CH8 - Bacteriology
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hflajkdfhalsjkdhflakjdfj
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Define “Bacteriology”
A branch of microbiology dealing with the identification, study, and cultivation of bacteria and with their applications in medicine, agriculture, industry, and biotechnology.
What are the general characteristics of bacteria?
Unicellular
Prokaryotic
Smallest free-living organisms
Some are spore-forming and considered the hardiest microorganisms.
Define “Unicellular“
No nuclear membrane and true nucleus
Define “Prokaryotic“
Does not have mitochondria (no powerhouse :C)
What two things does it mean when something is the smallest free-living organism?
No host needed
Present everywhere
What does it mean when something is spore-forming, and considered the hardiest organism?
Spore-forming.
Extra armor against heat, cold, toxic chemicals, and even nuclear radiation.
What are the structural components of bacteria? (8)
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Nucleoid
Plasmid
Capsule
Pilus/Pili
Flagellum/flagella
Fimbriae
What is the cell wall?
The superficial layer above the cell membrane
What is the cell membrane?
Plasma membrane made up of phospholipids and proteins
What is the nucleoid?
A bacterial chromosome; single circular piece of DNA
What is the plasmid?
Extra-chromosomal DNA
What is the capsule?
The protective later superficial to the cell wall
What is pilus/pili?
Used for attachment and genetic exchange (those exterior hairs)
What is flagellum/flagella?
Used for locomotion (propulsion tails)
If the flagellum/flagella is on one side of the cell, then it is?
Lophotrichous
If the flagellum/flagella is only one tail, then it is?
Polar
If the flagellum/flagella is all over the cell, then it is?
Pertrichous
What is fimbriae?
Non-flagellar; used to adhere/stick bacterial cells to one another
How are bacteria classified?
By General Morphology (shape), and by Cell-Wall Structure)
In shape classification, cocci consists of?
Clusters, chains, pairs, tetrads
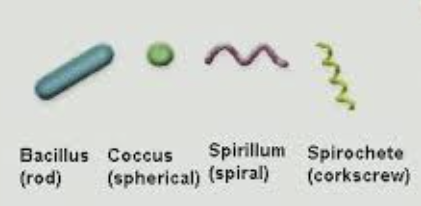
In shape classification, bacilli consists of?
(Pleomorphic) Cylindrical, coccobacilli, fusiform, palisading
In shape classification, spirochetes consist of?
External, rigid spirals
In shape classification, spirilla consist of?
Internal, flexible spirals
Define “pleomorphic“
Can come in many shapes and sizes
What defines the Gram-positive classification?
Thick peptidoglycan layer
What defines the Gram-negative classification?
Thin peptidoglycan layer
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
What defines the Acid-fast classification?
Has peptidoglycan layer
Mycolic acid, hydrophobic molecule
What defines the Cell Wall Deficient classification?
Has no cell wall
Gram stain is used in the lab for?
Differentiates bacteria into gram-positive and gram-negative, cocci or bacilli.
Acid-fast stain is used in the lab for?
Primarily used to identify mycobacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and certain other bacteria with waxy cell walls.
What is an endotoxin?
A cell wall component that acts as a toxin
What is an exotoxin?
Toxic substances secreted by bacterial cells
Define “Invasiveness”
Some bacteria are able to enter deep into tissues by disrupting cell membranes and tissue matrix.
Define “Genetic Recombination“
Bacteria are able to accomplish horizontal exchange of genes.
This way, virulence genes can be transferred between different species.
In genetic recombination, what is Transformation?
The uptake and incorporation of naked DNA into a bacterial cell.
In genetic recombination, what is Transduction?
The transfer of bacterial genes by a bacteriophage (virus-infected bacterium) from one cell to another
In genetic recombination, what is Conjugation?
The transfer of genetic material from a donor bacterial strain to a recipient strain
What is Antibiotic Resistance?
A natural consequence of drug exposure and result from the use and overuse of antimicrobial agents
In gram staining, gram positive cocci is colored?
Blue/Dark purple
In gram staining, gram negative cocci is colored?
Red/Pink
In gram staining, gram positive bacilli is colored?
Blue
In gram staining, gram negative bacilli is colored?
Pink
In gram staining, Crystal violet serves as?
Primary stain
In gram staining, Gram’s iodine serves as?
Mordant (dye fixative)
In gram staining, acetone alcohol serves as?
Decolorizer
In gram staining, safranin serves as?
Counter stain
In acid-fast staining, what color is carbolfuchsin?
Red
In acid-fast staining, what is acid-alcohol for?
Differentiation reagent
In acid-fast staining, what color is Methylene blue?
…blue.
What can acid-fast staining be used for in detecting?
Can be used to detect acid-fast bacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis
In acid-fast staining, what is the color of acid-fast bacteria?
Pink/red
In Bacteriology lab procedures, what is Culture?
Specimens are inoculated onto artificial(agar) media and incubated to allow the growth of bacteria.
The bacteria are then identified through biochemical tests.
In Bacteriology lab procedures, what are Susceptibility Tests?
Bacteria are tested against antibiotics to determine which antibiotic is most effective for therapy