HPHY 212 midterm pt2
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
list the steps of the scientific method
1- observation
2- question
3- hypothesis
4- experiment
5- analyze results
6-conclusion
7- report results
hypothesis
predicts relationship between IV and DV; must be testable
theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data
IV is _________________.
manipulated
DV _____________ on the _______________
depends / IV
identify the IV: Stretching prior to an exam will improve testing performance capabilities in cool conditions
stretching
identify the DV: Stretching prior to an exam will improve testing performance capabilities in cool conditions
test performance
Identify the IV: Oral ingestion of H(1)-and H(2)-receptor antagonists, known to attenuate the sustained postexercise vasodilatation, would reduce leg glucose uptake after a bout of cycling.
H(1)- and H(2)- receptor antagonists
Identify the DV: Oral ingestion of H(1)-and H(2)-receptor antagonists, known to attenuate the sustained postexercise vasodilatation, would reduce leg glucose uptake after a bout of cycling.
leg glucose uptake
Identify the IV: An excessively large alveolar to arterial oxygen difference (AaDO2) would contribute to reduced aerobic fitness in adults born very preterm with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
arterial oxygen difference
Identify the DV: An excessively large alveolar to arterial oxygen difference (AaDO2) would contribute to reduced aerobic fitness in adults born very preterm with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
aerobic fitness
Identify the DV: Deletion of MAFbx(knockout), a protein that helps initiate protein degradation, will prevent muscle atrophy in mice with spinal cord injury.
muscle atrophy
Ulcers
discontinuity in a bodily membrane; stomach ulcers are in the stomach lining
If the doctors treated ulcer patients with antibiotics to see if the ulcers stopped. What is missing from their study?
a control group
why do we need controls?
essential for measuring the effect of exposures
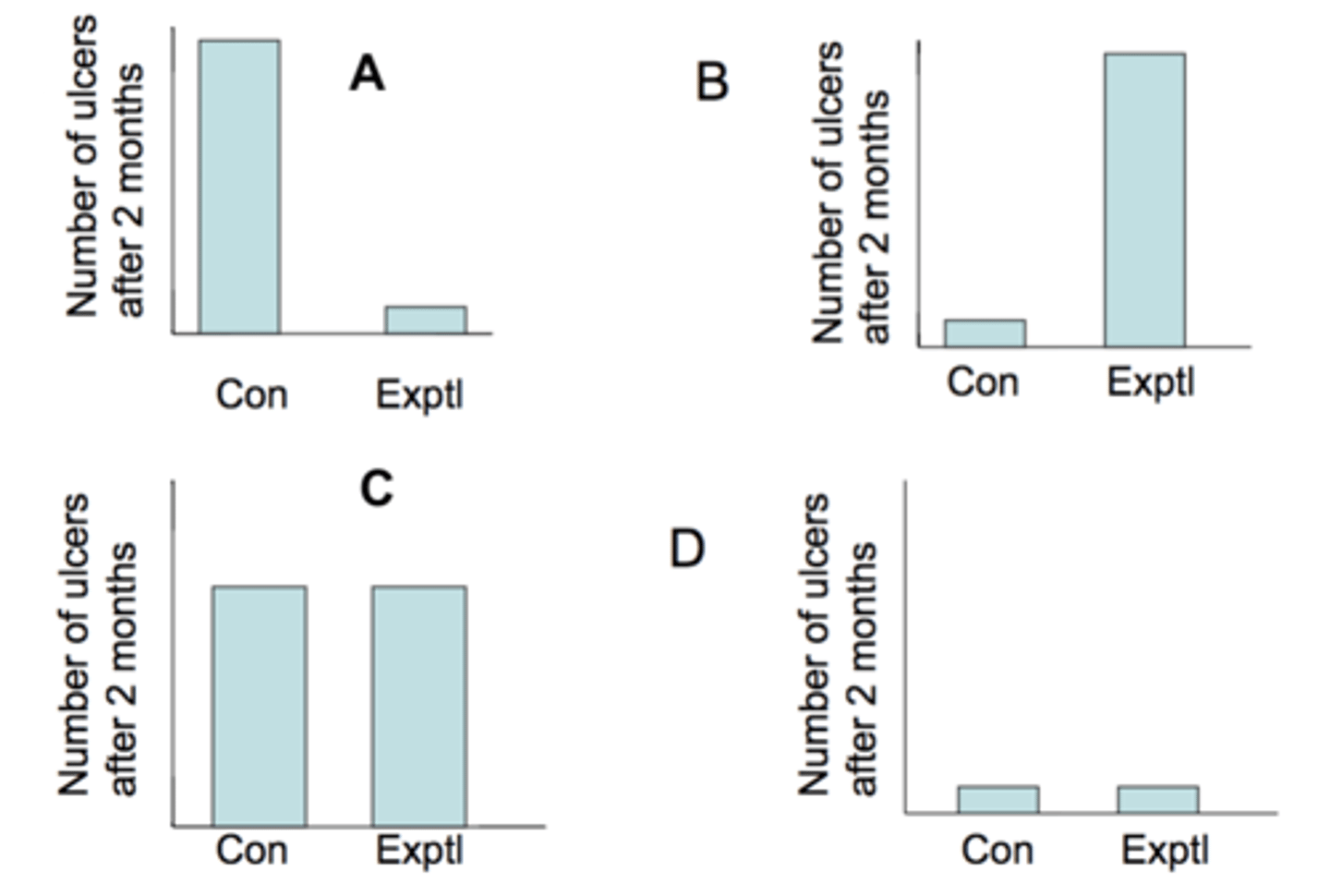
What results would you expect if the "excess
acid hypothesis" were supported?
C
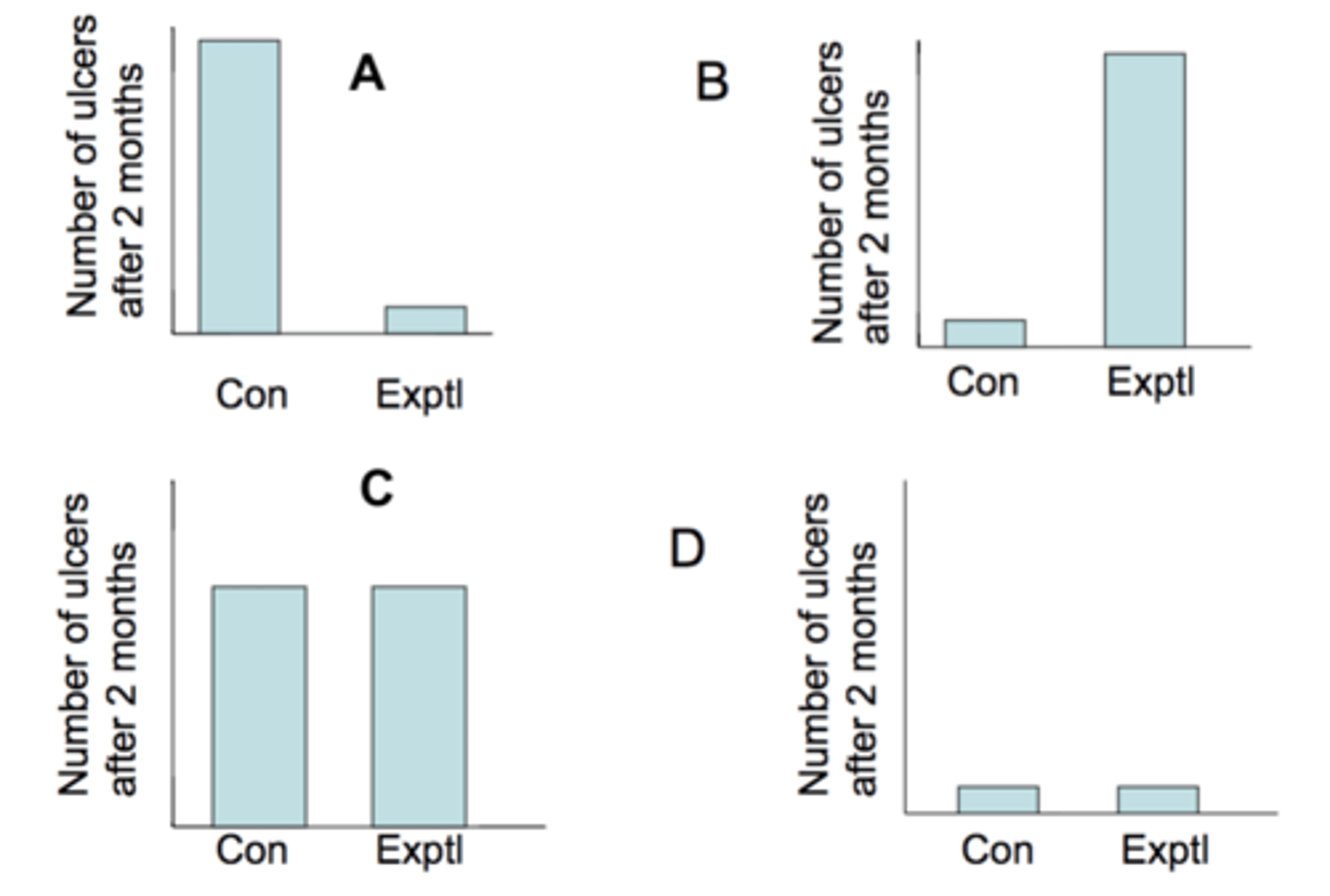
What results would you expect if the "bacteria
causes ulcers hypothesis" were supported?
A
When is the peer-review process initiated?
report results
who publishes the work?
journals
who initiates the peer review process?
journals
journals are run by what type of organization?
profit or non-profit
reviewers are:
experts from other universities
reviewers are paid approximately _______ per hour.
$0
advantages in the peer review system?
- establishes the validity of research since it is reviewed by other experts in that field
- provides valuable feedback so the researchers can revise and improve their work
- widely an accpeted and understood process
disadvantages in the peer review system?
- lengthy delays in the spread of research findings
- time-consuming process
- difficult to protect the anonymity
- bias
- sometimes accused of protecting established opinions and not being open to genuinely new ideas
- may not prevent the publication of poor research as review standards may be lower in less prestigious journals
If a manuscript is rejected by one journal ....
it can be submitted to any other journal
List in order of strength of evidence the reviews:
1- meta-analysis
2- systematic review
3- review
List in order of strength of evidence the scientific studies:
1- randomized controlled trial
2- cohort
3- case control
list the strength of evidence in order:
1- meta-analysis
2- systematic review
3- review
4- randomized control
5- cohort
5- case-contol
6- case report
7- expert opinion
Meta-analysis
- NEEDS a new piece of review
- systematic review of the literature
- integrates findings from many published studies
- new statistical analysis using all the data
Systematic review
- systematic review of the literature
- integrates findings from many published studies
- NO NEW statistical analysis
review
- review of the literature (NOT systematic)
- integrates findings from many published studies
- NO NEW statistical analysis
level of evidence:
The purposes of this paper is to provide a broad perspective on the current treatments described in the literature with respect subacromial impingement syndrome, consider the role of the subacromial space in impingement syndrome, describe the intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms considered to influence the subacromial space, and critique the level of evidence supporting these concepts.
review
level of evidence:
Randomized controlled trials were identified through an electronic literature search. Studies were considered eligible if they included interventions with resistive specific exercises. Six randomized controlled trials were included with 231 participants. Review of literature shows that in general, patients treated by Physical Therapists tended to do better than those who simply performed a home exercise program.
systematic review
level of evidence:
Randomized controlled trials were identified through an electronic literature search. Studies were considered eligible if they included interventions with resistive specific exercises. Six randomized controlled trials were included with 231 participants. No consistent statistical significant differences in outcomes between treatment groups were reported in the studies. Standardized mean difference (SMD) for pain was SMD - 0.19 (95% CI - 0.61, 0.22) and SMD 0.30 (95% CI - 0.16, 0.76) for function.
Meta-analysis
Random Controlled trial
- experimental process with a treatment/ intervention
- uses randomly assigned treatment and control groups
cohort study
- observational
- all subjects are from the same group and are linked by shared characteristics
- divided into subsets from the same group for comparisons
- can be prospective or retrospective
prospective
individuals are followed over time and data about them is collected as their characteristics or circumstances change
retrospective
individuals are sampled and information is collected about their past
Case- Control
- observational
- compares individuals with an existing condition / characteristic to group without
- always retrospective
- start with outcome and look back for exposure
level of evidence:
The charts of forty-six patients were reviewed. Half of the patients have impingement and half had no symptoms. Charts were reviewed for confounding factors.
case control
level of evidence:
Forty-six patients with impingement syndrome were recruited - half of whom were undergoing Physical Therapy and half of whom were not. After 4 weeks, strength, motion and pain were assessed.
cohort
level of evidence:
Forty - six patients were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 groups, one of which received a 4 - week intervention of strengthening exercises and the other the same intervention, supplemented by manual therapy. Outcome measures were strength, motion and pain.
random controlled trial
case report (case study)
- detailed characterization of few subjects
- observational
- often unique conditions
- no control
expert opinion
- direct knowledge obtained from an expert
- lowest level of scientific evidence
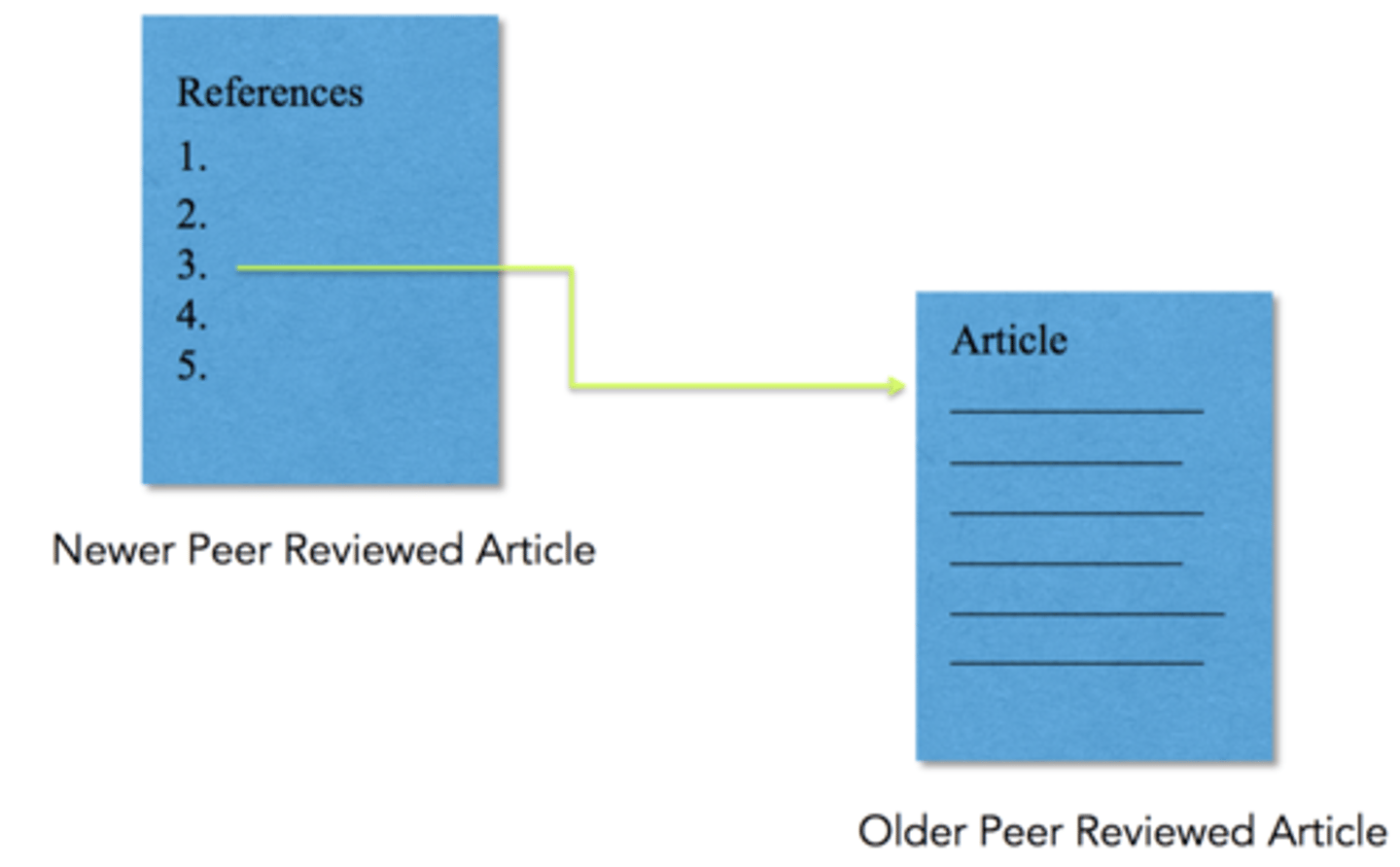
footnote chasing
the process of locating useful information by searching the reference sections of other papers
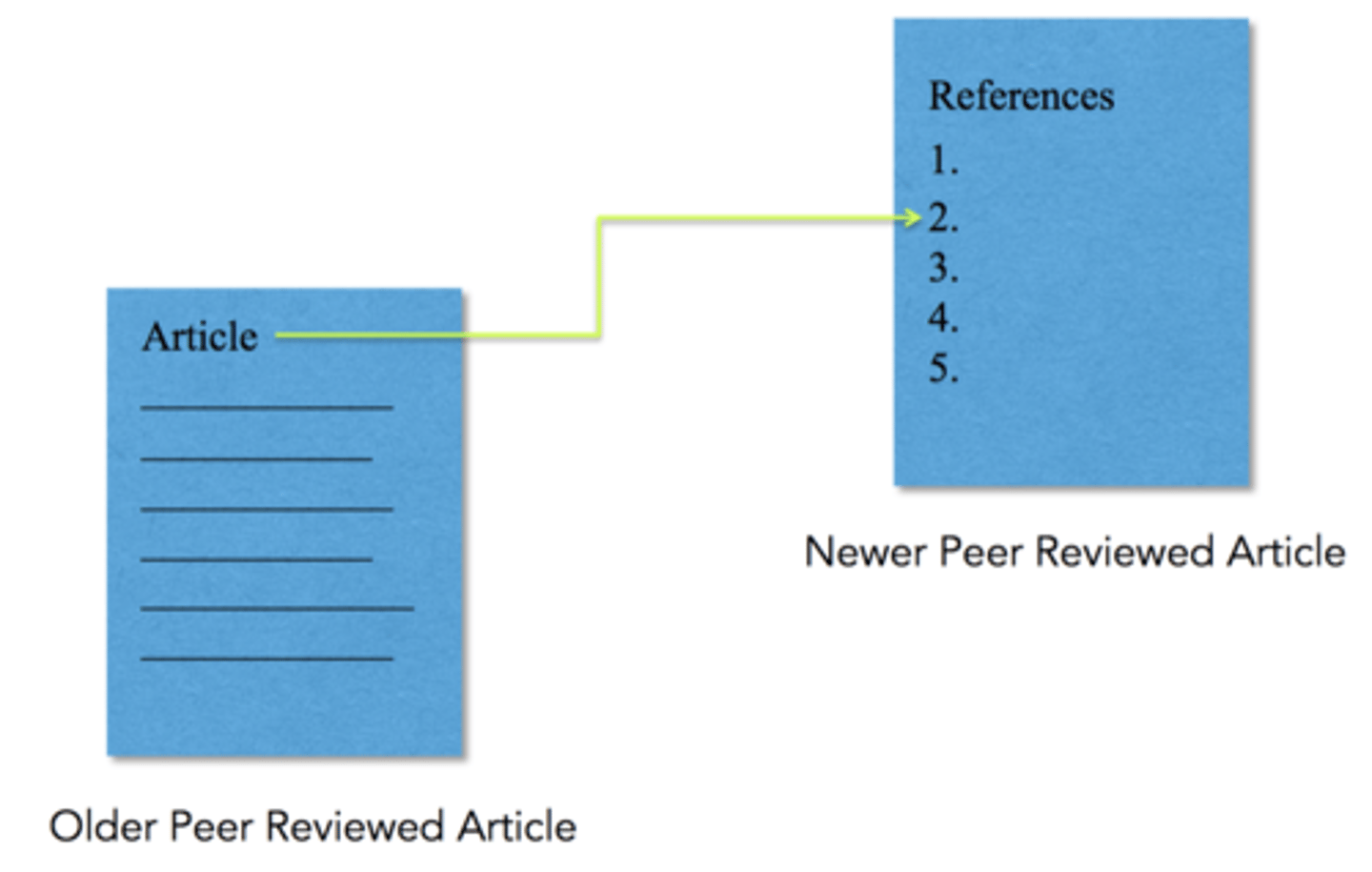
pearling
the reference lists of relevant articles are examined for articles that may have been missed by the database searches
boolean operators
AND, OR, NOT
identify boolean term:
concussion OR balance
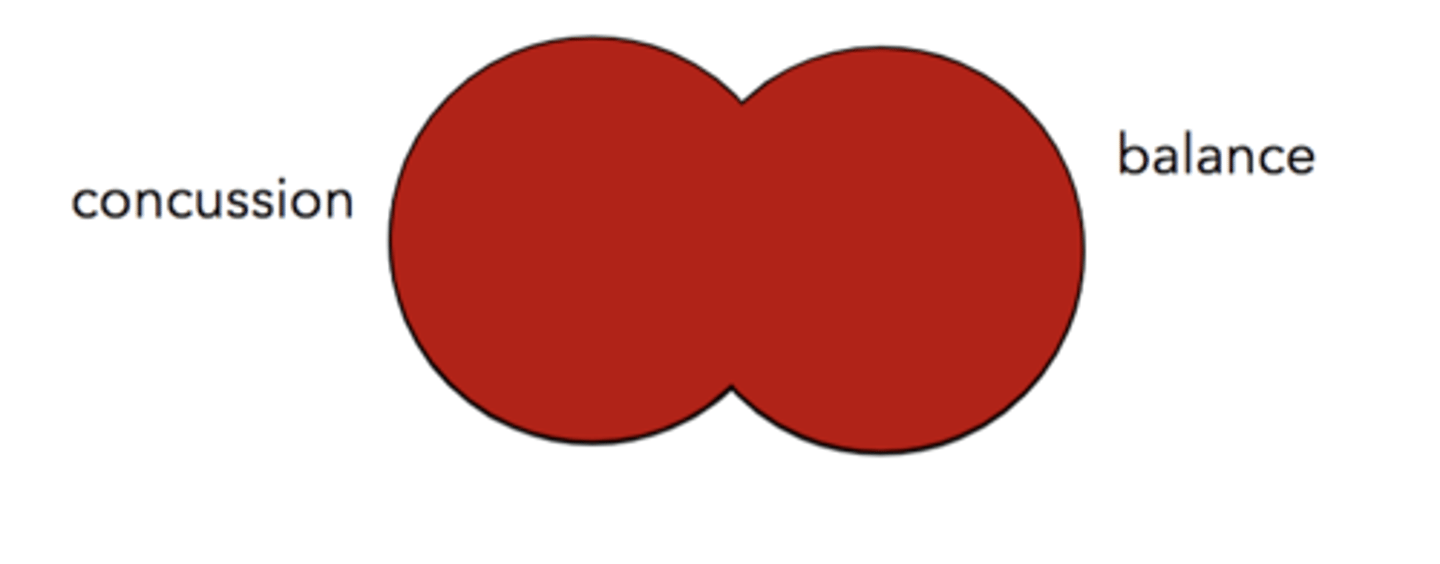
identify boolean term:
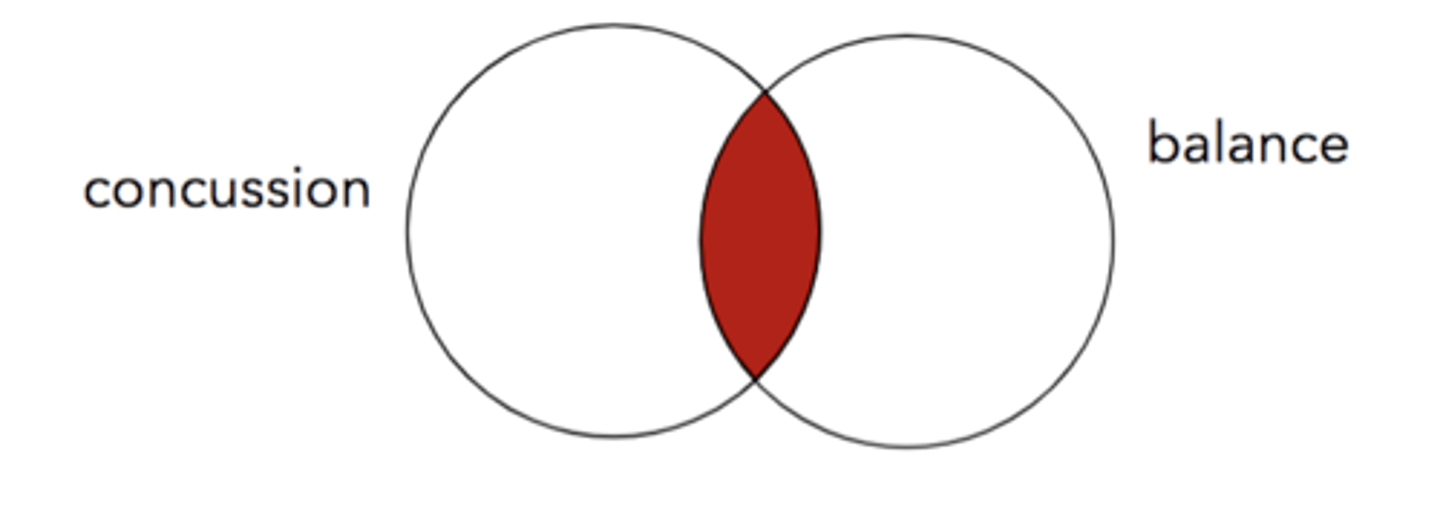
concussion AND balance
identify boolean term:
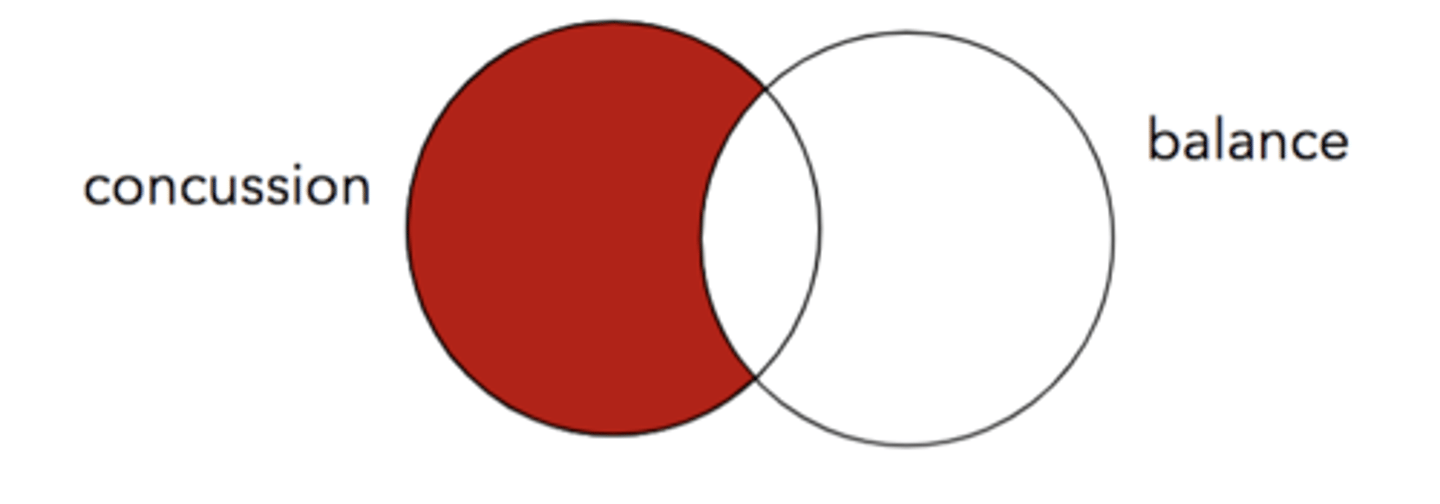
concussion NOT balance
MeSH
- Medical Subject Headings
- predefined set of terms to connect you to the information you need
- hierarchical classification system with 16 main branches and lots of sub-branches
- revised annually to reflect changes in the literature and research
Benefits of Open access
- author's research is available to more people
- the public should have access to the research they fund
- smaller libraries and low-income economies benefit
- makes use of modern technology
When did the Tuskegee Study start?
1932
When did the Tuskegee Study end?
1972
problems with the Tuskegee study
- no informed consent
- cruel and inhuman treatment
- risks far outweigh any gain
- subject did not have an option to say no
Belmont report
- respect for persons
- beneficence
- justice
respect for persons
- protecting the autonomy of people
vulnerable populations
- pregnant women
- terminal patients
- disabilities
- mental illness
- children
- immigrants
- impoverished
- prisoners
- language barrier
- elderly
- education
- minority
beneficence
- to do good
- helping find a cure
- benefits outweigh the possible risks
- low risk to subjects
- known risks
- payment
justice
- fair distribution of costs and benefits
IRB
institutional review board
roles of IRB
- meet and review all research proposals
- make decisions regarding study
- follow up on studies
- implement policies, procedures, and documentation for review and follow up
Who sits on an IRB?
- faculty
- clinicians
- community members
what are the factors for IRB approval?
- scientific merit
- perceived competence of investigators
- who are the subjects? are they vulnerable?
- risk/ benefit ratio
- how is the subject being informed?
When can a subject withdraw from a research study?
anytime
consent elements
- voluntary
- "vulnerable" subjects
- free to withdraw at any time
- informed consent form
animal ethics
- describe human-animal relationships and how animals ought to be managed and treated
why do we use animals?
- gene similarities
- genetic modification can induce human-like diseases
- the similarities are greater than the differences
by law reserachers cannot use animals when _______________ is avaible
alternative
how are unnecessary or pointless animal experiments mitigated?
- strict control over animal use
- animals are expensive
- limited biomedical funds
- trivial, irrelevant, incremental, or repetitive work is not funded or permitted
3 R's
- Replace
- Reduce
- Refine
Replace
- replace animal studies with other methods
Reduce
- minimize the number of animals used
refine
- methods which minimize the suffering and improve the animal welfare
AWA
- animal welfare act
- 1966
- regulates treatment, exhibition, transport
- enforced by USDA (united states department of agriculture
OLAW
- Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare
- NIH (national institute of health)
- develops, monitors, exercises compliance
- consists of vets, researchers, member of the public
- assurance document
- guide for care and use of lab animals
AAALAC
Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care
IACUC
- Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
- review and approve/ reject all proposed activities involving animals
- inspect every 6 months
- monitor and investigate
statistical inference
the drawing of conclusions about a population based on what you see in a sample from that population
Biostatistics
the application of
statistics to a wide range of topics in
biology
What percent of data are contained between +/- 2 standard deviations from the mean?
95%
Probability
- Probability is the degree of certainty, the chance, or the likelihood that something will happen
- anumber between 0 and 1 or 0% and 100%
- independence of events