A2.2 Cell Structure
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Cells as the basic structural unit of life
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the cell is the smallest unit capable of carrying out all vital functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction
Cell theory
States that all living organisms are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells
Deductive reasoning in cell theory
Using cell theory to predict that any newly discovered organism must be composed of one or more cells
Quantitative observation
Observations involving numerical measurements, such as measuring cell size using microscopes and graticules
Microscopy
The use of microscopes to observe structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
Temporary mount
A microscope slide prepared by placing a specimen in liquid under a coverslip for short-term observation
Staining in microscopy
The use of dyes to increase contrast by binding to specific cell structures so they become more visible under a microscope
Coarse adjustment knob
Used for rapid, large movements to bring the specimen roughly into focus
Fine adjustment knob
Used for small, precise movements to sharpen the image once roughly focused
Eyepiece graticule
A scale inside the eyepiece used to measure cell size when calibrated
Stage micrometer
A slide with a known scale used to calibrate an eyepiece graticule
Magnification
The number of times larger an image is compared to the actual specimen, calculated as image size ÷ actual size
Scale bar
A line on a micrograph that represents a specific actual length, allowing size estimation
Light microscopy advantages
Allows observation of living cells, colour images, and relatively simple preparation
Electron microscopy advantages
Much higher resolution and magnification, allowing detailed ultrastructure of cells to be observed
Freeze fracture microscopy
Technique where membranes are split to reveal internal membrane structure such as phospholipid bilayers
Cryogenic electron microscopy
Samples are rapidly frozen to preserve structure without chemical fixation, reducing distortion
Immunofluorescence
Uses fluorescently labelled antibodies to locate specific proteins in cells under a light microscope
Structures common to all cells
DNA as genetic material, cytoplasm mainly composed of water, ribosomes, and a plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
A phospholipid bilayer with proteins that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm
A water-based matrix containing enzymes and metabolites where many metabolic reactions occur
DNA as genetic material
Stores information needed for cell structure, function, and inheritance
Prokaryote
A cell lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, typically smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cell wall
Made of peptidoglycan, providing protection and preventing osmotic lysis
Nucleoid
Region in prokaryotic cells containing naked circular DNA not enclosed by a membrane
70S ribosomes
Smaller ribosomes found in prokaryotes and in mitochondria and chloroplasts
Eukaryote
A cell with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Compartmentalization
Separation of cell functions into membrane-bound organelles to increase efficiency
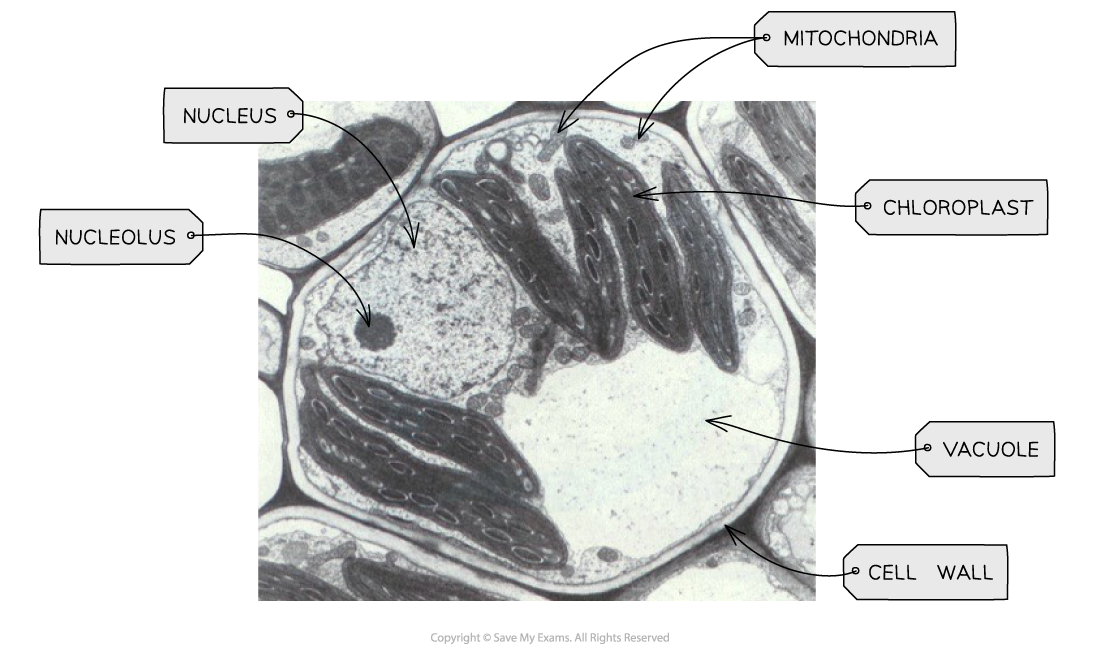
Nucleus
Contains chromosomes made of DNA bound to histones and controls gene expression
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane surrounding the nucleus with nuclear pores for transport
Nuclear pores
Protein complexes that regulate movement of RNA and proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm
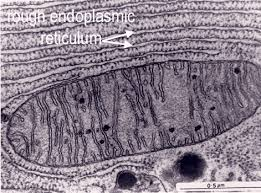
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Membrane system with ribosomes attached, involved in protein synthesis and transport
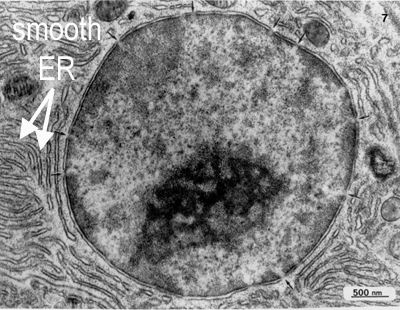
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage
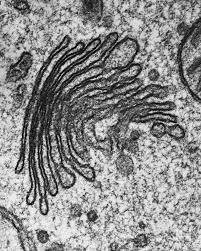
Golgi apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins into vesicles for transport or secretion
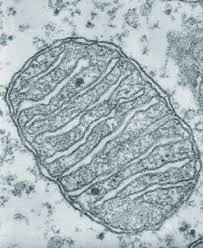
Mitochondrion
Site of aerobic respiration and ATP production, surrounded by a double membrane
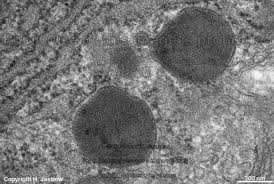
Lysosome
Vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes for intracellular digestion
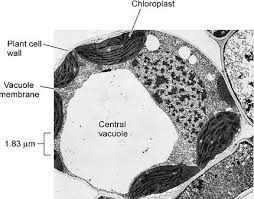
Vacuole
Large vesicle in plant cells involved in storage, support, and maintaining turgor pressure
Cytoskeleton
Network of microtubules and microfilaments that maintain cell shape and enable movement
Unicellular organism life processes
A single cell carries out homeostasis, metabolism, nutrition, movement, growth, response, excretion, and reproduction
Differences between plant and animal cells
Plant cells have cell walls, chloroplasts, and large vacuoles, while animal cells do not
Atypical eukaryotic cells
Cells with unusual structures such as multinucleate skeletal muscle cells or anucleate red blood cells
(HL) Endosymbiotic theory
Explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts as free-living prokaryotes engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells
(HL) Evidence for endosymbiosis
Presence of 70S ribosomes, naked circular DNA, double membranes, and independent replication in mitochondria and chloroplasts
(HL) Cell differentiation
Process by which cells become specialized due to differential gene expression triggered by environmental and developmental signals
(HL) Evolution of multicellularity
Multicellularity evolved repeatedly, allowing increased body size, division of labour, and specialized tissue
ibosomes are approximately 20–30 nm in diameter, which is below the resolution limit of light microscopes (~200 nm), while whole cells are much larger and can be resolved using light microscopy