Post transcriptional regulation- Exam 3
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
mechanisms of posttranscriptional gene regulation
control of alternative splicing
mRNA stability
translation
RNA silencing
proteome vs genome
genome: complete sequence of an organism’s genetic material (DNA): it is about 3 billion base pairs
approx. 20,000 protein coding regions have been identified
proteome: complete set of proteins an organism can produce; estimated about 100,000 produced; due to alternative splicing of mRNA transcripts
alternative splicing
generates different forms of mRNA from identical pre-mRNA (increases number of proteins)
expression of one gene gives rise to numerous proteins with similar and different functions
increases number of proteins made from one gene: # of proteins cell can make is not directly related to number of genes in genome
at least 2/3s of protein-coding genes in humans undergo this
prior to leaving the nucleus the introns are removed and exons exit the nucleus
introns
alternative splicing can produce different polypeptides from the same gene region because of these
may make it easier to produce proteins with different domains
they may be relics of ancient viruses
may aid in recombination
calcitonin
1 gene region that produces two distinctly different polypeptides
32 amino acid polypeptide that regulates calcium levels in the blood during childhood
splicing of exons 1,2,3, 4 create calcitonin
calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) regulates calcium levels in the brain and the peripheral nervous system: splicing of 1,2,3,5,6 create this
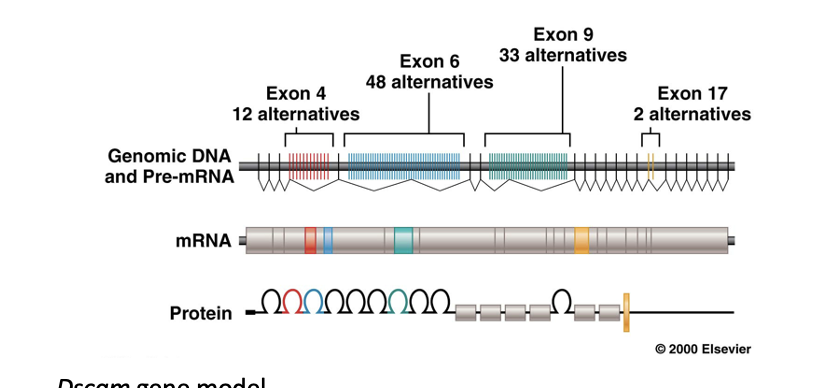
Dscam Gene
found in drosophila which produces a protein that guides the growth of axons
contains 4 exons that are highly variable with alternative forms that can be combined into over 38,000 unique polypeptides (isoforms)
these polypeptides guide the connections that develop among axons
cells express unique combinations of isoforms
each individual isoform will bind only to the same isoform enabling specific connections
Human homolog of Dscam
Dscam: abbreviation for Down’s syndrome cell adhesion molecule
in humans it is thought that the Dscam gene product codes for transmembrane protein that promotes cell-cell interactions
it is expressed at very high levels in fetal tissue
overexpression is seen in individuals with Down’s syndrome
not clear if the human homolog undergoes alternative splicing to the degree in drosophila
spliceopathies
mutations that affect regulation of splicing and contribute to several genetic disorders
ex: myotonic dystrophy
control of mRNA stability
steady-state level of mRNA: amount of mRNA in cell available for translation: determined by combination of transcription and mRNA degradation rates
half-life: mRNA is degraded at some point after synthesis, lifetime of mRNA varies; regulated by cell need
Three pathways of degradation
enzymes shorten length of poly-A tail :binding of poly-A binding protein to tail stabilizes mRNA
decapping enzymes removes 7-methylguanine gap- mRNA is now unstable
endonuclease cleave mRNA internally
proteosome
cylindrical structure that recycles amino acids
ubiquitin
a protein that tags proteins for recycling by the proteosome
translational and posttranslational regulation
p53 protein: if levels increase, the cell suffers DNA damage or metabolic stress → activates Chk2 ATM and ATR which adds PO4 to p53 protecting it from Mdm2
p53 is a transcription factor that induces transcription of Mdm2 gene (ubiquitin ligase, blocks transcription): adds ubiquitin to p53 send to proteosome
ubiquitin tags proteins (p53) for degradation by enzymes
lots of signals activate p53 and in turn it activates many downstream processes
cell survival signals activate Mdm2 allowing it to degrade p53
if PO4S are bound to N terminus of p53 Mdm2 cannot bind and p53 can continue to activate transcription of its targets