Bio446L exam 1 (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:39 PM on 9/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
1
New cards
What is the foundation to deeper structures
surface anatomy
2
New cards
What is anatomic variation
no two people are the same
3
New cards
What are the smallest structure that form the most vital functions of life
cells
4
New cards
Where do cells come from
all cells come by dividing from preexisting cells
5
New cards
TEM VS SEM
SEM creates an image by detecting reflected or knocked-off electrons, while TEM uses transmitted electrons (electrons that are passing through the sample) to create an image.
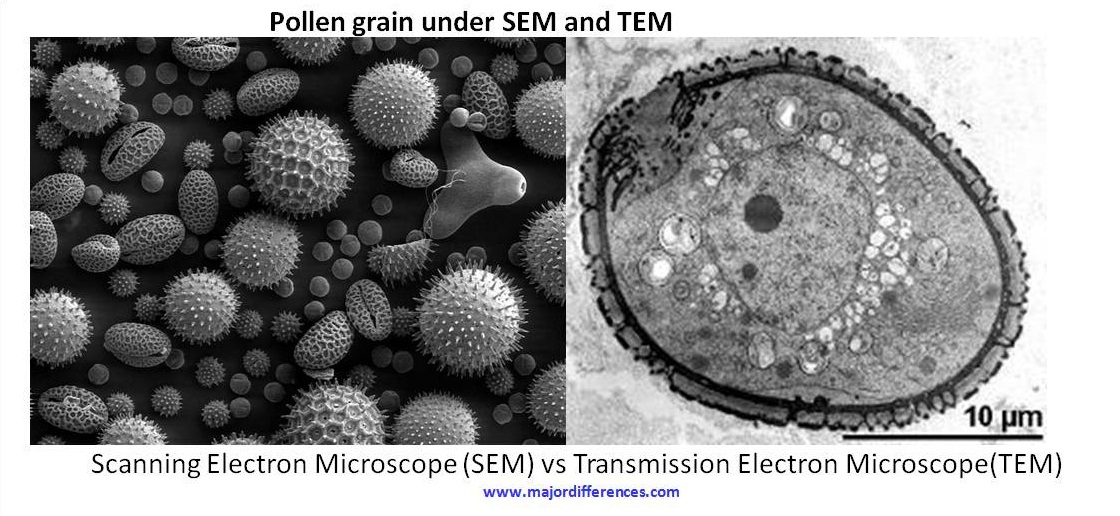
6
New cards
What two major compartments are cells divided by
cytoplasm and nucleus
7
New cards
What creates shape of cell
cytoplasmic skeleton
8
New cards
What is the main function of the plasma membrane
separates cytoplasm of cell from extracellular world and allows it to interact with outside world (is a dynamic structure)
9
New cards
What is achondroplasia
dwarfism that affects bone growth wherein cartilage doesn’t convert into a bone
10
New cards
What is the plasma membrane composed of
bilayer of lipids with hydrophobic inner layer and two types of proteins. integral/transmembrane proteins- proteins embedded or passing through plasma membrane and peripheral membrane proteins- associated with membrane but not embedded
11
New cards
What attaches to the outside of cell membrane
carbohydrates, proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids)
12
New cards
What is the glycocalyx
the outer covering of plasma membrane made from arbohydrates, proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids)
13
New cards
What is the lipid raft
cholesterol molecules that have clusters in the membrane, which helps plasma membrane operate
14
New cards
What is the phospholipid made of
polar head group (hydrophilic) and nonpolar fatty acid chain (hydrophobic)
15
New cards
How can things leave or enter the cell
through channels of proteins (vesicular transport) and by diffusion
16
New cards
What is endocytosis
vesicular transport where substances enters a cell
17
New cards
what is exocytosis
vesicular transport where substance leaves a cell
\
\
18
New cards
What is another name for endocytosis
phagocytosis
19
New cards
What is phagocytosis
when the plasma membrane engulfs a large particle
20
New cards
What is pinocytosis
known as fluid endocytosis and bulk-phase pinocytosis, is a mode of endocytosis in which small molecules dissolved in extracellular fluid are brought into cell
21
New cards
what is receptor-mediated endocytosis
has receptors on the surface, which tell the cell to bring something inside
22
New cards
What is an example of receptor-mediated endocytosis
Is low density lipid receptors looking for low density lipids. When many low density lipids interact with receptors it triggers things to happen in the cell. They then phagocytose in cell.
23
New cards
Does the body, cells and tissue constantly do to not waste material
recycle
24
New cards
How does the cell wall move
it is dynamic organelle
25
New cards
Why do cells communicate
to coordinate their function
26
New cards
What is synaptic signaling?
(longer route) cells (neurons) send signals down the nerves to tell muscles and other things to do stuff (involves neurotransmitters)
27
New cards
What is endocrine signaling
(longer route) tells cells what to do by sending hormones
28
New cards
what is paracrine signaling
sends signals to cells close
29
New cards
What is the engine of the cell
the mitochondria because it produces energy
30
New cards
What cells do not have mitochondria? Why?
red blood cells. They do not use energy because they transport oxygen or carbon dioxide. Also, terminal keratinocytes because they are dead
31
New cards
When are more mitochondria produced
cells that use larger amounts of energy
32
New cards
What has a similar look as the plasma membrane
the mitochondria because it has two membranes because they have different functions
33
New cards
What are the folds of the inner membrane of the mitochondria called and their purpose
cristae and it increases surface area because they want more surface area for generating energy
34
New cards
How does the mitochondria create energy
aerobic respiration and generates ATP
35
New cards
If a person has a mitochondrial deficiency diseases what will they have issues with
having energy
36
New cards
What organelles are involved in protein synthesis
RER and ribosomes
37
New cards
What is the function of ribosomes
to assemble polypeptides
38
New cards
What is the endoplasmic recticum
a set of interconnected channels that run through the cytoplasm
39
New cards
What does RER and SER synethsize
rer- proteins and ser-lipids and carb metabolism
40
New cards
Where are proteins from the RER sent
golgi apparatus
41
New cards
What are free ribosomes
are not attached to anything and interact with mRNA to assemble proteins
42
New cards
What are en-bound ribsomes
ribosomes attached to the er, then the proteins are collected in the cisterna and that protein will be sent to golgi apparatus
43
New cards
What is a process by en-bound ribosomes
sweating
44
New cards
What is the difference between free and ER-Bound polyribosomes?
look at pic
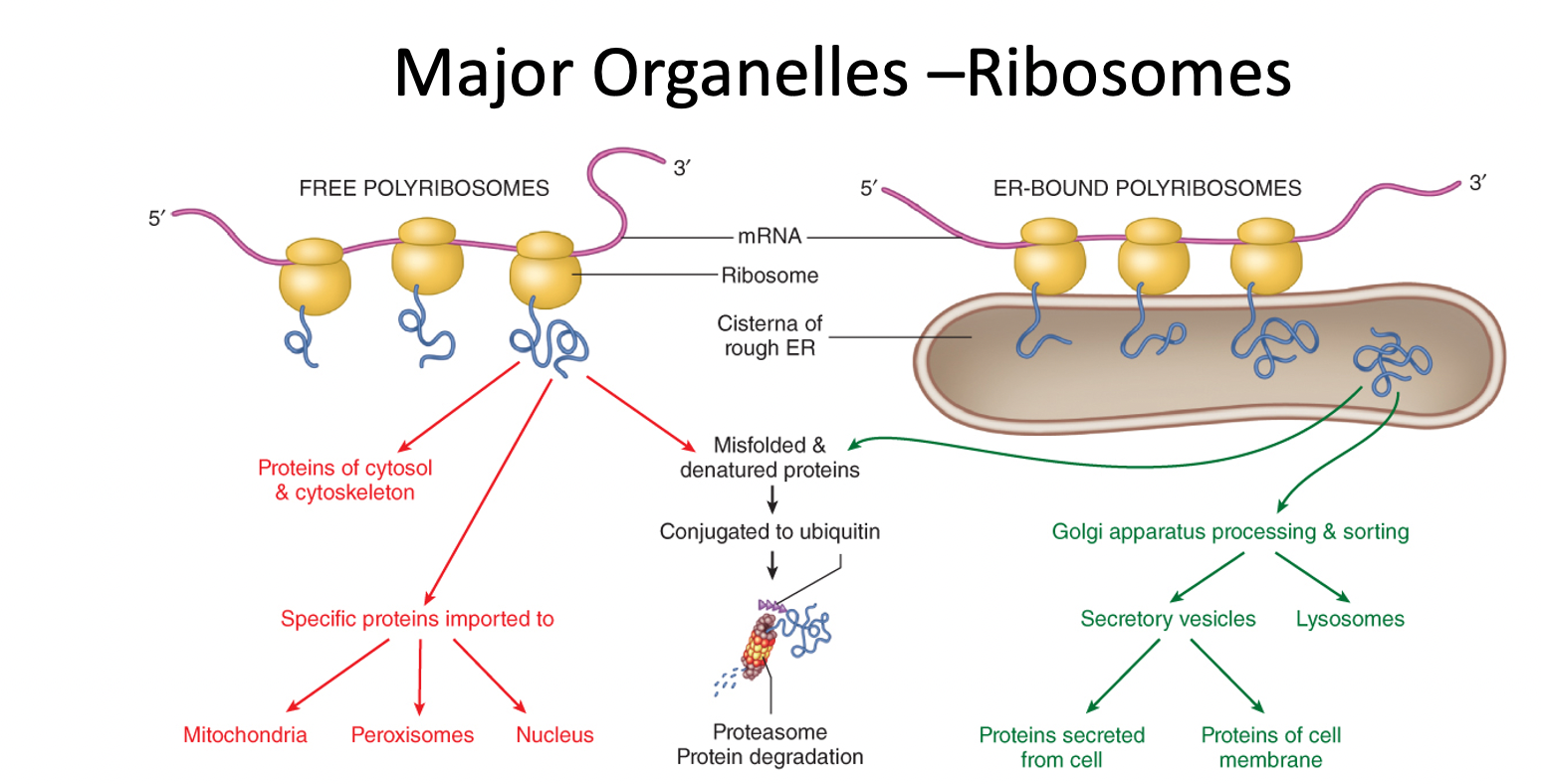
45
New cards
What do bad proteins cause
illnesses and disorders
46
New cards
what is Endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation (ERAD)
targets a bad/poorly folded protein and sends it out into cytoplasm where ubiquitin attaches to it. Proteasomes then degrade it. Degraded protein results in free amino acids to be reused.
MA: Parkinson’s, CF, HIV
MA: Parkinson’s, CF, HIV
47
New cards
What detoxifies drugs and alcohol
ser
48
New cards
What are transport vesicles
molecules that move proteins
49
New cards
What does golgi appartus do
modifies and takes the wrong product and refines it and completes it. Then put in shipping vacuoles (also know as secretory granules) to move in cell or be secreted by plasma membrane. if stay inside of plasma membrane it will give rise to lysosomes
50
New cards
What are lysosomes examples
through endocytosis the kidney tubule brings in materials in the lumen and the cell uses lysosomes to break it up to use or execute
51
New cards
What happens when you have too much hydroperoxide
Peroxisomes take it out
52
New cards
function of cytoplasm
•Determine shape of cells, Movement of organelles, and Movement of the cell
53
New cards
what are microtubles and functions
small hollow tubes that form near the nucleus and grow towards cell. They provide a pathway/connections for things to follow by creating a system of connections/guides vesicles in movement within cell
54
New cards
What structure is responsible for final creation of two daughter cells
microtubules
55
New cards
Why is actin filamnet the most important Microfilaments
it is in all cell types and
•provide anchorage and movement of membrane proteins
•Form structural core of microvilli
•Extension of cell processes
•Movement of cell
•provide anchorage and movement of membrane proteins
•Form structural core of microvilli
•Extension of cell processes
•Movement of cell
56
New cards
What is keratin
are important in epithelial cells because they help hold epithelial cells into a single sheet and to the underlying connective tissue
57
New cards
What is Vimentin
are mesoderm-derived cells that give rise to other tissues like muscle, glial
58
New cards
What are the two important
Intermediate Filaments
Intermediate Filaments
keratin and Vimentin
59
New cards
what is the cell nucleus
\
\
•Membrane-limited compartment containing genes
60
New cards
what does the cell nucleus contain
\
•Nuclear envelope:
\
•Chromatin:
\
•Nucleolus:
\
•Nucleoplasm:
\
•Nuclear envelope:
\
•Chromatin:
\
•Nucleolus:
\
•Nucleoplasm:
•Nuclear envelope: bilayer with perinuclear space between them and __nuclear pores__ which regulate transport between nucleus and cytoplasm
•Chromatin: chromosomal material
•Nucleolus: site of active rRNA synthesis which then leads to protein synthesis- when the chromatin is active- communicates to rest of the cell
•Nucleoplasm: material within nucleus that is not chromatin or nucleolus
•Chromatin: chromosomal material
•Nucleolus: site of active rRNA synthesis which then leads to protein synthesis- when the chromatin is active- communicates to rest of the cell
•Nucleoplasm: material within nucleus that is not chromatin or nucleolus
61
New cards
What proccess do stem cells give rise to new cells
when a stem cell divides one will stay behind to stay was a stem cell while the other one becomes a progenitor cell
62
New cards
What is apoptosis
the death of cells which occurs as a normal and controlled part of an organism's growth or development.
63
New cards
Why do we tan
to protect the stem cells of our skin
64
New cards
What are general characteristics of the Epithelium
\-anything that leaves or enters the body must pass through an epithelium'
\-largely packed cells with extracellular material between cells
\-Arranged in continuous sheets of either single \n (simple) or multiple (stratified) cells in thickness
\-have free surface which mean it is exposed to areas that is not part of the body is connected to connective tissue called basal lamina (basement membrane)
\-all are avascular (does not contain blood vessel because it would bleed)
\-have nerve supply
\-high capacity for renewal (come from stem cells)
\-largely packed cells with extracellular material between cells
\-Arranged in continuous sheets of either single \n (simple) or multiple (stratified) cells in thickness
\-have free surface which mean it is exposed to areas that is not part of the body is connected to connective tissue called basal lamina (basement membrane)
\-all are avascular (does not contain blood vessel because it would bleed)
\-have nerve supply
\-high capacity for renewal (come from stem cells)
65
New cards
how does Epithelium get nourishment
through the underlying tissue ex the basal lamaina
66
New cards
What are the two types of epithelia
\-covering
\-glandular comes from glands of the body
\-glandular comes from glands of the body
67
New cards
What do epithelial cells rest on
connective tissue
68
New cards
lamina propria; dermis
the connective tissue of the epithelia lining the cavity of internal organs called and what is it called in the case of the skin
69
New cards
What do evaginations in connective tissue form and why does it do this
it forms papillae to anchor the connective tissue and epithelium together
70
New cards
What is the basement membrane
\
Visible with light microscope using a specific stain. Usually formed by two laminae, basal and reticular
Visible with light microscope using a specific stain. Usually formed by two laminae, basal and reticular
71
New cards
what is the basal lamina
• Binds epithelium to underlying connective tissue \n • Composed of type IV collagen, glycoproteins (laminin and entactin), and proteoglycans \n • Only seen with an electron microscope
72
New cards
Why is the basal lamina type IV collagen unique
because it is secreted by epithelial cells, which is unique because all collagen comes from connective tissue cell. the collagen helps hold everything together
73
New cards
What is tight junction and another name for it
\-Zonulae occludens
\-Closes off intercellular space (fusion sites)
-Prevents diffusion between cells
\-prevents disease
\-Closes off intercellular space (fusion sites)
-Prevents diffusion between cells
\-prevents disease
74
New cards
How are tight junctions fussed
by proteins occludin and claudin
75
New cards
What is zonula adherens (junctions)
•Anchors cells together
•Connects cytoskeleton (actin filaments) of one cell to another
76
New cards
What is Desmosome (macula adherens) (junction)
strong spot links between cells (only in certain spots)
77
New cards
What is Hemidesmosomes (junction)
•Join epithelial cells to basal lamina
•Involve integrins (transmembrane protein)
78
New cards
Cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
•Cadherins
\-•Anchors actin cells in one cell to another
\-•Role in suppressing epithelial tumor cells
•Integrins
\-•Interact with basal lamina (laminin and Type IV collagen) and extracellular matrix of connective tissue, affect cell movement and shape (transmembrane proteins attach epithelial cell to a structure in connective tissue
\-•Anchors actin cells in one cell to another
\-•Role in suppressing epithelial tumor cells
•Integrins
\-•Interact with basal lamina (laminin and Type IV collagen) and extracellular matrix of connective tissue, affect cell movement and shape (transmembrane proteins attach epithelial cell to a structure in connective tissue
79
New cards
How do things get into the epithelial
go through the cell
80
New cards
Gap junctions
•Forms small diffusion channel (connexon) between adjacent cells (important for nerve or cardiac cells)
•Allow signaling molecules to pass through from one cell to the next
81
New cards
Specializations of Free Surface Cilia:
•Cilia: Move mucus & other substances
\-•Primarily found in trachea, bronchi, oviduct (contribute a lot to the respiratory system) (if the mucous is not removed then it can cause issues and blockage)
•Microvilli: Increase surface area (looks like a brush) (absorption)
\-•Brush border of kidney tubule cell
\-•Striated border of intestinal absorptive cell
•Stereocilia (long microvilli)
\-•Only in epididymis (male reproductive system) and sensory (hair) cells of inner ear
\-•Primarily found in trachea, bronchi, oviduct (contribute a lot to the respiratory system) (if the mucous is not removed then it can cause issues and blockage)
•Microvilli: Increase surface area (looks like a brush) (absorption)
\-•Brush border of kidney tubule cell
\-•Striated border of intestinal absorptive cell
•Stereocilia (long microvilli)
\-•Only in epididymis (male reproductive system) and sensory (hair) cells of inner ear
82
New cards
what does Microvilli have in it
Microvilli is a piece of tissue that flops down and has a skeletal component, which is actin filaments, which are anchored down by tied to the cytoskeleton
83
New cards
what is the terminal web
The group of actin filaments that runs underneath the surface of an epithelial cell where the microvilli is
84
New cards
A glands is a _____ and if it is a __ __it will have the same__ *_____*
epithelia and characteristics
85
New cards
What are the two types of epithelia
covering and glandular
86
New cards
Simple Squamous Epithelium characteristics
•Single layer
•Flat shape
•Allow active and passive movement of substances (gases, fluids, etc.) through tissue
\-happens in areas like lungs where alveoli exchange air with blood vessels
87
New cards
Simple Squamous Epithelium special names
•Endothelium (internal lining of heart and blood vessels)
•Mesothelium (internal lining of ventral body cavities)- heart or lung or reproductive cavity
88
New cards
What is Simple Cuboidal Epithelium characteristics
•Single layer
•Cube or hexagonal shape
•Secretions (e.g. tears), absorption (water)
-seen in the eye, kidney or gut
89
New cards
Simple Columnar Epithelium characteristics
•Single layer
•Tall and cylindrical shape
- Protective, secretion and absorption
90
New cards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium characteristics
•Multiple layers
•superficial layers flat
•deeper layers more cuboidal, deepest have continuous cell division
\-top layer is flat but is more cuboidal the deeper you go
\-the deeper cells are cuboidal cells are the progenitor cells (they divide and one moves up to the surface and becomes flat)
•superficial layers flat
•deeper layers more cuboidal, deepest have continuous cell division
\-top layer is flat but is more cuboidal the deeper you go
\-the deeper cells are cuboidal cells are the progenitor cells (they divide and one moves up to the surface and becomes flat)
91
New cards
Types of Stratified Squamous Epithelium
•Keratinized, cornified, dry (tough, water-resistant)- (outer layer of skin)
\-Non-keratinized, non-cornified, wet- (protection and make a barrier) (seen in mouth)
\-Non-keratinized, non-cornified, wet- (protection and make a barrier) (seen in mouth)
92
New cards
Simple Columnar Epithelium types
•Ciliated: Moves mucous and other substances (find mostly in airways)
•Non-ciliated
•Goblet cells (secrete mucus) (gland)
-Absorptive cells (have microvilli
•Non-ciliated
•Goblet cells (secrete mucus) (gland)
-Absorptive cells (have microvilli
93
New cards
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium characteristics
•Columnar
•Appears to be multiple layers but is not
•All cells attached to basement membrane
•Some cells do not reach free surface
•Secrete or may be ciliated
•Seen mostly in upper respiratory system
(it is fake because all the layers are attached to the basement membrane and do not make it to the surface)
94
New cards
Transitional Epithelium characteristics
•Special stratified epithelium that lines pelvis of kidney, ureters, urinary bladder and part of urethra
•Cells change shape according to the degree of distension of the organ.
95
New cards
Exocrine gland characteristics
•Secrete into ducts (open into an epithelium)
•Usually are divided into lobes and lobules
96
New cards
endocrine gland characteristics
•Ductless
•Secrete into extracellular fluids, diffuse into blood
-secrete typically hormones and secrete fluids into the bloodstream
97
New cards
exocrine glands
When an epithelium gland grows down and protrudes deeper in the connective tissue and hollows out and creates a duct then creates a secretory portion EX: sweat gland
98
New cards
endocrine gland
When an epithelium gland grows down and protrudes deeper in the connective tissue and the connecting tissue dies and the epithelial cells are deeper into the connective tissue and become invaded by blood vessels
99
New cards
What important action does the pancreas do
exocirne- the epithelial cells form acini that secrete digestive enzymes into the pancreatic duct
endocrine- the epithelial cell form a second type of gland that secretes into the blood called pancreatic islets
endocrine- the epithelial cell form a second type of gland that secretes into the blood called pancreatic islets
100
New cards
When you have an endocrine gland what are you more likely to have
blood vessels