Monosaccharides
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1
New cards
What are monosaccharides?
Monomers
2
New cards
What are monosaccharides classified by?
The number of carbons they possess.
3
New cards
What are three-carbon sugars called?
Trioses.
4
New cards
What are five-carbon sugars called?
Pentoses (e.g., deoxyribose, ribose).
5
New cards
What are six-carbon sugars called?
Hexoses (e.g., glucose, galactose, fructose).
6
New cards
What is the typical structure of monosaccharides?
Mostly ring structures, all attached to -OH group, one carbon atom usually outside the ring.
7
New cards
What is the ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in monosaccharides?
1:2:1.
8
New cards
What function do monosaccharides serve in the blood?
Easily transported, dissolving in plasma.
9
New cards
What energy-related function do monosaccharides fulfill?
Transfers and stores energy.
10
New cards
What can result from storing large quantities of monosaccharides in cells?
Osmotic problems.
11
New cards
What do monosaccharides build?
More complex molecules
12
New cards
What are the two isomers of glucose?
Alpha (a) D-Glucose and beta (B) D-Glucose.
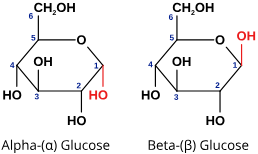
13
New cards
Why is glucose described as polar and hydrophilic?
It is soluble in aqueous solutions.
14
New cards
What do monosaccharides have that makes them very stable?
Strong covalent bonds.
15
New cards
What happens to glucose when it is oxidized during cellular respiration?
It gives out energy.