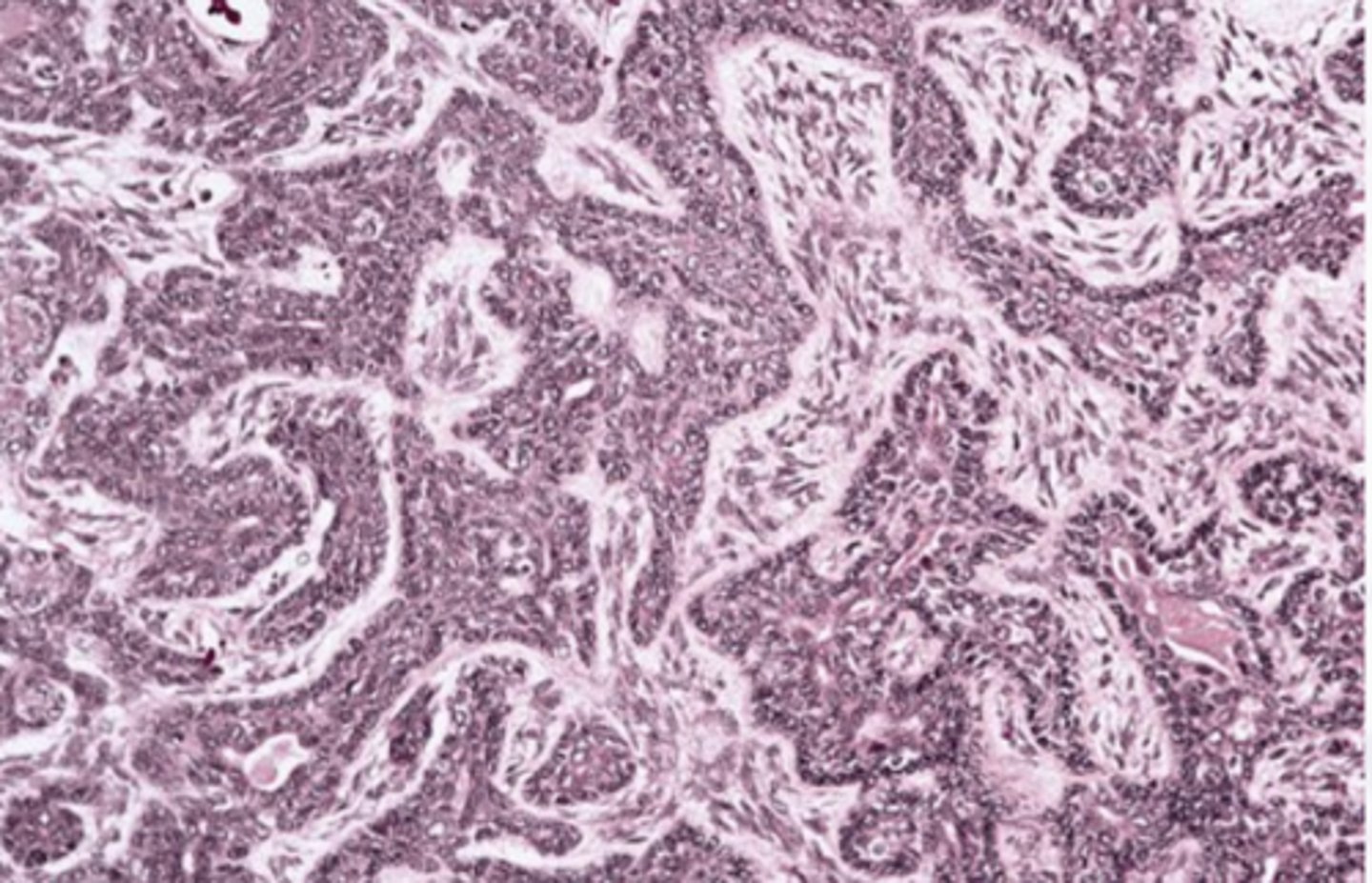
Basal Cell Adenoma
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Encapsulated Islands with palisaded cells or Jigsaw pattern
May form ducts
Once surgically removed, recurrence IS common for what benign oral pathology?
Basal cell adenoma
3 multiple choice options
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
exophytic & papillary
involves minor salivary glands
can look like an indentation
Ductal Papilloma
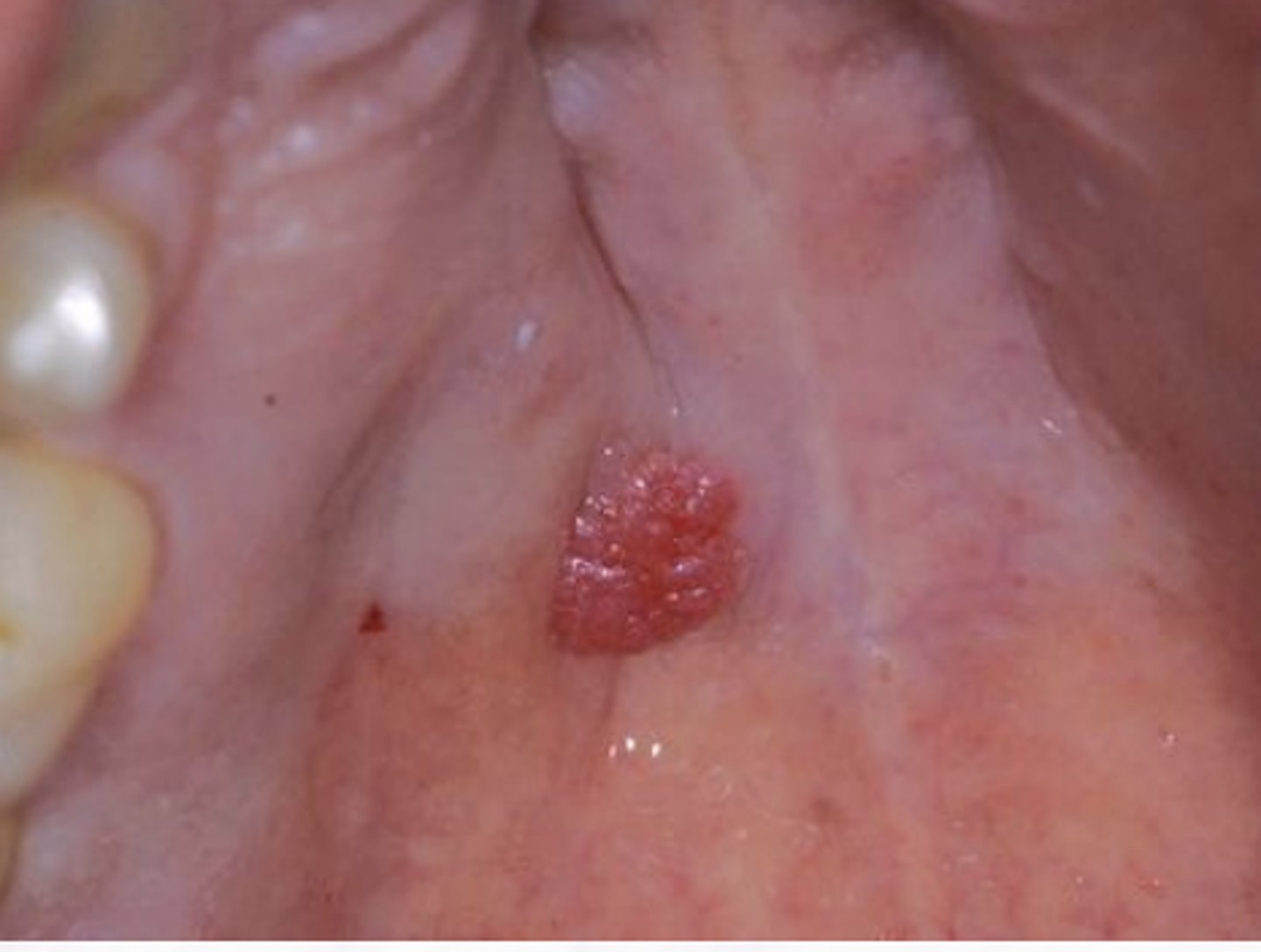
Ductal Papilloma
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Papillary projections
Inflammation
Intraductal
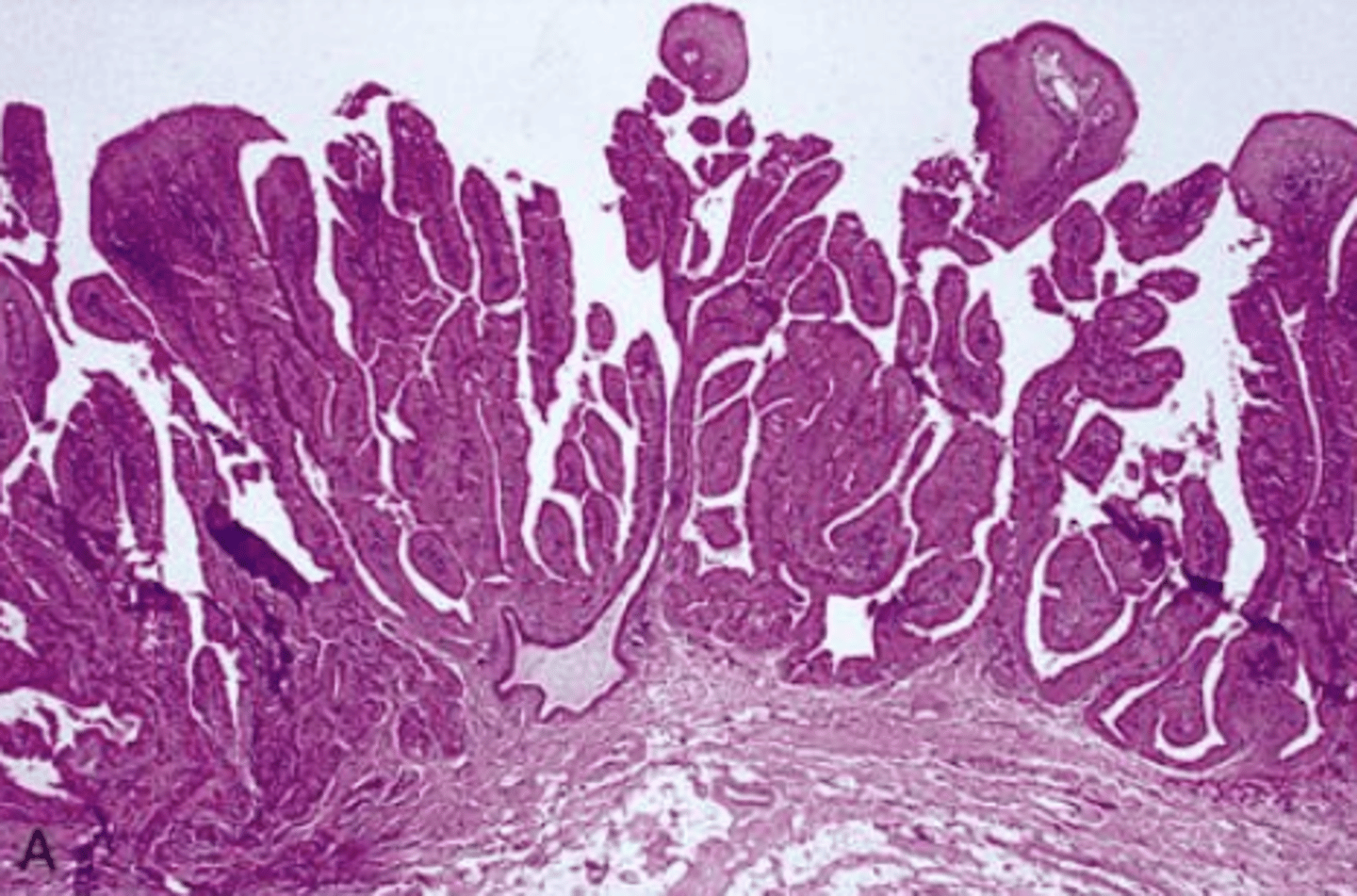
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Associated with smoking (8x)
Proliferation of oncocytic cells AND lymphoid cells
More common in males (6th-7th decade of life)
Slow growing mass of parotid gland
Warthin Tumor
Warthin Tumor
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Cyst lined by uniform rows of oncocytic (pink) cells
The lining is papillary in appearance
The cyst call is composted of abundant lymphocytes (purple)
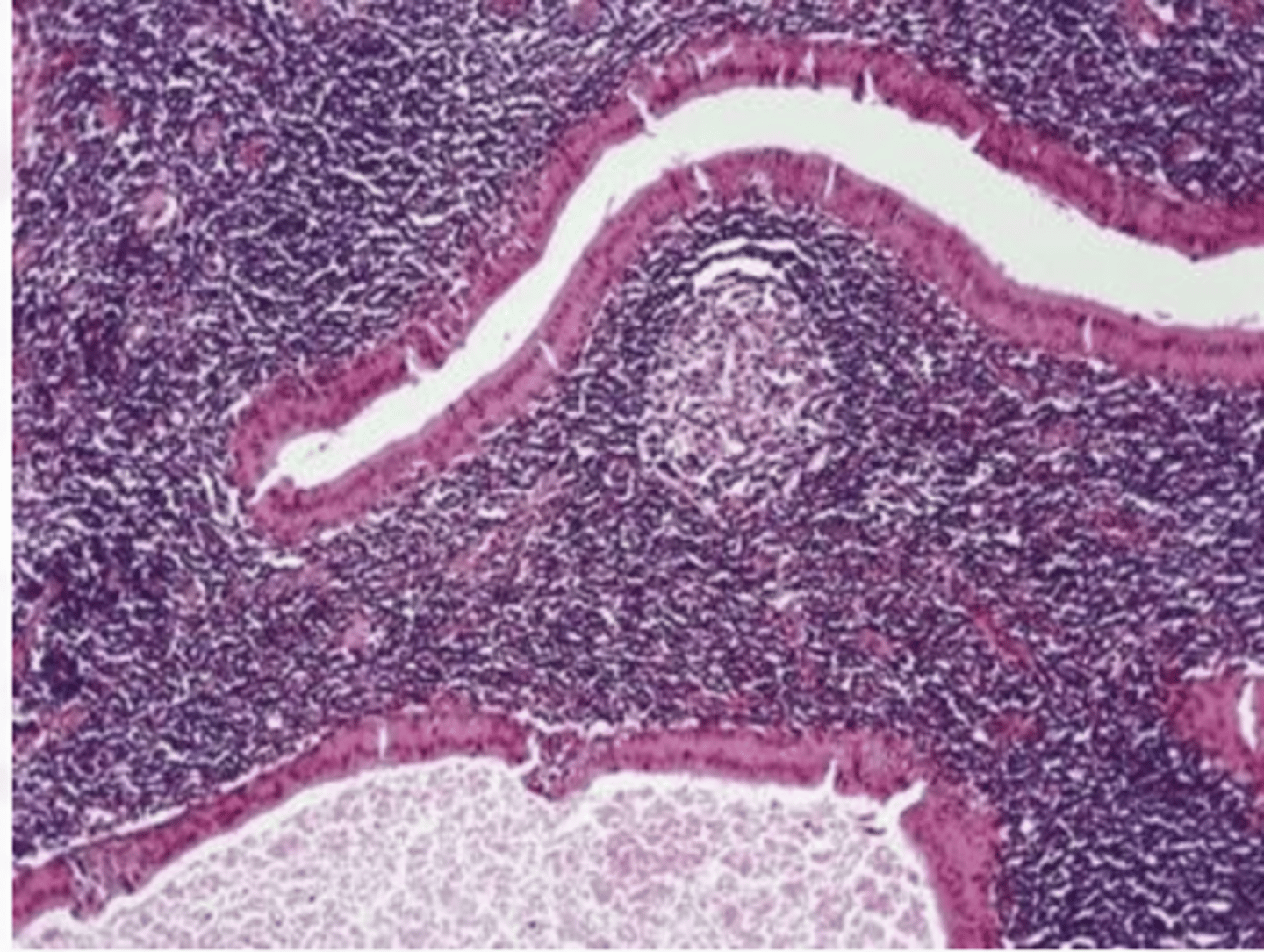
Oncocytoma is a ______ parotid salivary gland tumor
Rare
3 multiple choice options
Oncocytoma
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
-Large polyhedral cells with abundant granular cytoplasm -- Mitochondria!
-Cells are separated by thin fibrous septal
*Very pink histology~oncocytic means eosinophilic cytoplasm which always stains PINK!
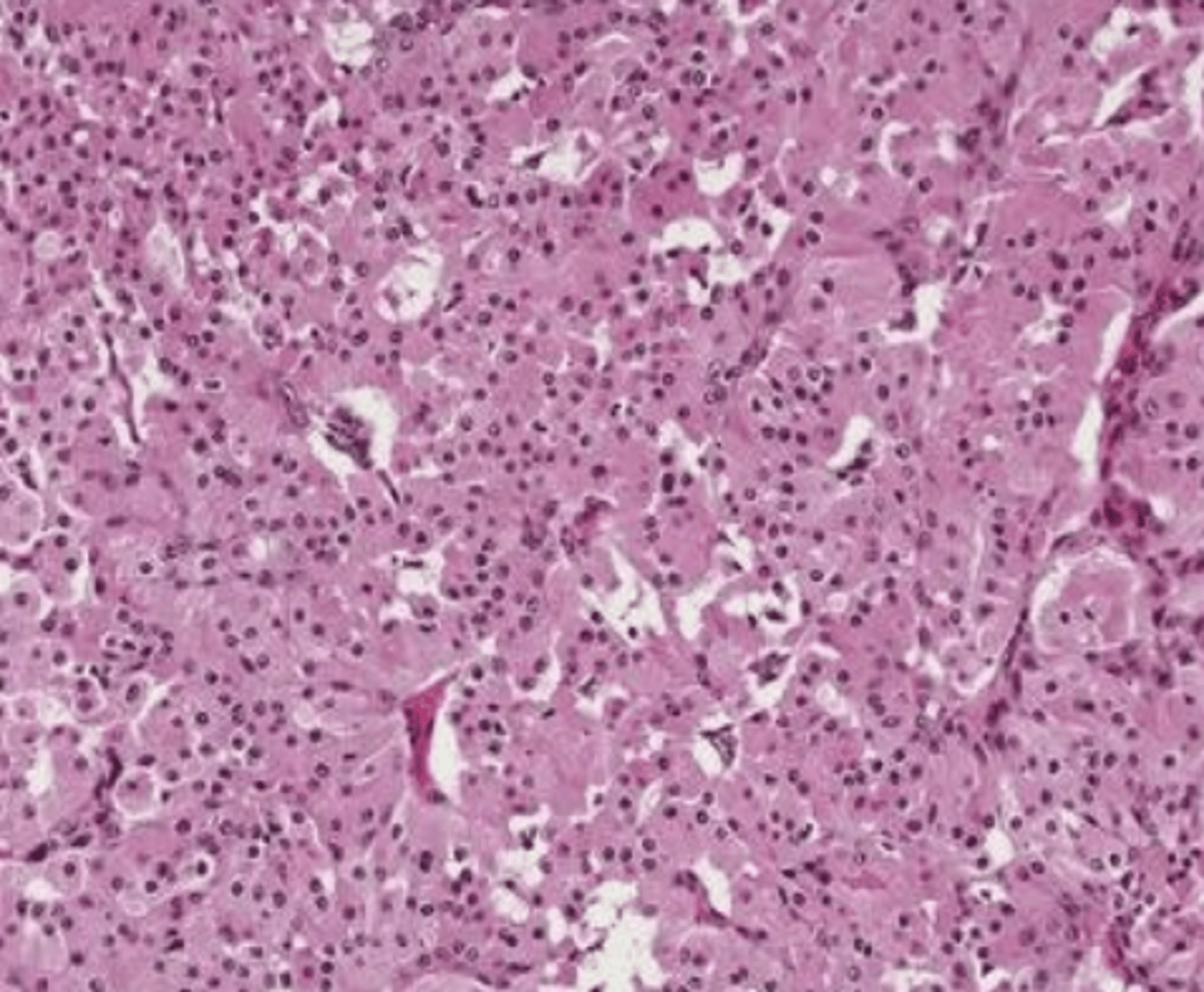
What is the most common malignant salivary gland tumor?
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
What is the most common malignant salivary gland tumor in children?
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Usually asymptomatic, but can have pain or palsy
Bluish mass & swelling
MAY mimic mucocele
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
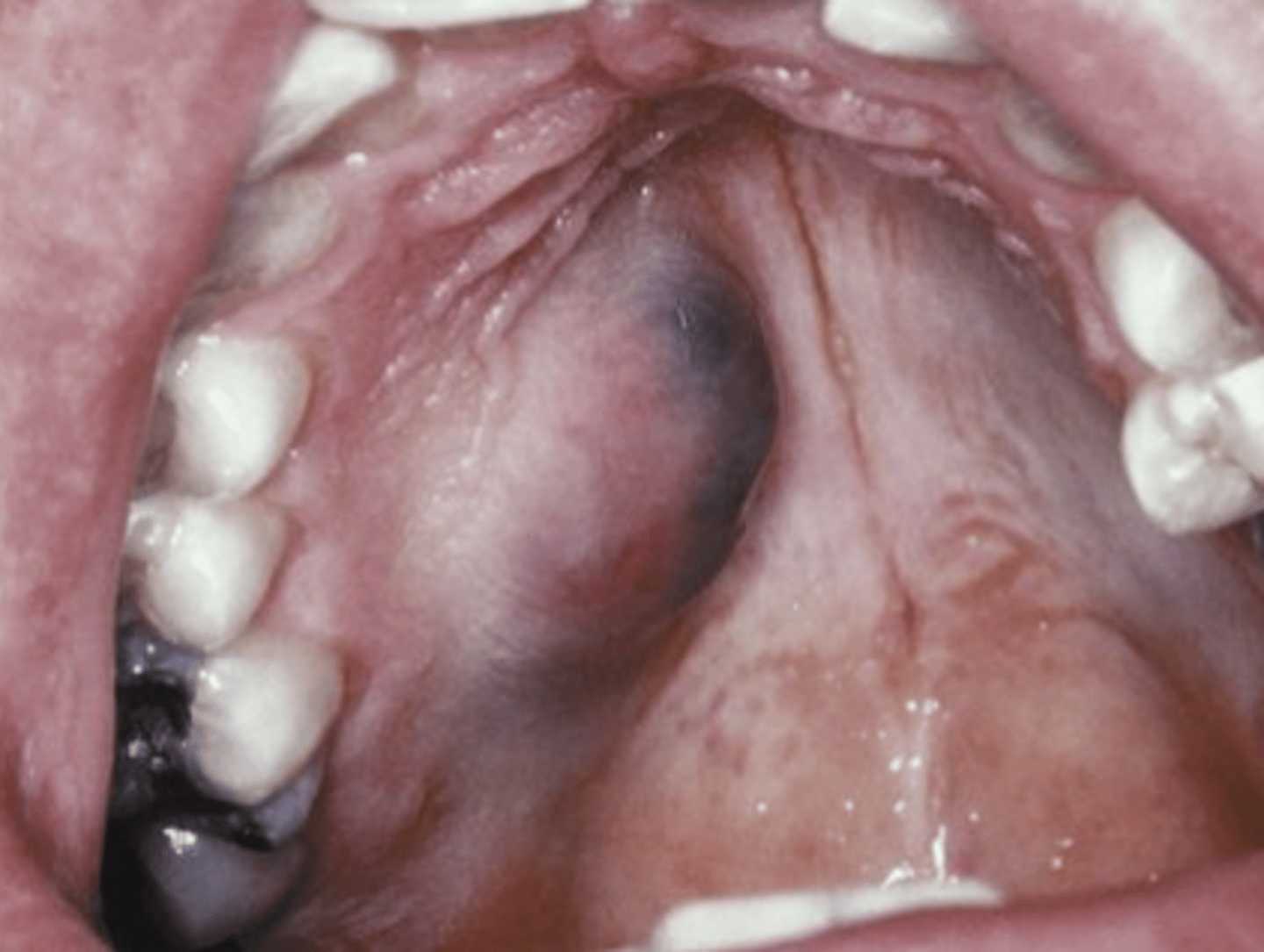
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
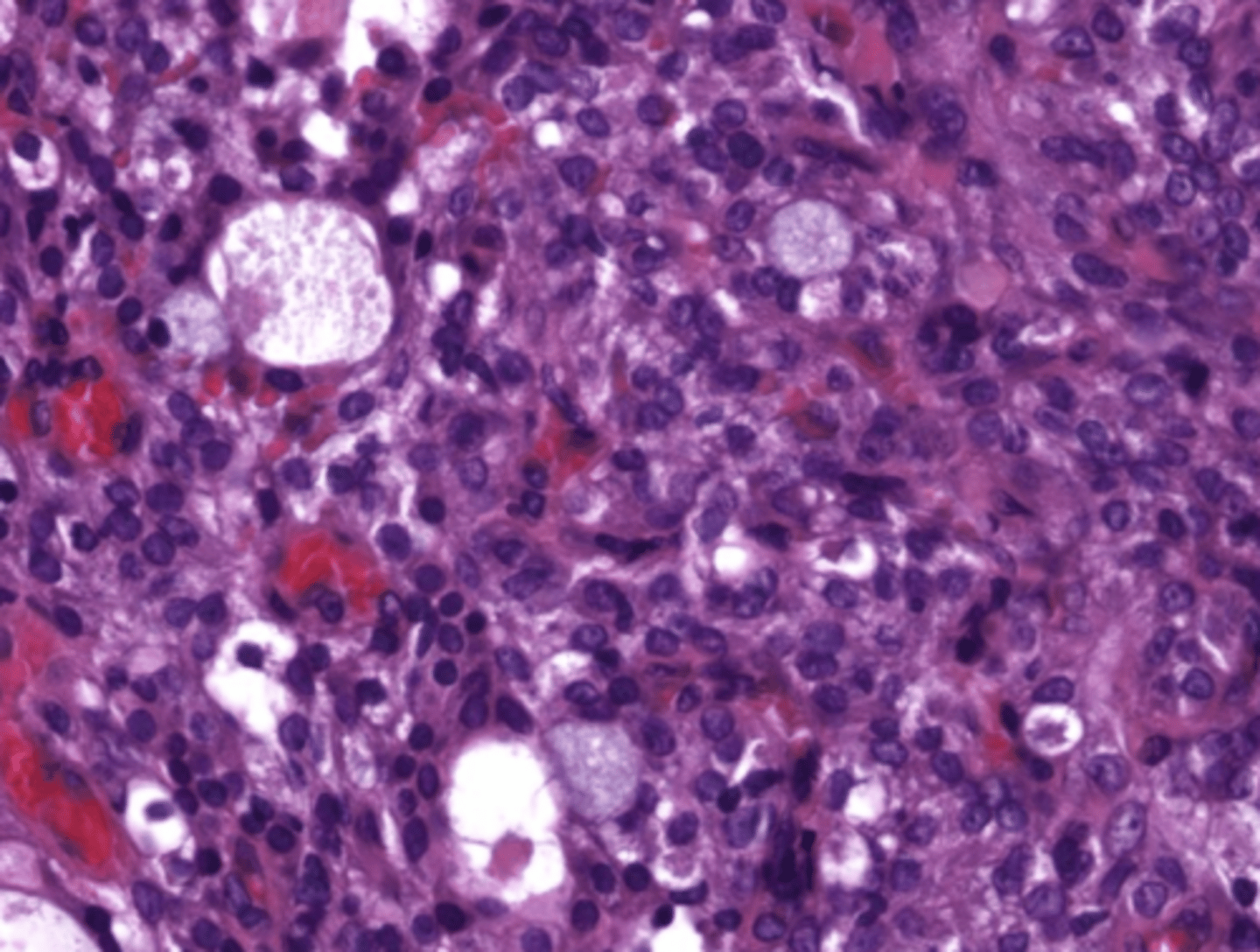
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Epidermoid cells
Mucous cell
Ductal structures
Cystic spaces
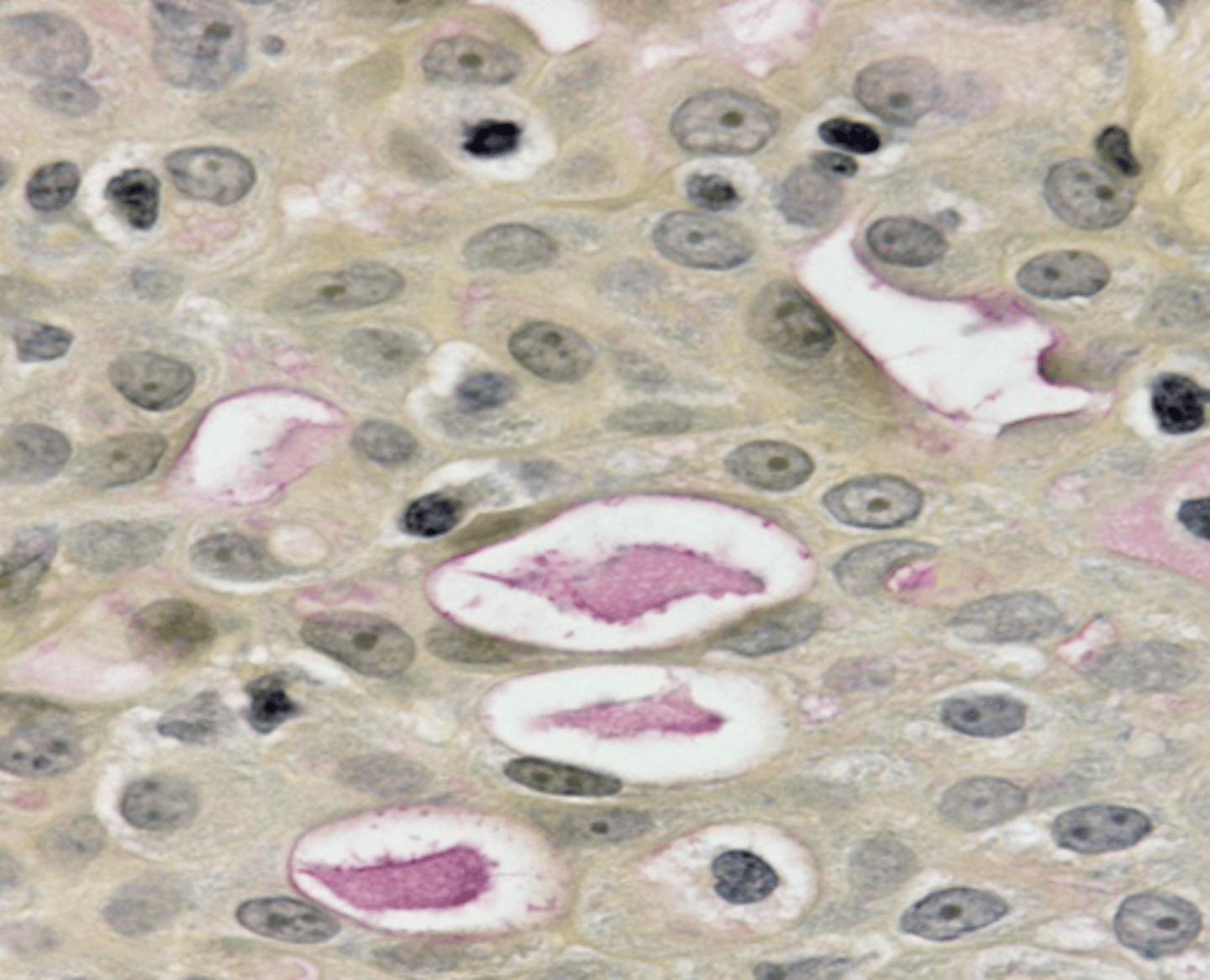
What stain is used to identify mucus cells and secretion?
Mucicarmine stain
For a lot of the malignant salivary gland tumors, treatment depends on what few things?
Grade, stage, and location of the tumor
or if its inoperable
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Painful or present with facial paralysis
50% in minor glands
Middle aged females
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
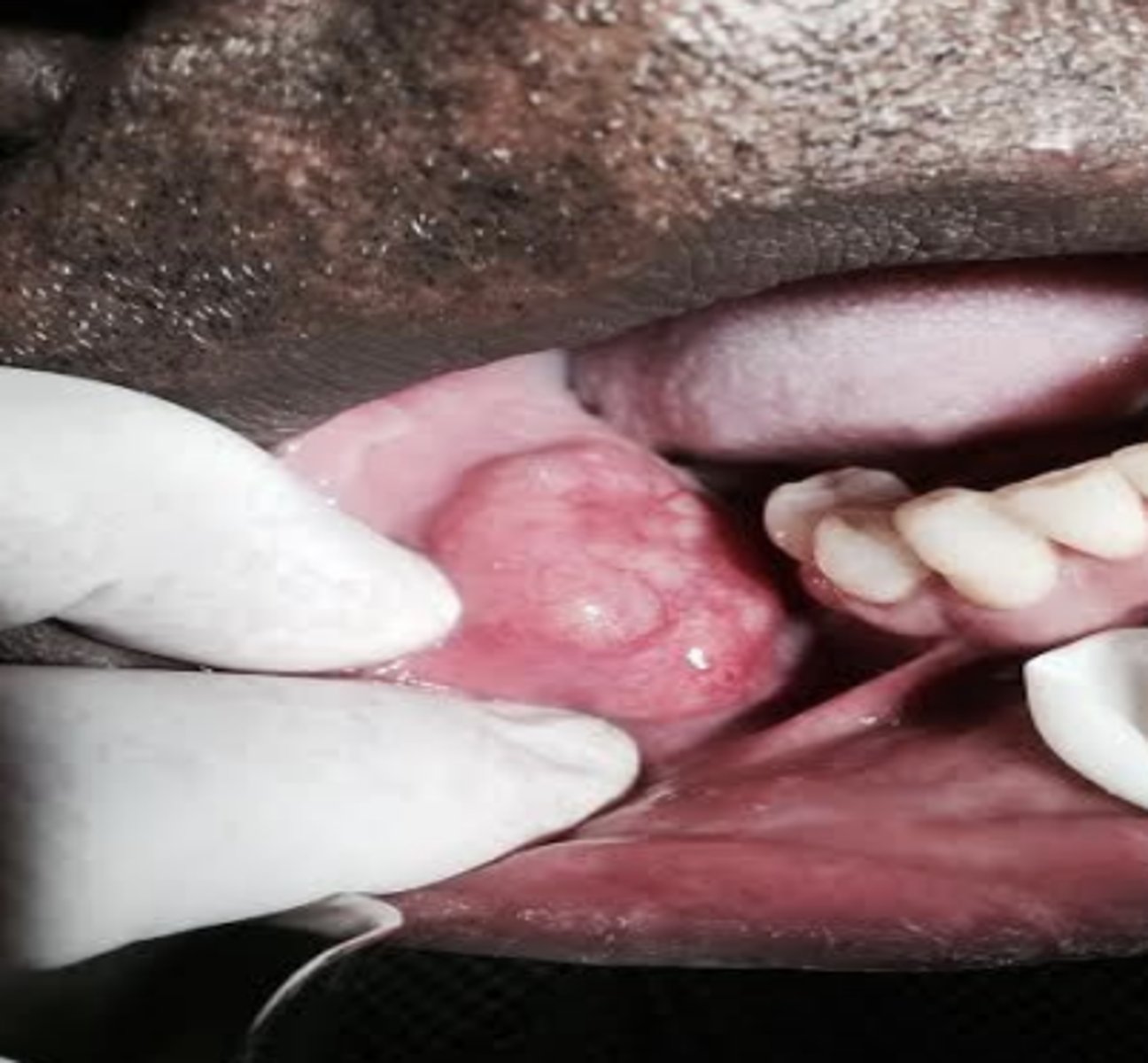
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Swiss cheese pattern
Islands with cribiform pattern
Myoepithelial cells and ductal cells present
Perineural and perivascular invasion
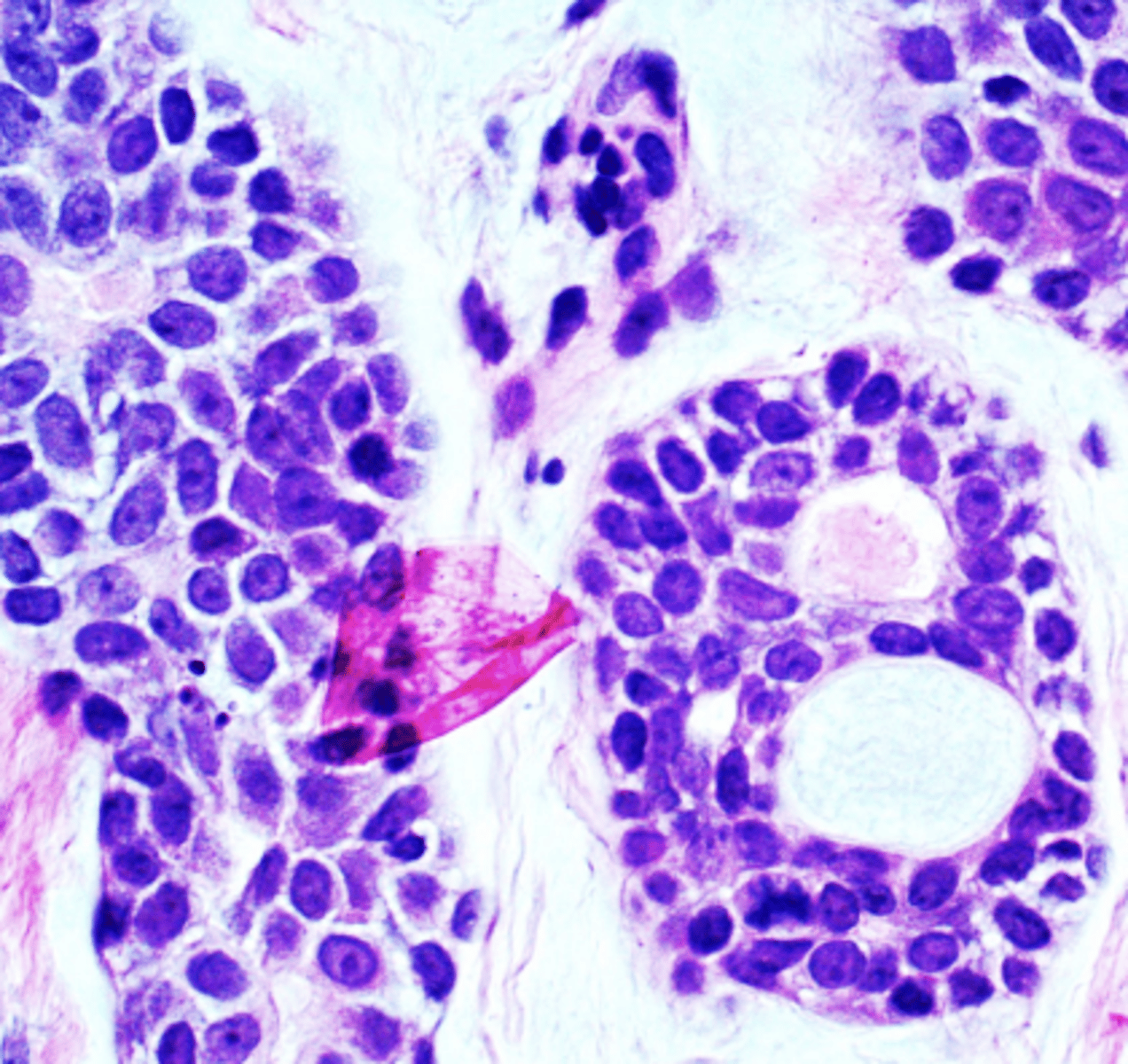
Which oral pathology is known as the "relentless tumor" and the survival rate decreases the longer the patient lives?
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Which oral pathology occurs almost exclusively in the minor salivary glands?
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma
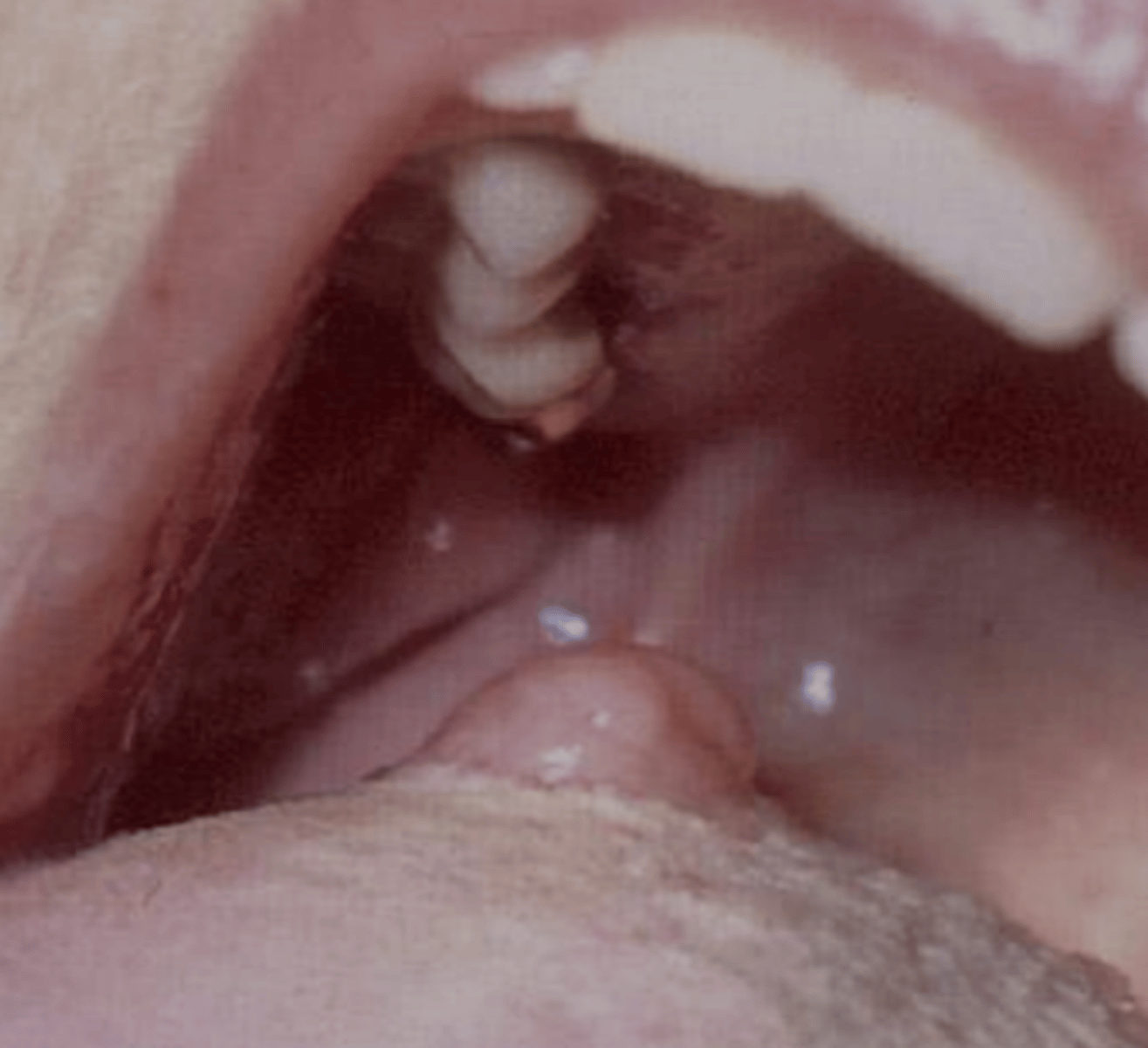
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma
What histologic characteristics are indicative of this oral pathology?
Various histologic patterns
Cells line up single file line like "Kindergarten filing"
Perineural and perivascular invasion
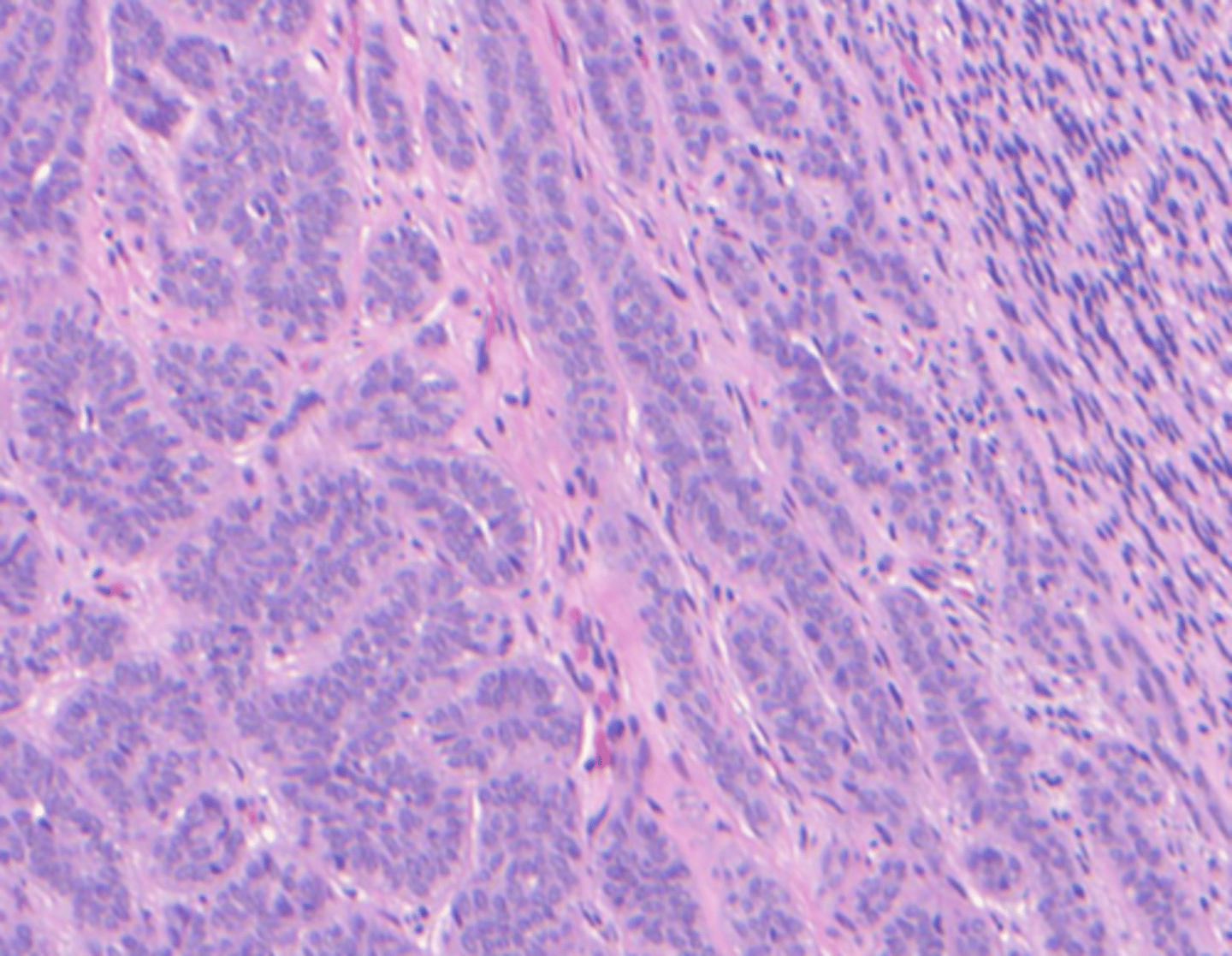
With surgical excision of the tumor, recurrence and death is rare for which oral pathology?
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma
These clinical characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Low grade malignant tumor
Serous acinar cells
most common site is parotid
Acinic Cell Carcinoma
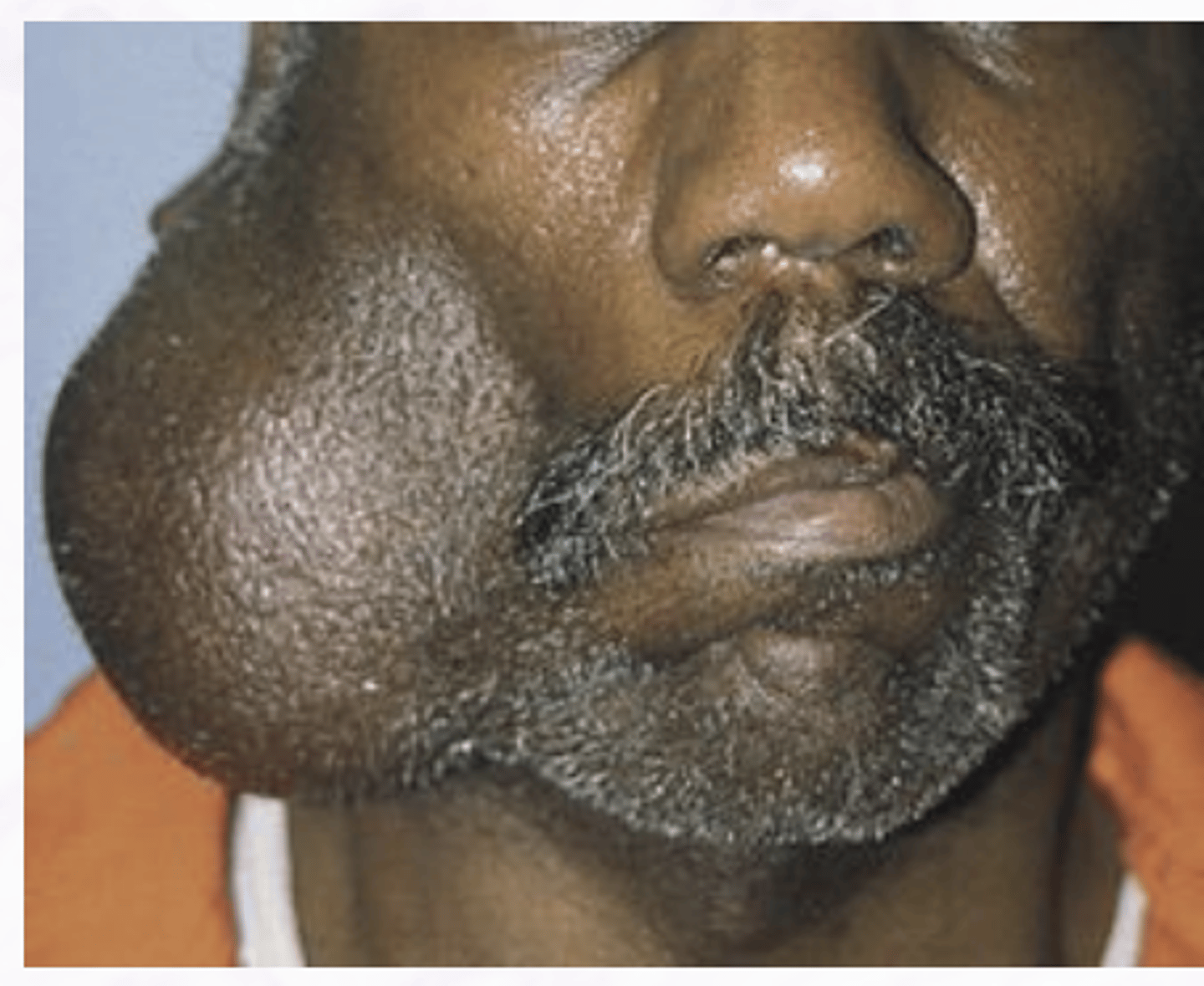
Acinic Cell Carcinoma
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Well circumscribed
May show infiltration
Serous acinar cells ---(cells containing abundant granular cytoplasm
Zymogen granules )
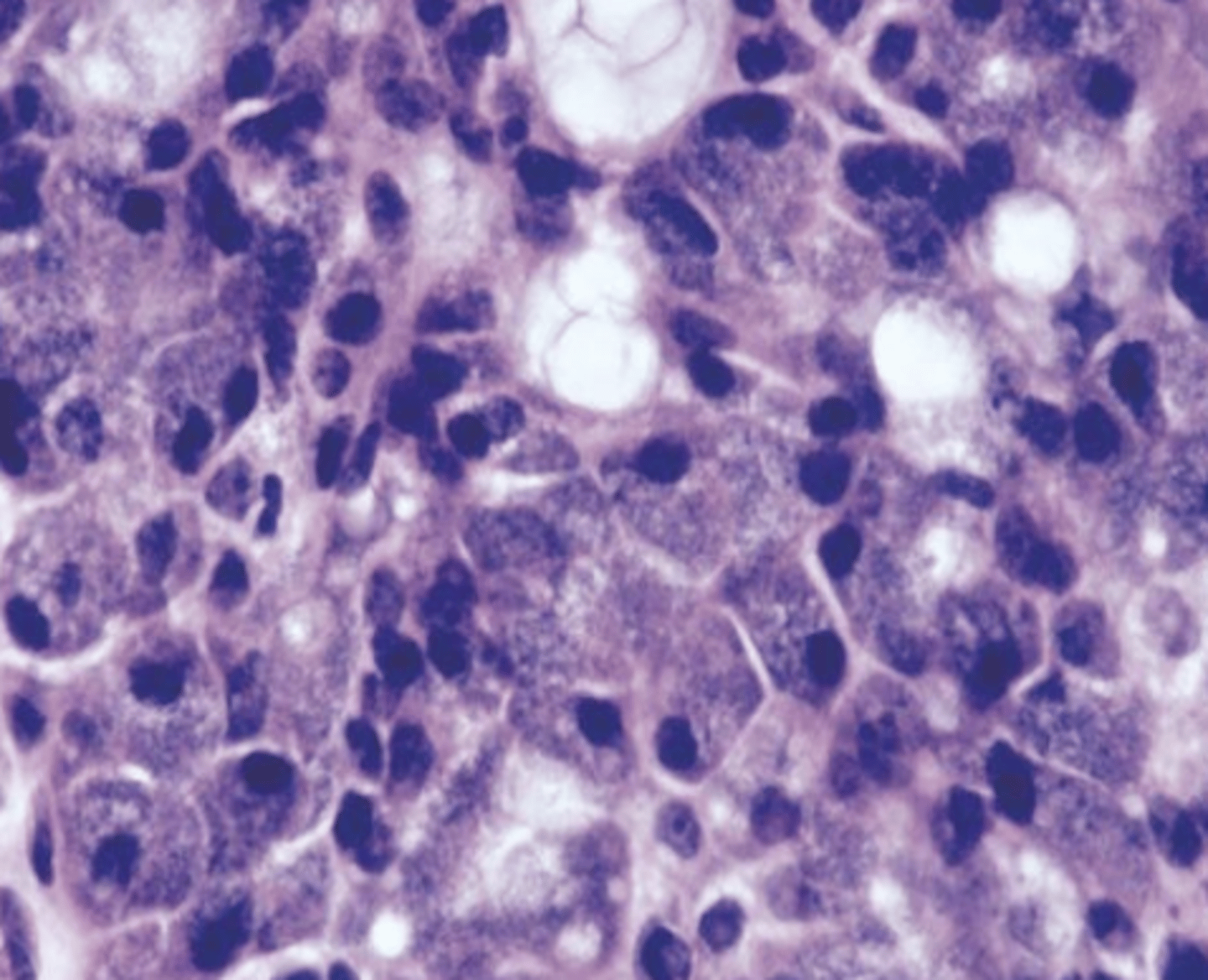
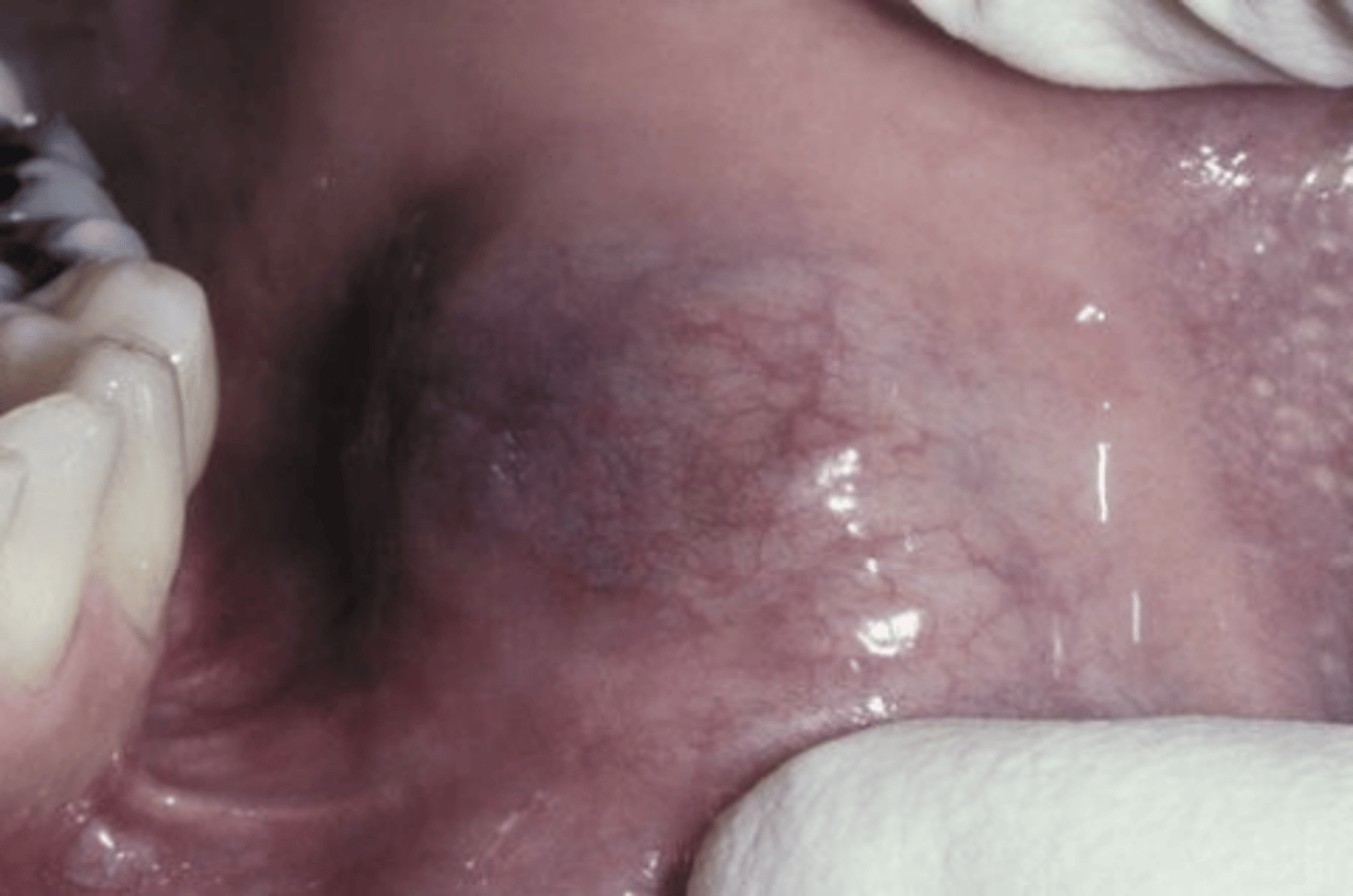
What type oral pathology used to be part of acinic cell carcinoma until it recently gained its own name/diagnosis?
Secretory Carcinoma
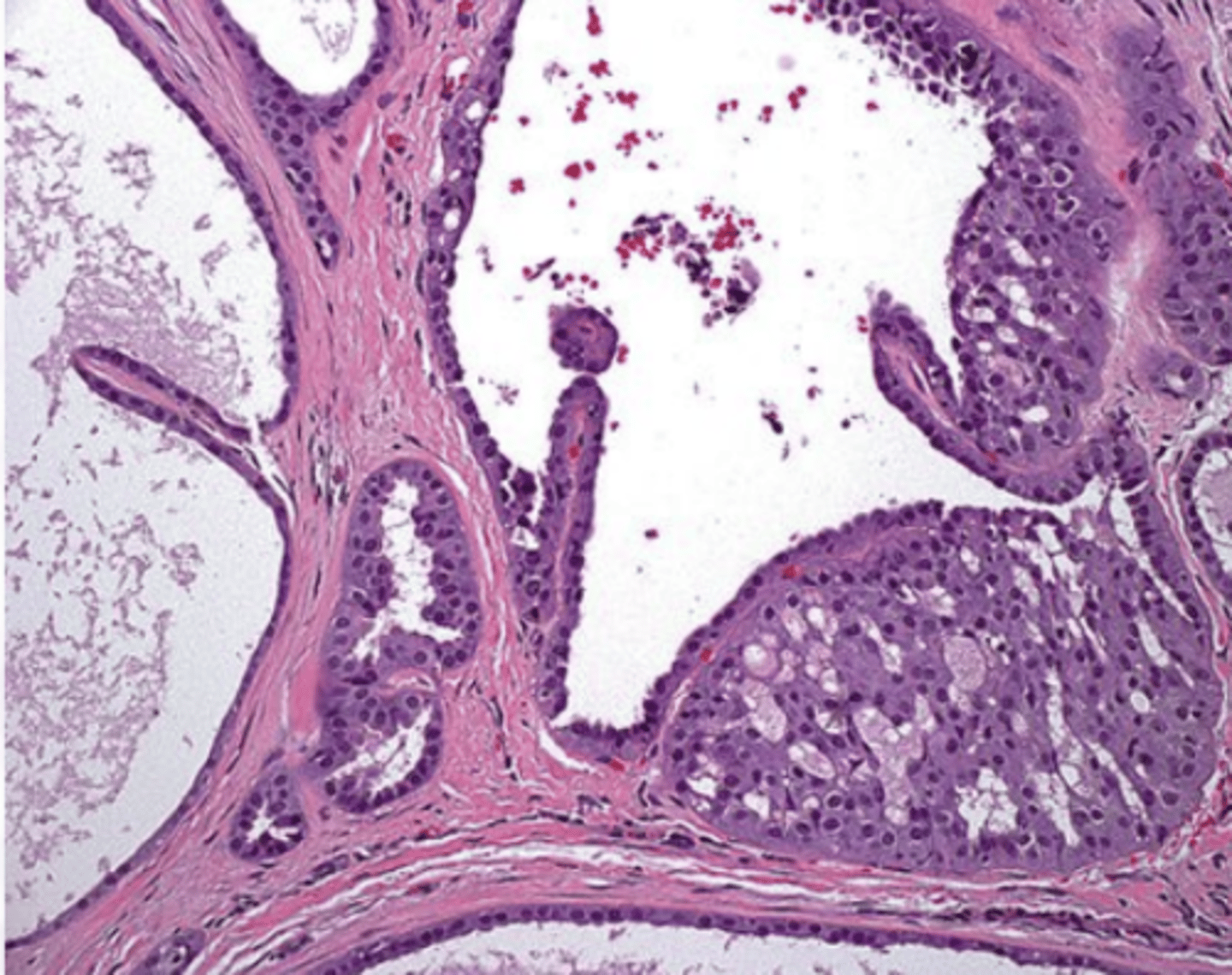
These histologic characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Zymogen poor
Very bland cytology
"Hobnail cells"
Carcinoma Ex PA is a malignant salivary tumor that can arise from which benign salivary tumor?
Pleomorphic adenoma
What can cause Carcinoma Ex PA?
History of pleomorphic adenoma that has been present for many years