Physical and Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Introduction to Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids contain the carboxyl group: a carbonyl with oxygen attached to the carbon that’s attached to a hydrogen
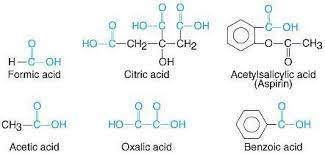
Some common carboxylic acids are shown below:
Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
- They are the most polar functional group due to the carboxyl group
- They have the highest melting and boiling points of all the functional groups
- They tend to form dimers in the solid, liquid, and gaseous phases
- this makes their apparent molar mass higher than their actual molar mass
- carboxylic acids up to 6 carbons long tend to be water soluble
- benzoic acid (benzene ring attached to carboxyl group) is soluble in hot water
Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are weak acids
Most carboxylic acids have a pKa of approximately 5
The dissociation reaction of acetic acid is shown below
- it will be similar for all carboxylic acids
- Acetic acid has a pKa of 4.74
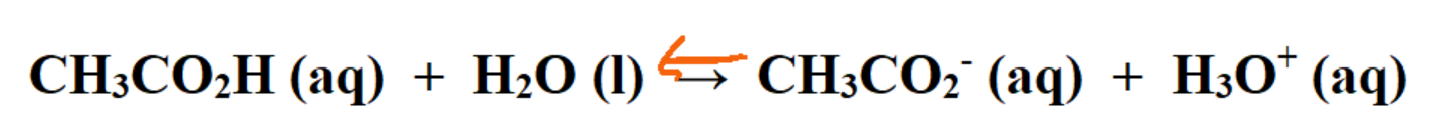
carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols because of
- the resonance effect of the anion
- inductive effect of the carbonyl group
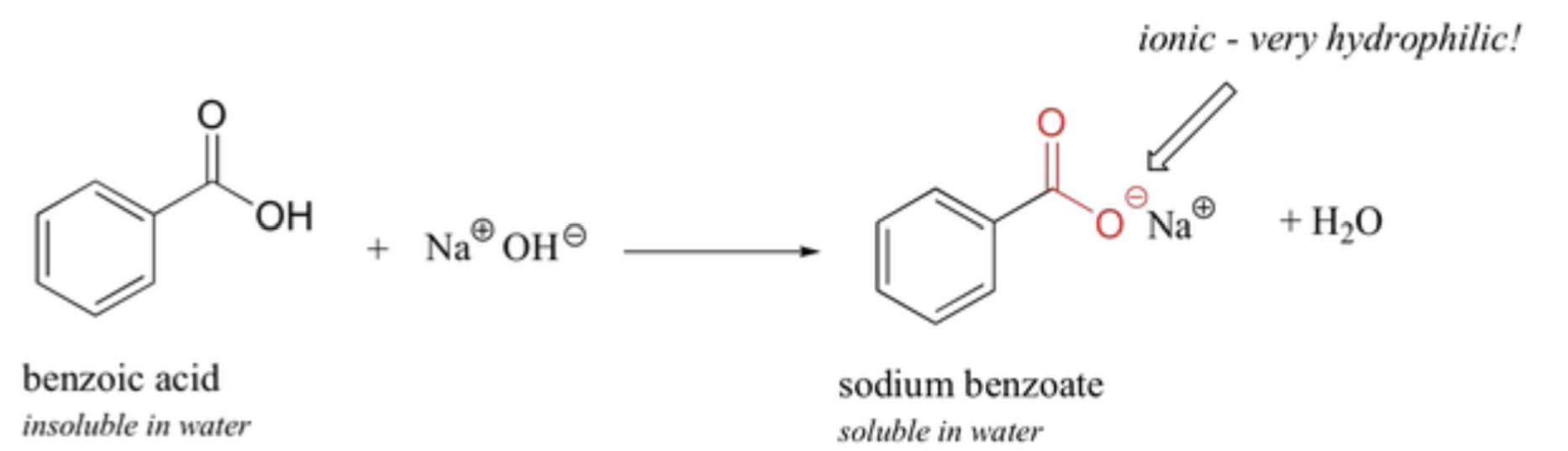
They can react with sodium hydroxide and sodium bicarbonate to form carboxylates (salts of carboxylic acids)
The reaction of benzoic acid with sodium hydroxide is shown below