Topic 2 Computer Organization
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
A hardware component of a computer system and can perform basic arithmetic, logical or input/output operations; essentially the ‘brain’ of the computer system. Also known as the ‘processor’.
Contains the Control Unit (CU); Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU); Memory Address Register (MAR); and Memory Data Register (MDR)
Control Unit
Fetches data or instruction from memory, decodes it into commands and controls transfer of among other units of the CPU (e.g. command to ALU for execution).
Part of the processor which coordinates all activities within it
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Performs all basic Arithmetic and Logical and input/output operations executes instructions
Primary Memory
The only storage that is directly accessible by the CPU; at any point in time, it may hold both data and instructions that are currently running on the computer system. These instructions are stored in Machine Code (1s and 0s)
Computer Systems
Consist of hardware and software components and follow the concept of input, process, output and storage model
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Stores the executing program instructions as well as any data that is needed. Instructions and data in the RAM are stored in unique memory locations and every such location has an address as well as content. The content is where the instructions and data reside, whereas the memory location is used by the CU to find, retrieve, and access the data in order to send it to the ALU for processing.
Read Only Memory (ROM)
Holds instructions and data in unique memory locations. Every such location has an address as well as content. Unlike the RAM however, the ROM is used to store permanent instructions and data that cannot be changed and are used to boot and operate the computer. As such, nothing can be altered in the ROM.
Registers
a small storage location that can hold data, usually a multiple of 8 bits.
Word
The size of the register in bytes
Memory Address Register (MAR)
holds the memory address of the data to be used by the ALU, so that the ALU can fetch the corresponding content from the memory and process it accordingly. The MAR may also hold the memory address of where data that has been processed will need to be stored.
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Holds the data that is to be used by the ALU and then saved to the RAM. ]
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Used as the primary source of RAM in a Computer System.
Preferred for the main RAM of a computer system.
Slower and cheaper than SRAM
Static RAM (SRAM)
Faster and More expensive than DRAM. A small section of SRAM is known as the cache memory is placed between the main RAM and the Processor
Cache
Holds information from the RAM that is most actively used, and accessed most frequently. Reading from the Cache speeds things up.
L1 Cache
Placed ont he microprocessor itself
L2 Cache
Placed between the primary memory and the microprocessor
Machine Instruction Cycle
Fetch instruction from primary memory to control unit
Decode instruction in control unit
Execute instruction
Store result of execution and check for next instruction
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Stores the Memory Address of next data/instruction to be decoded and executed by the ALU. In order for the MAR to communicated with the Primary Memory (RAM), it connects through the Memory Address Bus.
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Stores the Data itself taken most recently from the RAM, which is then used by the ALU/ This allows the processor (CPU) and Memory (RAM) to act independently, with the CPU not affected by differences in the speed of operation. The connection between the RAM and the MDR is accomplished by the Memory Data Bus.
Bus
set of wires that connect to components in a computer system. Buses are used as physical connections to carry information to the CPU. For example, the MDB transports data from/to the CPU, whereas the MAB states where the data is supposed to go.
Secondary Memory
Relatively slow memory that can be written-to (like RAM( but also is non volatile (like ROM); therefore the contents are not wiped when power is lost. This makes Secondary Memory a form of persistent storage. Has a relatively high storage capacity compared to primary memory. All information and data need to be coped from the secondary into RAM for the computer system to run.
Examples:
USB
HDD
SD
Magnetic Tape
Operating System.
Set of software that controls computers hardware resources and provides services for computer programs
Services of an Operating System
Peripheral communication'
Memory management
Resource monitoring and multitasking
Networking
Disk access and data management
Security
Peripheral Communication
All the hardware components of the computer system that exist outside the CPu. The OS is responsible for communicating directly with the hardware and providing an interface between hardware devices and applications
Peripheral Device Examples
Keyboard
Magnetic Card Reader
Microphone'
Monitor
Visual Display
Speakers
Memory Management
an OS is responsible for all the memory that is available in a computer system, therefor it must manage how memory is used by applications, and ensures that one application does not interfere with memory that is being used by some other application
Resource Allocation
An application running on a computer system uses up resources (including the amount of memory the application is occupying, or how much processing time is required). The OS is responsible for the efficient allocation of resources so that an application can run as effectively as possible
Networking
The OS manages connections with networks of other computer systems to allow the sharing of Network Resources
Data Management
The OS must have the ability to access data stored in memory. Data is stored using files, and the OS must keep track of files and their location in order to make the best use of memory available, provide fast access times, and ensure that an application does not overwrite another applications files
Security
Provides measures such as password authentication, magnetic cards, access rights to prevent unauthorized access
Application Software
Programs designed for the end-used that enable the completion of various tasks in order to increase productivity.
Application Software Examples
Word processors
Spreadsheets
Database management systems
Web browsers
Email
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
Graphic processing software
Word Processors
A software application that is used for the production of any sort of document. It includes tools for the composition, editing, formatting, and possibly printing of documents. The most common of all the main software applications.
Spreadsheets
A software application that is used for the organization and analysis of data. The data in a spreadsheet application is presented as cells organized in rows and columns these cells may contain numbers, text, or results of formulas that calculate and display values automatically on the basis of the contents of other cells.
Database management systems (DBMS(
manages (creates, queries, updates, stores, modifies, and extracts information) databases and is designed to provide an interface between users a database
Database
organized collection of data
Web Browser
Access, retrieve, and present content on the World Wide Web. Could be web pages, images, videos or other files and may be identified by a URI.
allows for the exchange of digital messages from a single author to one or more recipients. The author and the recipients do not need to be online simultaneously to exchange the email. the author of the email sends the email to the email server of the recipients, and when the latter connects to the server, they will receive the message.
Computer Aided Design CAD
Often used in engineering, manufacturing, and architecture to create, modify, and analyze a design. Can convert info like shape, materials, dimensions, etc with changeable values. Supports the design/development of rapid prototyping in manufacturing a system solution; saves time/costs associated to drawing and development; photorealistic rending/photo simulation in carious industries (architecture/video games/ simulators/etc) by using shading radiosity, reflection, etc.
Graphic Processing
manipulate visual images with functions such as move, erase, crop, colour, etc.
Graphical user interface (GUI)
Allows user to interact with software in different ways
Command Line Interface (CLI)
Where the user types in commands. Used in early software applications.
Features of an Operating System
Toolbar
Buttons, icons, menus, etc.
Menu
List of Commands you can choose
Dialogue Box
Communicates information to the user and allows option choice
Acronym to Remember Common Features of a GUI
WIMP
W - Windows
I - Icons
M - Menus
P - Pointers
Binary Digit (bit)
(b) the basic unit of information in computer systems and can have only two values, either 1 or 0.
Byte
(B) Formed by 8 bits
Two’s complement
The way most modern computers represent signed binary numbers
Most Significant Bit (MSB)
the bit position in a binary number having. the greatest value
Least Significant Bit
the bit on the right, which gives us the units.
What is the smallest negative number that can be stored in an 8 bit register
-128
What do you need to have to represent decimal numbers?
A Radix/Decimal Point
Hexadecimal Number System
Positional system that uses 16 digits (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F)
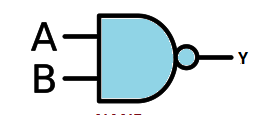
NAND
invert of the AND
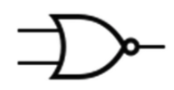
NOR
Invert of the OR
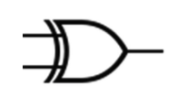
XOR
True whenever they’re different
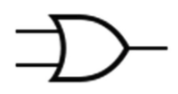
OR
When at least one is true
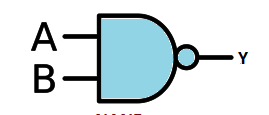
AND
When both are tru
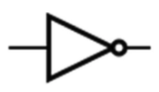
NOT
Opposite of a single value