Exam 1
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
steps of conception
Fertilization – Fallopian Tube -> Zygote (egg + sperm) -> Replication (cleavage) = Morula (16 cells) -> Traveling to the uterus! -> Blastocyst – cavity forms in ball of cells -> Implantation!
stages of human development
Preembryonic
conception to Day 14 (2 wks.)
Embryonic
Day 15 to 8 wks. -> after conception
Organogenesis
All organ systems are developing
When teratogens have the most damaging effects
Fetal
9 wks. until the end of pregnancy
embryonic layers
Ectoderm
CNS; special senses; skin; and glands
Mesoderm
Skeletal, urinary, circulatory, and reproductive organs
Endoderm
Forms respiratory system, liver, pancreas, and digestive system
teratogen exposure
Things in the environment that can cause harm to fetuses
Medications
Drugs
Alcohol
Viruses
Radiation
Lithium
Lead
Tetracycline
Education is important
Occupational exposures
viruses
amniotic fluid functions
Maintain body temperature
Source of oral fluid (swallowing) and a repository for waste (urine)
Promotes muscle development
Movement through the fluid
Cushions against trauma
Weightless state – allows symmetrical development
Antibacterial factors in fluid
Facilitates normal lung development
polyhydramnios
Too much fluid
> 2,000ml or 2L
GI malformations
Cord entanglement
Difficulty monitoring FHR
labor conmplications
oligohydramnios
Too little fluid
<300 ml
Renal abnormalities
Asymmetric growth and development
Not enough fluid to suspend fetus
umbilical cord
This is the baby’s lifeline
1 vein, 2 arteries
“AVA”
The vein carries the oxygenated blood
The arteries carry the deoxygenated blood
Wharton jelly prevents compression
Cushions the vessels
Average cord is 22 inches long, 1 in wide
Should be centrally inserted on placenta
placenta
One cell layer between mom and placenta
Functions
Endocrine: Hormones provide “direction” to mother’s physiology to prioritize supply of nutrients and oxygen needed for fetal growth (Respiratory & Nutrition)
Metabolic: Waste remover (Excretory)
Circulation: Interface between mom and fetus
placental hormones
Human Chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Contributes to morning sickness and nausea
Pregnancy tests
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
Stimulates maternal metabolism for baby nutrients
Increases maternal insulin resistance -> higher blood sugar but it goes to baby
Progesterone
Pregnancy hormone
Decreases the contractility of the uterus
Estrogen
Causes breast enlargement and tenderness
Increases vascularization
Nosebleeds and bleeding gums
placental metabolic function
High demand for glucose
Fetal metabolic waste products cross placental membrane for excretion by maternal kidneys
One cell layer separates maternal and fetal blood
Breaks occasional occur in this membrane
Mixing of maternal / fetal blood
Problematic for Rh- mothers
Blood will attack Rh+ fetus
placental and fetal circulation
Placental function is dependent on maternal circulation
Important to lay on their left side to avoid obstruction of aorta and IVC
fetal circulation
Blood travels through 3 shunts in fetal body
Shunt – alternative pathway
Ductus Venosus (liver bypass)
Connects UV to IVC
Liver processes nutrient rich blood
Enters the right atrium
foramen ovale
Opening between the right and left atrium to bypass right ventricle
Blood enters left atrium and down into the left ventricle
Pumps up to the ascending aorta
deoxygenated blood
From SVC to right atrium
From RA to RV and goes to the pulmonary arteries and meets resistance
Lungs are filled with fluid
Ductus Arteriosus (lung bypass)
Connects PA to aorta
Bypass pulmonary circulation and to the descending aorta
Back to the umbilical arteries to the placenta
fetal respiratory system
Respiratory
Surfactant – used to determine fetal lung maturity
Decreases the surface tension of the alveoli and expand the lung
L/S ratio is diagnostic marker (2:1)
Marker of lung maturity
fetal neuro system
Spinal cord develops from neural tube (ectoderm)
Chronic poor nutrition, hypoxia, drugs, or environmental toxins can damage CNS
Neural tube defects
Healthy development linked to folic acid
Spina bifida
dizygotic pregnancy
multiple eggs/sperms
2 sacs, 2 placentas
fraternal
di-mono
each fetus has its own sac but share placenta
di-di
Each fetus has its own placenta and sac
Sometimes the placentas can be fused
monozygotic pregnancy
fertilized ovum splits
identical
mono-di
Share a placenta but have their own sac
mono-mono
Share a sac and placenta – highest risk
nursing implications for conception
Complex interactions between genes and environmental factors to promote growth and development
First 3 months are CRITICAL for embryonic and fetal development
So how does this translate into nursing care & understanding
length of pregancy
1st trimester – LMP (last menstrual period) -> WK 13
Beginning of fetal stage
2nd trimester – WK 14 -> WK 27
Fetal growth aand development
3rd trimester – WK 28 -> WK 40
4th trimester
Postpartum period
maternal adaptations to pregnancy
Affect ALL body systems
Pregnancy is a stressful state
Why might this fact matter? --- How does it change your thinking about pregnancy?
Adaptations are unfamiliar and may cause concern or distress
Nurses must be aware of changes to support & educate
Consistent healthcare surveillance is of utmost importance
uterine changes
Size, shape, and position
Checkpoints at 12 wks. (near symphysis pubis), 20 wks. (near belly button), 38-40 (xiphoid process) wks.
lightening
3rd trimester
Baby drops into the pelvis
hegar sign
Softening of the lower uterine segment
Can be felt internally
Allows uterus to put pressure on the bladder
1st trimester
Contractility - Braxton Hicks
Practice contractions
Not labor
3rd trimester
Ballottment
16-18 weeks
press on abdomen and fetal movement confirmed if fetus rebounds against push
Quickening
Fetal movement
18-20 weeks
If pregnant before can be felt earlier
2nd trimester
cervical changes
Softens (Goodell sign)
Increased vascularization*
Friability – tissue is easily damaged (vaginal bleeding after exam / sex)
Mucous plug (operculum) forms
Chadwick sign – violet blue discoloration
vaginal changes
increased vascularity with thickening – heightened sensitivity
secretions increase, leukorrhea
breast and ovarian changes
Breast
increase in size and nodularity (including nipples)
colostrum production starts 2nd trimester – hPL
Beginning of breastmilk
Ovary
Enlarge at first, ovulation stops
CV changes in pregnancy
Physiologic anemia of pregnancy
Tiredness
Cold
Pallor
Dilution of RBCs
Require iron supplements
Increase in plasma -> less RBCs
Hypercoagulable state
Produce more clotting factors
Increase risk of DVTs
Preexisting heart disease at higher risk
PVCs and PACs increase
Respiratory Changes
Increased oxygen consumption
Increase metabolism
Pregnancy-related dyspnea
diaphragm compression
Hormonal changes -> Blood vessel proliferation & congestion (leaky capillaries) of resp tract
nosebleeds (epistaxis); voice changes; marked inflammatory response to infection (flu/covid)
GI changes
Mouth
Bleeding gums
Excessive salivation (ptyalism)
GI Tract
Decreased tone & motility
constipation
Nausea and vomiting
4-6 weeks thru 1st trimester
PICA
cravings in response to changing sense of taste
Ice, clay, laundry starch
(iron deficiency anemia)
genitourinary changes
Increased size
More urine
Fetal waste as well
Increased GFR (by 50%) = decreased serum & creatinine
Check medications
UTI Risk
Symptoms of Adaptations:
Bladder irritability
Nocturia
Pee at night
Frequency and urgency
integumentary changes
all caused by hormones
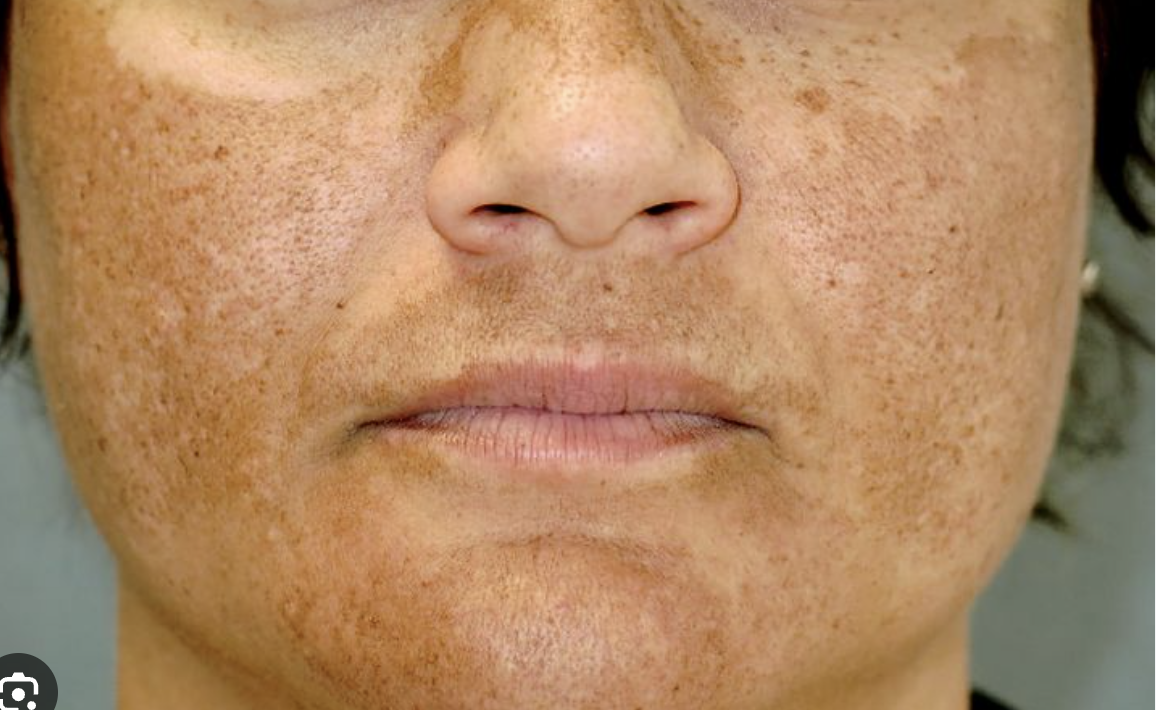
melasma
Facial discoloration
More pronounced in darker complexions
linea nigra
Fades postpartum
Dark line down the tummy
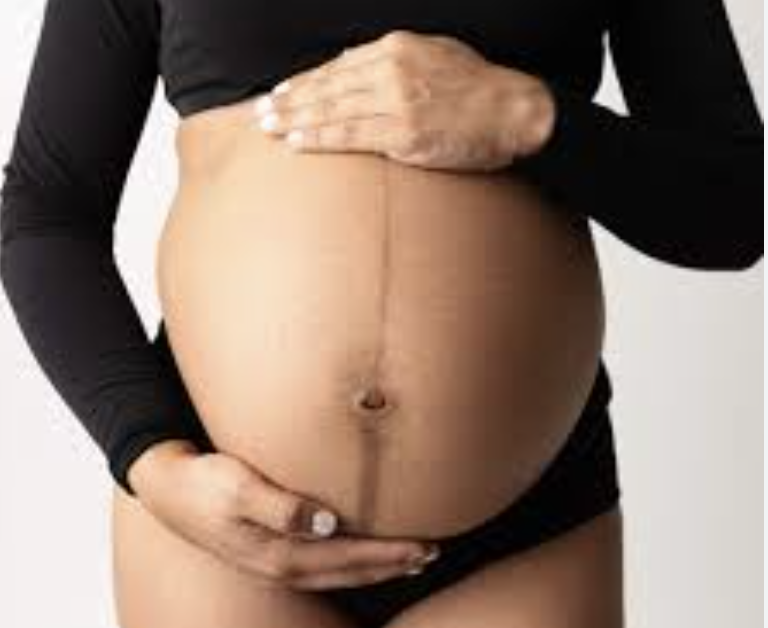

striae gravidarum
Stretch marks
angiomata
Spider veins
Estrogen increases capillaries
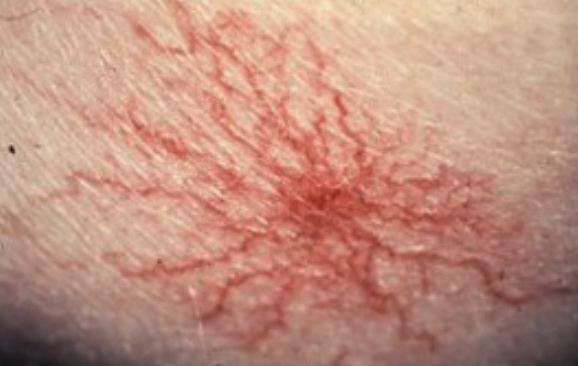
palmar erythema
Reddening of the palms
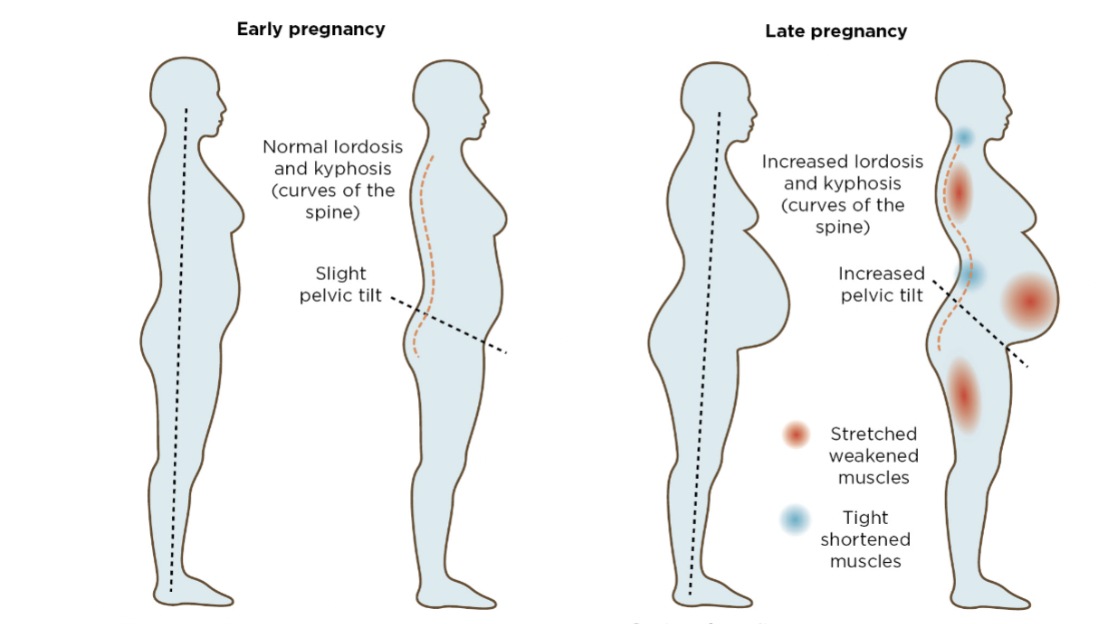
MS changes
Changing posture
Increased lordosis
Waddling gait
More pronounced in shorter moms
Softening of ligaments
other changes
Leg Cramps – changes in Ca & Ph metabolism; pressure of enlarging uterus
Very common
Charlie horse
Different from DVT
Pain, swelling, redness NOT NORMAL
Restless Leg syndrome
Prone to impaired balance!
Alterations in sleep
Belly and hormones
Endocrine changes
pregnancy tests
Serum vs. Urine
Detect hCG (begins at implantation and rises enough for detection by 7-8 days before expected period)
Home kits – accuracy depends on correct use
Certain foods, meds can affect results
First void in morning
presumptive signs
felt by client
Breast Changes
Tender/enlarged 3-4wks
Amenorrhea
4 wks
Urinary Frequency
6 – 12 wks
Fatigue
12 wks
Nausea & Vomiting
4 - 14 wks
Quickening
16-20 wks
probable signs
observed by HCP
Goodell Sign
Softening of the cervix – bc of vascularization
5 wks
Chadwick Sign
Blueish tinge to the cervix – estrogen and increase in vascularization
6-8 wks
Hegar Sign
Softening of the lower part of the uterus
6-12 wks
Positive Pregnancy Test
False positives
Other conditions can increase HcG
4-12 wks
Braxton Hicks
Practice contractions
16 wks
Ballottement
Fetus is bouncing on the cervix during internal exam
16-28 wks
positive signs
can only be explained by fetus
Visualization of embryo / fetus
5-6 wks
Transvaginal ultrasound
Fetal Heart Tones
6+ wks
Fetal movement (felt by HCP)
19-22 wks
Maternal Stages of Pregnancy
Accept the pregnancy
Initial reaction can vary
Emotional lability is common
Ambivalence
Identify with the mothering role
Idea of mother comes from life experience
Conflict resolution
Reorder relationships
Tension and conflict can arise
Mother and partner are influential
Intimacy may be affected
Establish a relationship with fetus
3 phases
1 acceptance
Accept the fetus
Accept the parenting role
Prepare for birth
Partner adaptations
Partner
+ & - feelings may be present
intense prep & learning
IPV
Intimate partner violence
Increases in pregnancy
Ask questions
responding to fear/concerns
LGBTQIA
Adaptations of other siblings
Response varies w/ developmental stage
Involvement is key
Prep & educate
Answer questions
Prenatal Care models
Traditional
1st trimester
Q4 wks until 28 weeks (third trimester)
Q2 wks until 36 weeks
Q1 wk until delivery
Group (Centering)
Grp with similar due dates
Low risk pregnancies
Individual assessment + group education & discussion
Individualized
More high risk pregnancies
Follow traditional model with more or less visits as needed
Initial prenatal visit
Prenatal Interview
Goal is ID risk factors
So....what types of questions will the HCP ask?
Physical Exam
Provides a baseline (VS, height, weight)
Comprehensive head to toe
Routine Testing
Cervical, urine, blood
Prenatal Interview
Date of LMP
Signs or sx
Test used?
How did you use it
Menstrual hx
Contraceptive hx
Past pregnancies
STI hx
Chlamydia increases risk for ectopic pregnancies
Hx of mood disorders
Maternal mood conditions are most commonly caused by pregnancy
Screening 2x pregnancy
Special diet?
Microwave lunch meat
limit coffee
Education?
Living environment/occupation?
Can be inhaling teratogens
Social support?
Stable relationships? (IPV)
Flu/covid/MMR/Chx pox
Rx & OTC drugs
Caffeine, etoh, tobacco, other
Discontinue use
Nagele’s Rule
Start with the date of LMP -> subract 3 months -> add 7 days -> add 1 year
Assumes you have a 28 day cycle
Assumes it was a full period
Need to know when LMP is
ultrasound
Best way
Used to date baby
Transvaginal
Measure crown to rump
GPTAL terminology
G/P (2-digit system)
Gravida: # of pregnancies (regardless of outcome)
INCLUDING CURRENT PREGNANCY
Parity: # of pregnancies carried past 20 weeks.
DOES NOT INCLUDE CURRENT PREGNANCY
GTPAL (5-digit system)
Gravida: # of pregnancies including this one
Term: delivery between 37-42 wks
Preterm: delivery between 20-36 6/7 wks
Abortions: delivery before 20 wks
Living: # living children (not pregnancies)
routine testing
CBC and Type & Screen
Anemia risk
Rh factor
Need RhoGAM if Rh-
Rubella & Varicella Titers
looking for immune or nonimmune status
Immune is good
CANNOT GIVE PREGNANT WOMEN LIVE VACCINES
Receive after birth if nonimmune
Can give flu, COVID, TDap
Hepatitis B
looking for reactivity
STI testing
RPR, VDRL, HIV (serum)
Gonorrhea & chlamydia (cervical swab)
Syphyllis can cause congenital defects if untreated in pregnancy
Pap Test
cervical cancer screen
Follow up testing
Maternal Assessment
Ask about well-being & concerns
Vital signs & Weight measurement
Urine (protein check)
Edema
Especially in third trimester -> preeclampsia
Fetal Assessment
Movement
kick counts
FHTs
110-160 bpm
doppler
Growth - fundal height
McDonald's measurement
Measuring tape from pubis symphysis to the top of the fundus
Correlates to how many weeks pregnant a women is
Needs to lie flat on her back
Additional Screening
1st Trimester
Transvaginal US
Nuchal translucency; dating; preg confirmation
Genetic abnormalities(11-14 wks)
2nd Trimester
QUAD test
NTD (AFP levels)
Chorionic villus sampling/ Amniocentesis
Noninvasive prenatal testing
Gestational Diabetes
Anatomy Scan / Ultrasound
3rd Trimester
H&H, STI
GBS screen (36-38 wks)
Rhogam (28 weeks & after birth maybe)
PTL
Edema
Gestational Diabetes Screening
Glucose Testing
Measuring the insulin response
24 to 28 weeks
Glucose Challenge Test
50 g glucose load, 1hr serum measurement
Elevated, than further testing
No need to fast
Glucose Tolerance Test
100 g glucose load; 3 hr serum measurement
Must fast before
Elevated = +dx
important Education
Good nutrition and food safety (listeriosis)
Iron; folic acid; weight gain
Physical activity (P. 280)
Maintain prior activity level
Posture & body mechanics
Belly bands
Kegel exercises
Rest & relaxation
Side-lying
Avoid compression of aorta and IVC
Avoid Supine hypotension
Prenatal vitamins & Other Medications --- must check with HCP
Folic acid
Substance use
Immunizations
Rh status
Personal Hygiene
UTI prevention
Oral health
Clothing
Loose fitting clothing
Employment
Travel
DVTs/VTEs
Breastfeeding preparation
1st trimester discomfort
Fatigue
Nausea & vomiting
Breast changes
Urinary frequency or incontinence
Mood swings
Vaginal discharge (leukorrhea)
Nasal stuffiness, bleeding gums, nose bleeds
Leukorrhea
2nd trimester discomforts
Skin changes
Joint, back, pelvic pain
Constipation, hemorrhoids
Supine hypotension
Varicosities of the vulva and legs
Flatulence, bloating
Heartburn
3rd trimester discomforts
Return of some 1st trimester discomforts
SOB and dyspnea
Heartburn and indigestion
Dependent edema
Braxton Hicks
Insomnia
1st trimester complications
Severe vomiting
Hyperemesis gravidarum
Electrolyte imbalances
Chills, fever
Infection
UTI, viral
Abdominal cramping/bleeding
Miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy
Burning during urination
UTI
2nd and 3rd trimester complications
Vaginal bleeding and cramping
Preterm labor
Chills, fever, aches
Infection
Back or flank pain
Kidney/PTL
Decreased fetal movement or absent FHR
Death or distress
Visual disturbances; facial swelling; severe headaches; muscular irritability; seizures
Hypertensive conditions; preeclampsia
Glycosuria
gestational diabetes
birth settings
Hospital
Most supplies
Birth center
Good for low risk
May not have the same pain management supplies that a hospital does
Can be sent to a hospital
Home birth
Not suitable for high-risk pregnancies
Must be attended to by a healthcare provider
labor support
Continuous labor support is beneficial
Best approach to have positive outcomes and delivery
Decreased pain medication
Shorter labor
Increased satisfaction
Increased changes of SVD
Reduced risk of C/S or assisted birth
Higher APGARS
Doulas – trained to provide physical, emotional, and information support
Cannot give clinical care
Some are certified
Definitely in birth centers
Birth plans
It’s a tool
Tentative!!!
Useful in prenatal settings to begin discussions of choices r/t labor and birth
nausea and vomiting
Increased HcG
Recommend
Smaller more frequent meals
Plain foods
urinary frequency
Uterus pressing on bladder
Recommend
Kegel exercises
Do not hold it
Avoid caffeine
Limit fluids before bed
Constipation
Progesterone increase
Decrease GI motility
Sharing water
Recommend
Laxatives
Fatigue
Higher stress on the body
Recommend
Take naps
Do not increase workload
Heartburn
Hormones allow acid reflux
progesterone and estrogen
Recommend
Smaller meals
Stay upright after eating
Drink water between emails
Avoid spicy foods
breast tenderness
Hormones and increase in blood flow
Estrogen
Recommend
Wearing comfortable bra
Cold compress
nosebleeds and bleeding gums
Increase estrogen creates increase vascularization
Recommend
Humidifier, Vaseline
Watch oral hygiene
Look at meds
Screen for anemia
backaches
Lots of MS changes to the body
Increase pelvic tilt
Increase curvature of spine – lordosis
Loosening of ligaments
Recommend
Rest when possible
Do not increase activity
Heating pads
Proper body mechanics
Good shoes
varicosities
Iliac veins become compressed
Increase blood volume
Recommend
Compression socks
Avoid standing long
Elevation
Do not cross legs
hemorrhoids
Estrogen increased vascularization
Enlarged uterus
constipation
Recommend
High fiber/laxatives
Fluids
Warm bath
Topical creams
braxton hicks
Body's way to pair uterine muscles to contract better for during labor
Recommend
Warm compress
Change position
Move around
Release bladder often
weight management pregnancy
Depends on BMI (Pre-pregnancy)
Underweight (<18) OR twin pregnancy
28-40 lbs.
Normal (18.5-24.9)
25-35 lbs.
Overweight (25-29.9)
15-25 lbs.
Obese (≥30)
11-20 lbs.
First Trimester
2-4 lbs. total
Underweight/Normal
1 lb. / week
Overweight/Obese
<1lb / week
important dietary needs
Iron
Anemia is a common problem
Increased blood volume does not increase RBCs
Iron supplementation may be necessary
Review teaching
Iron can cause constipation
Folic Acid
Included in PNV
Important for neural tube defects
Other vitamins & minerals
PNV
food precautions
Mercury
Can impact CNS of fetus
Follow guidelines for daily limits
Deli meats / hotdogs
Reheat to steaming hot
Kills listeria and other bacteria
Unpasteurized cheeses
Avoid
Same reasons as deli meat
special nutrition considerations
Adolescents
Nutrition battle
Have additional nutrient needs for themselves
Additional monitoring or fetal growth
Encouraged for higher calorie diets
Risk for small birth weight babies
Vegetarian diets
Monitor for susceptible deficiencies
Refer to dietitian
high risk pregnancy
A condition threatens the health of the mother, fetus, or pregnancy
1 in 4 women
When do you assess risk factors?
First trimester interview appointment
risk factors
Biophysical Factors
Genetics
Medical conditions (Diabetes)
Nutrition
Psychosocial Factors
Substance use
History of violence
Cultural practices
Sociodemographic Factors
Poverty
Ethnicity
Parity
Single
Environmental Factors
Radiation
Pollution
Pesticides
modifiable vs nonmodifiable
Modifiable
Education
Follow-up care
Monitoring
Nonmodifiable
Determine need for additional testing
Consider referral to maternal fetal medicine
antepartum testing for high risk
Biophysical
Kick counts
Ultrasounds
Biochemical
Amniocentesis
Chorionic Villus Sampling
Maternal Assays
Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Nonstress test (NST)
Vibroacoustic Stim
Contraction stress test
Indications for further testing
Risk factors identified
Diabetes
Hypertension
Prior medical conditions (lupus, renal disease, heart disease)
Fetal growth problems
Amniotic fluid alterations
Previous pregnancy complications or stillbirth
Suspected fetal compromise (decreased movements)
Post term pregnancy
daily fetal monitoring count
**noninvasive
Movement is a reassuring sign of fetal health
Count movements for 2 hours or until 10 movements reached
Babies have 20-minute nap cycles
Establish a baseline
No fetal movement for 12 hours – fetal alarm signal!
ultrasonography
Transvaginal
1st trimester
Confirm pregnancy
Check FHR
Genetic testing
Measure nuchal fold thickness on baby
Abdominal
Fetal scan 2nd trimester
Baby is big enough to visualize
Gender reveal
Anatomy scan to check development
One for low risk
Repeated for high risk
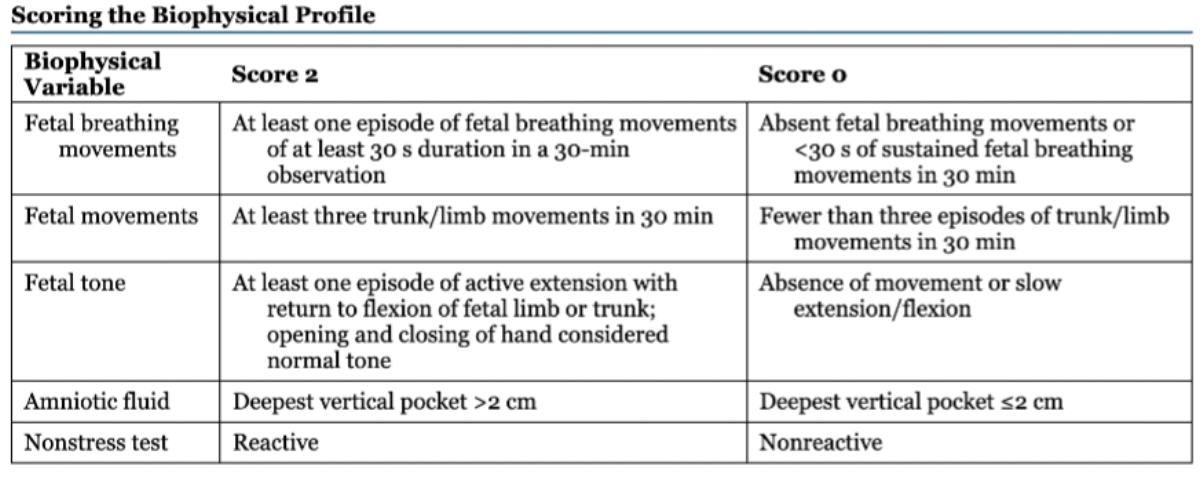
biophysical profile
Score of 8-10 is normal
Below 8 is suspect
If really low they induce labor or C-section
amniocentesis
Genetic testing for AMA
Having another baby or family member with congenital problems
Checking fluid for lung development
Can be done but risky in 1st trimester
Usually done in 2nd trimester
Complications
Cramping
Contraction like pain
Potential for hemorrhage
Infection
Risk of miscarriage
Potential of mixing of blood
Give RhoGAM after procedure
Chorionic Villius Sampling
Sample of chorion
Can be done 1st trimester 10-13 wks.
Relatively safe
Complications
Cramping
Bleeding
Pain
RH testing and RhoGAM
noninvasive prenatal testing
Test blood sample
Can identify trisomy 13, 18, and 21
Safer and preferred to amniocentesis and CVS
Can figure out gender
Towards end of first trimester
maternal assays
Alpha beta protein level
Drawn from blood
Determines risk of neural tube defects
Elevated = further testing
nonstress test
NST
Picture of baby in that moment
Top belt assesses uterine activity
Bottom assesses fetus
Looking for reactive
Failure = nonreactive
vibroacoustic stim
Vibrate mom's abdomen
Look for baby to twitch and react to the stimulation
Movement, increase in FH
contraction stress test
Not until patient is ok to deliver
Give pt oxytocin to bring contractions
Squeezes and stops blood flow to baby
Healthy fetuses should tolerate contractions with reserved oxygen
failure of any test
Biophysical profile