Bio B2.1 Membranes & Membrane Support Study
DEFINE: POLARITY
POLARITY: Imbalance of elecron charge leading to molecules having a slight - or + charge
Ex. Water & C-O or O-H
DEFINE: NON POLARITY
NON POLARITY: No imbalance in electron charge, balanced molecule
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
DEFINE: POLARITY
POLARITY: Imbalance of elecron charge leading to molecules having a slight - or + charge
Ex. Water & C-O or O-H
DEFINE: NON POLARITY
NON POLARITY: No imbalance in electron charge, balanced molecule
DEFINE: AMPHIPATHIC
AMPHIPATHIC: Containing both a - and + side within the molecule
Ex. Phospholipid
DEFINE: HYDROPHOBIC & HYDROPHILIC
Water-fearing & Water-Loving
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SAT. & UNSAT. In PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Structure within the formation of the unsaturated and saturated lipid. Due to unsaturated containing a double bond (1 or more), the structure limits the amount of tight packing of fat that can be done and is much healthier for the human body. In contrast, saturated condensly packs and results in unhealthy fat if overabundant.
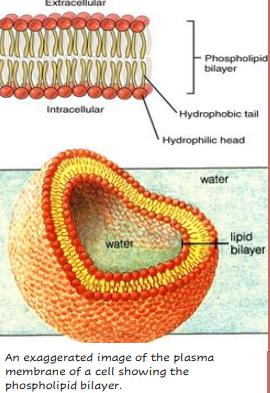
DRAW: PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER AND DESCRIBE DRAWING ACCURATELY.
**Must accurately explain too
IDENTIFY THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTEGRAL & PERIPHERAL PROTEINS
IDENTIFY SPECIFIC EXAMPLES BETWEEN THE TWO TYPES OF PROTEINS & THE FUNCTIONS OF THOSE SPECIFIC EXAMPLES.
INTEGRAL: Remains withi the phspholipid bilayer beyond the hydrophobic portion. (hydrophobic)
PERIPHERAL: Located on the surface of the membrane, whether intracellular or extracelluar (hydrophilic)
idk I have to do more research for examples…
Draw Mosaic Model!
All drawings of cell membranes should include:
1. Phospholipids - arranged in a bilayer, with the hydrophilic polar (heads) and hydrophobic non-polar regions (tails) identified.
2. Glycoproteins and glycolipids located on the EXTRACELLULAR side of the membrane.
3. Integral proteins should be embedded within the bilayer
4. Peripheral proteins should be anchored to one side (inside or outside the cell)
5. Cholesterol may be included in animal cell membranes – interspersed between the fatty acid tails with one end (due to polar O) attached to the phospholipid head.
[Cholesterol is essential in regulating the fluidity of the membrane. Cholesterol (1) reduces fluidity when it increases at high temperatures due to increased motion of the molecules and (2) increases fluidity when the temperature decreases due to decreased
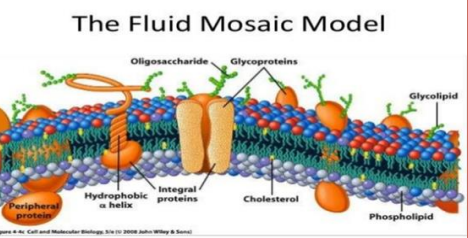
Define Glycostylation
The attachement of carbohydrate to the backbone of a protein through an enzymatic reaction.
Glyco=Carbohydrate=sugar
Explain Passive Transport in your Own Words
& Analyze the difference between:
Simple Diffusion Vs. Facilitated Diffusion Vs. Osmosis
Passive Transport is the movement of particles naturally (meaning no usage of external energy) in order to move these particles from HIGH concentration to LOW.
SIMPLE DIFFUSION: The movement of particles from high to low for smaller particles naturally
FACILITATED DIFFUSION: The movement of larger particles from high to low through protein channels naturally
OSMOSIS: The movement of WATER from high to low through between the semi-permeable membrane until equilibrium between solvent and solute solutions are reached.
Explain Active Transport in Your Own Words
& Analyze the differece between:
Protein Pumps Vs. Endocytosis Vs. Exocytosis
Active Transport is the movement of molecules or ions through the semi-permeable membrane from LOW to HIGH concentration (against the concentration gradient) which REQUIRES external energy
PROTEIN PUMPS: Carrier Proteins which move substances against the concentration gradient (low to high-bc its apart of active transport)
ENDOCYTOSIS: The process of bringing materials inside of the cell.
EXOCYTOSIS: The process of vesicles merging to the plasma membrane to secrete their contests outside of the cell.
OSMOSIS: Differentiate betwen Hypotonic, Hypertonic & Isotonic
Hint: Utilize Crenation & Lysis
ALSO: COMPARE & CONTRAST THE DIFFERECE BETWEEN TUGOR PRESSURE & PLASMOLYSIS WITHIN PLANT CELLS & WHY THEIR CELL WALLS ALTERS THE EFFECTS OF HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC & ISOTONIC
Hypotonic —> Water in —> Too much leads to potetial burst within the cell membrane (Lysis)
Hypertonic —> Water Out —> Too little leads to scallopped edges (Crenation)
Isotonic —> In & Out —> Perfect Equilibrium between what goes in and out of the cell membrane :)