4.2.4 Financial Markets & Monetary Policy
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
What are the 4 core functions of money?
a medium of exchange - Money avoids the problems of barter
A store of value
A measure of value/unit of account
Standard for deferred payment
What are the 6 characteristics of money?
Durability: Money must be able to withstand being used repeatedly
Portability: Money must be easily transportable so it can be easily transferred to other individuals,
Divisibility: It is also preferable that money can be divided into smaller units of value,
Acceptability: Money must be widely accepted for it to be usable for different types of transactions,
Scarcity: Money must be in limited supply to ensure its value remains relatively stable,
Security: Money must also be extremely difficult to counterfeit, as if it is easily duplicated it will cease to become a medium of exchange
What is narrow money?
The basic amount of notes and coins and operational deposits/reserve balances at the Bank of England.
–money that can be accessed ‘on demand’.
What is Broad money?
all notes,coins,deposits in savings accounts and other less liquid assets
What does liquidity mean?
How easily an asset can be turned into cash.
Cash is a highly liquid asset, whereas property for example is more illiquid.
What is a stock?
security that represents the ownership of a fraction of the corporation.
Units of stock are called "shares" which entitles the owner to a proportion of the corporation's assets and profits equal to how much stock they own.
When is a bond issued?
by governments and corporations when they want to raise money.
What is a bond yield?
return on the capital invested by an investor.
Formula for Yield
Yield formula = coupon/market price x100
What are the 3 types of financial market?
Money market
Capital market
Foreign exchange market
What is the money market?
provides short term , typically 24 hrs to 12 months, finance to individuals, firms and governments
includes interbank lending
What is the capital market?
provides medium to long- term finance to firms and governments
includes companies issuing shares or corporate bonds, or governments issuing bonds to finance their borrowing requirements
What’s the difference between the primary capital market and the secondary capital market?
The primary capital market is where newly issued securities are sold by companies or governments
The secondary capital market is where previously issued shares or bonds are traded e.g. The London Stock Exchange is an example of a secondary capital market
What is the foreign exchange market?
different currencies are bought and sold
What’s the difference between the spot market and the future market?
The spot market involves the immediate exchange of foreign currency
The forward market involves the exchange of foreign currency at some specified time in the future.
What’s the difference between the money and capital market?
Money market - where commercial banks provide short term loans to each other
Capital market - businesses obtain funds to finance long-term growth
What’s the role of financial markets in the wider economy?
To facilitate saving by businesses & households
To lend to businesses and individuals
To facilitate the exchange of goods and services
To provide forward markets in currencies and commodities
To provide a market for equities
How do financial markets in the wider economy lend to businesses and individuals?
Mortgages for home-buyers
Loans / credit for small and medium sized enterprises
How does the financial market in the wider economy provide forward markets in currencies and commodities?
allows companies & individuals to hedge against uncertainty for example by buying their currencies & commodities months in advance
How does the financial market in the wider economy provide a market for equities?
Allows businesses to fresh equity capital e.g. to fund their expansion
Equity markets provide a market for capital control, a market discipline on listed businesses
What is a financial market?
any exchange that facilitates the trading of financial instruments, eg stocks, bonds, commodities
What is debt?
Amount owed by the borrower to the lender
What is equity?
Amount of money a company’s owner has put into

Lets say you purchased this house for £400,000 10 years ago.
You sell the house for £540,000.
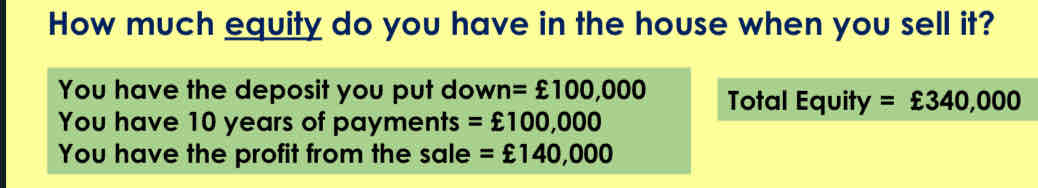
What are commercial banks?
high street/retail banks e.g. Barclays, HSBC & NatWest
provide services to customers e.g: foreign exchange, insurance and brokerage services
How do Commercial banks make money?
By offering interest on savings, and lending out this money to other people at a higher interest
savers deposit money into their chosen bank, receiving interest in return
borrowers receive money in the form of loans/mortgages paying interest
What are the main roles/function of Commercial banks?

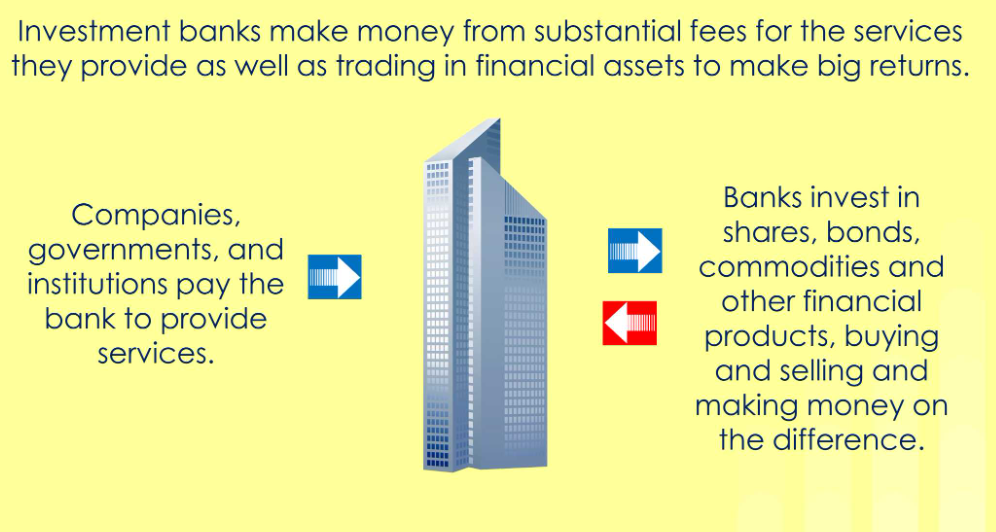
What’s the key function of investment banks?
help companies/government raise finance by giving advice
arranging new issues of shares/corporate bonds
helping them to manage the risk in doing so

How do IBs make money?
How do banks create credit?
extending loans to businesses and households
do not need to attract deposits from savers to do this
When a bank makes a loan, it credits their bank account with a bank deposit of the size of the loan/mortgage.
new money is created.
What is the Credit Multiplier? Give the formula.

What is QE?
creation of new money electronically to buy bonds in the financial market with the aim to stimulate AD
Inflation is an effect of QE, what can the BOE do?
Reduce money supply by selling their assets
Reduces spending in the economy
Describe the process of QE
bank buys gov bonds using money they have created
Then used to buy bonds from investors = increases the amount of cash flowing in the financial system
Encourages more lending to firms and individuals = cost of borrowing lower
Encourages more investment, spending = leading to more EG —> also lead to inflation (money supply increasing)
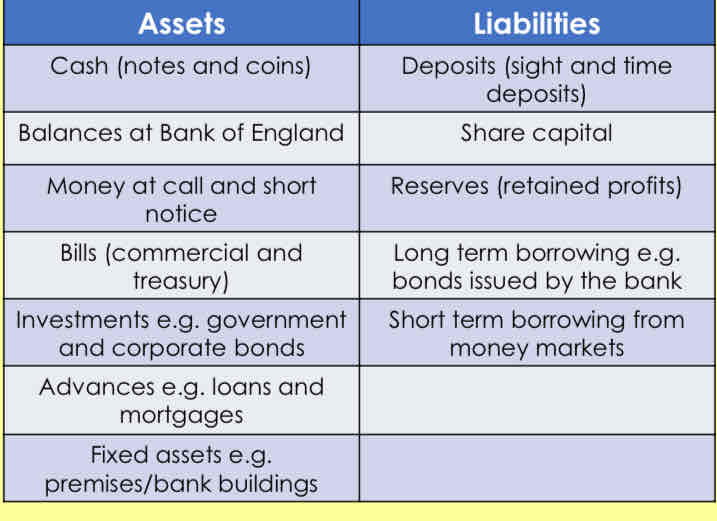
What are balance sheets?
comprised of assets & liabilities
total assets must equal total liabilities
For a commercial bank
What are assets?
What are liabilities?
➢an asset is any claim that the bank has against others
➢a liability is any claim that others have on the bank
What does a commercial banks balance sheet look like?
What happens if commercial banks balance sheets are not liquid enough?
loss of confidence amongst consumers in the ability of the bank to meet its liabilities
For a commercial bank to succeed, why it is important that a large portion of these assets are as liquid as possible?
the bank will struggle to meet its liabilities as and when they fall
liquid assets do not tend to be very profitable but less liquid assets carry a greater burden of risk.
What are commercial banks 3 core objectives?
1. Profitability- commercial banks have a requirement to ensure investors receive a return on their investment through dividends. Banks with weak profitability will likely see their share price fall and find new investment harder to attract.
2. Liquidity- Commercial banks must ensure that they have enough liquidity to meet the demands of their depositors, who can withdraw their money at any time.
3. Security - Commercial banks seek to ensure that their assets are as secure as possible. An example of a secured loan is a mortgage.
An unsecured loan, such as a credit card, is riskier for the bank as there’s no underlying asset acting as security, the balance between the different types of asset is important in determining the banks overall stability.
What types of loans can you get from a bank/lender?
business
Overdraft
Credit card
Mortgage
Personal loan
Payday loan
What does the central bank take action to do?
influence the manipulation of IR, ER, supply of money and credit
What are the functions of a Central Bank?
manages the currency, money supply & IR
Issue physical cash securely & use methods to prevent fraud
How does a reduction in IR affect AD?
C = reduce OC of saving, households with variable mortgage rates benefit through low repayments ( increases disposable income)
I = cheaper for firms to borrow from commercial banks, use these to form R&D/innovation
G = gov debt repayments lower, gov can issue more bonds to contribute to higher levels of gov spending
X-M = reduces flow of note money into econ (rate of return is lower than other countries) = weakens ER as it increases supply of £ on forex markets
What is the BOE considered to be?
lender of last resort = if there is no other method to increase the supply of liquidity when it’s low
If institution is close to collapsing bank might lend to them
Banks will avoid borrowing from the BOE = suggest that bank is experiencing financial difficulties
What are some responsibilities of the BoE?
promote safety of financial firms
protect & enhance the resilience of the financial system = prevent future financial crises
What factors do the MPC consider when setting the bank rate?

Draw a diagram to show a contraction in the money supply

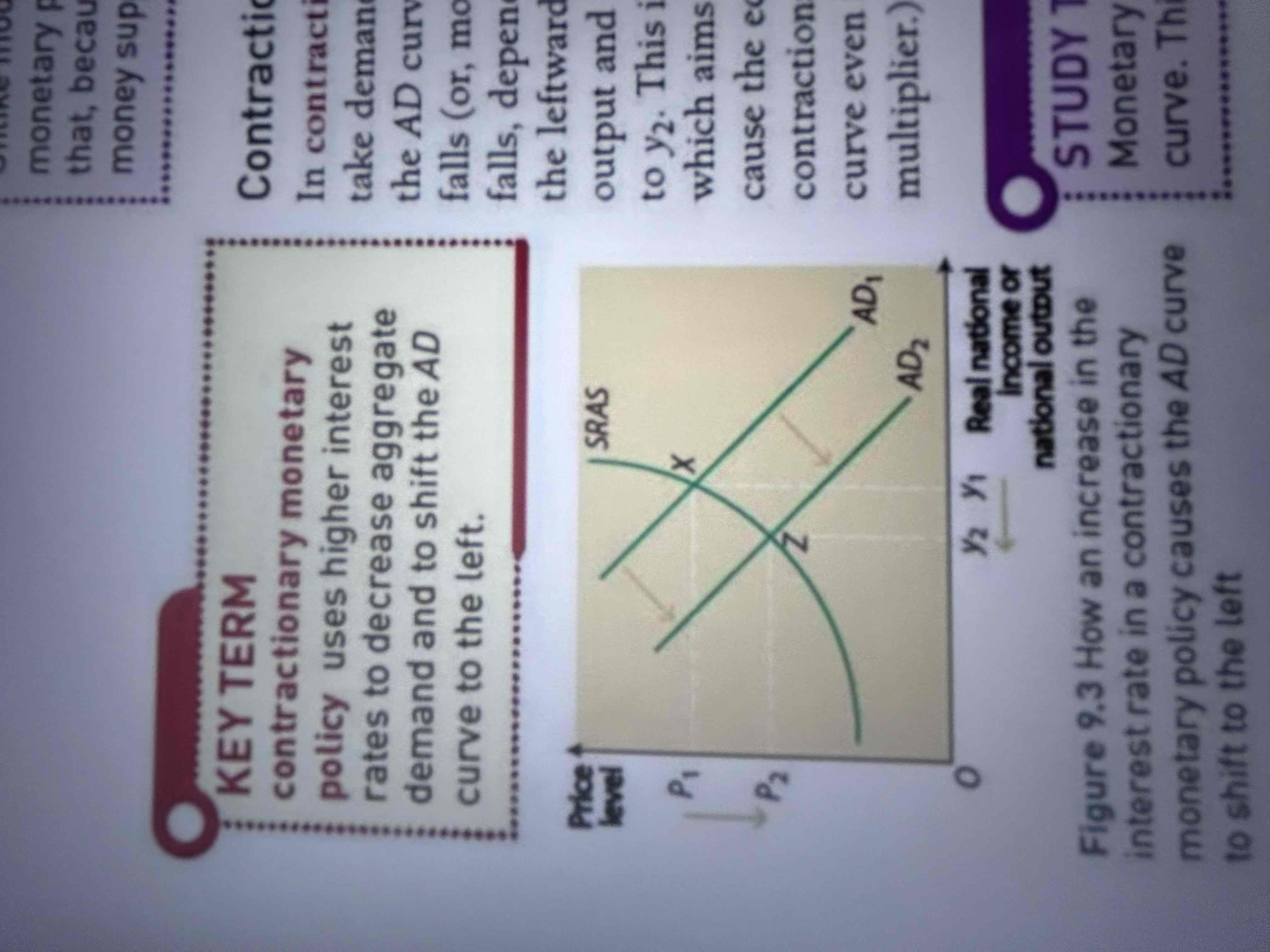
What is contractionary monetary policy?
uses higher interest rates to decrease AD and shift AD curve inwards to left.
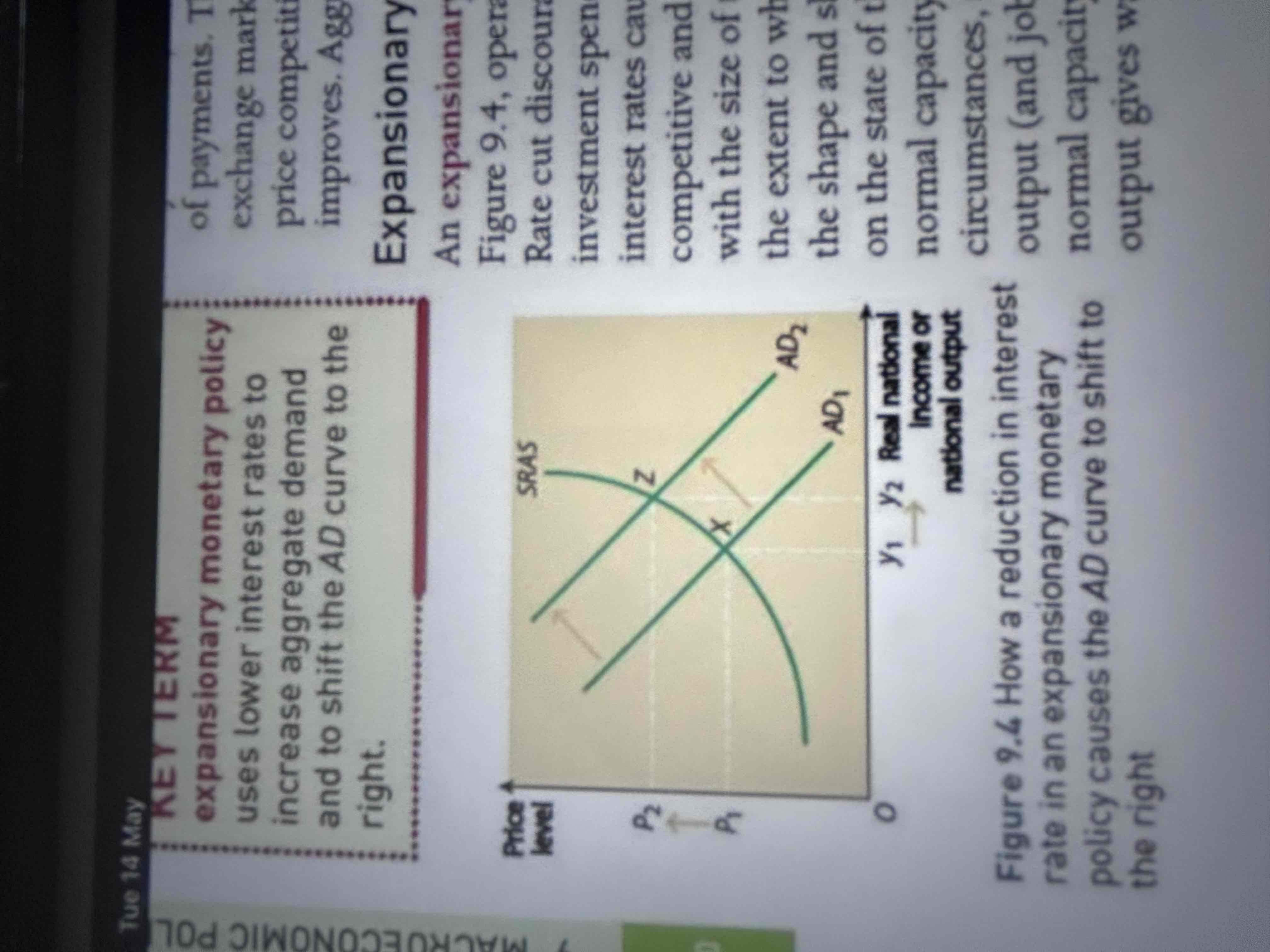
What is expansionary monetary policy?
uses lower interest rates to increase AD and to shift AD curve to right
What is fiscal policy?
involves the use of taxation, public spending and the government’s budget to achieve the gov’s policy objectives
What is the budget deficit?
government spending exceeds government revenue
Represents a net injection of demand into the circular flow of income and a budget deficit is expansionary
What is a budget surplus?
when G<R
Represents a net withdrawal from the circular flow and hence a BS is contractionary
What are the three macroeconomic policies?
monetary policy - includes interest rates, tax, debt
Fiscal policy - gov spending, money supply
Supply side - productivity
How do the government receive money?
through taxes and borrowing money if in debt
Where does the government spend its money?
healthcare
Education
National defence
Councils
Welfare benefits
Social protection
Debt interest
Police
Transport
What are the main taxes?
corporation tax
National income tax
Inheritance tax
VAT road tax
NICs
Council
How does fiscal policy affect AD?
expansive fiscal policy can be created through increasing GS or decreasing Income tax
Causes AD to increase
Increased consumption
GDP increases
How does fiscal policy affect AD?
expansionary fiscal policy increases AD
Gov will increase spending and cut taxes
Lower taxes will increase consumers spending because they have more disposable income
Worsens gov budget deficit
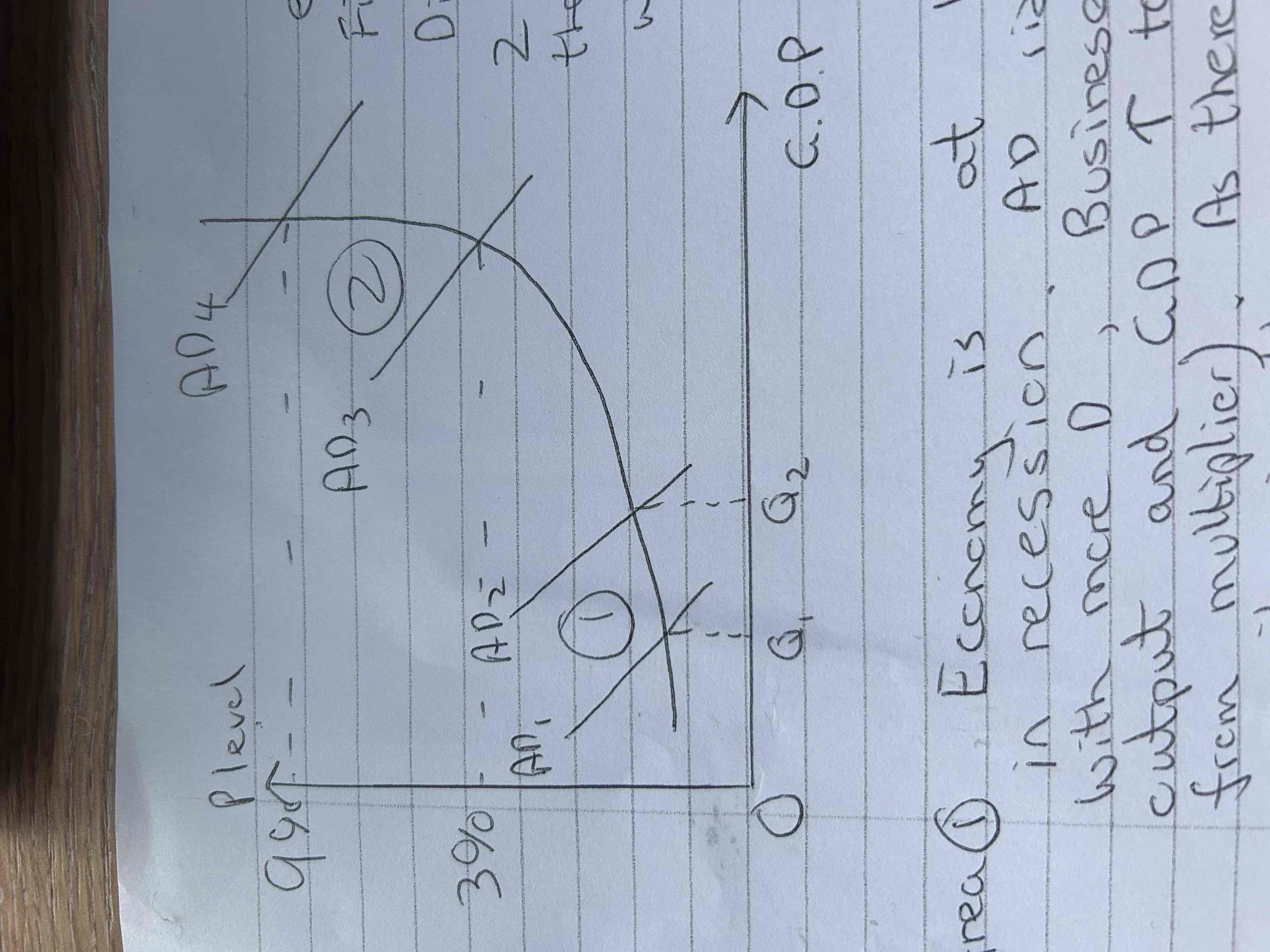
So expansive fiscal increases AD
Diagram shows 2 areas on the AS curve when AD could rise

How can fiscal policy affect supply?
Changes in income tax rates and can have a significant effect on work incentives in the labour market. Consider 40% or say 15% tax???
Higher government spending on education & training, can increase human capital / productivity to lift the long-term trend rate of growth.
Changes in corporation tax changes profits and investment
if Y tax / corp tax falls may help S side as efficiency rises. (incentives to work / more Bus investment)
What’s the criticism of all policies, what’s another criticism of fiscal policy?
The government may have poor information about the state of the economy.
Time lags. To change econ it could take several months.
Crowding out. (fiscal only) Higher government spending will crowd out the private sector. This is because the government have to borrow from the private sector who will then have lower funds for businesses
What are the main objectives of the UK tax system?
Raise money
Lower Y tax helps incentives to work.
Tax de merits ALTER D FOR SOME GOODS
Redistribute Y / Wealth with benefits. Help poor Y end
Manage econ to alter AD via Y tax changes
What are the two types of tax?
Direct taxes – are directly on your circumstance– usually through “pay as you earn” (y tax). Also corporation tax.
Indirect taxes – include VAT and a range of excise duties on oil, tobacco, alcohol. The burden of an indirect tax can be passed on by the supplier to the final customer
What are the types of direct tax?
Income Tax = Biggest rev earner, Progressive tax system
Corporation Tax
Capital gains tax - sell an asset for greater than purchase Price pay tax on gain
Inheritance tax
National insurance
What is the purpose of indirect tax?
1. Generate tax revenue for a government.
2. Discourage consumption of ‘harmful’ products
The burden of an indirect tax can be passed on by the supplier to the final customer
What’s an example of an indirect tax?
A unit tax (specific ) is a set amount of tax per unit sold, such as a 10p tax on packets of cigarettes.
VAT
The percentage of VAT is 20%, on most goods except,,what?
no/low VAT:
newspapers
Children’s clothes
Food and drink (chocolate covered biscuits,ice cream, crisps)
What is progressive tax?
involves a tax rate that increases as taxable income increases.
It imposes a lower tax rate on low-Y earners and a higher tax rate on higher earners
Formula for average tax
Average tax = tax paid/ income X 100

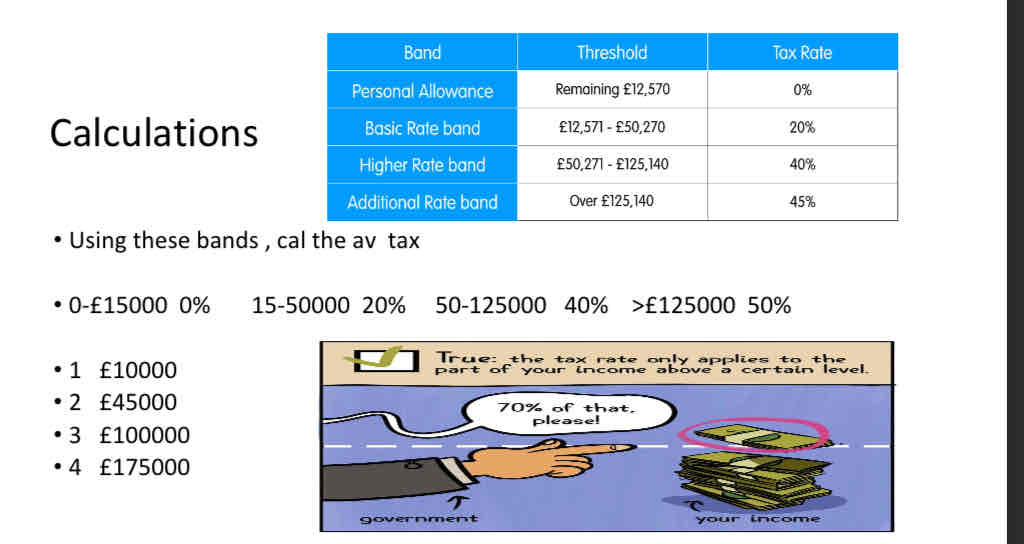
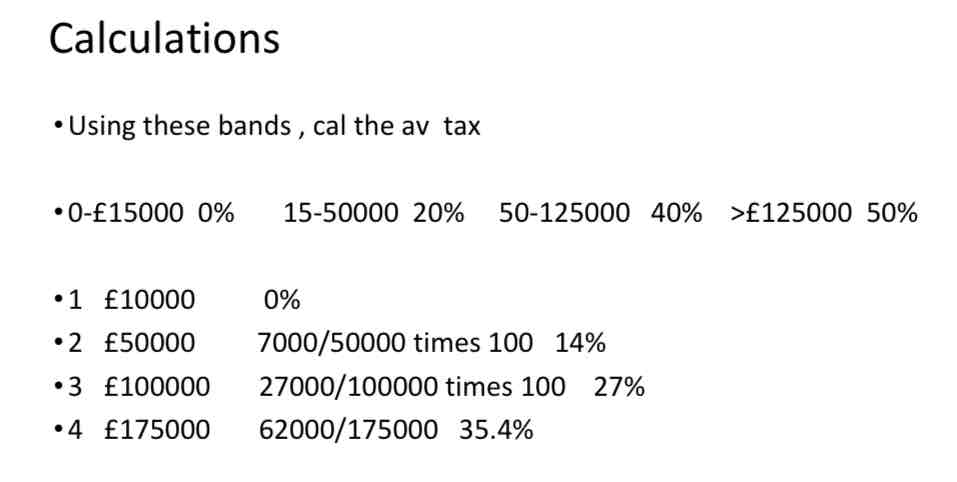
What happens for regressive taxes?
the average rate of tax is greatest for those on lower incomes.
• VAT
• The tax on national lottery tickets (12%)
• Exercise duties on smoking and alcohol and betting and gaming duties • Higher fuel duties
On 10000 spend all so pay 20%
vat av tax 2000/10000 20%
If on say £500000 spend say 200000 pa vat is £40000
Av tax 40000/500000 times 100 = 8%
So as Y rises vat as proportion of vat falls.....regressive
What does the pattern of consumption in the economy refer to?
refers to trends or predictable which consumers purchase goods or services over time
How does fiscal policy influence the pattern of consumption on an economy?
exercises duties- taxes of cigarettes, decreases consumption
Govt spending via subsidies- spend on merit goods such as the NHS
Fall in income tax, changes rate of consumption
Fall in corporation tax, increase in price changed the budget spending power
Tax of demerit goods (e.g alcohol)
What are the pros and cons of indirect taxes?
Pros:
raises a lot of money for infrastructure, to pay welfare benefits, NHS, education, public/merit goods
Used to change the pattern of consumption
Reduces demand for petrol via positive ext.
Cons:
Indirect taxes are regressive meaning low income people are hit the hardest
Many cause cost-push inflation causing VAT to increase the prices causing costs to increase
Petrol/cigarette taxes have no effect on their demand
Why do some indirect taxes have no effect on their demand, like the taxes on cigarettes and alcohol?
raises a lot of money
IDR taxes less likely to distort choices that people have between work and leisure, have less of a negative effect on work incentives
Higher IDR taxes allows a decrease in direct tax rates, lower income tax rates so people work harder
What are arguments against using indirect taxation?
IDR taxes are regressive
May cause cost push inflation
Does the cig/petrol tax work?
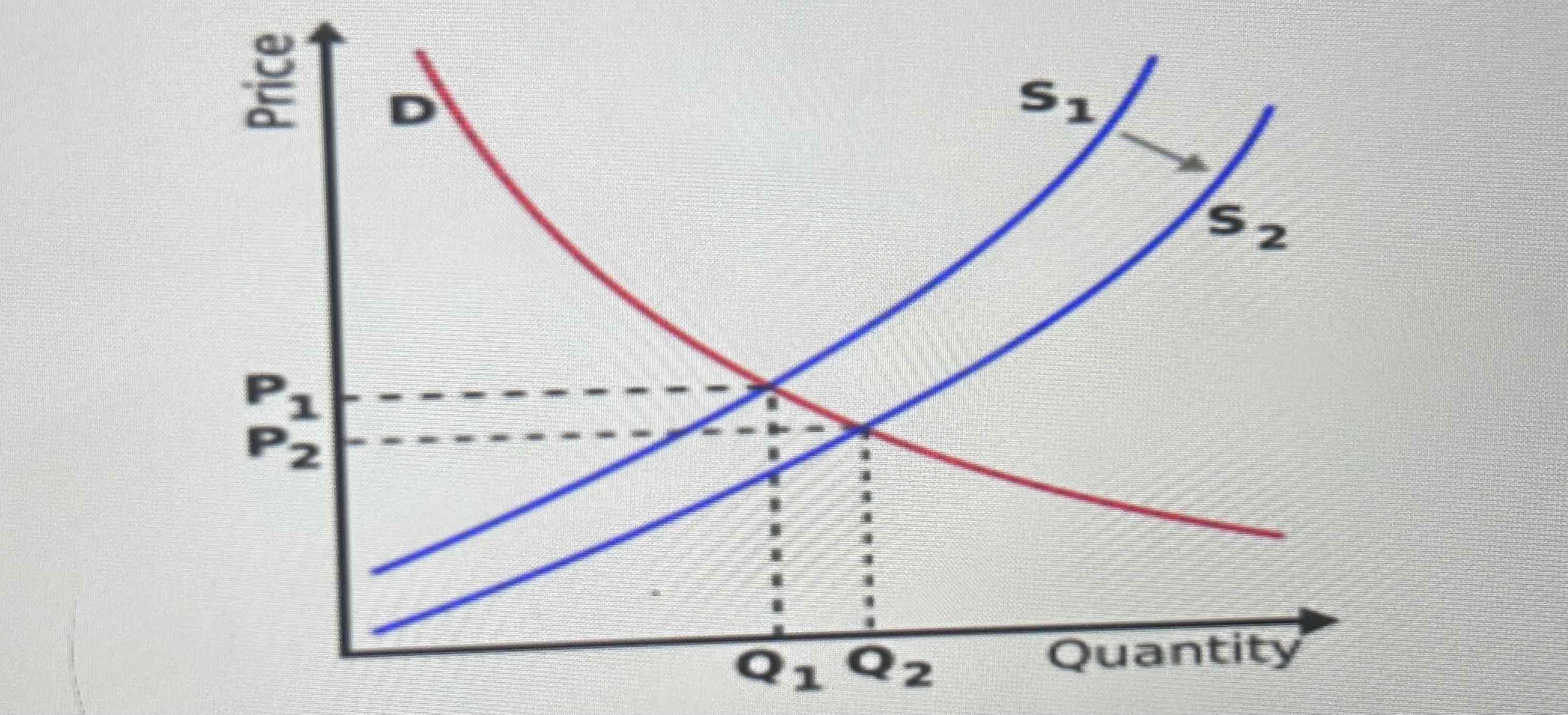
Draw a D/S diagram showing IDR taxation causing a deadweight loss of welfare to society:
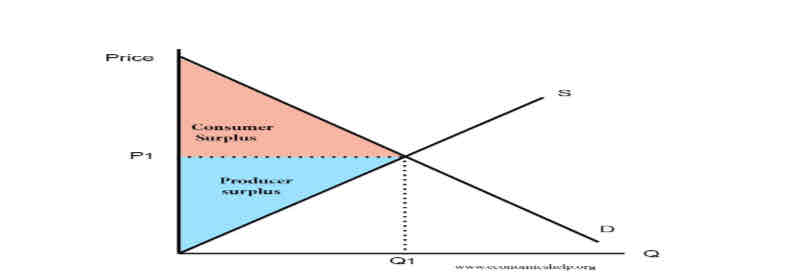
What is consumer surplus?
difference between the price that consumers pay and the price that they are willing to pay.ie consumers save money that can be spent elsewhere to increase their welfare
What is producer surplus?
difference between the price that producers get and the price that they are willing to supplly at.. Eg P is £9 but could S at £5 PS is £4 EXTRA PROFIT, so their welfare rises due to PS
Arguments for and against using indirect taxation

Arguments for direct taxation
What is regulation?
a rule or directive made and maintained by an authority.
the action or process of regulating or being regulated, "the regulation of financial markets"
Why do banks need regulating?
to protect consumers, ensure the stability of the financial system, and prevent financial crime.
Why Regulate?
Moral hazard
Systemic risk
run the risk of more financial crashes like 2008 and ‘the lost decade’ in terms of real income growth—> impacts economy
What can regulators do?
aims are to reduce the risk of moral hazards
can raise, or impose, a minimum level of assets that banks need to maintain in order to meet their liabilities.
This mitigates against the risk of a liquidity crisis (bank run) or insolvency (losses are too big).
Which 3 measurements help assess the risks?
➔ Liquidity Ratios (Reduces risk of liquidity crisis)
➔ Capital Ratios (Reduces risk of liquidity crisis)
➔ Leverage ratios (Reduces risk of insolvency )
Who helps with financial regulation?
The Bank of England
Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA)
Financial Policy Committee (FPC)
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
Who is the UK banking industry regulated by, what do they do?
FCA = regulates financial firms to ensure they’re being honest to consumers and they seek to protect consumer interests, aims to promote competitions in the interests of consumers
PRA = promotes safety & stability of banks, building societies, investment firms
What do the FPC do?
regulates risk in banking & ensures the financial system is stable
Clamps down on unregulated parts & loose credit
Monitors overall risks to the financial system as well as individual groups being regulated
“Too big to fail”
What does this refer to?
a theory in banking and finance that asserts that certain corporations are so large and so interconnected that their failure would be disastrous to the greater economic system, and therefore should be supported by government when they face potential failure
What is moral hazard?
any situation in which one person makes the decision about how much risk to take, while someone else bears the cost if things go badly.
Conditions necessary for moral hazard
Information asymmetry.
Where one party holds more information than another. The bank knows their own accounts better than outsiders.
A contract affects the behaviour of two different agents.
E.g. If you are insured, then you may have less incentive to take care against risks. With large banks, they felt the government would have to bail them out if things went wrong.
What is an asset?
economic resources owned by a company likely to generate future benefits or cash flows.
What is a liability?
refer to things that you owe or have borrowed.
A liquidity ratio refers to
the number of liquid assets to overall assets.
Use of liquidity ratio:
require banks to hold enough liquid assets to pay any unexpected short term demand in liabilities.
Central banks and regulators might require anywhere from 60-100%.
Formula for liquidity ratio
Current Assets/Current Liabilities