Exam 1 Review: Exercise Science and EKG Fundamentals
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
PNF
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation, a mode of flexibility training which is comprised of assisted stretching that alternates passive static stretching with muscle contractions.
reliability and Validity
A measure must be reliable to be valid, but a reliable measure isn't always valid
Wellness
continuous and intentional effort to remain healthy and reach one's highest potential for well-being across multiple dimensions (emotional, social, spiritual, environmental, intellectual, physical).
Health
The overall condition of a person's body and mind, or the absence of injury or illness
Muscular endurance
The ability of a given muscle to exert force, consistently and repetitively, over a period of time.
Muscular power
Great force production over a short period of time, such as in fast leg kicks and explosive jumping.
Muscular strength
The amount of force you can put out or the amount of weight you can lift.
Wingate test
A supramaximal test used to measure anaerobic power.
Functional residual capacity
Volume of air remaining in the lungs after normal tidal expiration.
Total lung capacity
Total volume of air in the lungs at maximal inspiration.
Inspiratory reserve volume
Volume of air that can be inspired beyond normal tidal inspiration.
Residual volume
Volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximal expiration.
Vital capacity
Maximal volume of air that can be expired after maximal inspiration.
Tidal volume
Total volume of air moved per breath (inspired + expired).
Inspiratory capacity
Maximal volume of air that can be inspired after normal tidal expiration.
Augmented limb leads
In the Mason Likar EKG system, leads aVR, aVL, and aVF make up this category.
Standard limb leads
In the Mason Likar EKG system, leads I, II, and III make up this category.
Precordial leads
In the Mason Likar EKG system, leads V1 - V6 make up this category.
EKG lead 1 view
From RA to LA.
EKG lead 2 view
From RA to LL.
EKG lead 3 view
From LA to LL.
EKG lead aVR view
From LA and LL to RA.
EKG lead aVL view
From RA and LL to LA.
EKG lead aVF view
From RA and LA to LL.
Couplet FIB
A grouping of two PVCs together (one followed by another one, then back to a normal beat).
Bigeminy
An organization of PVCs that occur in a cycle of a normal beat, followed by a PVC, followed by a pause, then a normal beat.
ACSM moderate exercise
Defined as exercise at 40 - 60% VO2R.
ACSM vigorous exercise threshold
The minimal exercise intensity threshold at which ACSM deems exercise to be vigorous is 60% VO2.
Dyslipidemia risk factor
ACSM's defining criteria for dyslipidemia as a positive risk factor for cardiovascular disease include Age ≥ 45 men / ≥ 55 women:
LDL ≥ 130,
Obesity ≥ 30 BMI,
Hypertension ≥ 140/90,
HDL < 40,
Total cholesterol ≥ 200,
Neg Risk, high HDL-C ≥ 60.
Signs and Symptoms of cardiovascular issues
Pain, discomfort;
Shortness of breath;
Dizziness or syncope;
Orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea;
Ankle edema;
Palpitations;
Intermittent claudication;
Known heart murmur;
Blood pressure classification
A BP reading of 120/78 mmHg would be classified as normal blood pressure.
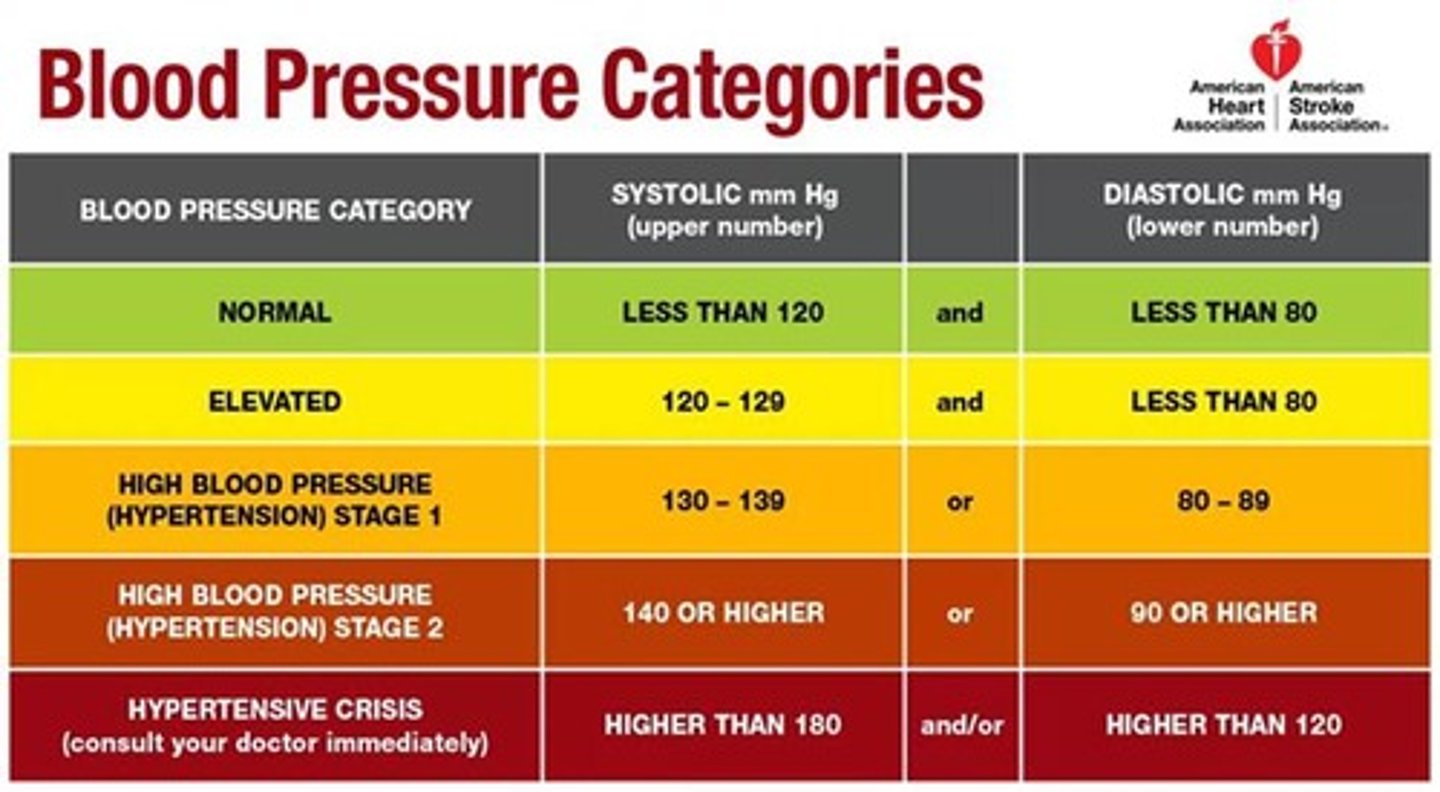
Normal blood pressure
less than 120 AND less than 80
Hypertension stage 2
A BP reading of 132/92 mmHg would be classified as.
Hypertension stage 1
A BP reading of 136/88 mmHg would be classified as.
T wave
An elevated ST segment, with an inverted T wave, is considered a hallmark sign of a myocardial infarction.
P wave
Reflects atrial depolarization as the impulse is initiated by the SA node and spreads through the atria.
PR segment
Reflects the period of time where the impulse from the SA node is detected and continued by the AV node through the bundle of HIS and to the bundle of branches.
QRS segment
Can reflect ischemia if depressed (>1mm), flat or down sloping.
QT interval
Reflects the amount of time it takes for the ventricles to depolarize and repolarize.
Rate pressure product
Used to reflect myocardial demand/myocardial oxygen consumption.
HR*SBP
Rate pressure product and SBP only is a myocardial demand indicator.
ACSM
Considered the leader in the field of exercise science.
Testing order
Correct order for multiple tests on the same day: Resting values, body composition, strength, aerobic, flexibility.
Fick's equation
VO2 = QxA-VO2 is known as.
Hypertension
Not a major sign/symptom suggestive of cardiovascular, pulmonary, or metabolic disease according to ACSM.
Blood pressure
Force Exertated on Arterial walls .
High serum HDL cholesterol
Considered a NEGATIVE risk factor for cardiovascular disease (Beneficial).
Work
Work = force x distance.
Energy
The capacity to perform work.
Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
Calculated as ⅓ (SBP - DBP) + DBP.
Power output (W)
Calculated for a 195lb person performing a 1.5 hr stair step exercise at 30 steps/min with a 12 in step.
Air displacement plethysmography (Bod Pod)
Considered the gold standard for fat mass assessment.
Fasting plasma glucose
A level of >/= 126 mg/dl puts an individual at a positive risk factor for diabetes.
Physical activity
Defined as bodily movements produced by the contraction of skeletal muscle that substantially increases energy expenditure.
Exercise
Planned, structured, and repetitive bodily movements done to improve or maintain one or more components of physical fitness.
Medical clearance
Needed if a participant indicates dyspnea at rest and light activity during a pre-health screening.
Two component model of body composition
Comprised of fat mass and total body mass.
Skinfold measurement
A technique to estimate body composition that takes less time than hydrostatic weighing, is portable, and can be conducted in the field.
Components of health-related fitness
Body Comp, Cardio Resp INduance, muscle flex, muscle strength.endurance
Einthoven's triangle
A combination of RA, LA, LL electrodes during an EKG assessment, which makes leads V1, V2, and V3.
Work input vs work output relationship
Indicates that work input is greater than work output.
Cardiac cycles
The atria and ventricles do not occur at the same time.
Pulmonary circuit of blood flow
The flow of oxygenated blood from the ventricle to the active tissue.
Pulmonary function testing
Recommended for individuals who are regular smokers and are 35 years old.
Progressive endurance-type exercise
During such exercise, stroke volume typically increases proportionately with the work rate until about 50-60% of maximal work levels.
Total peripheral resistance
Affected by blood viscosity, blood type, blood vessel diameter, and blood length.
Abnormal pulmonary function tests
Can relate to an increased risk of all forms of cancer.
Valid exercise tests
Tests that report consistent results for an individual every time a test is done.
Reliable exercise tests
Tests that report the correct value for an individual.
Obesity and stroke
Research has demonstrated a strong relationship between obesity and the development of stroke.
GAP junctions
Hold cardiac tissue tightly together to allow signals to move quickly via desmosomes from one cardiac cell to the next.
Bundle branch block
Usually detected by abnormalities in the ST segment.
Systolic blood pressure
A measure of blood vessel pressure when your heart beats.
Diastolic blood pressure
A measure of the pressure in the blood vessels between heartbeats.
Blood pressure
Usually refers to arterial blood pressure, the pressure exerted on the arterial walls during the cardiac cycle.
Benefit of physical activity
Decreases morbidity and mortality through primary prevention strategies.
Mason likar EKG electrode placement system
Uses 12 different electrodes to create 12 different views of the heart.
Heart rate during exercise
Typically increases proportionately with the work rate until maximal work levels.
Stroke volume
The volume of blood ejected by the left ventricle per minute.
Tiffeneau-Pinelli Index
Defined as FEV1/FRC.
Systolic blood pressure drop
A drop in systolic blood pressure below standing resting pressure or with increasing workload accompanied by signs or symptoms.
Most accurate VO2 test
Maximal exercise test with spirometry.
Least accurate test for VO2
Non exercise prediction.
Recommended frequency for cardiovascular endurance exercise at mod high intensity
3-5 days/week.
%VO2 range to be mod int ex
40-60%.
Factors impacting joint range of motion
Joint structure, skin/tissue injury, body temperature, age, gender.
PNF
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation.
ACSM recommendation for frequency of flexibility
2-3 days a week or more.
Timing for each component of PNF stretching
3-6 sec contraction with 10-30 sec assisted stretch.
Hypertrophy
An increase in the number of myofibrils, actin, myosin, and sarcoplasm content.
Transient Hypertrophy
An increase in muscle size due to fluid accumulation in the muscle that occurs soon after or during exercise.
Power
The amount of force a muscle can produce within a certain time.
Power formula
Power = work / time.
Thorstensson test
The name of the test done to determine fiber type.
Wingate cycle test
Test done to determine anaerobic power.
Activities to be done 2-3 times a week
Leisure activities, stretching, and strengthening exercises.
Reasons for an adequate warmup
Stretch postural muscles, increase blood flow to muscles, increase core temperature, begin O2 disassociation, increase metabolic rate, reduce injury and cardiovascular event risk.
Volume in exercise
Volume is a product of frequency, time, and intensity.
FITT-VP
Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type, Volume, Progression.
Obese
BMI over 30.