Muscular System Test Review
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
5 major functions of muscular system
Produce movement
Maintain posture
Stabilize joints
Generate heat
Guard opening
Excitability
ability to receive and respond to a stimulus (1st property)
Contractility
ability to shorten with force when stimulated (2nd property)
Extensibility
ability to stretched out or extended (3rd property)
Elasticity
ability of muscle fiber to return to its original or resting length (4th property)
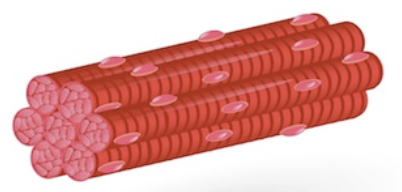
Skeletal
voluntary; striated (multinucleai); attached to bones
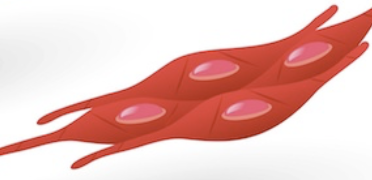
Smooth
involuntary; not started; hollow organs
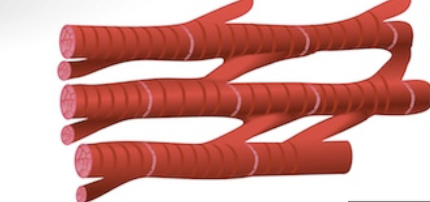
Cardiac
involuntary; striated; heart
Levels of organization
actin + myosin filaments, sarcomere, myofibril, muscle fiber, muscle fascicle, skeletal muscle
Insertion
bone that moves during contraction
Origin
bone that stays still during contraction
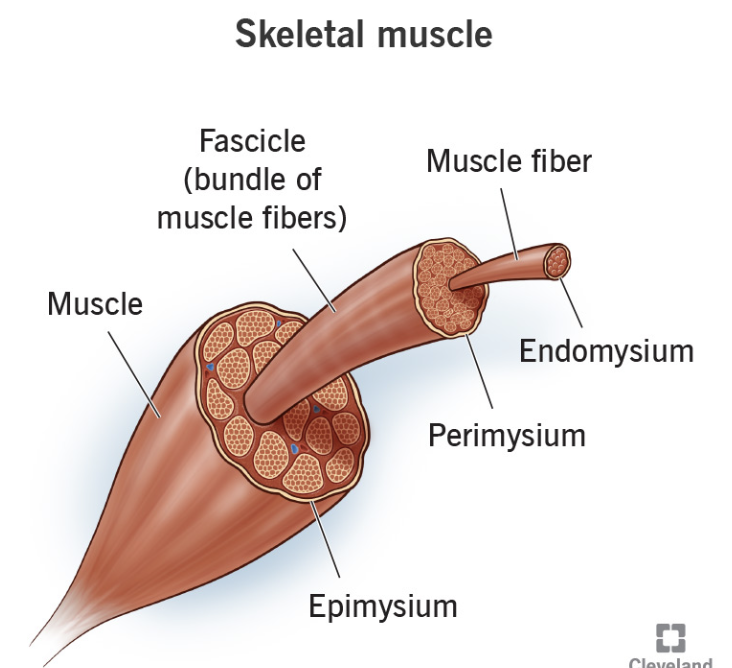
Epimysium
covers skeletal muscle
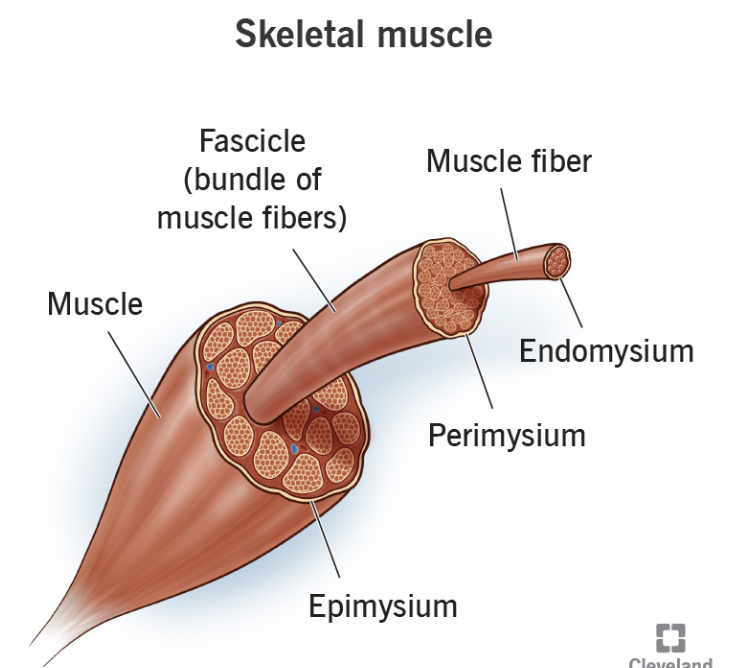
Perimysium
covers fascicle (bundles) of fibers
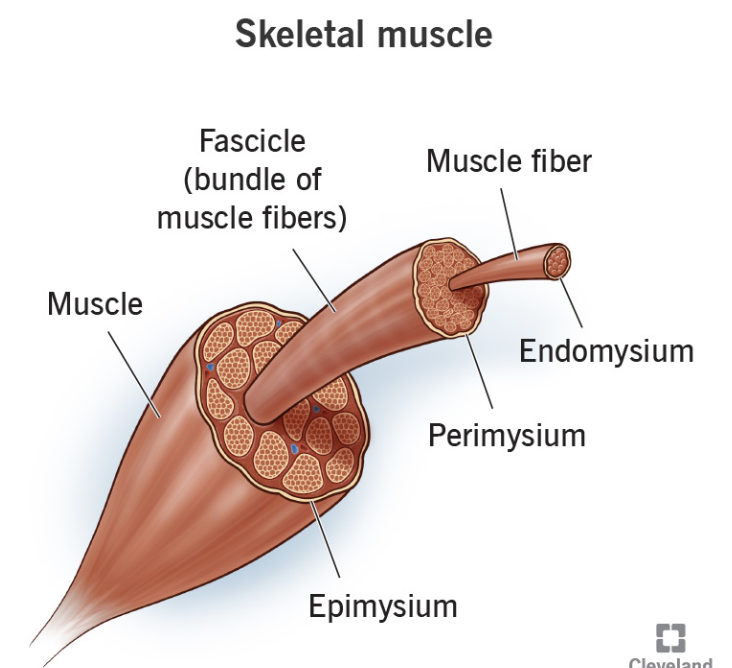
Endomysium
around single muscle fiber
What is a neuromuscular junction?
Where a motor neuron and skeletal muscle fiber communicate
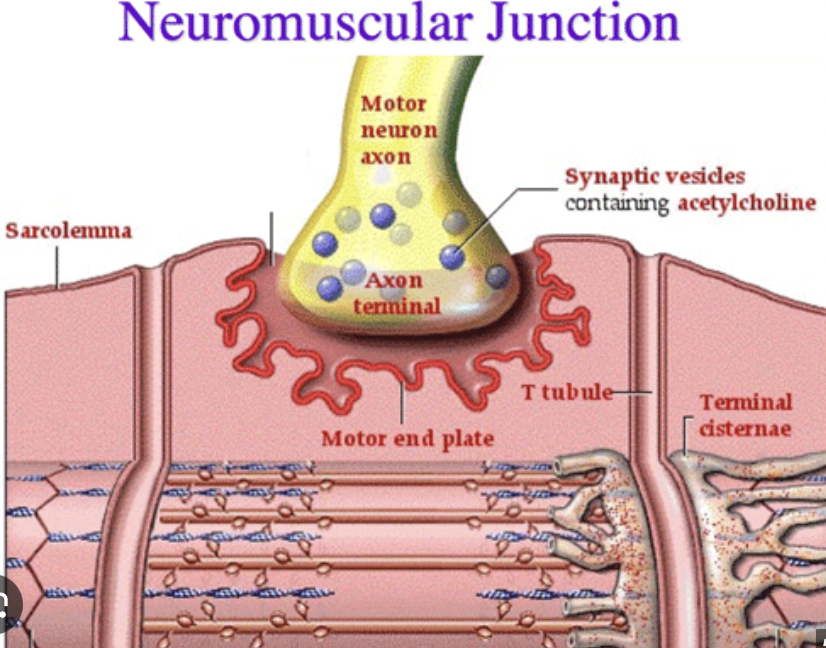
What is a motor unit?
the basic "on/off" switch for muscle movement; consisting of one motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls
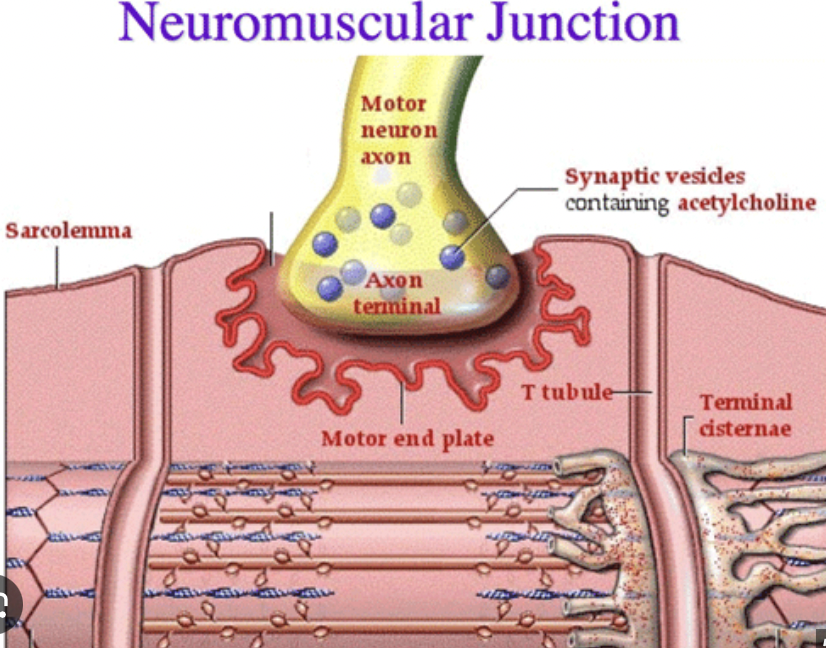
Axon Terminal
end of the motor neuron
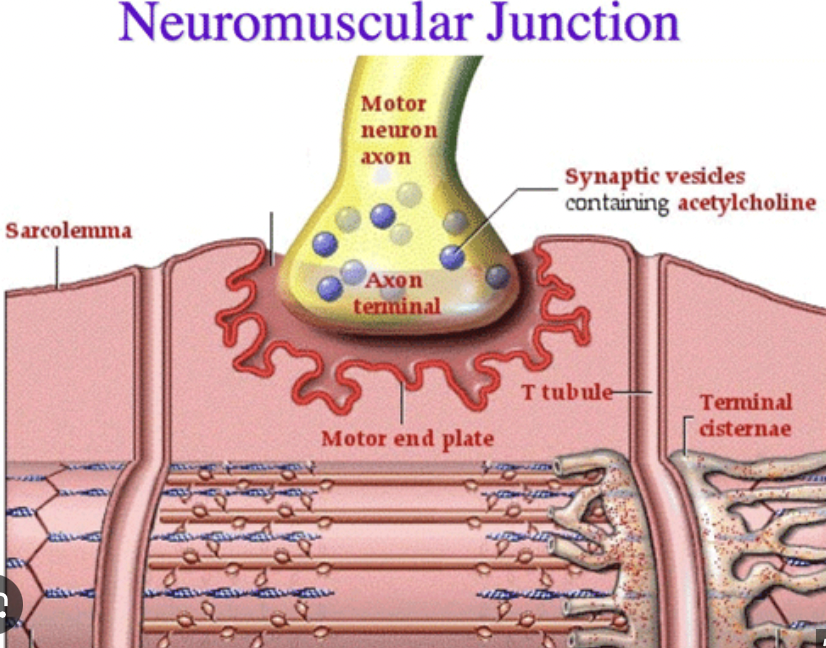
Synapse
the space between neuron + muscle
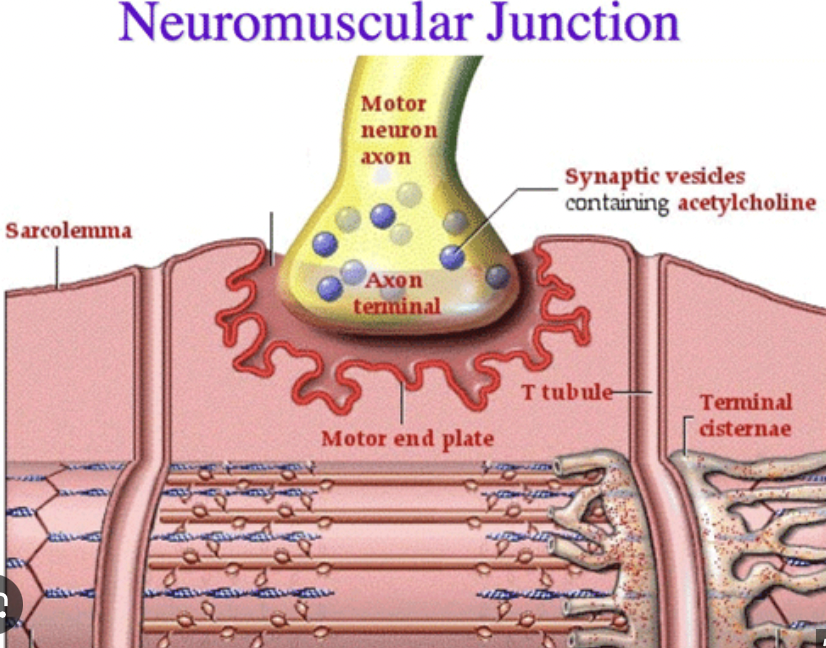
Synaptic Vesicle
Vesicles hold acetylcholine
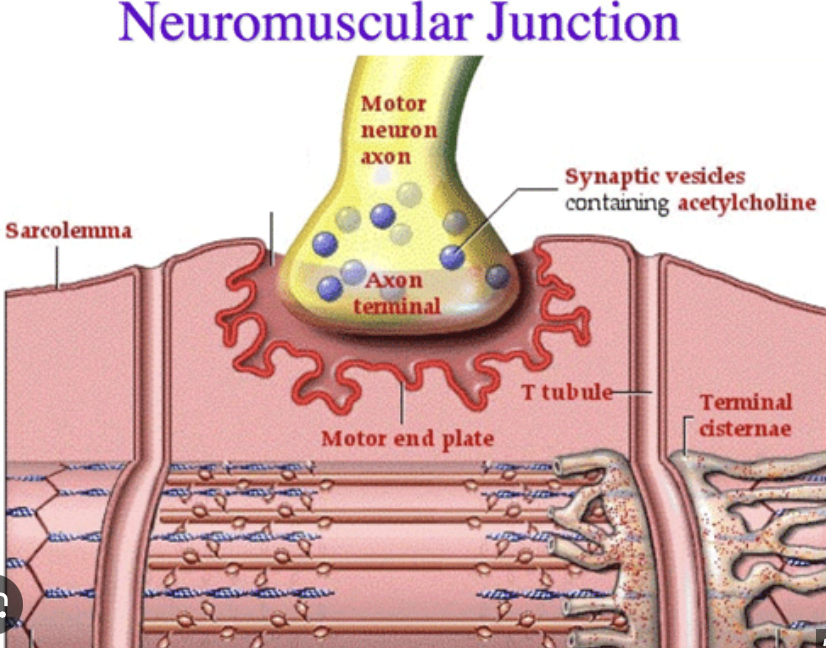
Muscle Fiber
muscle cell
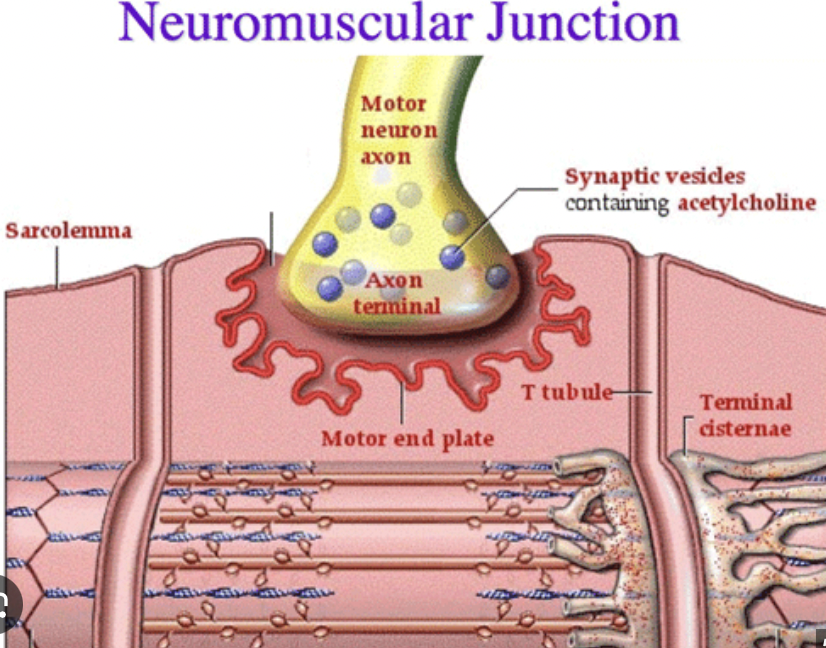
Step 1: An action potential (an impulse from the brain) makes its way down a motor neuron to an axon terminal. This will cause what neurotransmitter to be released from the synaptic vesicles into the synapse…
acetylcholine (Ach)
Step 2: As the action potential travels down the sarcolemma and T-Tubules, this will be released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum…
Ca 2+ (calcium)
Step 3: Once Ca2+ has entered the sarcoplasm, it will bind with…
troponin
Step 4: Once Ca2+ bind with troponin, troponin will change shape causing what protein to also change shape and “move”…
tropomyosin
Step 5: When troponin and tropomyosin change shape, what can myosin form with action?
cross bridge
Step 6: Myosin will now side action towards the M-line, this is called a…
powerstroke
Step 7: If these two things are still present, this cycle will repeat itself
Ca 2+ (calcium) and ATP
Cube-shaped bones that contain mostly spongy bone are called
short bones
Bone-destroying cells known as osteoclasts are activated by the hormone…
parathyroid hormone
What kind of tissue is the forerunner of long bones in the embryo?
hyaline cartilage
There are four stages in the healing of a bone fracture.
hematoma formation, fibrocartilage callus formation, bony callus formation, bone remodeling