Conjunctiva, Cornea, Sclera, Limbus
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
where is the conjunctiva located?
covering the anterior sclera & inner eyelid
NOT ON CORNEA
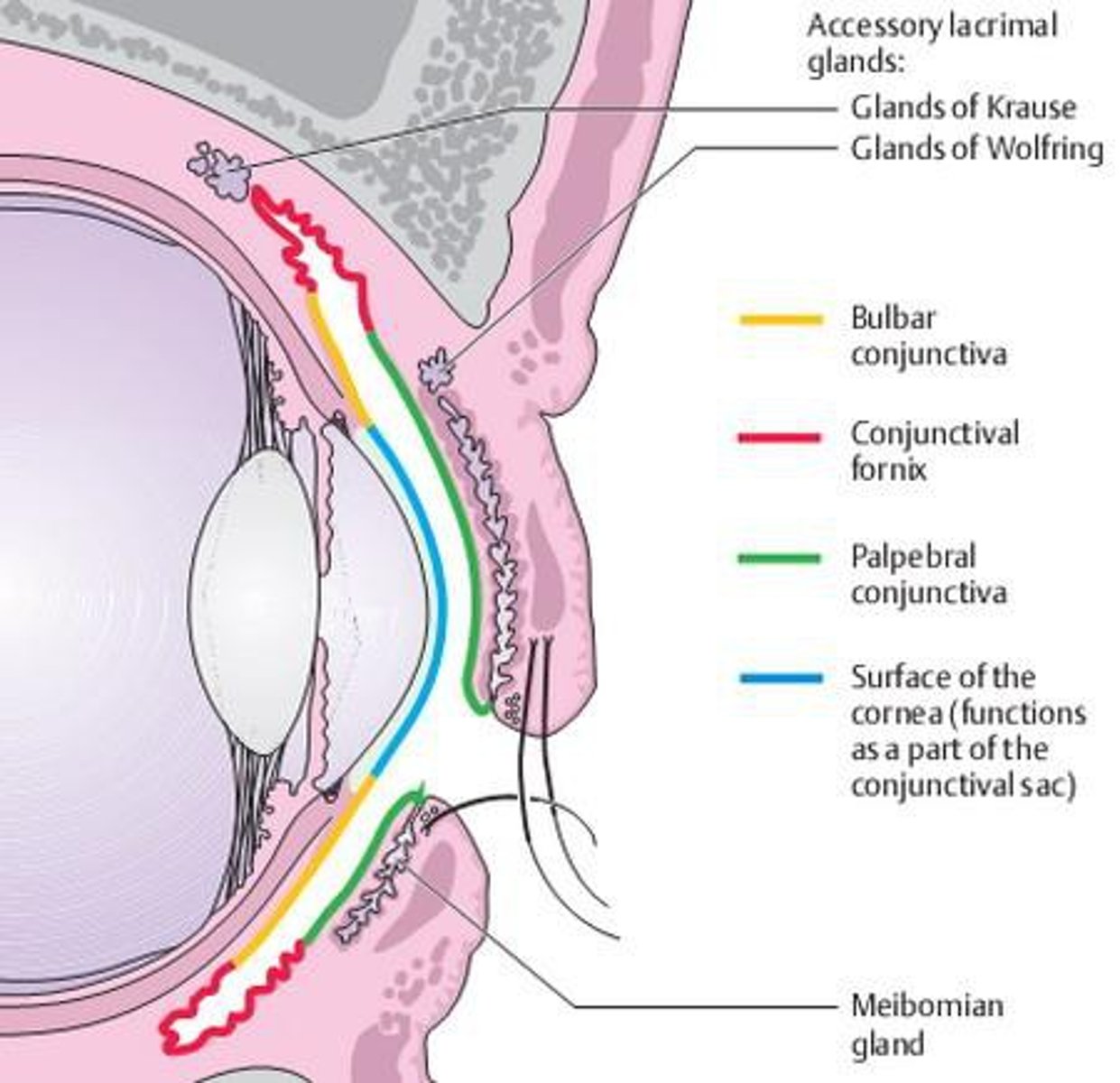
the conj can be broken into... (3)
bulbar, fornix, palpebral
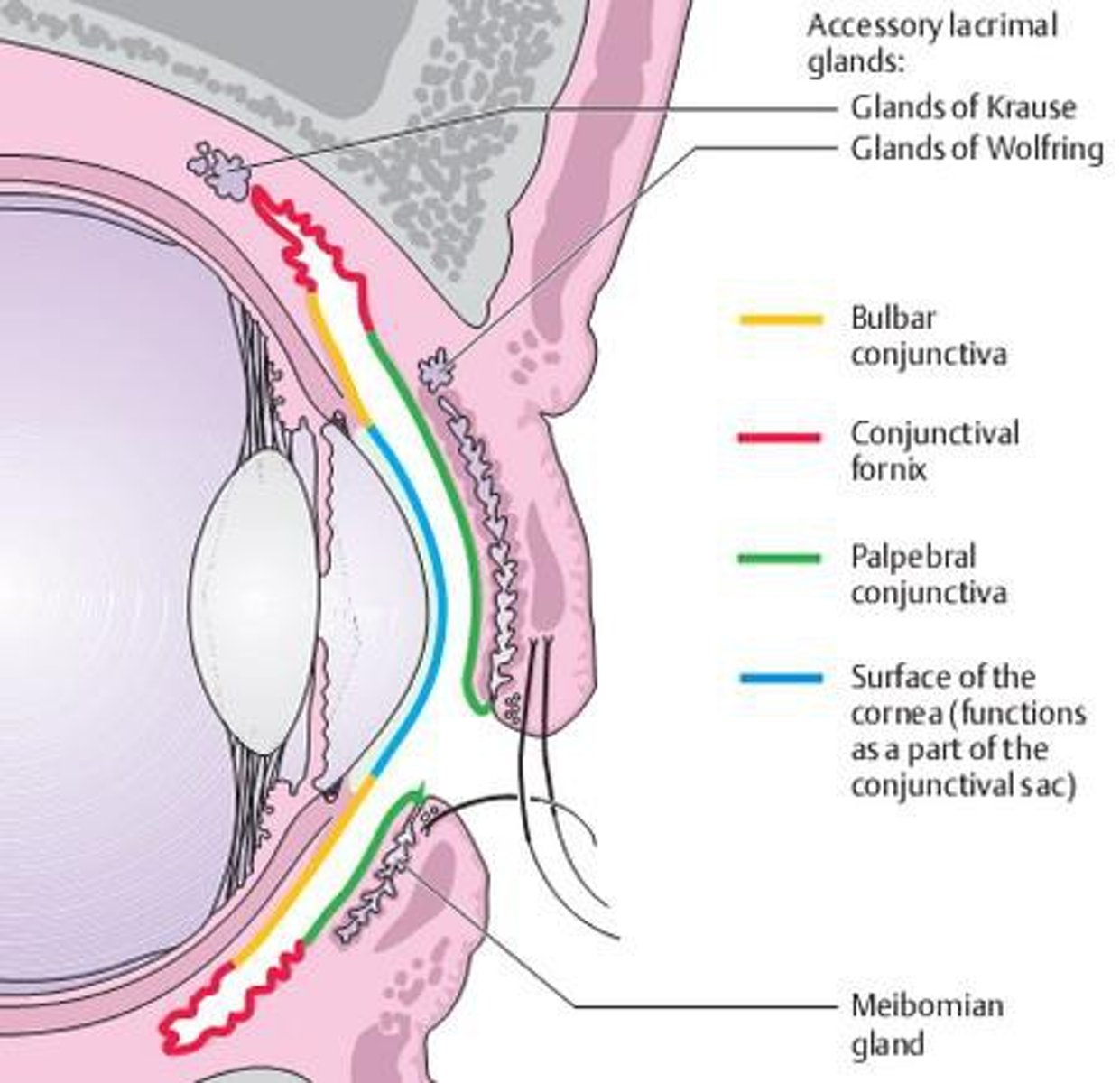
where is the palpebral conj located?
covering the inner eyelid
where is the bulbar conj located?
covering the sclera
where is the conjunctival fornix located
U-turn between the bulbar & palpebral conj
all conjunctiva is composed of an ____ layer and a _____ layer
epithelium & stroma
what cell is responsible for secretions in the conjunctiva?
goblet cells
the palpebral conj can be broken into...
marginal, tarsal, orbital
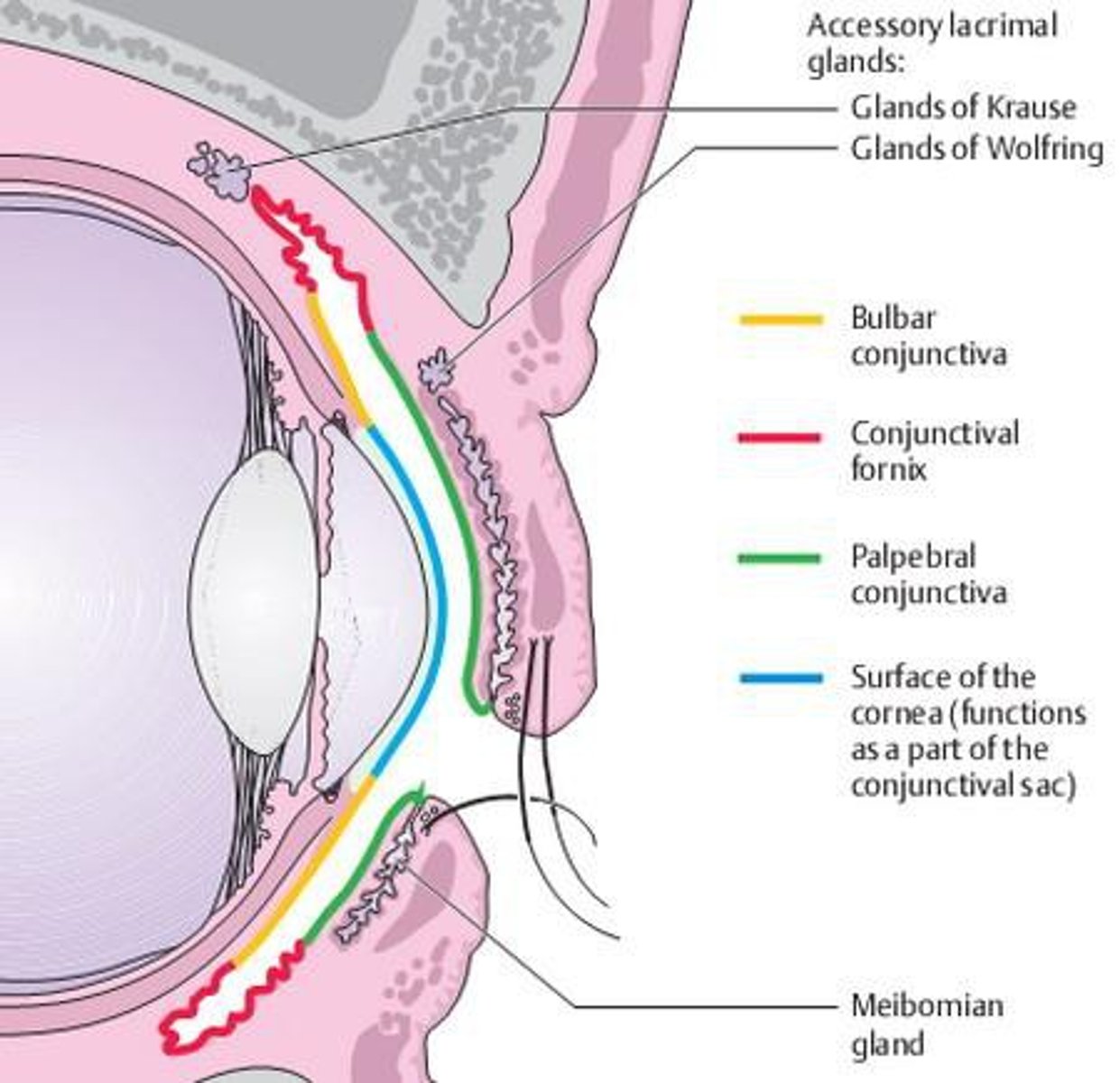
what type of epithelium is in the palpebral marginal conjunctiva?
stratified squamous
what type of epithelium is in the palpebral tarsal conjunctiva?
stratified columnar
what type of epithelium is in the palpebral orbital conjunctiva?
stratified colmnar
the conjunctiva is thickest at what portion?
fornix
what type of epithelium is in the conjunctival fornix?
stratified columnar
t or f: the conjunctival fornix is present superiorly, inferiorly, medially, and laterally
false, there is no fornix in the medial canthus, the plica semilunaris is there instead
the conj fornix is held in place by...
muscle fascia/aponeurosis
what type of epithelium is in the bulbar sclera conjunctiva?
stratified columnar
what type of epithelium is in the bulbar limbal conjunctiva?
stratified squamous
most common type of collagen
type I
collagen used for wound healing
type III
collagen found in basement membranes
type IV
collagen used for anchoring
type VII
what is the main cell junction found in conjunctival epithelium?
leaky tight junctions
t or f: melanocytes/melanin granules are present in the conjunctiva
true
t or f: conjunctival stem cells can be found in the conjunctiva epithelium
true
what is the difference between a cell with a high content of keratin vs melanin?
keratin - stability/structure to cells
melanin - protection from oxidative stress
unkeratinized conjunctival epithelium is directly continuous with... (3)3
corneal epithelium
eyelid epidermis (keratinized)
nasolacrimal drainage epithelium
goblet cells of the conjunctiva originate at _____
basal layer of epithelium
t or f: goblet cells are capable of merocrine, apocrine, and holocrin secretion
true (merocrine is most common)
where is the density of goblet cells greater: medial or lateral canthus?
medial
inflammation will __(increase/decrease)__ the number of goblet cells
increase
apical surface modification of conjunctival epithelium
microvilli & glycocalyx
the conjunctival stroma can be broken into what 2 layers?
outer adenoid & deep fibrous
what type of tissue makes up the conjunctival stroma?
loose CT
what components are present in the outer adenoid layer?
lymphocytes, APCs, lymphatic vessels, blood vessels, collagen type I
what components are present in the deep fibrous layer?
fibroblasts, collagen type I, lymphatic vessels, blood vessels,
few lymphocytes
pingueculae
raised, yellow thickening of the conj stroma
caused by cellular proliferation, deposition of hyaline, and elastotic degeneration
pterygium
triangle-shaped growth of the conj extending into the cornea
caused by degeneration of collagen and fibrovascular proliferation in stroma
t or f: both pingueculae and pterygium are disorders of the conjunctival stroma
true
what is the difference between crypts of Henle and microvilli in conjunctiva?
crypts - folds in epithelium AND stroma
microvilli - fold in epithelium
does the plica semilunaris contain both conj epithelium and stroma?
yes
third eyelid is also called...
nictitating membrane
where are the conjunctival blood vessels more numerous: the palpebral or bulbar portion?
palpebral
where are the conjunctival lymphatic vessels more numerous: the outer adenoid or deep fibrous layer?
outer adenoid
what immune cells do you expect to find the the conj stroma?
neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, dendritic cells
where are lymphoid cells more numerous: the palpebral or bulbar conjunctiva?
palpebral
t or f: conjunctival stroma contains lymphoid follicles that grow as we age
false, the lymphoid follicles get smaller as we age
all lymphatic vessels lead to...
the heart
circle of teichmann
smallest lymphatic vessels that encircle the cornea
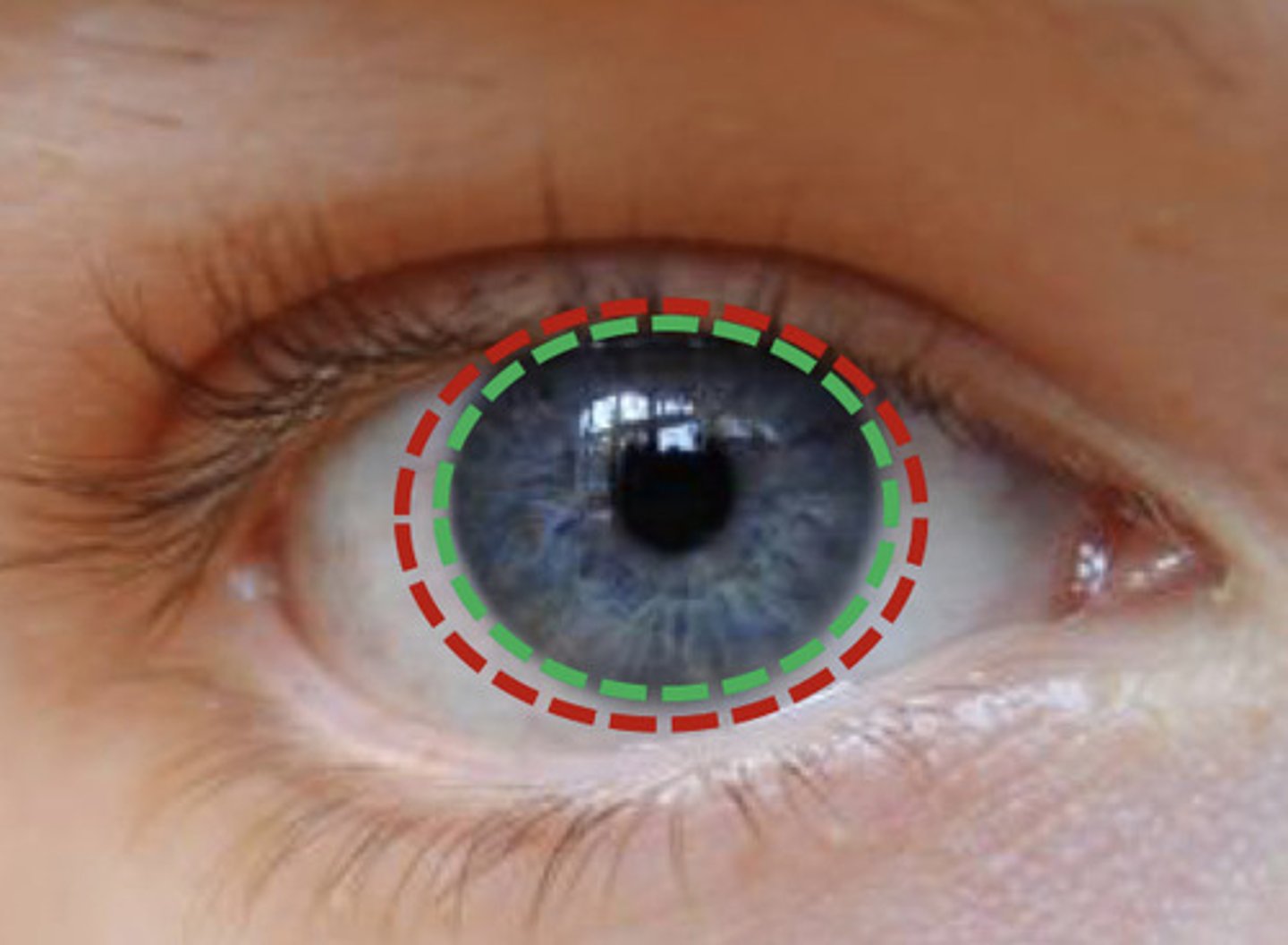
radial lymph vessels
peripheral to circle of teichmann
vessels are slightly bigger than the circle of t
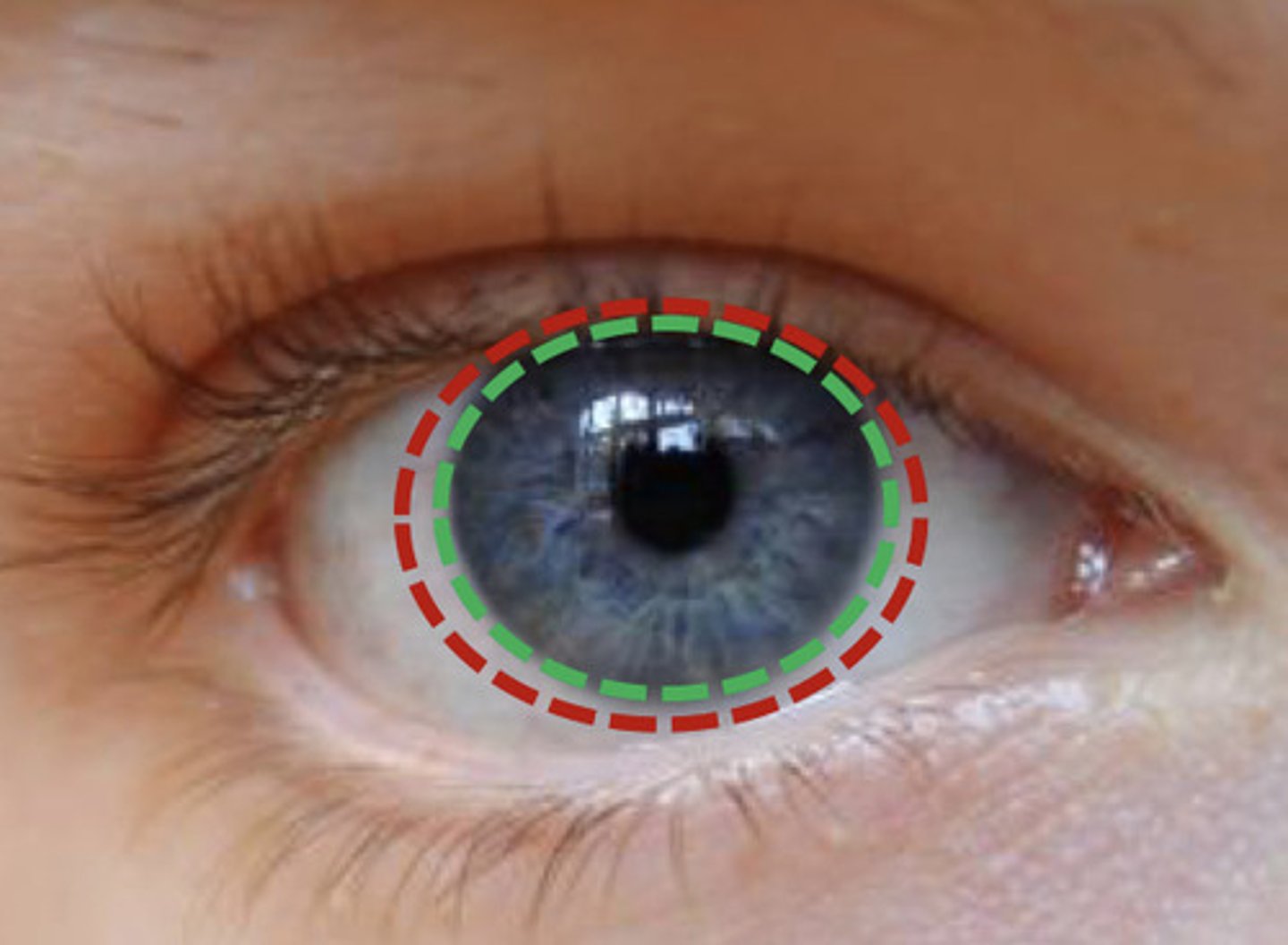
pericorneal lymphatic ring
largest lymphatic vessels circling the cornea
outwards from the limbus
peripheral to radial lymph vessels
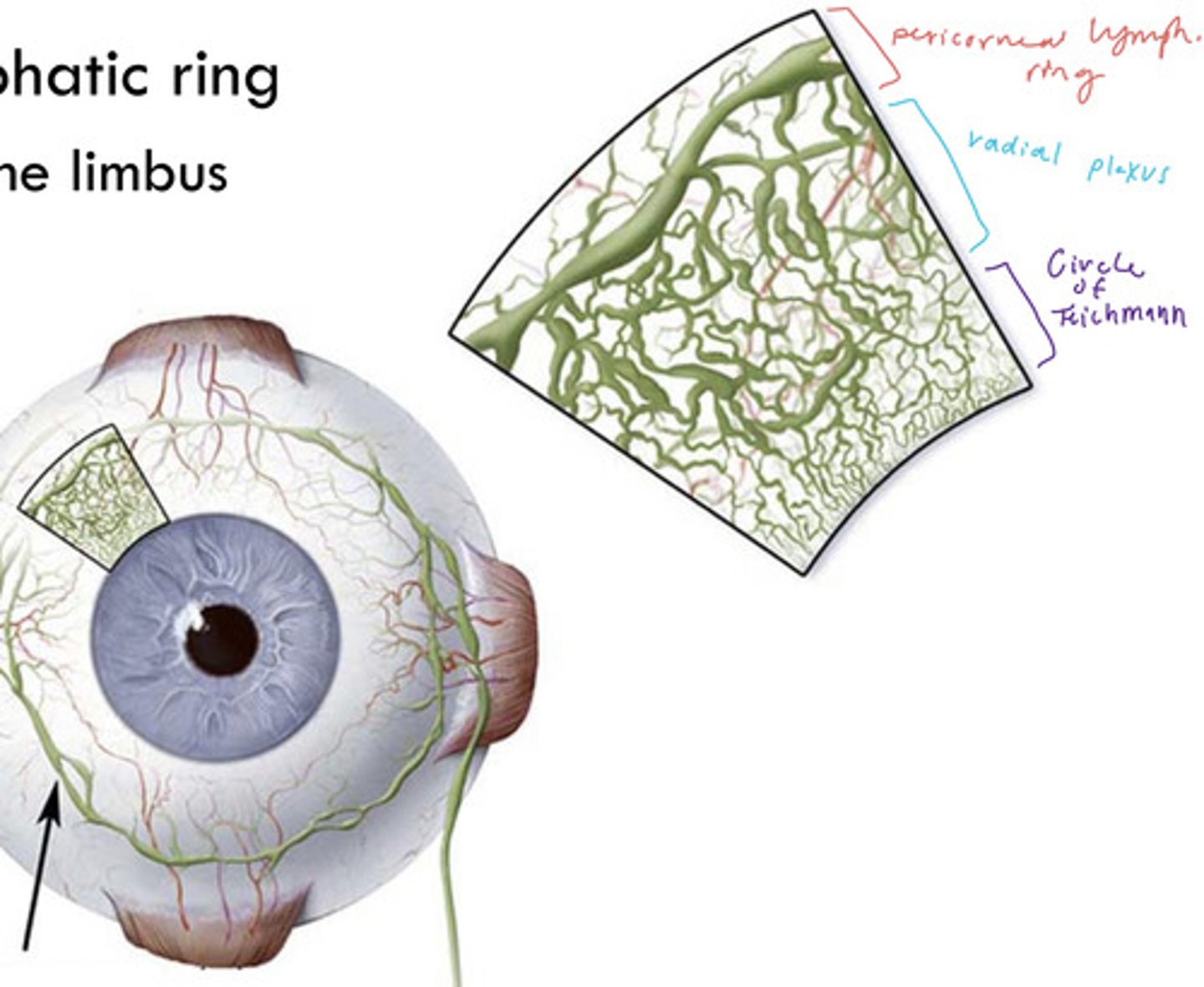
lymph flows from cornea -> ____ -> ____ -> ____ -> ____ -> ____ -> heart
circle of teichmann -> radial lymph vessels -> pericorneal lymphatic ring -> superficial parotid/submandibular nodes -> deep cervical lymph node
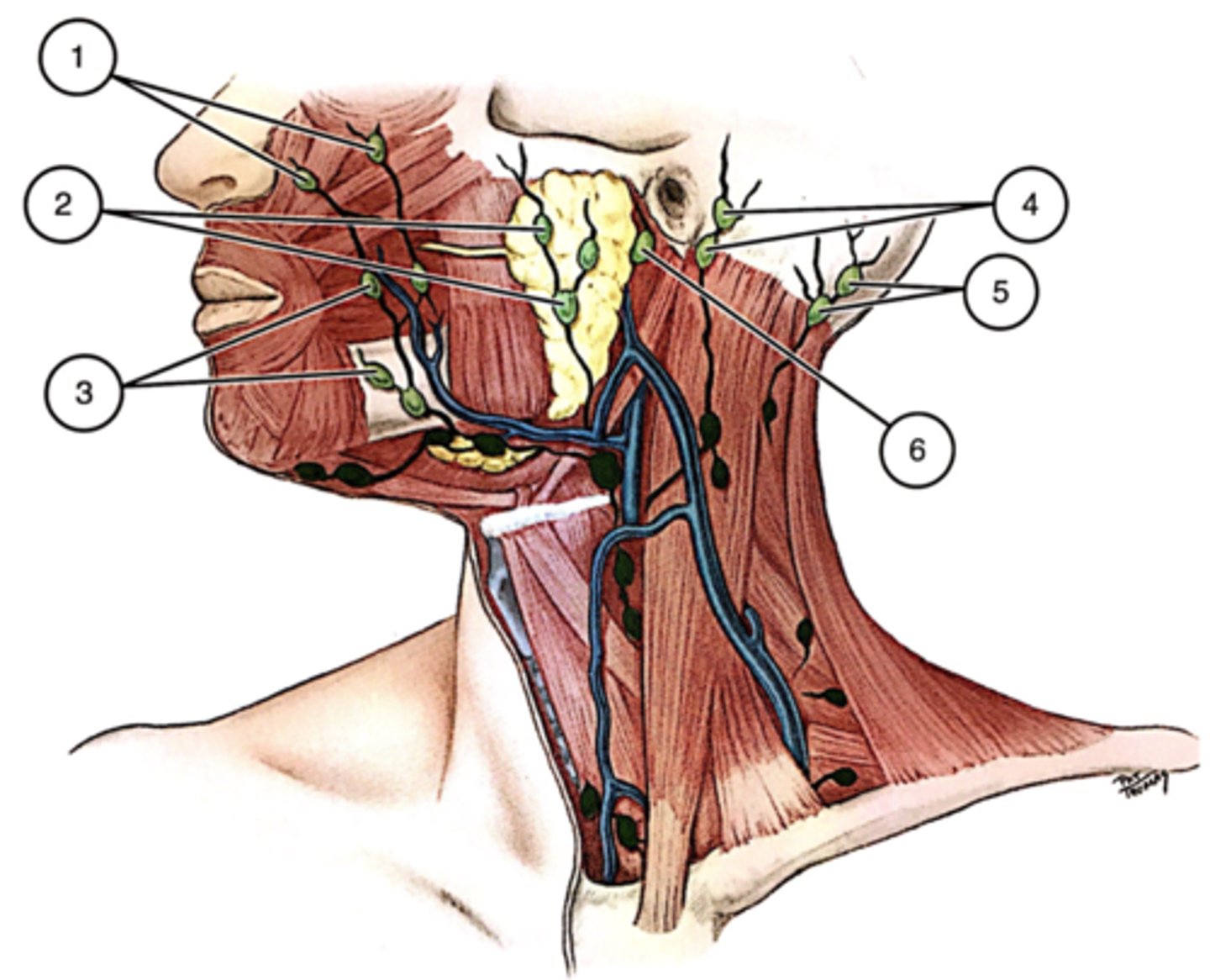
the parotid lymph nodes receive drainage from...
lateral lids & conj
the submandibular lymph nodes receive drainage from...
medial lids & conj
the deep cervical lymph node receives drainage from...
the parotid & submandibular lymph node
function of conjunctiva
prevent desiccation
increase mobility
provide a barrier against microorganisms and foreign bodies
inflammatory response from goblet cells
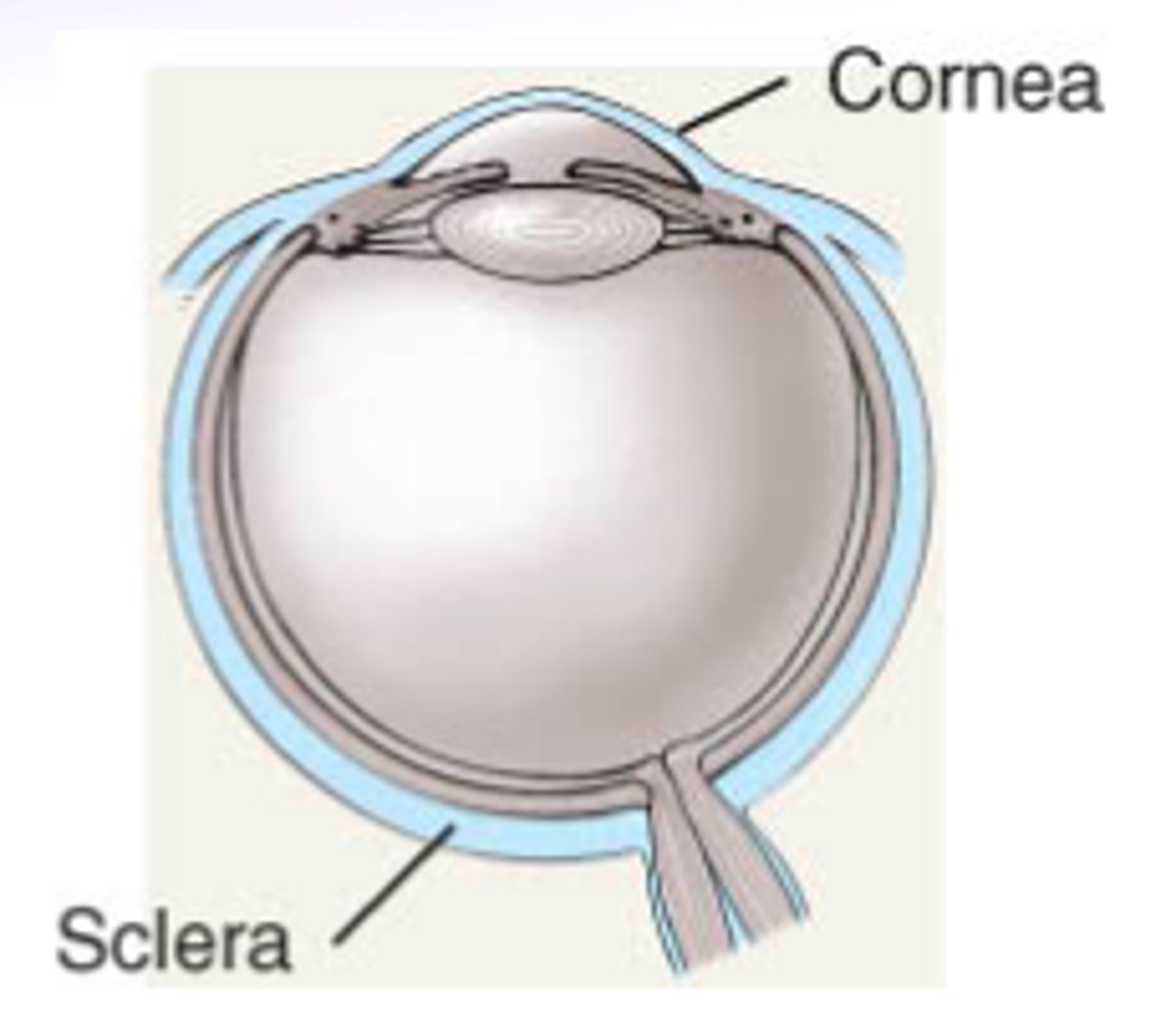
fibrous tunic
sclera + cornea
megalocornea
enlarged cornea
microcornea
small cornea
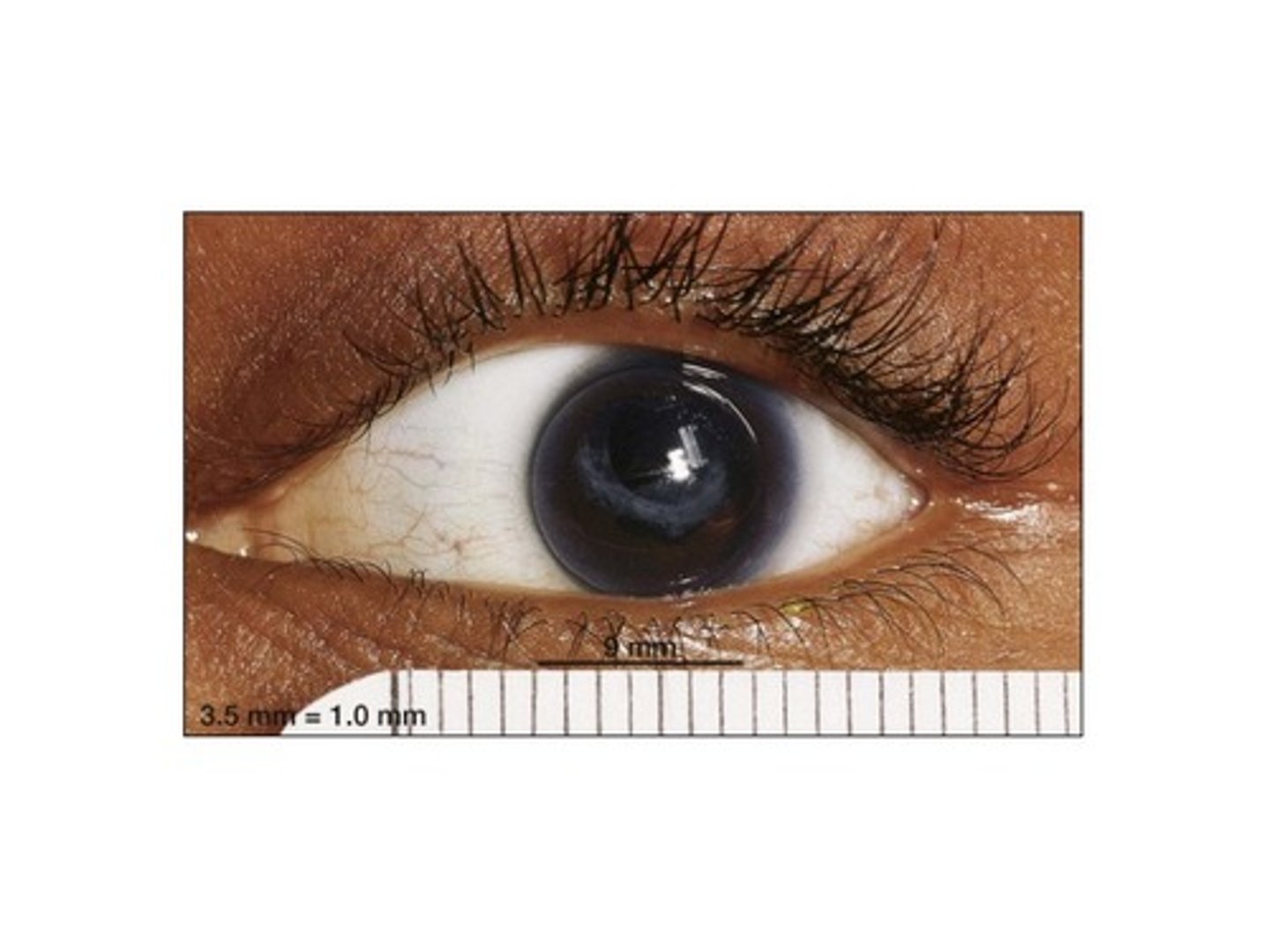
which is thicker: the central or peripheral cornea?
peripheral
which has a larger radius of curvature: the anterior or posterior surface of the cornea?
anterior
external scleral sulcus
junction between the cornea & sclera
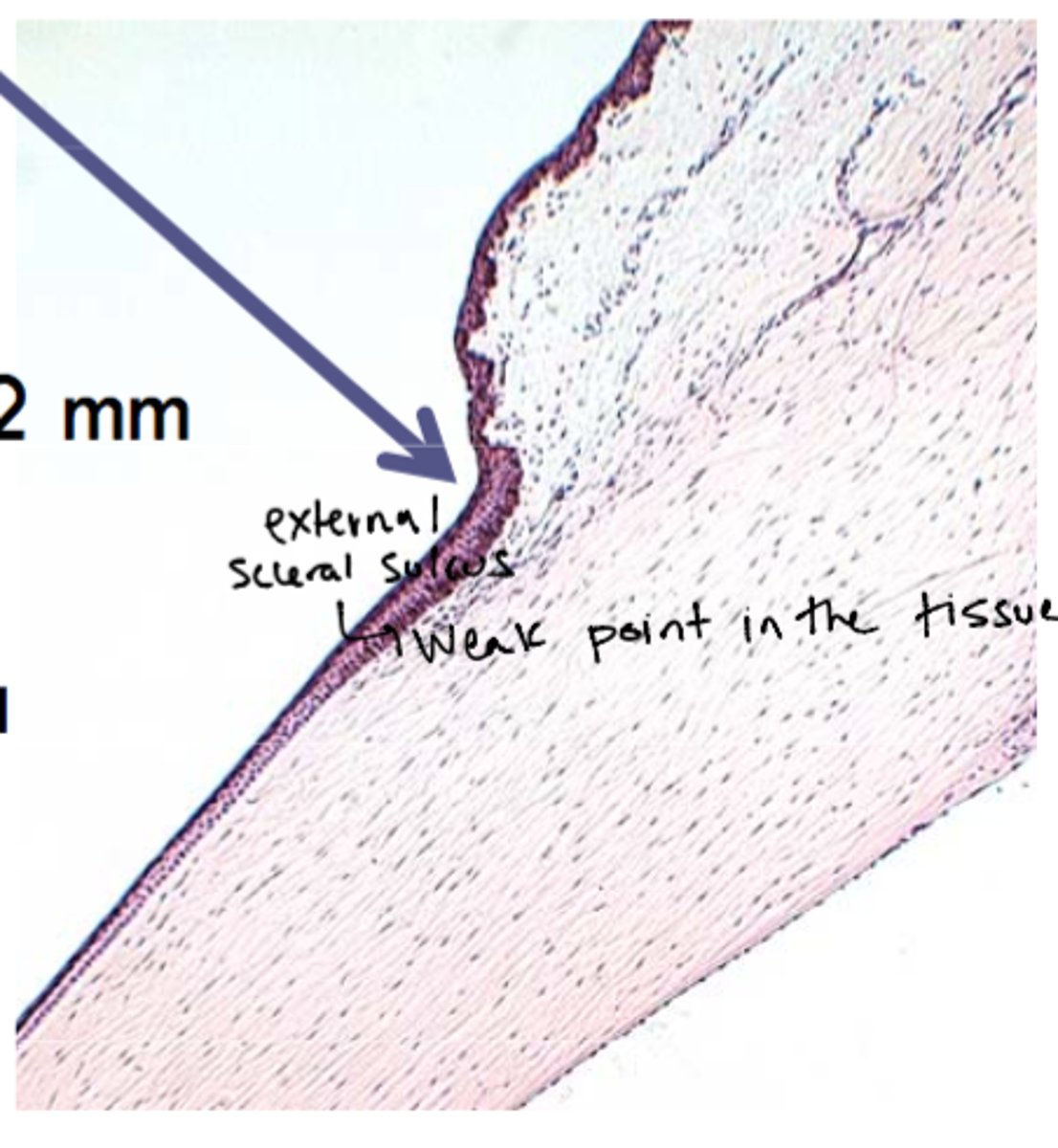
which has a larger radius of curvature: the cornea or sclera?
sclera
where does the cornea get most of its nutrients?
O2 mostly from environment/tears
all other nutrients from aqueous humor
5 layers of the cornea
epithelium
Bowman's membrane
stroma
Descemet's membrane
endothelium
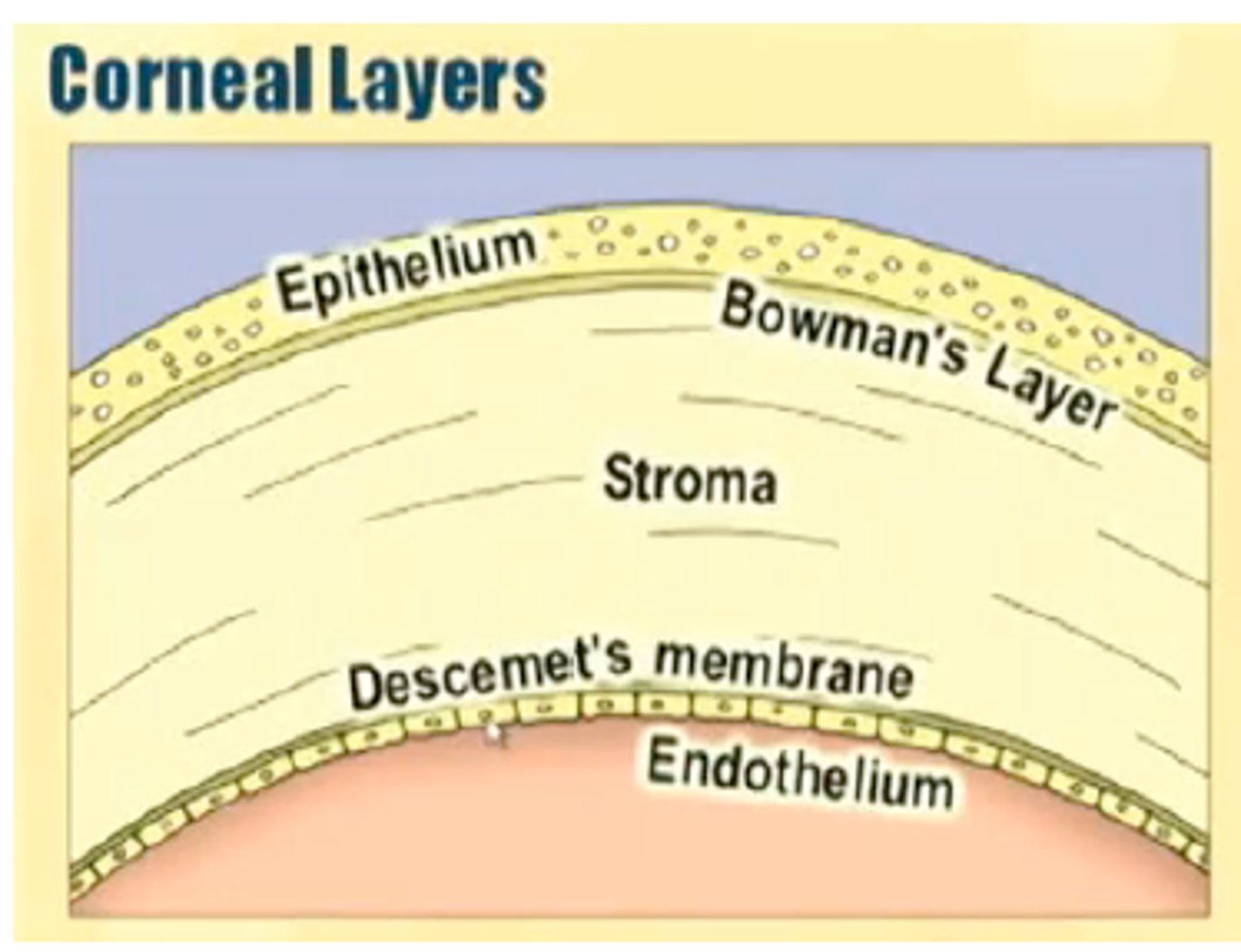
what type of tissue is corneal epithelium?
unkeratinized statified squamous
3 main cells types/layers of corneal epithelium
basal cells, wing cells, superficial cells
the basement membrane of corneal epithelium is made by...
basal cells
the basal cells are attached to the basement membrane by...
hemidesmosomes
how many layers of basal cells are in the corneal epithelium?
1
what is the shape of basal cells?
columnar
what junctions are between basal cells?
gap & desmosomes
the wings cells are attached to the basal cells by...
desmosomes
how many layers of wing cells are in the corneal epithelium?
2-3
what is the shape of wing cells?
polyhedral with wing-like projections
what junctions are between wing cells?
gap & desmosomes
how many layers of superficial cells are in the corneal epithelium?
2-3
what is the shape of superficial cells?
squamous
what junctions are between superficial cells?
desmosomes & complete tight junctions
as you move toward the apical surface of the corneal epithelium, the number of tight junctions _______ and the number of gap junctions _____
tight junctions increase
gap junctions decrease
corneal epithelial cells have 2 types of apical surface modification to increase their surface area. what are they?
microvilli & microplicae
which tissues have a mucin glycocalyx?
conj, cornea, and limbus epithelium
t or f: the most superficial cells of the cornea are viable
true
t or f: corneal epithelial cells are constantly being shedded from the surface
true
what characteristics of the corneal epithelium contribute to its transparency?
smooth surface (tear film)
lack of intercellular space (decrease light scatter)
smaller & fewer organelles
t or f: corneal epithelial cells have a long lifespan
false
the basement membrane is also called...
basal lamina
2 layers of a basement membrane
lamina lucida & lamina densa
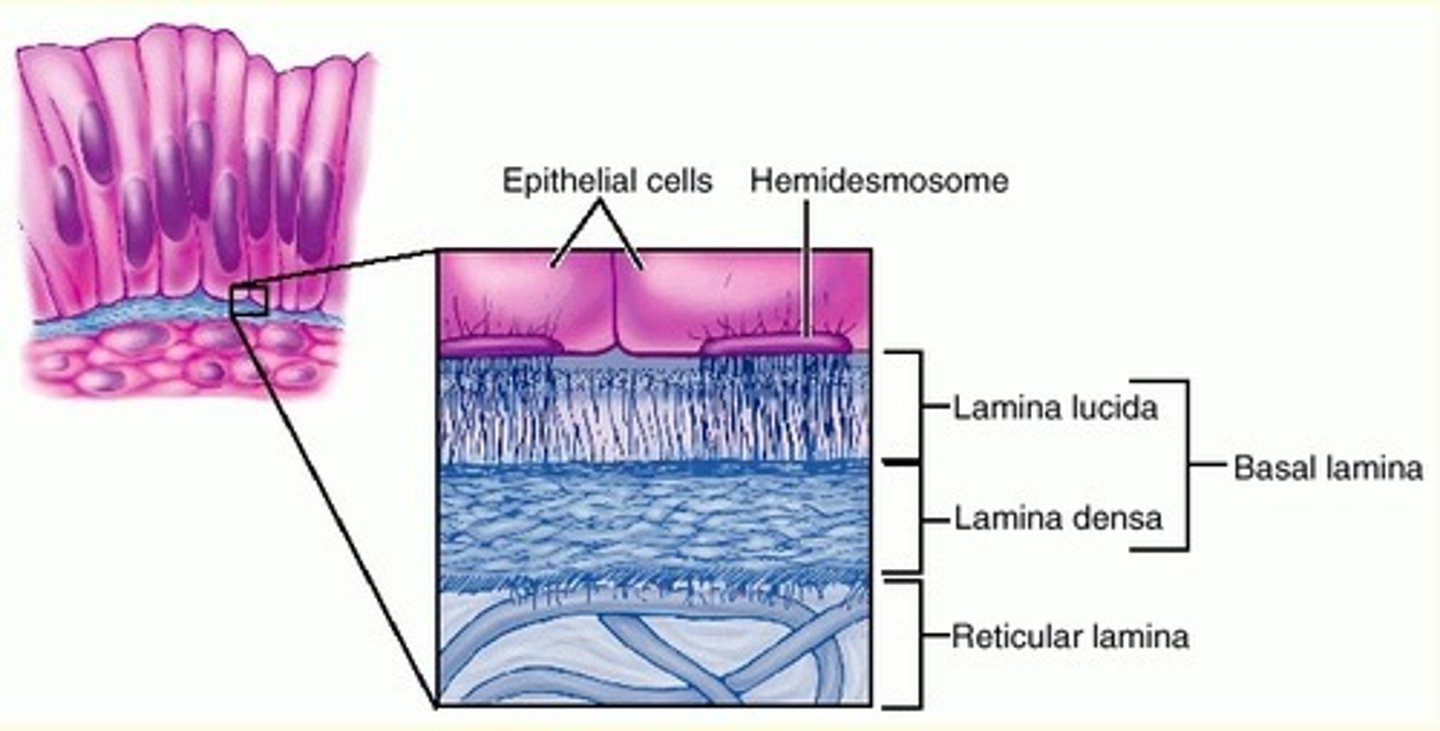
what component is found in the lamina lucida?
laminin
what component is found in the lamina densa?
collagen IV
what layer is underneath the corneal epithelial BM?
Bowman's layer
t or f: basal epithelial cells are able to regenerate the BM quickly
false, regeneration can take months
function of BM
attach the epithelium to underlying tissue
t or f: fibroblasts are present in Bowman's layer
false, Bowman's is acellular
what components are found in Bowman's?
tightly packed collagen type I & VII
ground substance
t or f: Bowman's layer is regenerated quickly by fibroblasts
false, Bowman's cannot be regenerated; it is created in utero and does not contain any cells
what percentage of water is held in the corneal stroma?
78%
what components are found in corneal stroma?
collagen type I organized into lamellae
ground substance
keratocytes
APCs
what are the important proteoglycans/GAGs in the corneal stroma?
keratocan, lumican, decorin
anterior vs posterior corneal stroma: which is more ordered?
posterior
anterior vs posterior corneal stroma: which has more interweaving?
anterior