Lecture 1 - World of Economic Growth
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
How is economic growth typically measured
GDP
Why study GDP growth
GDP captures something that humans care about
consumption + investment
but
GDP ignores important things that also matter
e.,g., leisure, health & goods produced in underground economy
GDP positively correlated with other things
life satisfaction, health, human rights
Measurement problems - how to incorporate quality improvements
Why study economic growth?
doesnt happen automatically
matters - more consumption, better health etc
varies massively across time, countries, regions
can be stimulated and hampered by gov policies
How to compare GDP levels
To make meaningful comparisons across time and across countries correct using Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
What does PPP do
shows relative value of currencies across countries
Convergence
idea that low income countries have higher growth rates so they catch up to higher income countries (converge)
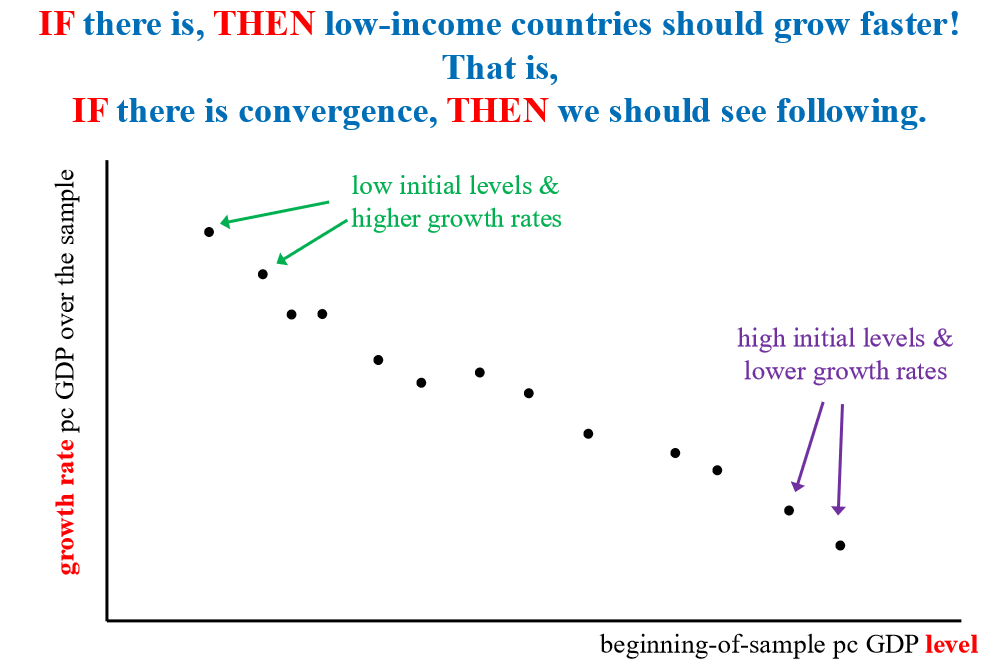
The negative relationship and convergence
Is the negative relationship not only neccessary for convergence, but also sufficient?
Unconditional convergence below
Unconditional convergence
No country characteristics conditioned on
Conditional convergence
Much more evidence if countries are ‘similar’
similar technology levels
similar investment rates
similar population growth rates
industrialised countries
part of same unions e.g. EU
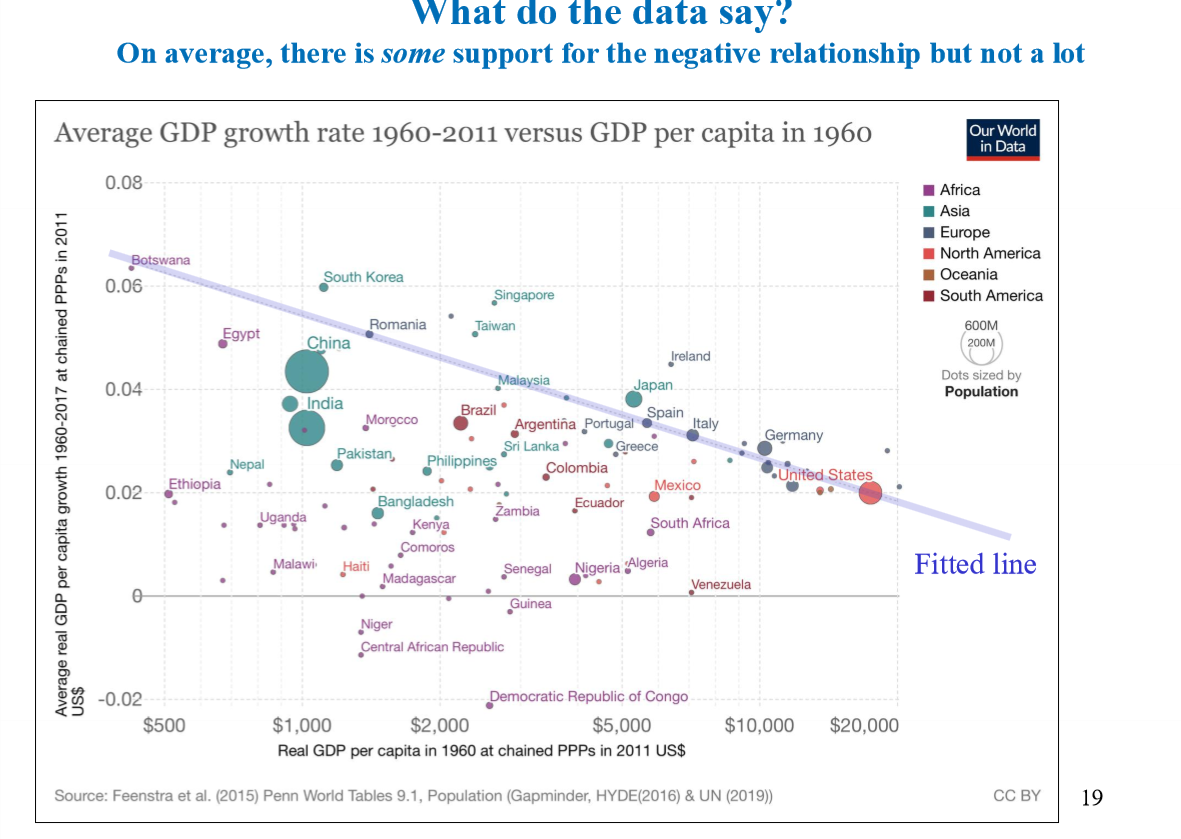
Is there convergence?
If low income countries save more - countries can grow by allocating a large share of GDP to investment instead of consumption
What does a log scale show
Growth in percentage change not absolute values
Problem with aggregate GDP
averages hide distributional differences
not everyone equally affected by recession
some people lose jobs others unaffected
GDP down by 2% but some lose 100% of income
Is long-term growth affected by the presence of business cycles? ie what would UK GDP series look like without business cycle fluctuations
Smooth line - same average growth rate
A higher average growth rate (connecting the peaks) - peaks represent potential, however peak may also represent an overheated situation that is not sustainable // higher growth possible in a more stable environment e.g. bc more willingness to invest under certainty
A lower average growth rate as business cycles bring creative destruction //innovative entrepreneurial activity is needed for growth, but a necessary side effect is volatility
Does growth affect the prevalence of recessions?
Growth happens bc entrepreneurs take risk → higher business cycle volatility
More growth → better institutions → lower volatility
Why did ‘Eurasians’ end up doing so much better than the other continents?
Once everybody started as ‘hunter-gatherers’
Eurasians: access to plants/animals useful for farming (e.g. domesticable horses)
Farming → Surplus to support ‘thinkers’ & specialisation
Living with animals → People become immune to germs
Thinkers → Invent guns and steel
Dominate hunter-gatherers on other continents
Interact with those not immune to germs
Dominate hunter-gatherers on other continents
IR time period
1750 - 1820
18th C
Factors behind 1st IR
1) Protection of property rights
2) Atlantic trade
3) Enlightenment
4) Agricultural revolution
5) ‘High’ wages and cheap coal
6) Financial revolution?
Protection of property rights
Credible commitment to not expropriate
Invstmt requires protection of property rights
Earlier, UK kings abused property rights
UK civil war and glorious revolution 1688-89
laws that limit power of kings
Why wasn’t power given to a new elite in the UK
(related to property rights protection)
Landowners (Tories) vs merchants (Whigs)
Two diverse powerful groups with different interests created a delicate power struggle
Atlantic trade
Atlantic trade → resources increased
Atlantic trade and protection of property rights →
Advantages of Atlantic trade not absorbed by aristocratic elite
seen by UK and Netherlands growing, and France, Portugal and Spain less so
Enlightenment
New Revolutionary View:
Mankind can improve upon its fate by scientific inquiry, especially empiricism and reason
Religious dogma was challenged
Importance of Interaction Factors
Many smart people in diff countries before the enlightenment
Came up with brilliant inventions
But often lost
Watershed moment: Invention printing press (1450)
IDeas could be easily preserved and easily disseminated
China had invented a printing press before Gutenberg but progress hampered by lack of alphabet
Following combo helpful
Enlightenment freed up the mind and resulted in having a religion that wasn’t to oppressive
A particular invention to disseminate info
Convenient alphabet
Agricultural Revolution
Stimulated by protection of property rights
Adding turnips allowed for more efficient crop rotation → productivity increased
Cows ate turnips so shared use of lands was problematic
so land had to be enclosed and this pushed poor people to cities releasing manpower and creating labour for factories
Causation between AR and IR
1. Agricultural Revolution released manpower and helped the industrial revolution.
2. Industrial revolution attracted manpower from farming which triggered agricultural revolution.
What type of wage behaviour would distinguish the two stories?
If #1, then wages in industry should ↓ due to inflow of workers from agriculture.
If #2, then wages in industry should ↑ due to increased demand for man power.
Data indicates that #2 is more plausible.
High wages and cheap coal
1) Wages in England were ‘high’ due to economic expansion (rural manufacturing, agricultural productivity increases + growth of cities)
2) Coal was abundant and cheap, so energy costs not a problem for initially very inefficient machines ( and coal had long term advantages as opposed to peat which was used in the Netherlands)
Above → labour saving innovations
‘high’ wages means high enough so that using machines was even cheaper, workers not well off
Role of Finance
UK Financial Revolution (after glorious revolution of 1688)
BOE: Created in 1694 and lender of last resort in 1760
Emergence of a stock market
Financial development known to be important for economic growth during other episodes
But role of finance for 1st Industrial Revolution disputed
Most financing did not come from banks (UK banks didn’t do much long-term lending)
However, Heblich and Trew (2019) using a unique regional data set document that bank access was important for industrialisation and TFP increases.
Was 1st Industrial Revolution a Success Story?
Yes if focus on economic growth narrowly defined
Lots of important aspects ignored:
Working conditions
Living conditions (overcrowding in cities)
Colonial expansion (for imports of raw materials & export finished goods)
Environment