4.5 Species and taxonomy
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is a species?
A group of organisms that can (interbreed to) produce fertile offspring
Suggest why 2 different species are unable to produce fertile offspring
● Different species have different chromosome numbers → offspring may have odd chromosome number
● So homologous pairs cannot form → meiosis cannot occur to produce gametes
Explain why courtship behaviour is a necessary precursor to successful mating
● Allows recognition of members of same species → so fertile offspring produced
● Allows recognition / attraction of opposite sex
● Stimulates / synchronises mating / production / release of gametes
● Indicates sexual maturity / fertility
● Establishes a pair bond to raise young
Describe a phylogenetic classification system
● Species (attempted to be) arranged into groups, called taxa, based on their evolutionary origins (common ancestors) and relationships
● Uses a hierarchy:
○ Smaller groups are placed within larger groups
○ No overlap between groups
Name the taxa in the hierarchy of classification
1. Domain (largest / broadest)
2. Kingdom
3. Phylum
4. Class
5. Order
6. Family
7. Genus
8. Species (smallest)
How is each species universally identified?
A binomial consisting of the name of its genus and species, eg. Homo sapiens
Suggest an advantage of binomial naming
Universal so no confusion as many organisms have more than one common name.
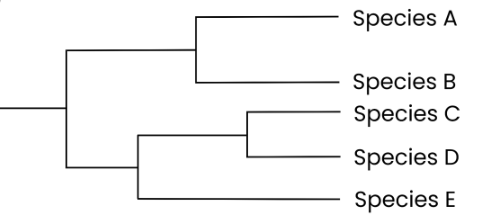
How can phylogenetic trees be interpreted?
● Branch point = common ancestor
● Branch = evolutionary path
● If two species have a more recent common ancestor, they are more closely related (eg. C & D)
Describe two advances that have helped to clarify evolutionary
relationships between organisms
1. Advances in genomesequencing → allowing
comparison of DNA base sequences
● More differences in DNA base sequences → more distantly related / earlier common ancestor
● As mutations (change in DNA base sequences) build up over time
2. Advances in immunology → allowing comparison of protein
tertiary structure (eg. albumin)
● Higher amount of protein from one species binds to antibody against the same protein from another species → more closely related / more recent common ancestor
● As indicates a similar amino acid sequence and tertiary structure
● So less time for mutations to build up