Lecture 1 | Introduction to Evolution
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Evolution (organic/biological)
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations
Scientific Method
Used by evolutionary biologist
Ask a question about the world
Formulate hypotheses
Test hypothesis with experiments/analyses
Draw conclusions
Proximate questions
Immediate cause of a trait and how does a trait work
ex: birds migrate due to environmental cue
Ultimate question
Asks how a trait came to be over time
WHY did it evolve
ex: birds migrate due to increased fitness several generations ago
These are the questions of evolutionary biology
Uses for evolutionary thinking and questions
Medicine
ex: development of resistance to antibiotic?
genetics
ex: what genetic mechanisms cause or prevent disease?
Sociology, psychology, anthropology
ex: why does every human appear unique?
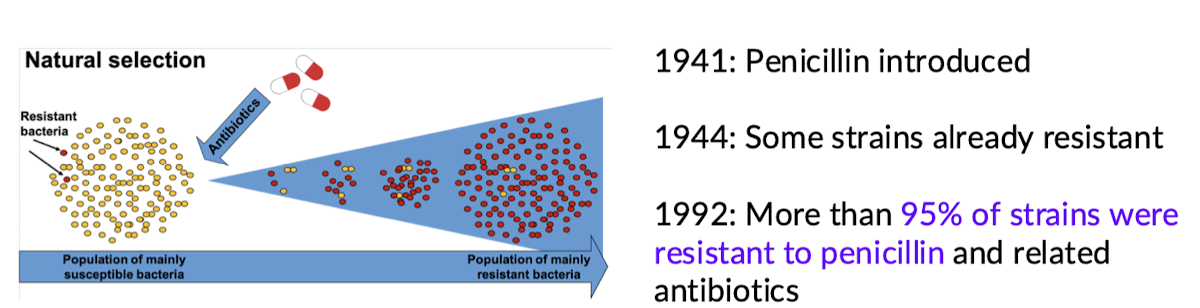
How has evolutionary change driven bacterial resistance
Most people that have ever lived have died from microbial infections
For bacterial pathogens, antibiotic resistance represents a vexing problem for medicine and is a key example of rapid evolutionary change
ex: MRSA
What evolutionary process is most likely responsible for the evolution of antibiotic resistance?
Natural selection
Evolutionary biology discoveries about antibiotic resistance
Bacterial mutants that are resistant to antibiotics occur in low frequency in most natural populations of bacteria
The use of antibiotics intensely selects for these resistant mutants
The increased usage and diversity of antibiotics is selecting for more and more multiple drug resistant bacteria
The evolution of the antibiotic resistance in bacteria is extremely rapid. We can observe the evolution occurring over a period of time
What does this graph show?
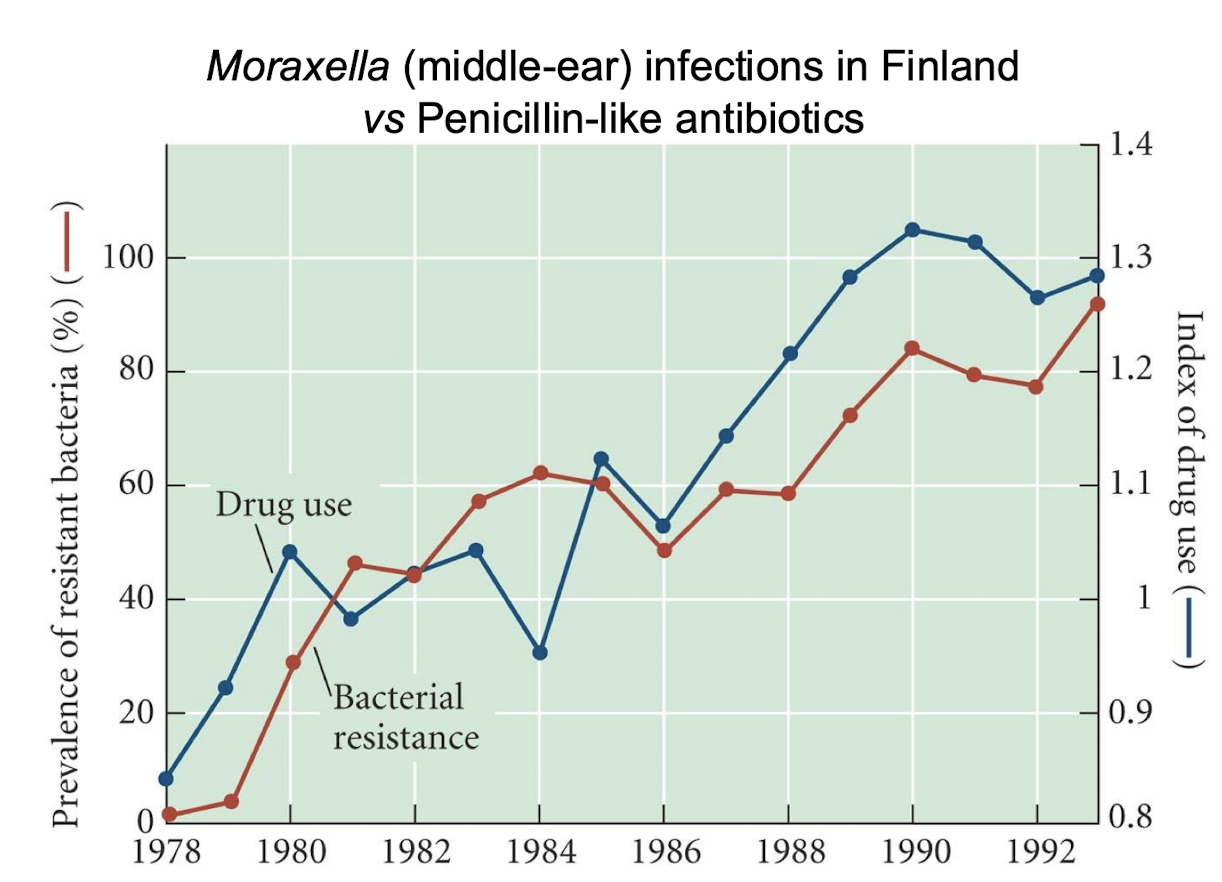
Shows the arms race between drug use and bacterial resistance to treat infections
ask drugs are used, bacterial resistance identically follows afterward
Charles Darwin
Presents The Origin of Species in 1859
started a scientific revolution
only 150 yrs ago
relatively young
industrial Revolution allowed the advancement of his ideas
Where did Darwin’s ideas come from?
Thinking was influenced by many previous naturalists
main ideas were modifications or combinations of existing ideas
Evolutionary thought in the ancient era
While no specific mechanism has been demonstrated, evolutionary ideas have existed for 1000s of years
Essentialism
The philosophical belief that entities have a fixed essence or set characteristics hat define their fundamental nature
proposed by Plato/Aristotle
does not take into account imperfections/variation for the “essence”
Variation was often ignored by biologists of the time
Scala naturae
Key idea of essentialism proposed by Aristotle
creates a hierarchy/gradation from the inanimate to lower life forms to plants and invertebrates as a higher life form
No changes were expected in species over time
Carolus Linnaeus
Catalogues nature and established the framework of modern classification in Systema Naturae
classified species, all intended to relate life in its closeness to “The Creator”
Uniformitarianism
Ancient geological formations can be explained by mechanisms that we can still observe today (erosion, deposition, magma flows)
processes that cause small, gradual changes can result in massive changes over long time periods
fundamental to evolutionary biology
Jean-Baptiste Lamark/Lamarckian evolution
Inheritance of acquired characteristics: species vary because each has different needs and strongly exercised organs can attract more “nervous fluids”
ex: if a giraffe needs to reach to a tree, its neck will become stretched and longer
Incorrect but was among the first to propose a mechanism to explain adaptation in nature
Darwin’s Life
Consumed interest in nature throughout his life
took a position as naturalist on a five-year voyage on HMS Beagle
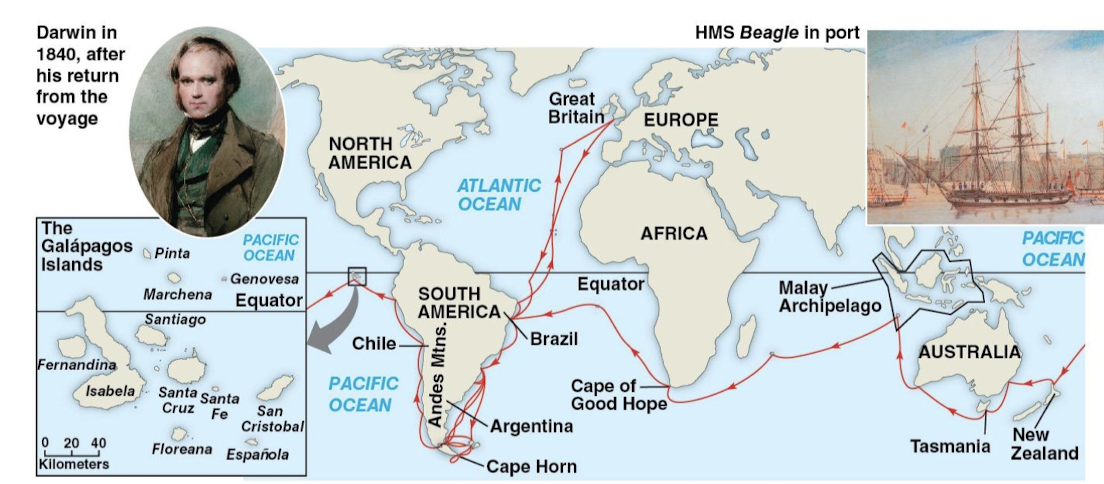
travelled to South America and Galápagos Islands
Observations after Darwin’s voyage
Ornithologist John Gould observed that birds collected on the islands looks vaguely similar but are morphologically different
different enough to be species
Triggered idea by Darwin that different species evolved from common ancestors
Thomas Malthus
British economist hat made the point that Human growth is faster than food production and famine will be the result
led to Darwin’s idea of the struggle for existence: there are usually more individuals born than can survive
Main ideas that Darwin forms
All organisms have descended with modification from common ancestral forms of life
Chief agent of modification is natural selection
Alfred Russel Wallace
Described a very similar theory of natural selection to Darwin
Spent all his time collecting specimens in Southeast Asia
Darwin gave him credit and presented at a meeting of the Royal Society in London
The Origin of Species
Based on a 500 page abstract that detailed Darwin’s ideas
5 big ideas of evolutionary theory
Evolution: Change over time
Common Descent: All life has descended
Gradualism: Changes have occurred incrementally
Population changes: Changes in the proportions of individuals with particular traits in populations
Natural Selection: Heritable differences impact ability to survive and reproduce
Controversy around Darwin’s Ideas
Evolution by descent with modification from common ancestors was universally accepted
Natural selection was not
Mutationists held that all change over time is caused by major mutations that could form entirely new species in a single generation
Names “Hopeful Monsters”
Blending inheritance
Leading mechanism of inheritance in the 1800s
Inherited material from two parents “blends together”
Leads to the loss of variation
Particulate inheritance
A lesser known, but correct, model of inheritance
The idea that parents pass on discrete “heritable units” (genes)’
Mendel documented this model in experiments with peas in the 1860s