Part 2: Cost of Cancer
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
ACS stands for
American Cancer Society
According to the ACS healthcare costs have been rising dramatically due to 3 factors. List them.
infectious diseases being replaced/ outnumbered by lifestyle related chronic diseases like cancer
The aging (“graying”) of America
The high cost of medical technology
NCI stats: Cancer care is ~___% of all healthcare costs
5%
According to the ACS what is another factor that can affect overall cost of treatment that is related to cancer prevention and controll?
Significant delays between gaining new knowledge (and tests) and implementing that knowledge / tests
Give 3 example of the delays of tests/ knowledge and their implementation
Papanicolaou (pap) smear: perfected in 1943 → implemented 1970s
mammograms: available 1950s → promoted in the 1980s
Surgeon general warned about hazards of smoking in 1964→ 1980s tobacco initiatives implemented
term. Epidemiology
def. the study of the demographics of disease
def. the study of the distribution of and determinants of disease and injuries in human populations
term. epidemiology
In what group of people is cancer most prevalent in?
minority groups, specially African Americans
Why is cancer most prevalent in minority groups? (5 reasons)
They are more exposed to risk factors→ specially those related to tobacco use and diet
They are poor, less educated
deprived of safe & healthy environment
less likely to have health insurance
less likely to seek medical care
term. Etiology
def. the study of the cause of disease
What causes cancer initiation
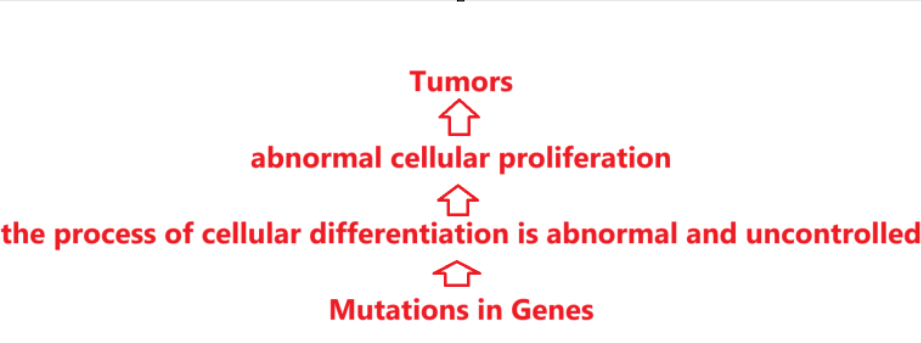
the mutations in genes that cause abnormal and uncontrolled cellular differentiation include:
mutations in genes that:
promote growth→ force the growth of cells
suppress growth → allow for the uncontrolled cellular growth
For many tumors, BOTH mutations may be required for full malignancy
term. Oncogenes
def. cancer causing genes
How many oncogenes have we identified?
over 200
3 cancers that are primarily linked to genetics?
Breast CA
Colon CA
Retinoblastoma
The average adult has ____cancer cells in the body at any given time
1M
If we have ~1M cancer cells in the body at any given time, how come we don’t get cancer?
The immune system is able to get rid of them
That is why some people believe cancer is a weakness/ deficiency in the immune system & it’s ability to identify and fight off cancer cells
term. Proto-oncogenes
def. genes that are responsible for controlling cellular proliferation
anti-oncogenes aka
tumor suppressor genes
anti-neogenes
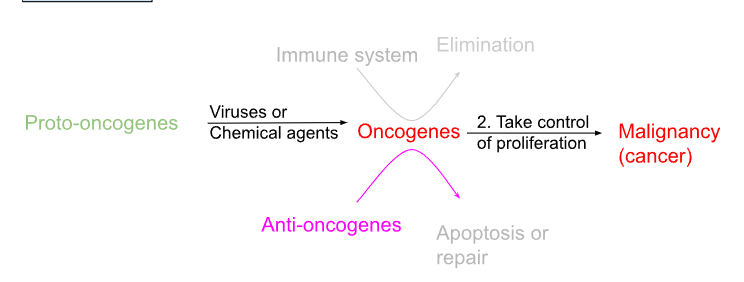
How can proto-oncogenes become cancer (i.e. result in a malignancy?
term. Prognosis
def. the probable outcome of disease
term. Carcinogen
def. a cancer causing agent
term. carcinogenesis
def. cancer formation/ production