runestone academy ap csp unit 4
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
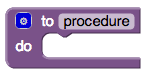
procedure
\-named group of programming instructions that may have parameters/return values
\-referred to by different names (method or function) depending on the programming language.
\-referred to by different names (method or function) depending on the programming language.
2
New cards
for-each counting loop
block that repeatedly processes one or more instructions until some condition is met

3
New cards
repeat until loop
\-Block that repeats its code until the boolean condition evaluates to true.
\-If the condition evaluates to true initially, the code is not executed at all
\-There can be an infinite loop if the ending condition never evaluates to true.
\-If the condition evaluates to true initially, the code is not executed at all
\-There can be an infinite loop if the ending condition never evaluates to true.

4
New cards
Logo
\-programming language invented in the 1960s by Seymour Papert
\-used to draw simple and complex geometric shapes.
\-used to draw simple and complex geometric shapes.
5
New cards
iterative thinking
thinking process of repeatedly processing a limited number of steps
6
New cards
step-wise refinement
thinking process of moving one small step at a time when developing a program
7
New cards
design thinking
\-iterative process
\-consists of understanding the user; challenging assumptions; & redefining problems to identify strategies/solutions that might not be instantly apparent
\-empathize, define, ideate, prototype, test
\-consists of understanding the user; challenging assumptions; & redefining problems to identify strategies/solutions that might not be instantly apparent
\-empathize, define, ideate, prototype, test
8
New cards
step 1 of design thinking (empathize)
investigating & understanding users to identify the program requirements through surveys, user testing, or interviews
9
New cards
step 2 of design thinking (define)
analyzing the problem & determining the program specifications
10
New cards
step 3 of design thinking (ideate)
brainstorming possible solutions through paper prototypes or making a list of ideas
11
New cards
step 4 of design thinking (prototype)
Creatively build simple solutions
12
New cards
step 5 of design thinking(test)
Evaluate the solutions
13
New cards
hypothesis
explanation that can be tested by experimentation written in if/then format
14
New cards
simulation
\-Mimics real-world events with the purpose of drawing inferences
\-Involves removing specific details/simplifying functionality.
-Facilitates the formulation & refinement of hypotheses related to the objects/phenomena under consideration.
\-Computer simulations usually make some simplifying assumptions about the real-world object being modeled.
\-Involves removing specific details/simplifying functionality.
-Facilitates the formulation & refinement of hypotheses related to the objects/phenomena under consideration.
\-Computer simulations usually make some simplifying assumptions about the real-world object being modeled.
15
New cards
randomness
\-lack of pattern/regularity
\-sequence of events has no order
\-sequence of events has no order
16
New cards
deterministic
process that is completely predictable
17
New cards
pseudo random number generator (PRNG)
-Algorithm that generates a series of numbers that appear to be random but are determined by it
-Simulation (abstraction) of real randomness
-Simulation (abstraction) of real randomness
18
New cards
seed
tells the PRNG where to begin in the sequence
19
New cards
pseudo random numbers
requires seed, mod, & formula
20
New cards
linear congruential generator (LCG)
-PRNG that uses a linear function
-Does not require much memory
-Does not require much memory
21
New cards
random event
-event that cannot be predicted with certainty
-i.e. flipping a fair coin, rolling a die, picking a card from a well shuffled deck.
-i.e. flipping a fair coin, rolling a die, picking a card from a well shuffled deck.
22
New cards
random block
block that gets pseudo-random numbers

23
New cards
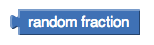
random fraction block
block that only generates values between 0 & 0.99
24
New cards
model
abstraction that provides a simplified representation of some object/phenomenon
25
New cards
fair coin
flipped coin that would come up heads 50% of the time over a large number of coin flips
26
New cards
modular arithmetic
-system of arithmetic for whole numbers in which the numbers “wrap around” upon reaching a certain value (the modulus)
-i.e. a 12-hour clock "wraps around" to 1 after 12
-i.e. a 12-hour clock "wraps around" to 1 after 12
27
New cards
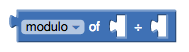
mod operator
returns the remainder when a number is divided by another
28
New cards
computing innovation
\-executes a program as a fundamental part of its function
\-i.e. picture editing software, self-driving car
\-i.e. picture editing software, self-driving car
29
New cards
data
-information formatted in a certain way
-i.e. text on paper, bytes stored electronically
-i.e. text on paper, bytes stored electronically
30
New cards
computing innovations w/ data
\-input
\-processing
\-storage
\-output
\-processing
\-storage
\-output
31
New cards
data privacy
assures that personal/corporate confidential information is collected, used, protected & destroyed legally & fairly
32
New cards
data security
controls access to personal information, protecting against its unauthorized use & acquisition
33
New cards
data storage
\-archives data
\-2 types of storage (hard data & remote data)
\-2 types of storage (hard data & remote data)
34
New cards
hard data
\-RAM
\-Hard Drive
\-flash drives
\-solid state
\-Hard Drive
\-flash drives
\-solid state
35
New cards
remote data
cloud computing
36
New cards
personally identifiable information (PII)
\-information about an individual that identifies, links, relates, is unique to, or describes them.
\-i.e. social security number, age, race, phone number(s)
\-i.e. social security number, age, race, phone number(s)
37
New cards
cookies
\-Small files or bits of data that are stored on your computer.
\-Placed when you access a site
\-Placed when you access a site