biol 117 lecture 1 study questions
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
How can you determine if a trait is genetic?
Look into the family history and take genetic tests/ it runs in families ex: twins
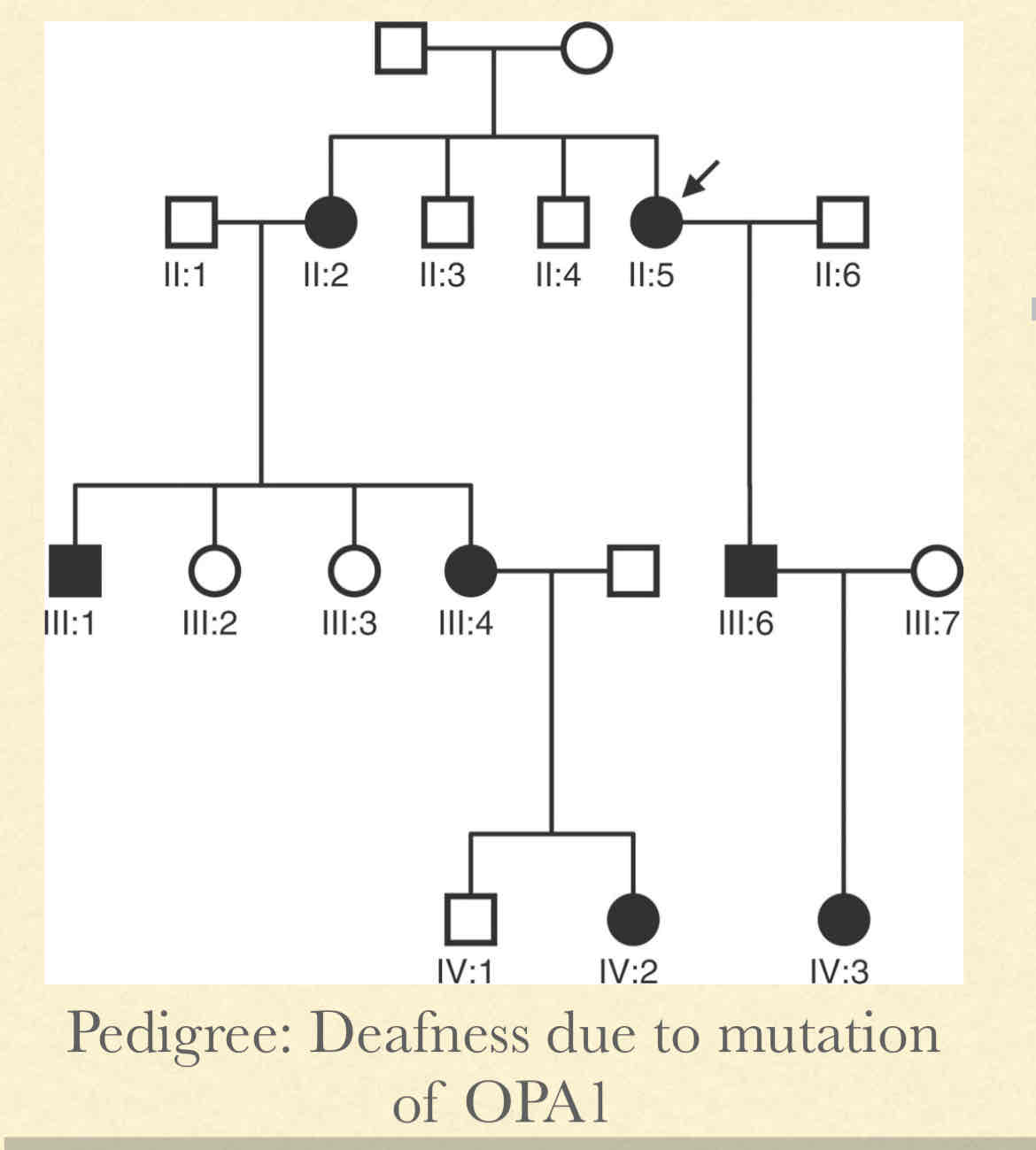
What is an autosomal dominant or dominant inheritance?
Concepts:
Only one defective copy of allele causes phenotype to be expressed
Both females and males can pass phenotype to either sex of children
Pedigree Observations:
Equal and both females and males
Happens in most generations
Children of affected parents will have 50% chance risk for inheriting phenotype
Unaffected parent will not produce affected children
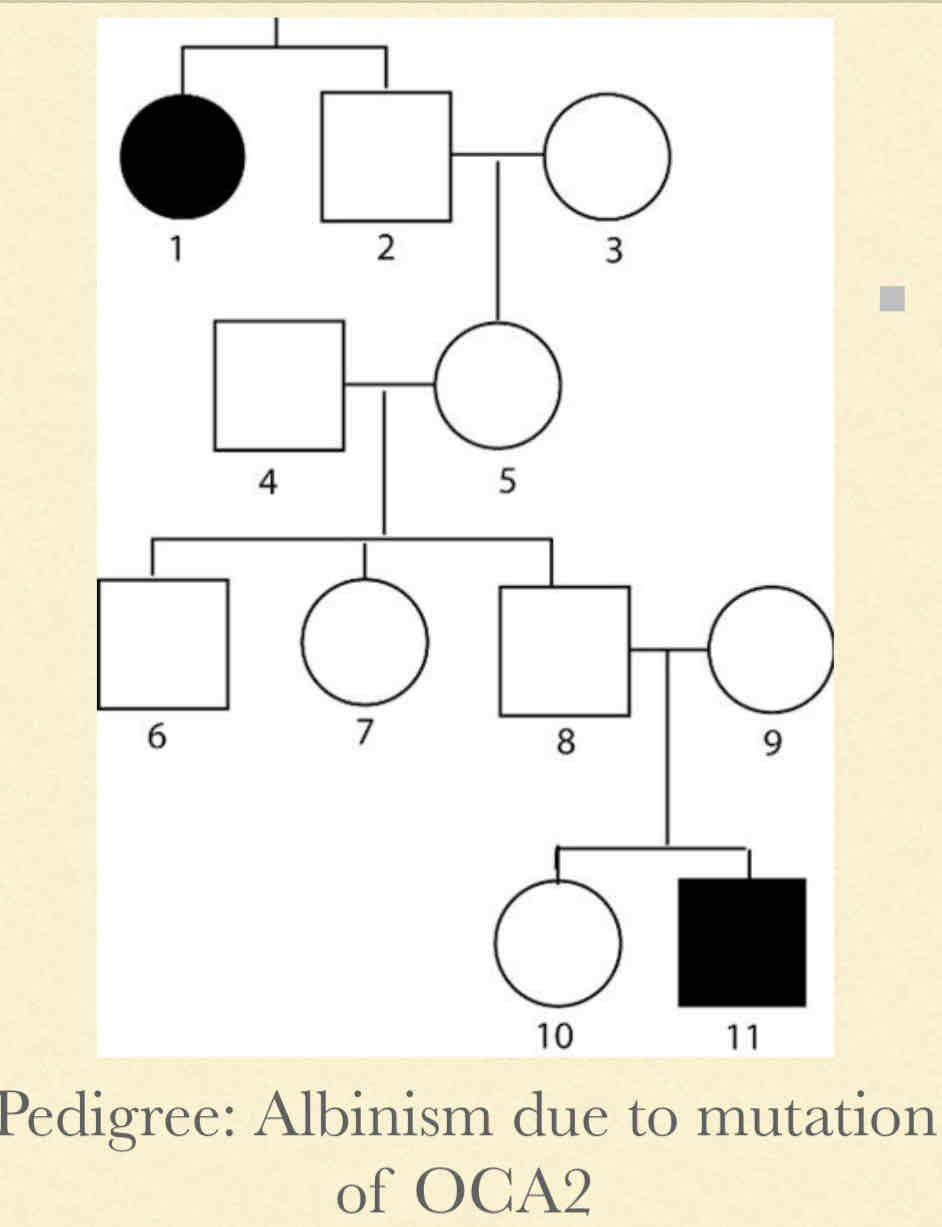
What is autosomal recessive inhheritance?
Concepts:
Must have mutant copy in both alleles for phenotype to be expressed
Pedigree Observations
Tends to “disappear” in generations
Equal in both females and males
If both parents are carriers their children will have 25% chance risk for inheriting phenotype
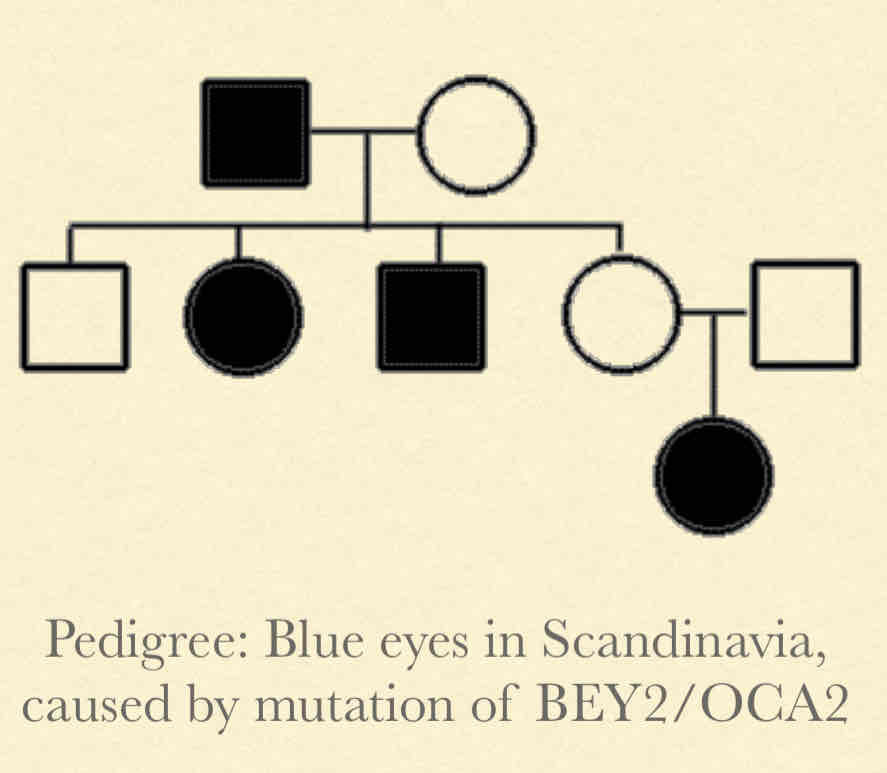
What is Pseudo-Dominant Inheritance
Concepts:
Both copies of allele have to be mutant to cause phenotype
Carrier rate is high
Pedigree Observations:
Equal and both females and males
Tend to “skip” in most generations
Both parents affected, all children will be affected
Could be dominant with reduced penetrance
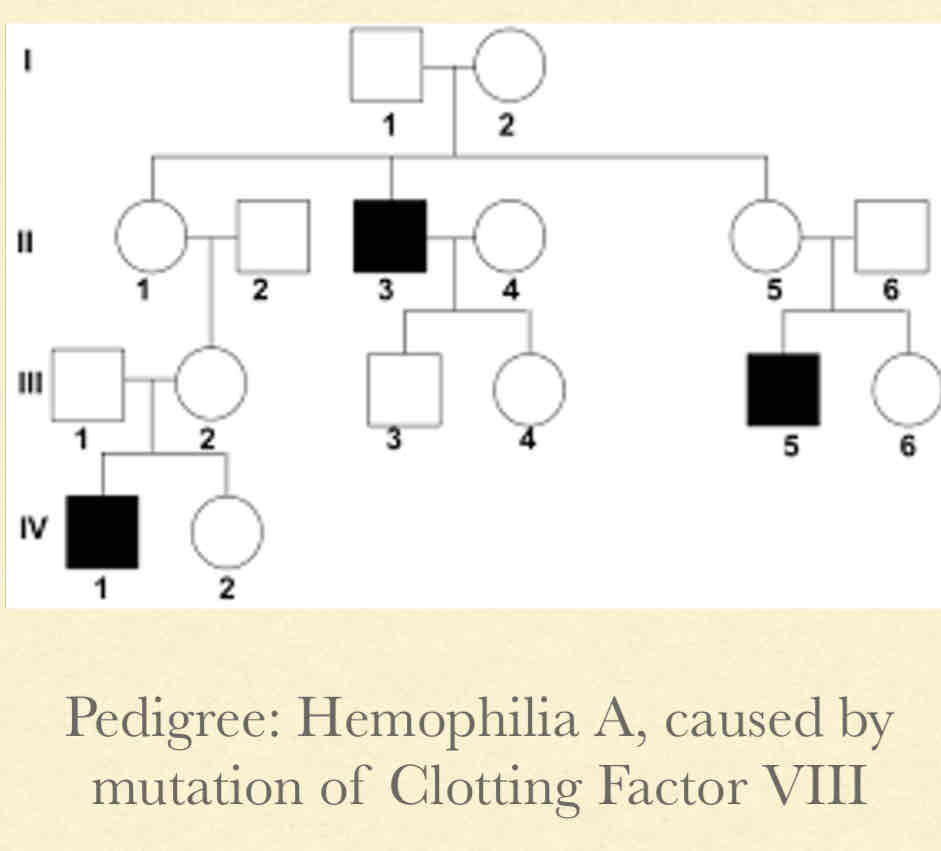
What is X-linked inheritance?
Concepts:
Only one X- linked chromosome from men will always express a mutation
Usually recessive
No male to male transmission
Pedigree Observations:
Happens mostly in males
Daughters of affected male will always be carriers
Tend to “skip” a generation
Why are recessive traits difficult to identify as “genetic”?
are rare and hard to find, only can be found in large families
Why are pseudo-dominant traits difficult to identify as “recessive”?
They follow a autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
What are some complicating factors in pedigree analysis?
Risks modified by:
Mosaicism, environmental factors, De Novo mutation, incomplete penetrance, age-related penetrance (ex: Alzheimers)
Data collection complicated by:
small families, adoptions, divorce, early death