Chemistry: Chemical analysis (Paper 2)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a pure substance?
Single compound or element
Not mixed with any other substance
Melts at a specific fixed temperature
Has a specific fixed boiling point
(impure melt & boil at a range of temps)
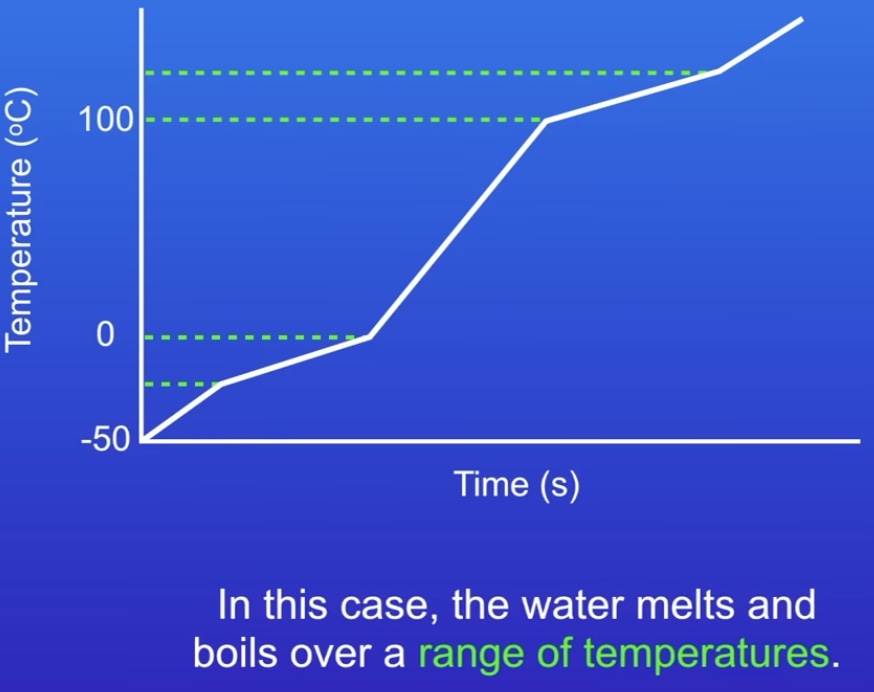
How can we measure purity?
If the melting and boiling point are a horizontal line, the substance is melting/boiling at a fixed point therefore pure.
The image is impure
What is a formulation?
A complex mixture that had been designed as a useful product
The quantity of components is measured
E.g. Fuels, cleaning products, paints, medicines
What is the process of chromatography?
Draw pencil line at the bottom
Dot the ink on the line
Dip the paper in a solvent
Solvent travels up the paper and carries the ink
What is the stationary and mobile phase in chromatography?
Paper is stationary phase (Doesn’t move)
Solvent is mobile phase (does move)
What result will occur in chromatography?
Pure compound - single spot
Compounds in a mixture separate into different spots
More soluble substances travel further up paper
How does chromatography help identify unknown substances?
Calculate the Rf value

What are some disadvantages of chromatography?
Could have the same Rf value
Use a different solvent
Rf value might not be in the database
How to test for gases?
Chlorine - Bleach litmus paper
Oxygen - Relights splint
Hydrogen - ‘Squeaky pop’
Carbon Dioxide - Turns limewater (calcium hydroxide) cloudy
Results of flame tests
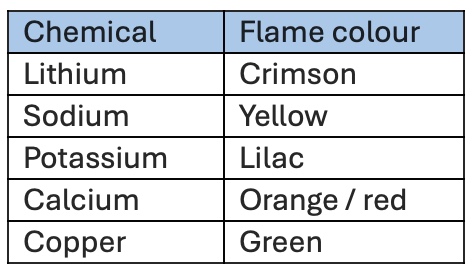
Process of flame test
Sterilise wire in water & in bunsen burner flame
Place sample onto wire
Put wire into blue bunsen burner flame
Observe colour result
What makes flame tests unreliable? What can be done for an accurate result?
Difficult to distinguish colour
Sample contains mix of metal ions - mask flame colour
Flame emission spectroscopy is more accurate
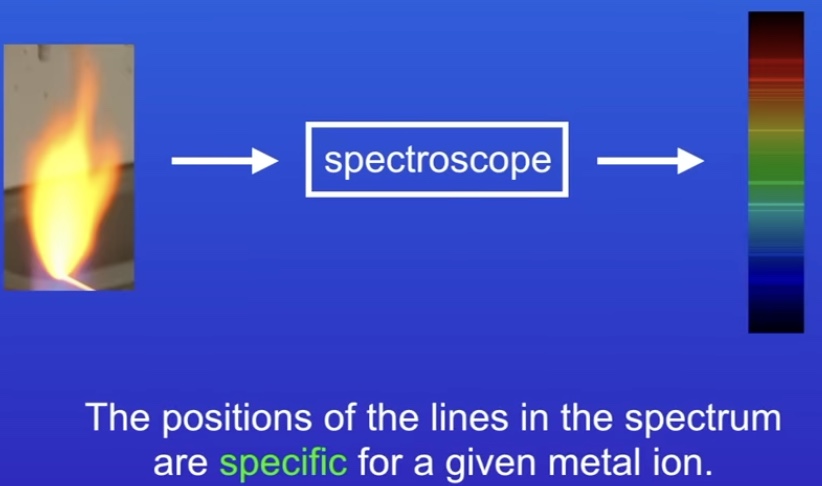
What is flame emission spectroscopy?
Metal ion in solution placed into flame
Light is passed through machine (Spectroscope)
Converts into line spectrum
Advantages of flame emission spectroscopy
(Concentration is visible)
Rapid
Accurate
Sensitive
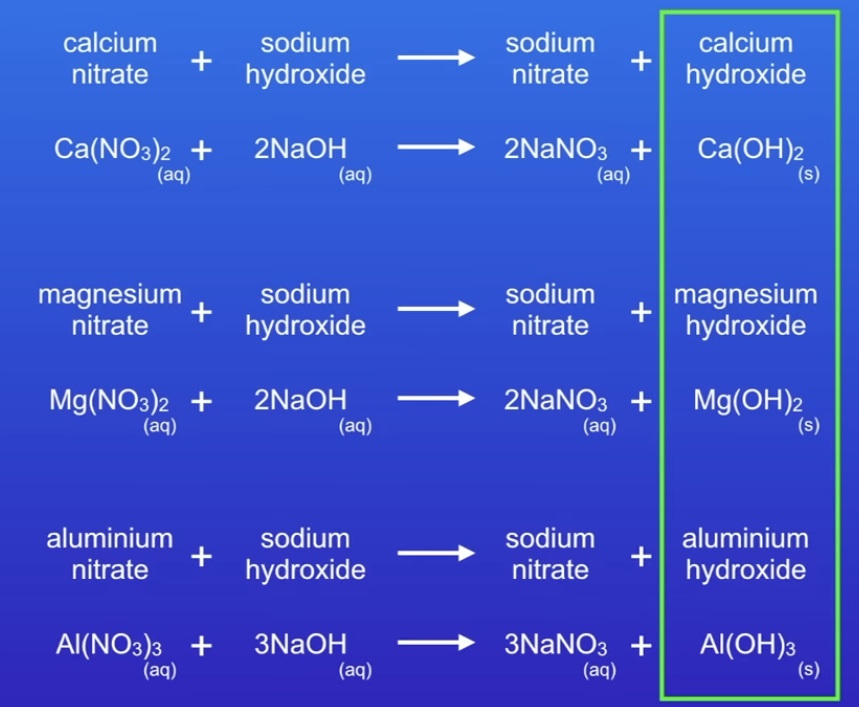
Result of Cations in NaOH solution
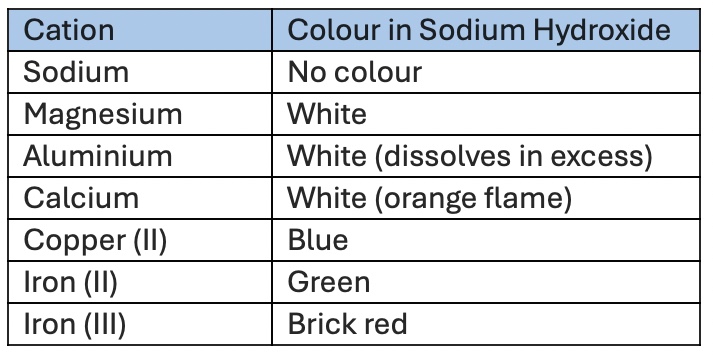
Balanced equations of Cations in NaOH
Forms sodium nitrate and hydroxide
1 2 → 2 1
Aluminium 1 3 → 3 1
How to test for Carbonates
Add dilute acid
Forms CO2 (fizzing)
Bubble through limewater (cloudy)
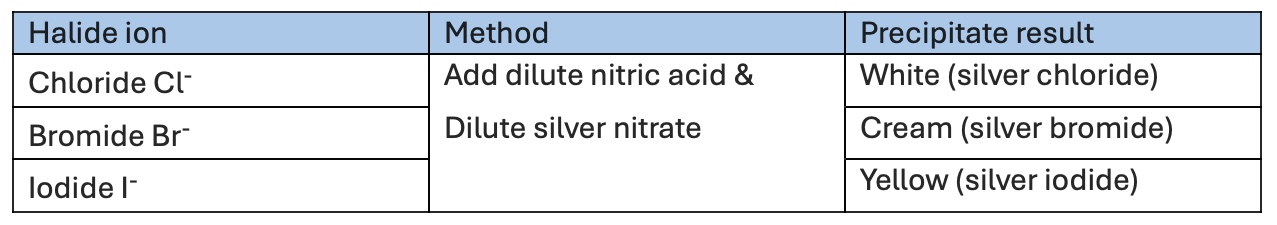
How to test for Halides?
How to test for SO42- or non-metal ions
Add hydrochloric acid & barium sulphate
White precipitate