Chapter 10: Shores
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
1
New cards
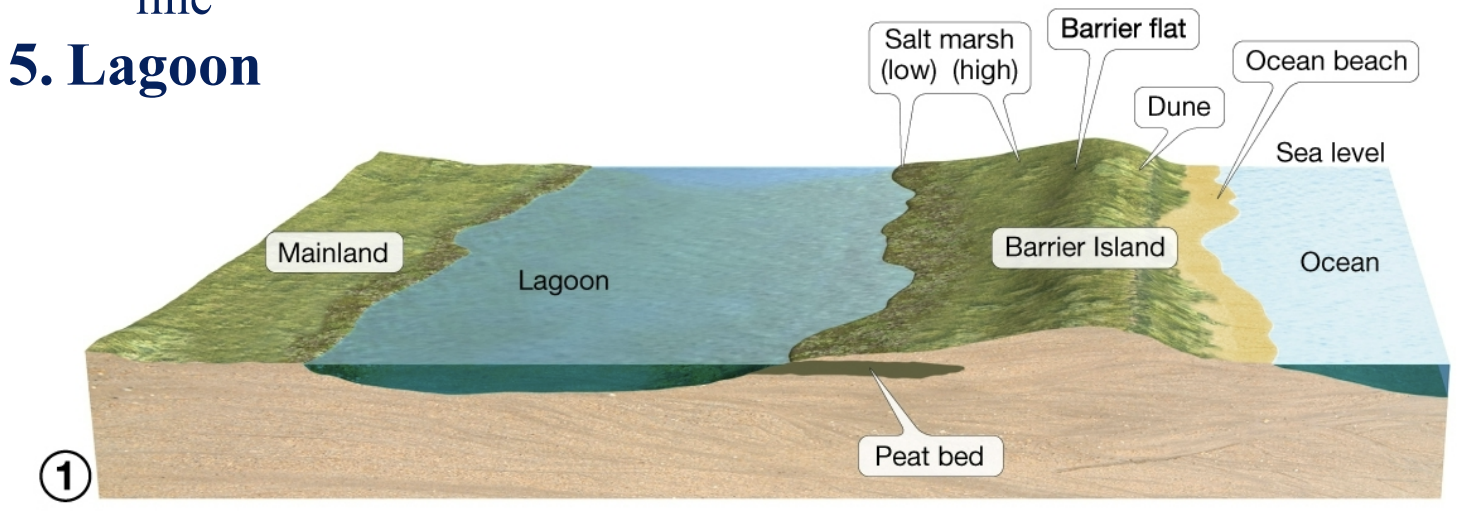
barrier island features
ocean beach, dune, barrier flat, salt marshes, lagoon
popular building sites, ppl love to live near oceans
popular building sites, ppl love to live near oceans
2
New cards
ocean beach
closest part of the island to the ocean
3
New cards
dune
stabilized by grasses, protect lagoon from strong storms
4
New cards
barrier flat
grassy area that forms behind dunes
5
New cards
salt marshes
inland of barrier flat, high salt marsh extends to highest spring tide line, low salt marsh extends from mean sea level to high neap tide line
6
New cards
lagoon
btwn. mainland and barrier island. peat bed underneath lagoon and barrier island
7
New cards
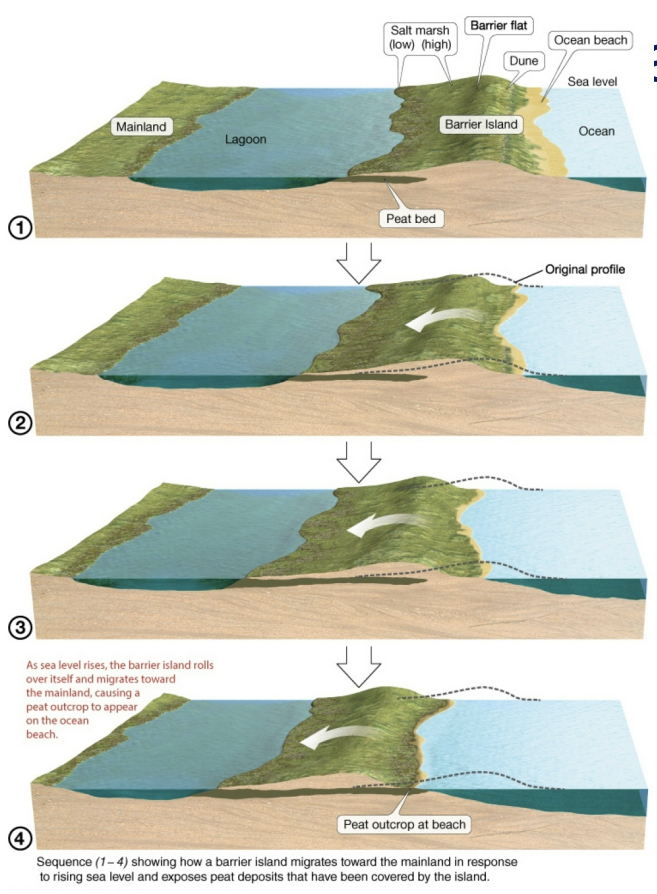
barrier island migration
migrate landward over time due to rising sea levels, older peat levels found on ocean beach
8
New cards
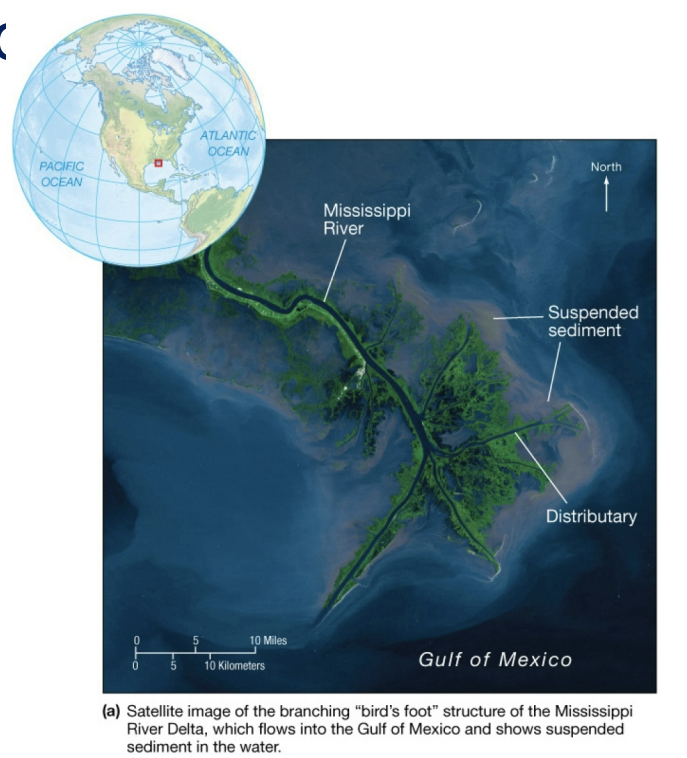
deltas
triangular deposits of sediment where rivers empty into oceans or seas
high productivity, high O2 \[ \]
high productivity, high O2 \[ \]
9
New cards
distributaries
branching channels carrying sediment to ocean
10
New cards
delta shoreline components
shoreline smoothed when erosion exceeds deposition.
large fisheries, high productivity,
nile river delta currently eroding
large fisheries, high productivity,
nile river delta currently eroding
11
New cards
nile river delta
currently eroding, if longshore drift carries sediment deposits, curved delta front similar to nile river delta will form.
12
New cards
beach compartments
rivers that supply beach sediment
beach itself
offshore submarine canyons
beach itself
offshore submarine canyons
13
New cards
beach starvation
human activities block supply of sand to beach compartments.
Dams across rivers block sediment
longshore transport process continues to operate in absence of river sediment input. if all streams supplying sediment are dammed, beaches will disappear
Dams across rivers block sediment
longshore transport process continues to operate in absence of river sediment input. if all streams supplying sediment are dammed, beaches will disappear
14
New cards
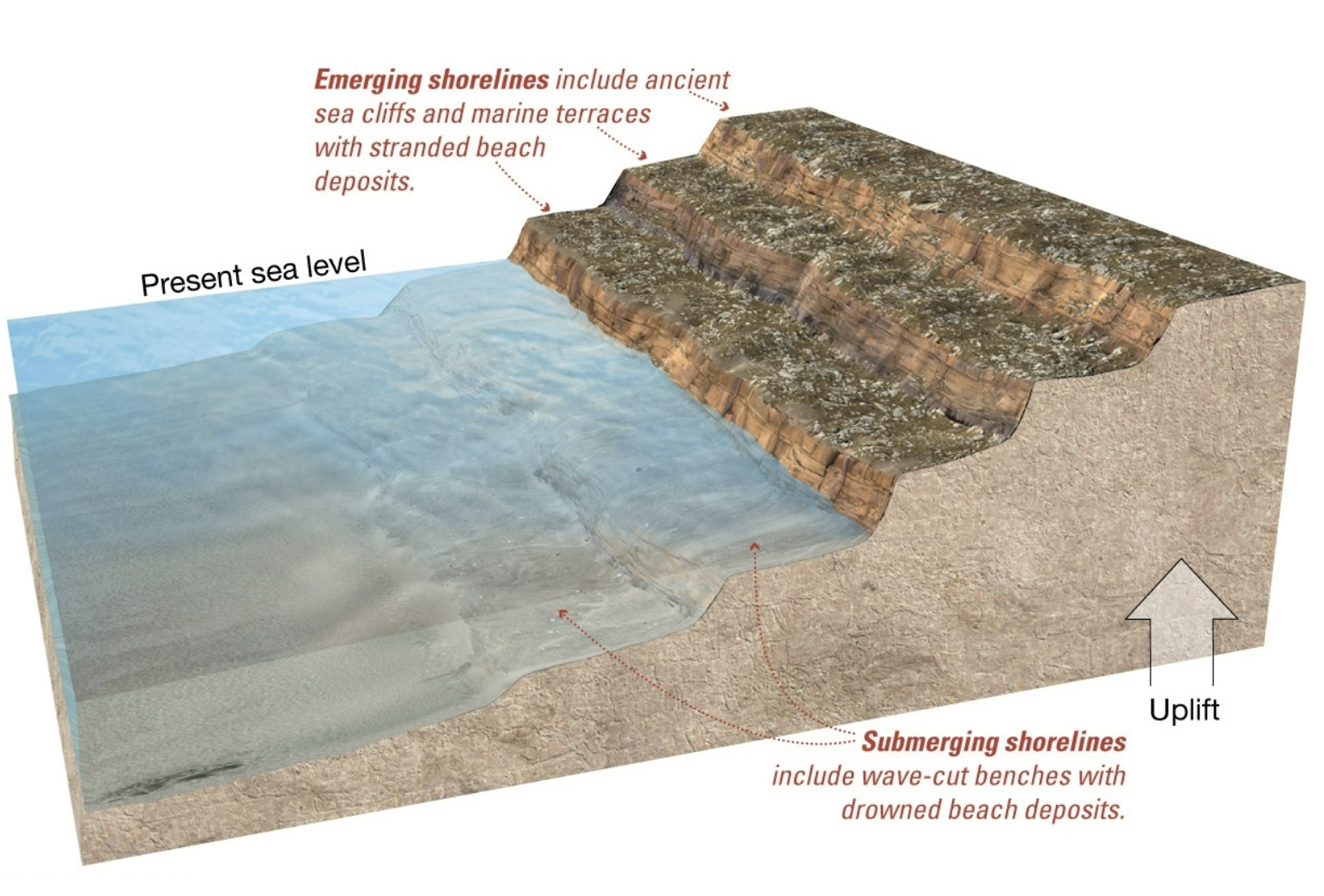
emerging shorelines
shorelines rising above current sea level.
marine terraces (flat platforms backed by cliffs),
stranded beach deposits (indication that former shoreline has risen above sea level)
US Pacific coast
marine terraces (flat platforms backed by cliffs),
stranded beach deposits (indication that former shoreline has risen above sea level)
US Pacific coast
15
New cards
submerging shorelines
shorelines sinking below current sea level
drowned beaches
submerged dune topography, drowned river valleys,
US Atlantic coast is one
drowned beaches
submerged dune topography, drowned river valleys,
US Atlantic coast is one
16
New cards
marine terraces
stranded beach deposits at diff levels
17
New cards
two major processes for sea level change
local tectonic processes raise or lower crust
worldwide changes in sea level
worldwide changes in sea level
18
New cards
movement of earth’s crust
tectonic movements
isostatic adjustment
changes in relative sea level, land changes, not sea
isostatic adjustment
changes in relative sea level, land changes, not sea
19
New cards
tectonic movements
crustal uplift, localized folding, tilting
pacific coast
pacific coast
20
New cards
isostatic adjustments
earth’s crust sinks under heavy loads of ice, piles of sediment.
rebound of crust after removal
rebound of crust after removal
21
New cards
eustatic sea level changes
worldwide, due to changes in seawater volume or ocean basin capacity.
caused by formation of inland lakes, decrease in sea level, sea floor spreading rate changes
formation of glaciers
caused by formation of inland lakes, decrease in sea level, sea floor spreading rate changes
formation of glaciers
22
New cards
sea floor spreading rate
changes: shape of ocean basins change due to tectonic movement
basin = larger, volume =larger, sea level falls, bc same amount in bigger container.
basin = larger, volume =larger, sea level falls, bc same amount in bigger container.
23
New cards
pleistocene epoch
2 million-10k years ago, 4 ice ages affected earth
it was 120 m (400 ft) sea level lower
if all ice melts today, sea level rises another 70 m (230 ft)
it was 120 m (400 ft) sea level lower
if all ice melts today, sea level rises another 70 m (230 ft)
24
New cards
hard stabilization
structures built to decrease coastal erosion and interfere with sand movement.
“armoring of shore” sand traps,
“armoring of shore” sand traps,
25
New cards
4 major types of hard stabilization structures
groins and groin fields
jetties,
breakwaters
seawalls
jetties,
breakwaters
seawalls
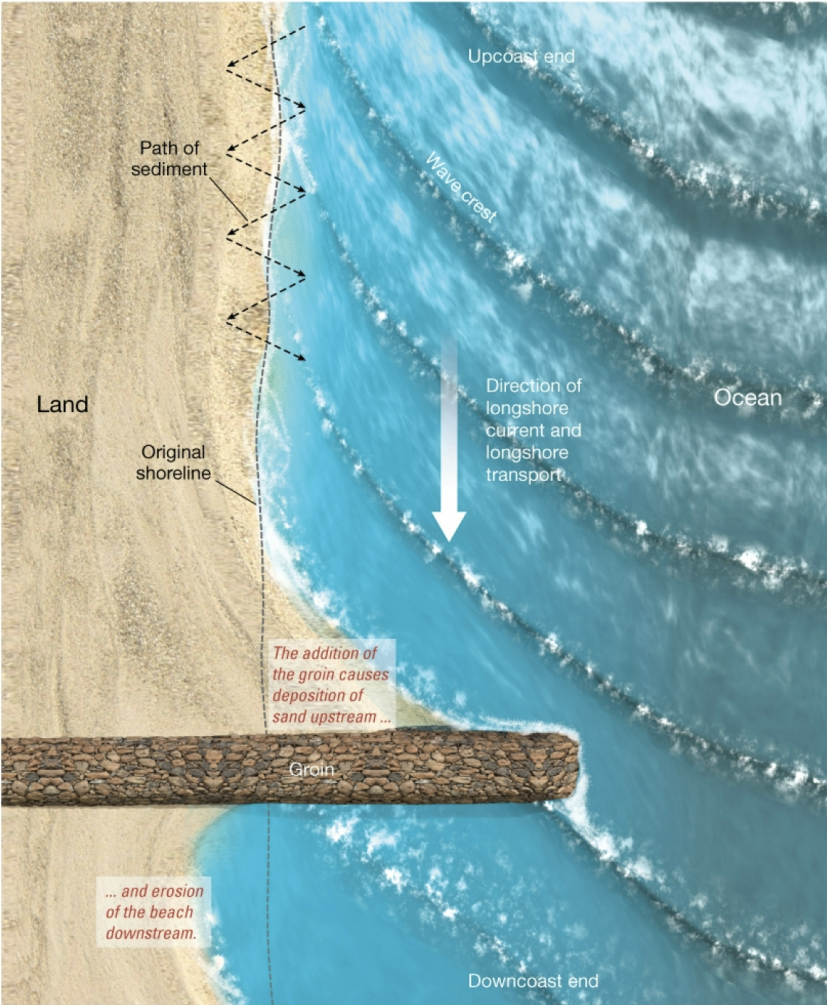
26
New cards
groins and groin fields
perpendicular to beach: built of rip rap, large blocky material
traps sand upcoast, causing erosion downcoast of longshore current
another groin downcoast, causes groin field. sand distributed differently, no additional sand on beach
traps sand upcoast, causing erosion downcoast of longshore current
another groin downcoast, causes groin field. sand distributed differently, no additional sand on beach
27
New cards
Jettie
similar to groin, built perpendicular to shore in pairs.
protects harbor entrances and only secondarily traps sand.
cause more upcoast deposition and downcoast erosion
protects harbor entrances and only secondarily traps sand.
cause more upcoast deposition and downcoast erosion
28
New cards
breakwaters
parallel to shore, protect harbor from waves, cause excessive erosion, requires dredging to keep area stable
29
New cards
seawalls
most destructive
parallel to shore, armor coast and protect developments
one large storm removes beach, wave activity eventually destroys structure, needs maintanence
parallel to shore, armor coast and protect developments
one large storm removes beach, wave activity eventually destroys structure, needs maintanence
30
New cards
alternatives to hard stabilization
construction restrictions
beach replenishment
relocation
beach replenishment
relocation
31
New cards
construction restrictions
simplest alternative, limit building near shore
national flood insurance program encourages construction
national flood insurance program encourages construction
32
New cards
beach replenishment
Sand added to beach/longshore current
costs between $5 and $10 per cubic yard
Sand must be dredged from elsewhere
costs between $5 and $10 per cubic yard
Sand must be dredged from elsewhere
33
New cards
relocation
move structures rather than protect them in areas of erosion
allow humans to live in natural balance with beach processes
allow humans to live in natural balance with beach processes
34
New cards
coastal waters characteristics
salinity, temp, coastal geostrophic currents
35
New cards
halocline
represents salinity variations with depth in water column
36
New cards
isohaline
uniform salinity from surface to deeper layers
freshwater runoff causes lower surface salinities at coast
combo of these two causes vertical mixing, moderate salinity, and water column that is isohaline
freshwater runoff causes lower surface salinities at coast
combo of these two causes vertical mixing, moderate salinity, and water column that is isohaline
37
New cards
isothermal
water temp is uniform throughout water column
38
New cards
thermocline
temp variation with depth.
in low and high latitude regions, water is isothermal year round
in midlatitude areas, surface temps are coolest in winter and warmest in summer
in low and high latitude regions, water is isothermal year round
in midlatitude areas, surface temps are coolest in winter and warmest in summer
39
New cards
coastal geostrophic currents
move circular path
generated in coastal areas by wind and runoff
wedge of freshwater runoff on coast generates surface flow towards open ocean
generated in coastal areas by wind and runoff
wedge of freshwater runoff on coast generates surface flow towards open ocean
40
New cards
davidson current
coast of Washington and Oregon
41
New cards
estuaries
partially enclosed coastal body of water in which freshwater runoffs from a river dilutes the input of salty ocean water
42
New cards
4 types of estuaries
coastal plain estuary
fjord
bar built estuary
tectonic estuary
fjord
bar built estuary
tectonic estuary
43
New cards
coastal plain estuary
forms as sea level rises and floods existing river valleys. Also called drowned river valleys – Chesapeake Bay
44
New cards
fjord
forms when sea level rises and floods an existing glaciated valley. These valleys typically are U shaped and have steep walls with glacier debris near ocean entrances
45
New cards
bar built estuary
includes lagoons that separate barrier islands from the mainland. They are generated from sand bars that are deposited parallel to the coast by ocean wave processes – U.S. Gulf coast and East Coast
46
New cards
tectonic estuary
forms with faulting or folding of rocks that generate a geologically dropped location that the sea floods
San Fran Bay
San Fran Bay
47
New cards
vertically mixed estuary
shallow, low-volume. Net flow from head to mouth of estuary, salinity increases from the head to the mouth of the estuary
48
New cards
slightly stratified estuary
salinity increases from head to mouth at all depths. Two distinct layers, less-saline(less dense) upper layer and more saline(more dense) lower layer
49
New cards
highly stratified estuary
deep with upper layer salinity increasing from head to mouth
50
New cards
salt wedge estuary
wedge of salty water from ocean moves in under river water
51
New cards
estuaries and human activities
threatened by human populations
breeding grounds and nurseries
human activities can damage estuarine environments
breeding grounds and nurseries
human activities can damage estuarine environments
52
New cards
columbia river estuary
salt wedge estuary
principal conduit for logging industry
increased sediment load
dredging of sediment carries increased pollution risk
principal conduit for logging industry
increased sediment load
dredging of sediment carries increased pollution risk
53
New cards
chesapeake bay
slightly stratified
large seasonal changes in temp, salinity, dissolved o2
max freshwater river flow in spring
large seasonal changes in temp, salinity, dissolved o2
max freshwater river flow in spring
54
New cards
issues with chesapeake bay
waters become anoxic from May-August.
major kills of commercially important blue crabs, oysters, and other bottom dwelling species
increased nutrients from sewage and agricultural causing algal blooms and environmental issues
major kills of commercially important blue crabs, oysters, and other bottom dwelling species
increased nutrients from sewage and agricultural causing algal blooms and environmental issues
55
New cards
lagoons
protected shallow water bodies landward of barrier islands.
bar built estuary
restricted circulation with ocean, therefore 3 distinct zones.
bar built estuary
restricted circulation with ocean, therefore 3 distinct zones.
56
New cards
freshwater zone
near head of lagoon
57
New cards
transitional zone
middle of lagoon
58
New cards
saltwater zone
near mouth of lagoon
59
New cards
laguna madre
along Texas coast, btwn. Corpus Christi and Rio Grande.
protected by Padre Island, barrier island 160 km long
hypersaline
large seasonal variations
ocean water flows as a surface wedge over denser lagoon water
protected by Padre Island, barrier island 160 km long
hypersaline
large seasonal variations
ocean water flows as a surface wedge over denser lagoon water
60
New cards
marginal seas
large semi isolated bodies of water
result from tectonic events that isolated ocean crust btwn. continents or created behind volcanic island arcs
Mediterranean and Caribbean sea
result from tectonic events that isolated ocean crust btwn. continents or created behind volcanic island arcs
Mediterranean and Caribbean sea
61
New cards
mediterranean sea
remnant of tethys sea
Shallow and narrow connection to Atlantic Ocean and Black Sea
Irregular coastline, divides it into subseas, like the Aegean and Adriatic Sea
underwater sill or ridge separates mediterranean into two major basins
Shallow and narrow connection to Atlantic Ocean and Black Sea
Irregular coastline, divides it into subseas, like the Aegean and Adriatic Sea
underwater sill or ridge separates mediterranean into two major basins
62
New cards
mediterranean circulation
unique pattern due to middle east heat
large surface in flow from Atlantic to replace evaporated surface h2o
opposite of most estuaries
large surface in flow from Atlantic to replace evaporated surface h2o
opposite of most estuaries
63
New cards
wetlands
ecosystems with water table close to surface
generally saturated, fresh or coastal
efficient at cleaning polluted water. remove agricultural runoff
generally saturated, fresh or coastal
efficient at cleaning polluted water. remove agricultural runoff
64
New cards
salt marshes
btwn. 30 and 65 degrees latitude
support salt tolerant grasses and other halophytic low lying plants: cordgrass, salt meadow cordgrass
support salt tolerant grasses and other halophytic low lying plants: cordgrass, salt meadow cordgrass
65
New cards
mangroves
tropics below 30 degrees latitude
salt tolerant trees, shrubs, palms
tall tripod like root systems
caribbean, florida, southeast Asia
salt tolerant trees, shrubs, palms
tall tripod like root systems
caribbean, florida, southeast Asia
66
New cards
characteristics of coastal wetlands
diverse plants and animals
most productive
enormous economic benefit
nurseries for more than half of commercially important fish species in SE US
most productive
enormous economic benefit
nurseries for more than half of commercially important fish species in SE US
67
New cards
what do coastal wetlands do
soak up farmland runoff
remove inorganic nitrogen compounds
“nature’s kidneys”
protect shoreline
1 acre of wetland can filter 2.76 million liters of water each year
remove inorganic nitrogen compounds
“nature’s kidneys”
protect shoreline
1 acre of wetland can filter 2.76 million liters of water each year
68
New cards
loss of wetlands
more than half of US wetlands have vanished
filled in and developed
originally 87 million hectares, now 43 million.
49\.7 % remain
EPA established office of wetland protection.
tasked with enforcing regs against pollution and identifying important ones
filled in and developed
originally 87 million hectares, now 43 million.
49\.7 % remain
EPA established office of wetland protection.
tasked with enforcing regs against pollution and identifying important ones