Chapters 1-7
1/286
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
287 Terms
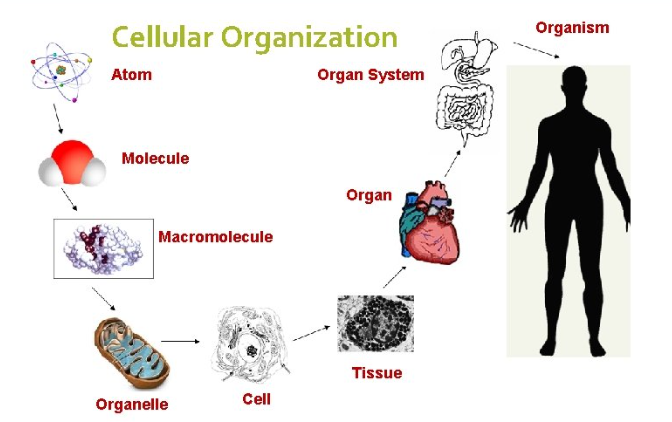
Levels of Organization
Atom, Molecule, Macromolecule, Organelle, Cell, Tissue, Organs, Organ systems, Organism
Movement
Digestion
Responsiveness
Absorption
Growth
Circulation
Reproduction
Assimilation
Respiration
Excretion
Fundamental characteristics of life (taken together, these 10 characteristics constitute metabolism)
Life depends on the availability of the following
Water, Food, Oxygen, Heat, Pressure
An organism needs a relatively stable internal environment to survive. Concentrations of water, nutrients, and oxygen plus conditions of heat and pressure must all be balanced to maintain this
Homeostasis
Receptor: Detects change that occurs in the internal environment. The information is sent to the control center.
Control center: Measures how far the change is from the set point and determines the appropriate response to fix the imbalance.
Effector: The change is corrected.
Main components of Homeostasis
The pancreas releases glucagon when blood sugar level is too low and insulin when blood sugar level is too high. When the body is trying to maintain balance and stabilize.
Negative Feedback
Childbirth and blood-clotting, which aims to amplify the initial stimulus instead of stabilizing. This feedback is positive because it goes beyond the balance in order to protect and heal the body.
Positive Feedback
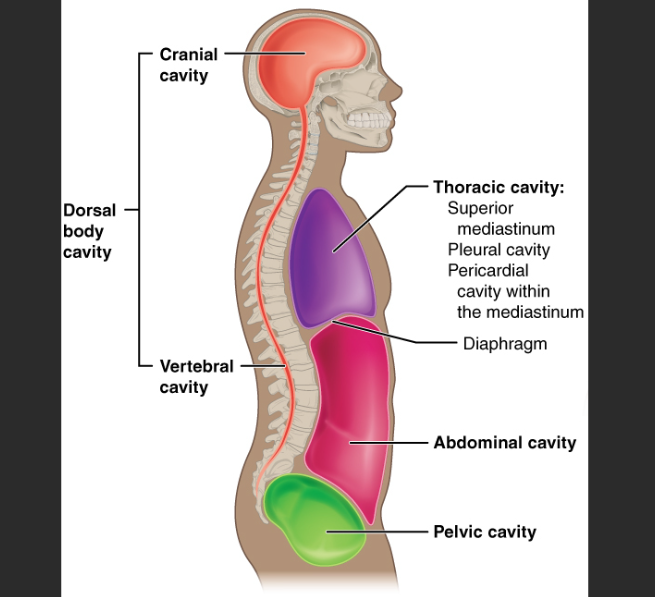
Cranial cavity: Brain
Vertebral canal: Spinal cord
Thoracic cavity: Heart & lungs
Pleural cavities: Lungs
Pleural membrane: Lines the pleural cavity
Pericardial cavity: Heart

Pericardium
Lines the pericardial cavity
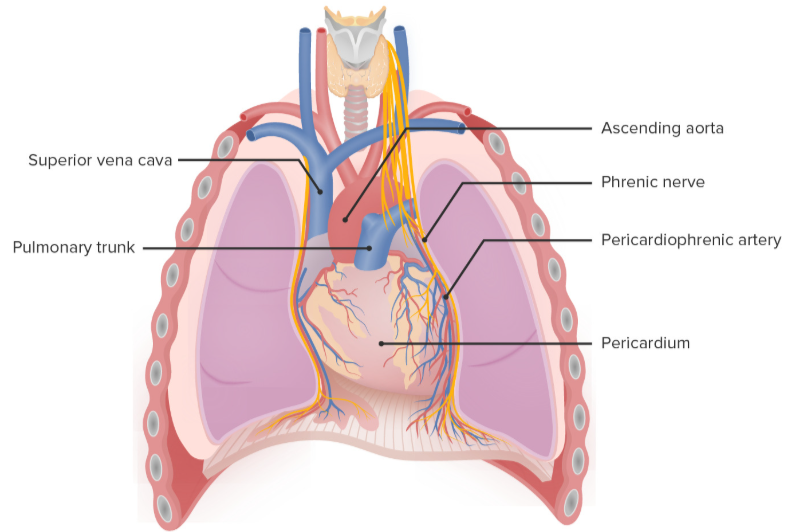
Mediastinum
Contains the heart, esophagus, trachea and thymus
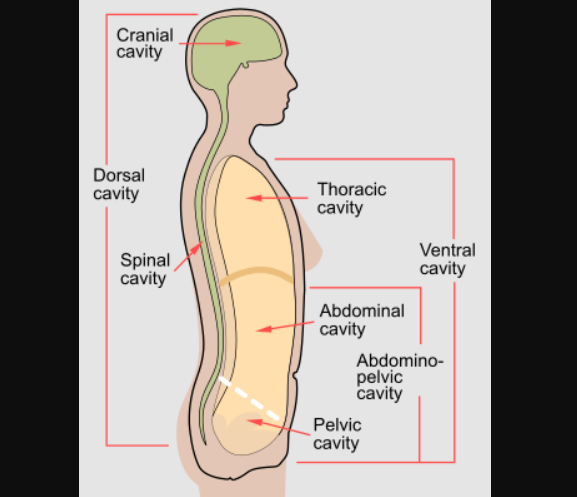
Abdominal cavity: Contains the liver, spleen, stomach, etc
Abdominopelvic cavity: Abdominal cavity + pelvic cavity
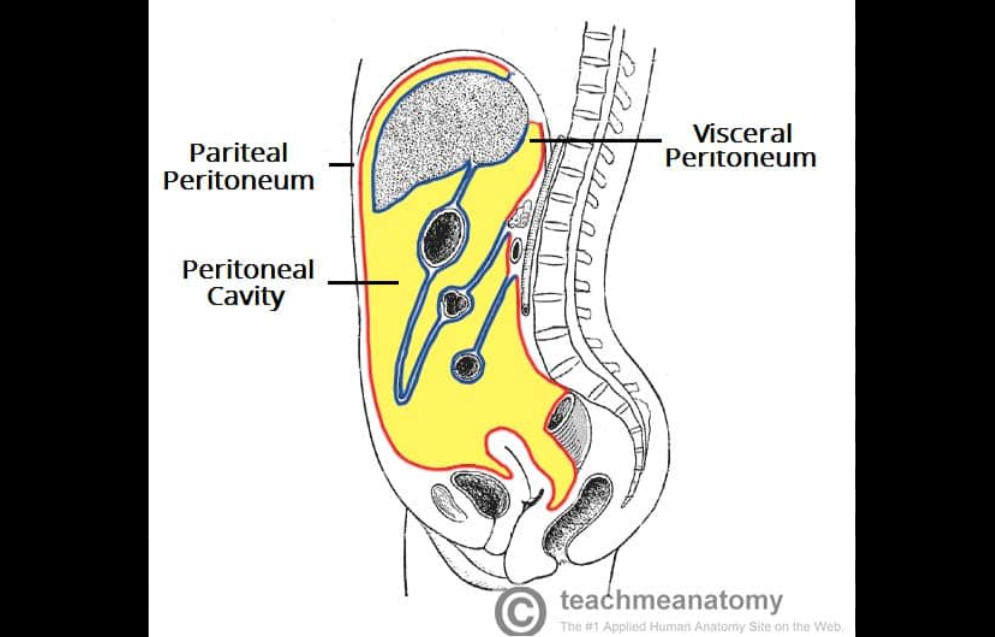
Peritoneal membrane
Lines the abdominopelvic cavity
Contains the urinary bladder, reproductive organs, lower intestines, etc.
Pelvic cavity
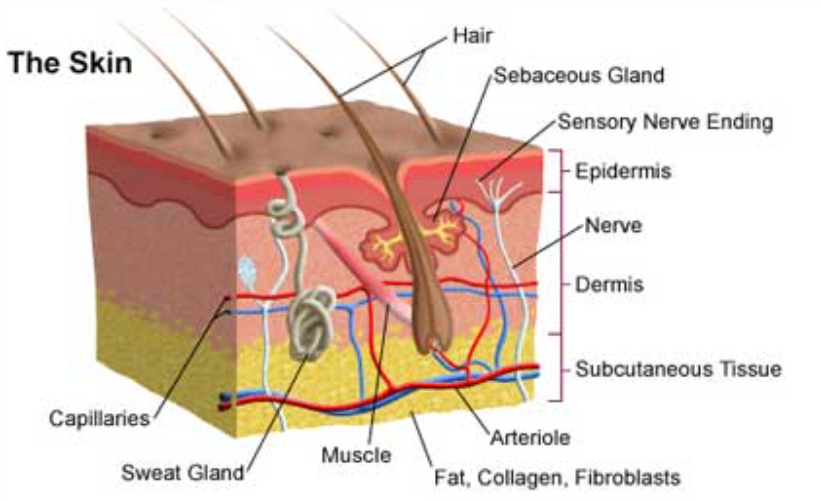
Integumentary Organs: skin, hair, nails, skin glands.
Functions: covers body, protects, helps to regulate body temperature

Skeletal - Organs: bones and ligaments.
Functions: supports, protects, stores inorganic salts, houses blood-cell forming tissue

Muscular: skeletal muscles.
Functions: body movements, posture, produces body heat
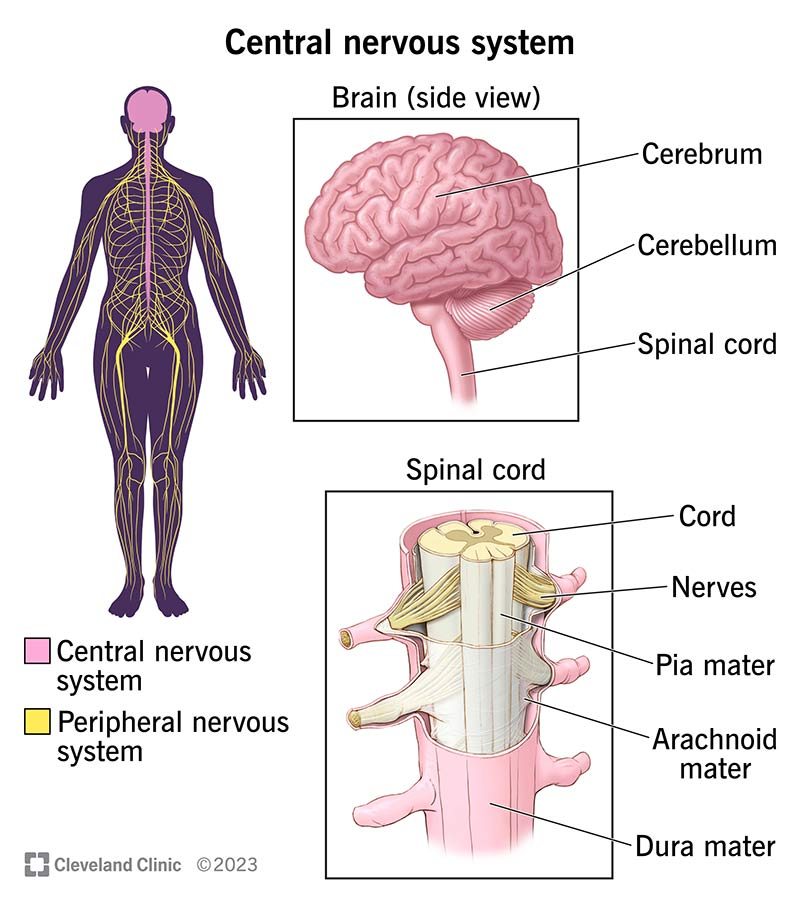
Nervous Organs: Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves and receptors.
Functions: produce sensations, controls muscles & glands
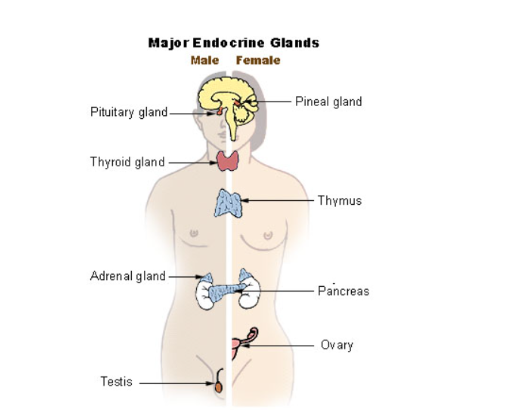
Endocrine - Organs: hormone-producing glands.
Functions: acts on specific target cells to control certain physiological functions

Cardiovascular - Organs: heart, blood, and blood vessels.
Functions: transports oxygen and nutrients to cells, transports waste away
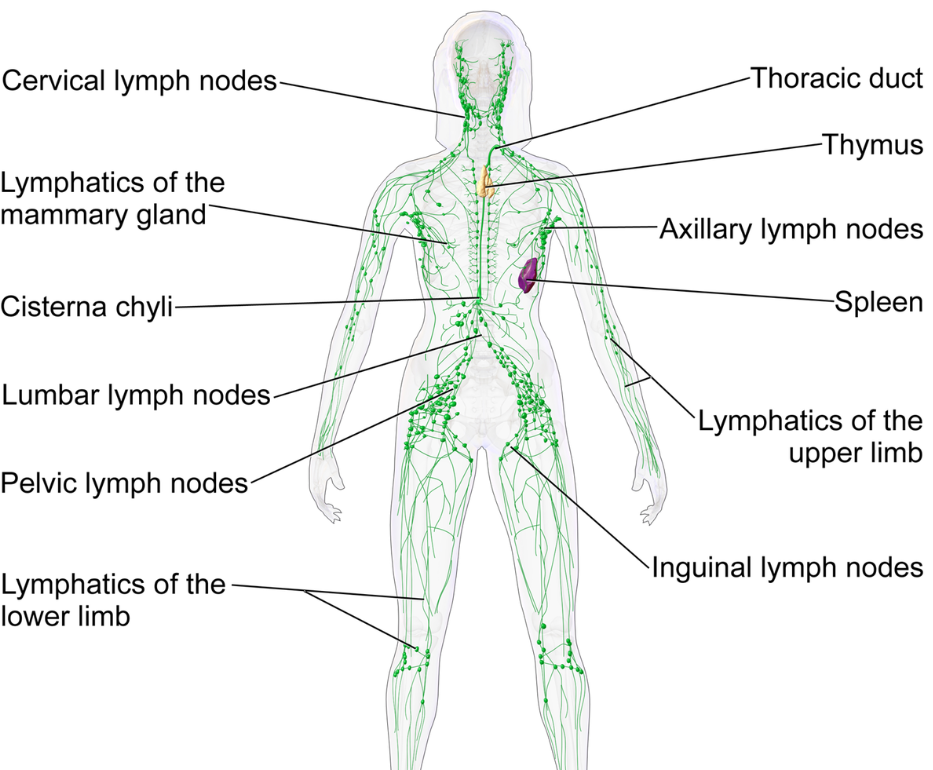
Lymphatic - Organs: Lymph vessels and lymph organs.
Functions: drains excess fluids from tissues, involved in immune responses
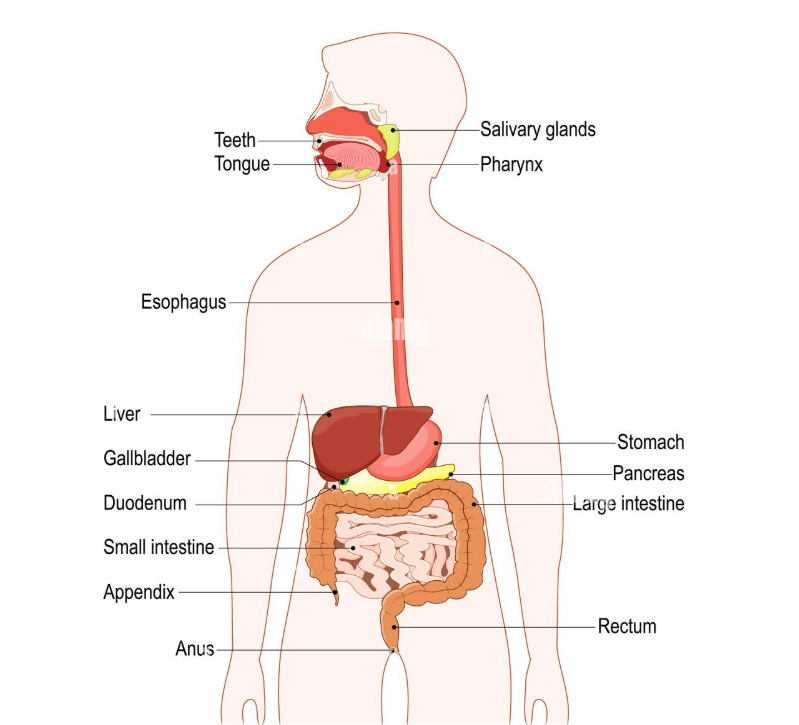
Digestive - Organs: mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, etc.
Functions: digests food and absorb nutrients
Respiratory - Organs: Lungs and air passageways.
Functions: exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between air and blood

Urinary - Kidneys & urinary bladder
Function: filters blood, produces urine, removes metabolic wastes from the blood.

Reproductive Organs: Gonads, and external and internal reproductive structures that differ in the male and female
Functions: enable the reproduction of the human species from generation to generation.
Superior and Inferior body parts
A body part above another part & a body part below another part.
Anterior and Posterior
Ventral toward the front & Dorsal towards the back
Medial & Lateral
Toward the midline of the body & Towards the side
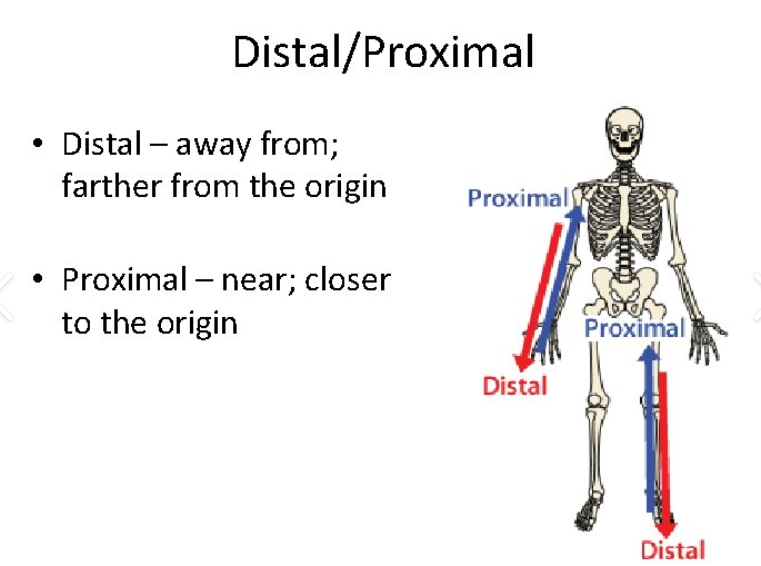
Proximal and Distal
Closer to the to the trunk & Farther from the trunk.
Superficial and Deep
Situated close to the surface & Situated away from the surface.
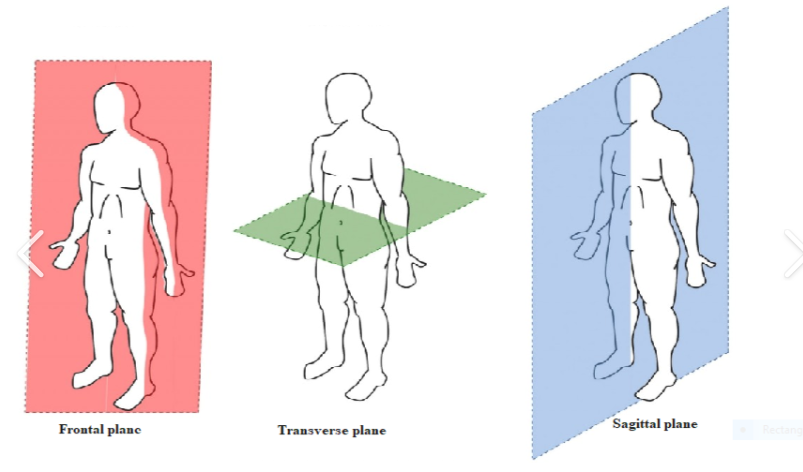
Midsagittal: Centrally divides body into equal left and right portions.
Sagittal: Divides the body into right and left portions.
Transverse (horizontal, cross-sectional)
Divides the body into superior and inferior portions.
Coronal
Divides the body into anterior and posterior sections.
Elements are composed of tiny particles called atoms.
Matter is anything that takes up space
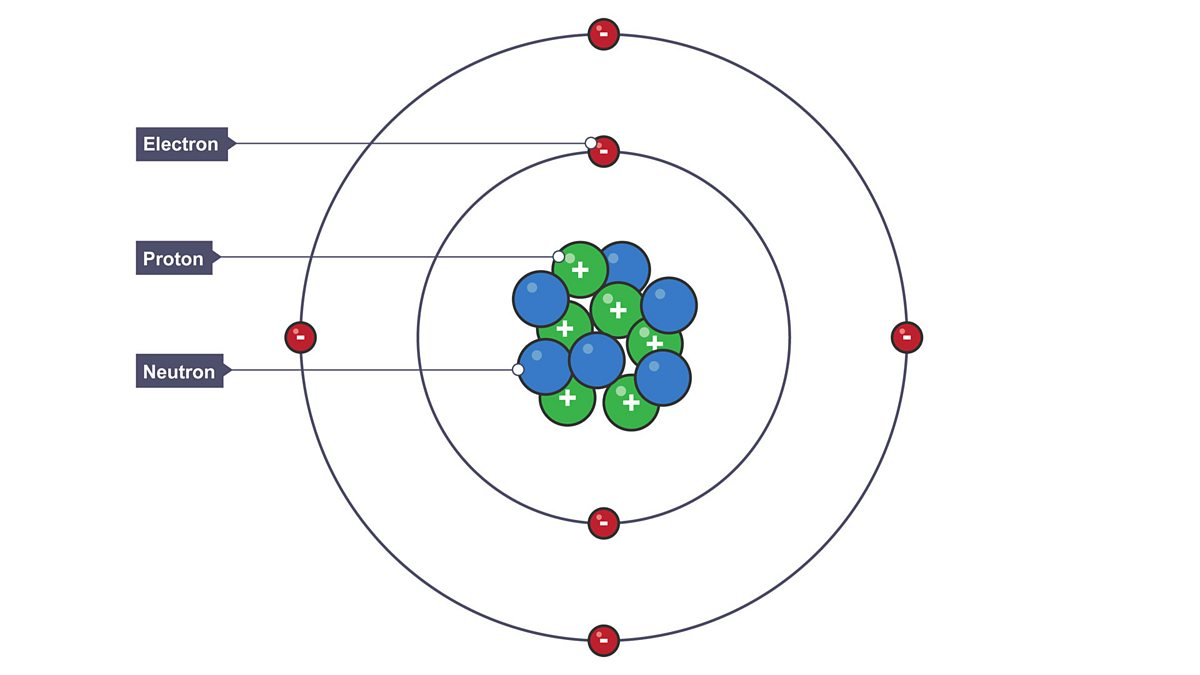
Atomic Structure
An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons in orbit around the nucleus.
Which has a positive charge? Negative charge?
Proton & Electron (Neutron has NO charge)
Which two each have a mass of 1?
Proton and Neutron
Atoms form bonds by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons.
Atoms are the most stable with two electrons in their first energy shell, and eight electrons in the second shell.
Ionic bonds: When atoms gain or lose electrons, they become ions with a charge. Whether they gain or lose electrons will depend on what?
Whether it is easier to complete the outer shell or empty the outer shell
Ø + charged ions and− charged ions attract each other to what?
Form an ionic bond.
Covalent bonds:
They’re formed when atoms share electrons in order to become stable with filled outer shells.
A molecule is formed when two or more atoms combine. If atoms of different elements combine, the resulting structure is a compound.
Molecule and compounds
A molecular formula represents the number and types of atoms in a molecule.
Two or more atoms or molecules can be joined in a process called synthesis.
Larger molecules can be broken into smaller ones in decomposition reactions.
Exchange reactions occur as parts of molecules trade places.
Substances that release ions in water
Electrolytes
If hydrogen ions was released in water, they’re called ___ . If they release ions that combine hydrogen ions in water, they’re called ____.
Acids; Bases
pH represents the concentration of hydrogen ions [H+] in solution. If it’s less than 7, the substance is acidic. If it is more than 7, the substance is a base (alkaline substance.
7 is neutral pH. Between each whole number of the pH scale there is a tenfold difference in hydrogen ion concentration.
Why is water important to life?
Dissolves and transports materials within the body and also participates in certain chemical reactions
List and describe two gases important to life
Oxygen is used by organelles to release energy from nutrients.
Carbon dioxide is a waste produced when some metabolic process release energy.
List salts important to physiology
Salts that provide ions of sodium, chloride, potassium , calcium, magnesium, phosphorous, sulfur, etc.
The 4 important groups of organic substances in the cell
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
Organic Substances
It must contain carbon and hydrogen but may contain other elements as well.
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates provide energy for cellular activities and are composed of what 3 elements?
C, H, and O
Carbohydrates are made from what?
Monosaccharides (simple sugars).
Disaccharides are two monosaccharides joined together. Polysaccharides (starch), are built of many sugars.
Humans synthesize the complex carbohydrate glycogen.
What 3 elements do lipids all contain?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Fats supply energy and are built from what?
Glycerol and three fatty acids.
Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are called saturated
Those with one or more double bonds are called unsaturated.
Contain glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group, and are important in cell structures.
Phospholipids.
Complex ring structures, and include cholesterol, which is used to synthesize the sex hormones
Steroids
List functions of proteins:
Used as structural materials, energy sources, certain hormones, receptors on cell membranes, antibodies, and enzymes to catalyze metabolic reactions.
Which proteins contain 4 elements?
C, H, O, N
Building blocks of proteins
Amino acids. Each of which has an carboxyl group, amino group and side chain called the R group.
Proteins have a primary, secondary and tertiary structure.
They also have unique shapes, which determine how they function. This unique shape is called their conformation.
Protein shapes can be irreversibly altered by pH, temperature, radiation, or chemicals.
Denaturation
Nucleic acids
They form structures called genes and take part in protein synthesis.
Ø Which 5 elements do nucleic acids contain?
C, H, O, N, P
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids called?
Nucleotides
Nucleic acids are of two major types, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
Stores the molecular code in genes. It has two strands and four different bases.
Nucleic acids are of two major types: RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Functions in protein synthesis. It has one strand and four bases.

A cell consists of three main parts: the nucleus, that houses the genetic material, the cytoplasm, that contains the organelles, and the outer boundary, called the plasma (cell) membrane.
Basic structure

The cell membrane is extremely thin and is selectively permeable. The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell, participates in signal transduction, and helps cells adhere to other cells.
The basic framework of the cell membrane consists of a double layer of phospholipids, with fatty acid tails making of the interior of the membrane.
Many types of proteins are found in the cell membrane, including some which are transmembrane and some that are peripheral. What are some of the functions of these substances?
The proteins can function as receptors, for passage of materials across the membrane, for cellular adhesion, for cell identification, etc.
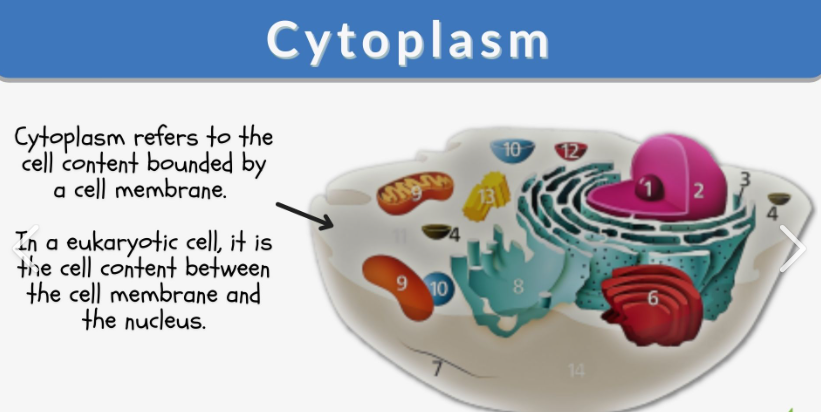
Consists of a clear liquid called cytosol, a supportive framework or cytoskeleton, and networks of membranes and organelles.
Cytoplasm
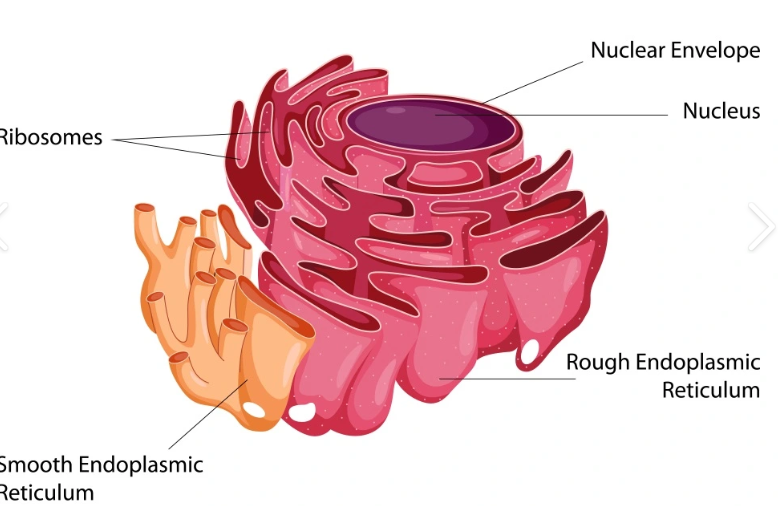
Endoplasmic reticulum
Made up of membranes and provides a tubular transport system inside the cell.

Rough ER: Why does it appear rough?
Because of attached ribosomes. It synthesis and transport PROTEINS for the cell?
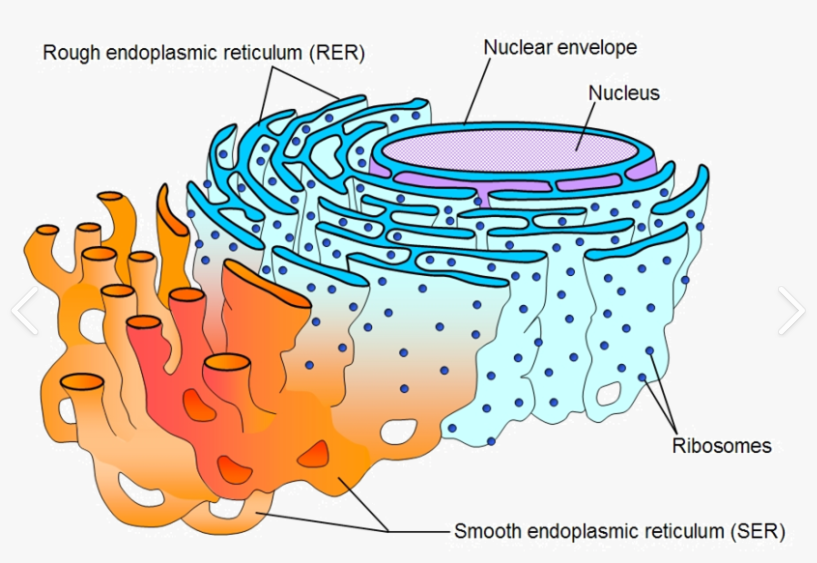
Smooth ER: Why does it appear smooth?
It has no attached ribosomes. It synthesizes LIPIDS (fats) for the cell?
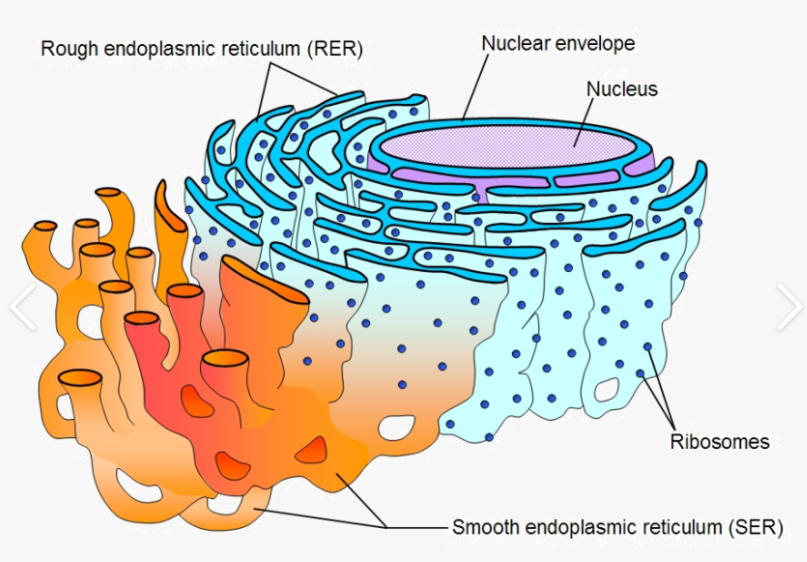
Where are the ribosomes found?
In the cytoplasm and attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum.
What are ribosomes composed of?
Protein and RNA. They produce PROTEINS
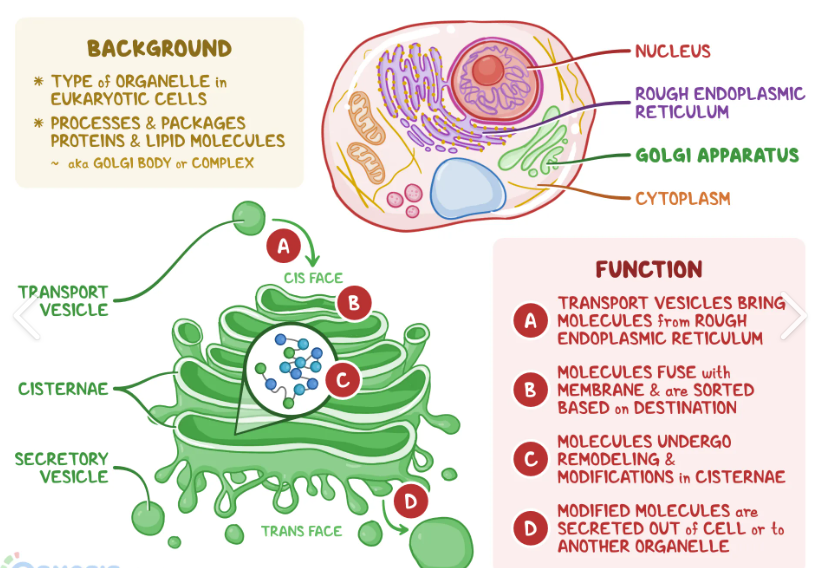
Golgi apparatus is composed of flattened sacs and it packages the cells products. Why would a cell want to do this?
To transport materials to the outside of the cell
Mitochondria
Contain enzymes needed for aerobic respiration and are the major sites at which food energy is captured and stored in a molecule called ATP .
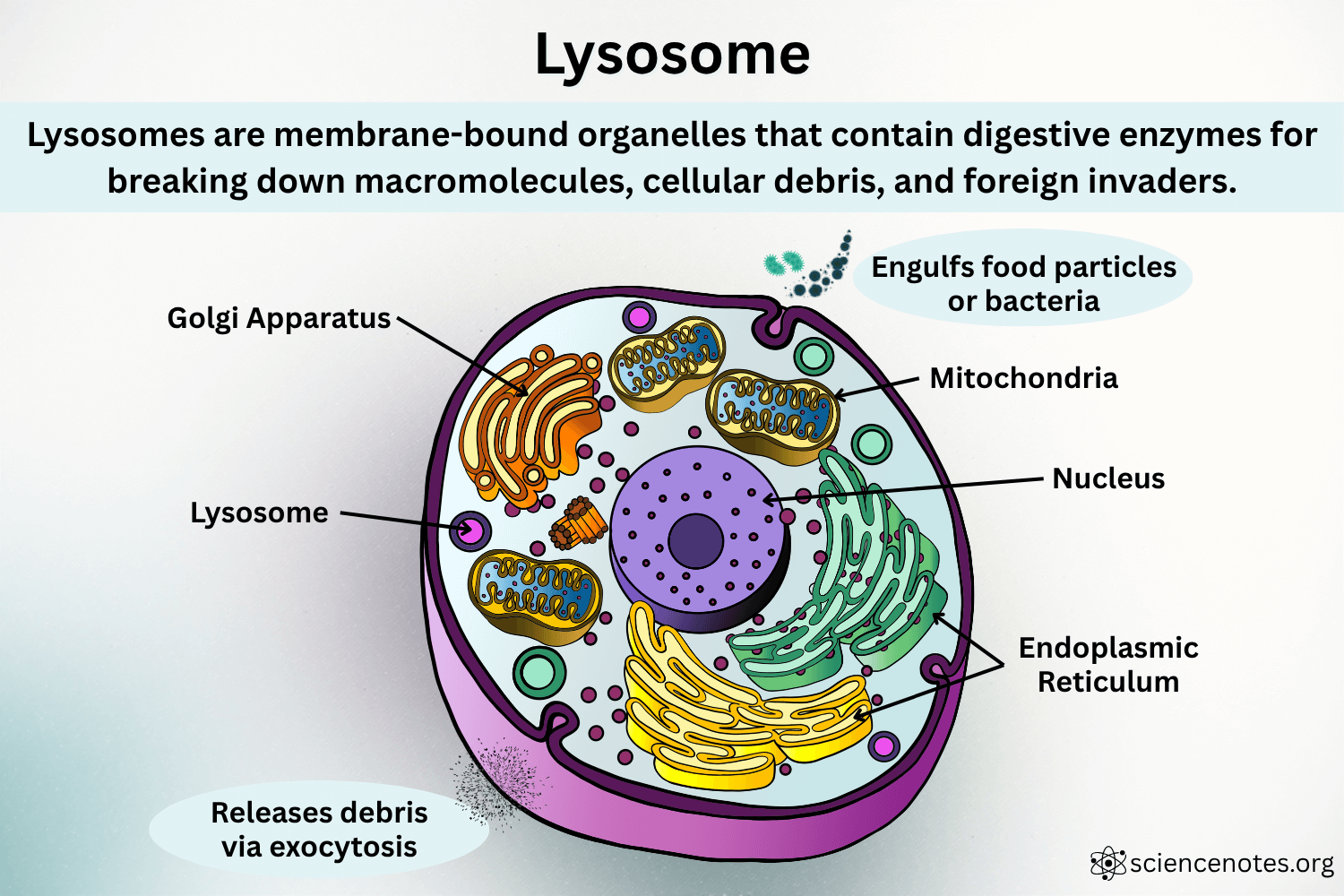
Lysosomes contain enzymes to break down cell components, bacteria, nutrient molecules, toxins and drugs.
They are sometimes called the "garbage disposals" of the cell.
What contain enzymes that function in the synthesis of bile acids, breakdown of lipids, degradation of rare biochemicals, and detoxification of alcohol.
Peroxisomes
Microfilaments, made of protein actin, cause various cellular movements.
Microtubules, made of the globular protein tubulin, make spiral patterns
Both are threadlike structures that serve as the cytoskeleton of the cell.
A structure made up of two hollow cylinders called centrioles. Their function during mitosis is to enable the correct distribution of chromosomes during cell division
Centrosome
Cilia & flagella
Motile extensions from the cell. Cilia is shorter
What is Cilia’s function in the human body?
Causes movement of substances across the surface of the cell.
What is the only flagellated cell in the body?
Sperm cell
Form from part of the cell membrane, and carry liquid and solid materials into the cell.
Vesicles
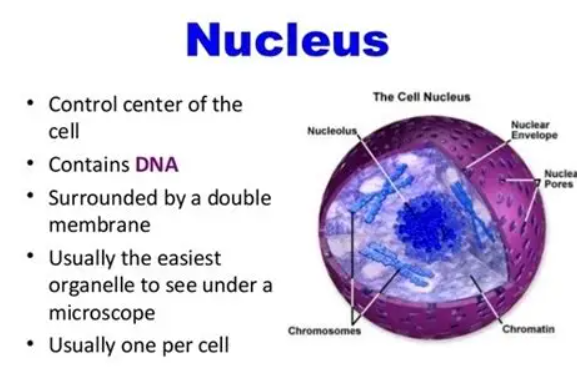
The nucleus bounded by a double-layered nuclear envelope (membrane) containing complex openings called nuclear pores, that allow the passage of certain substances.
The nucleolus is INSIDE of it. No membranes.
What chemicals is a nucleus made of?
Proteins and RNA for construction of ribosomes
What chemicals is the chromatin made of?
DNA and proteinacuoles
The cell membrane controls what substances pass through it. What is passive transport?
When mechanisms of movement across the membrane require NO ENERGY from the cell (diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and filtration). No cell in general.
Movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration to reach equilibrium.
Diffusion. Oxygen, carbon dioxide, fats, etc.
The substance that moves by ____ is water.
Osmosis
This uses membrane proteins that function as carriers to move molecules (such as glucose) across the cell membrane.
Facilitated Diffusion
A solution with the same osmotic pressure as body fluids is called isotonic. One with higher osmotic pressure than body fluids is hypertonic. Lower osmotic pressure is hypotonic.
Tonicity
Because of hydrostatic pressure, molecules can be forced through membranes by the process of filtration. In the body, blood pressure is a type of pressure causing filtration. Where does this occur?
Blood capillaries and kidneys .
Moves substances from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. Requires transport proteins (pumps).
Active Transport
Energy in the form of ATP is also required. Why would the body want to spend energy to acquire (or get rid of) something?
To get materials needed by cells or to eliminate waste products
In the process of endocytosis, molecules that are too large to get transported by other means are engulfed by an indentation of the cell membrane and carried into the cell surrounded by a vesicle.
The reverse process is called exocytosis.