ECON look at so you dont forget ofr hte final exam
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are the criteria of all the four key market structures
Pefect competition
Many firms
Low entry and exit
Undifferentiable goods
Monopolsitc competition
Many firms
Low entry and exit
Differnetiable goods
Oligopolistic competition / monopolistic competition / imperfec t competion
Dominated by small adn large number of firs
High entry and exi tbarrers
Monopoly
Impenetrable exit and entry barriers
One firm serves th eamrket
okay so the MMOL for this is that there is two normal people in a fightning area (many firms) and they are faling form the sky (easy entry and exit barriers) they are all the same colour (undiffferntated). Becuase of so many people the person exits the market and goes to a large single tower that’s kida run down and broken down , this represetns the (impefect copmetion) adn there is a rainbow colour of people in there (differnetiated goods) and the octupus oligopoly picks up and rips out of it and throws out (easy entry an dexi tbarreirs) and then you go to this area where there is a small number of powerful fimrs and you can’t exit (high barriers to exit) then a single monopoly firm comes in and tells and you can’t exit at all.
How do you draw impefect copmetion
same as the monoply firm model but far more elastic
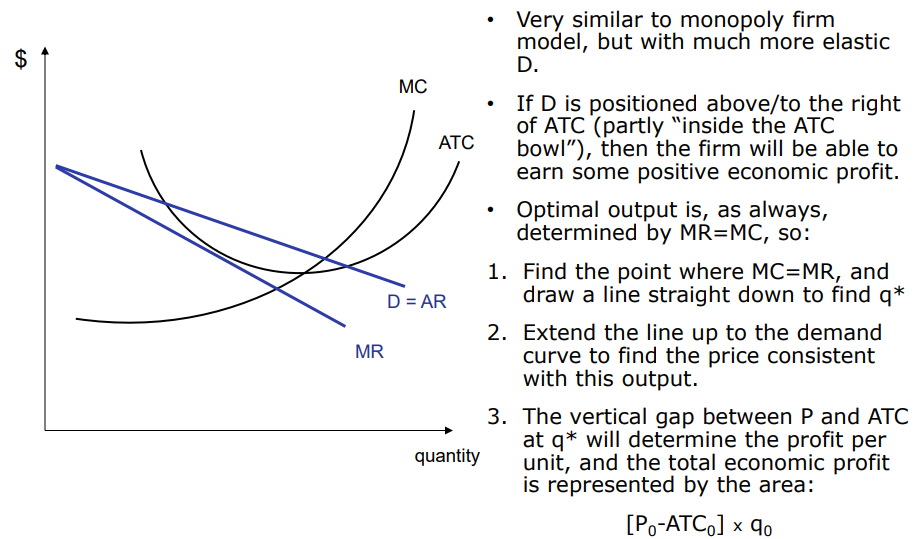
what are the kidns of models that you need to draw in temrs of hte markte strucures
Monopoly scenario
Imperfect competion / monopolstic competion (monopoily but it’s more elastic)
Perfect coepotiotn
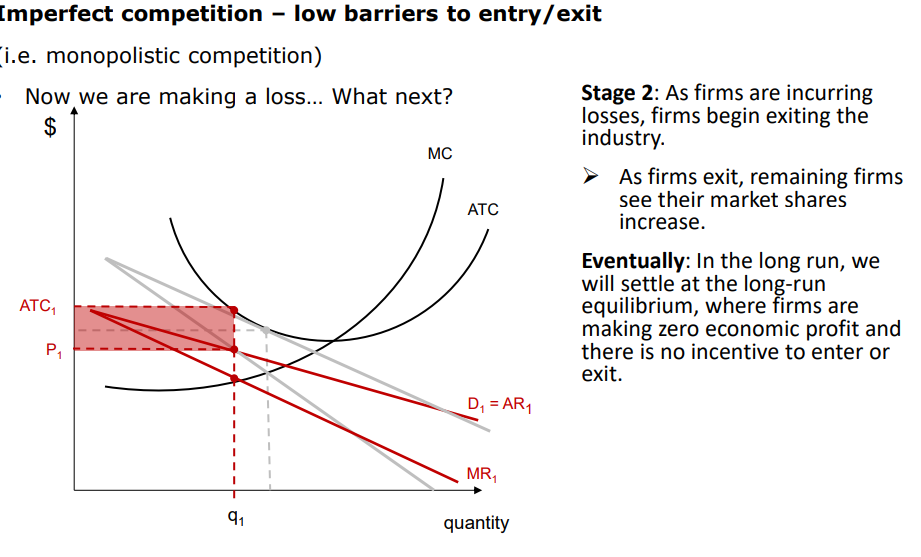
Explian how under the imperfect competiton / monopoilstic competion how it would reutn if a loss was being made
If a loss was being made more firm will exit hte markte nad reduce supply eventuially leading to the price to increase and reach the equilibrium point again from the once loss that was being made at a lower price
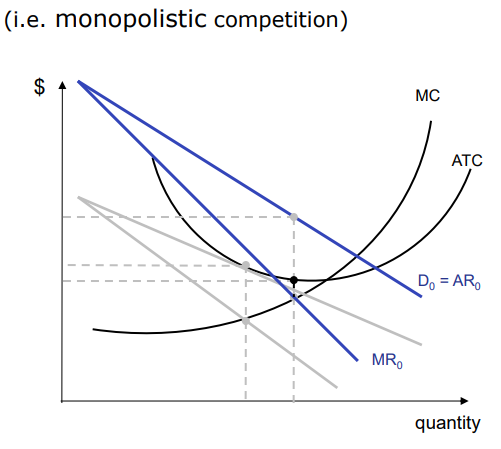
Explain how under the monopolistic compeoiton / imperfect compeotiton, the market will return to equilibrium after there has been a profit
So the increase in price will cause the supply to increase to yield some of the profits being made as represented by the increase in supply, increase in supply will lower the price so that it returns to the makret equilibrium scenario as before.
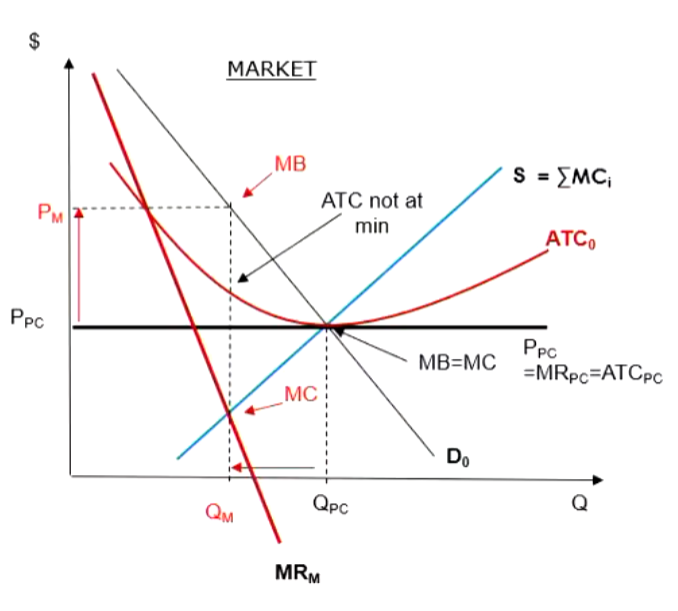
How would you draw a monopoly diagram and a perfectly competitive market, and how would you draw it if there was a welfare analysis scenario
You need to include a demand curve
for the monoply the ATC needs to cut where the MC is and the MR intersect he MC is going up to demadn and to the left will find the price adn the ATc, the gap between the two will be the profit that is left over.
draw the price of the perfectly copmetive going straihg through the middle of teh S and D curve
Lablel the P and Q as (PC = perfeclty compoetive) and (M = Monopoly)
How do you adress the dillemas in game theory and what else do yuo need ot mention
Mention if a Nash equilibrium .exists in the market and if it does explain what it is and how it affects it.
Adressing the dillemas
mention that there is two possible scenarios that could happen and the optimal scenario cna’t happen because they can’t collude
They can’t ensure that one person will meet the obligations as set by the other nad how do you know that they’ll support teh agreement if there was one that was made there is no gurantee.
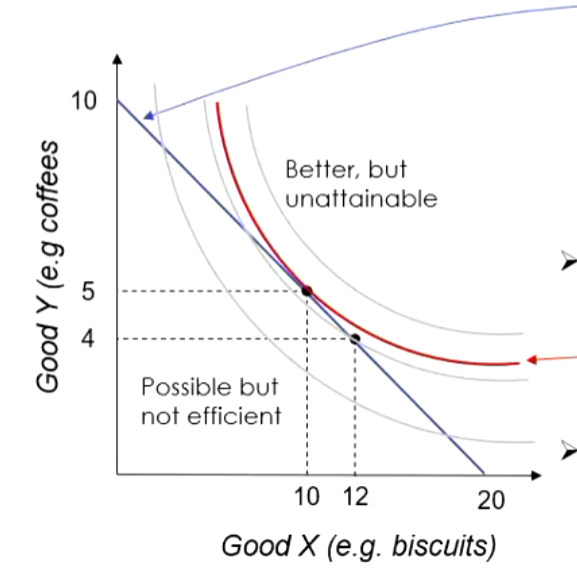
What does the indifferernce curve represent and how do yo ucaluclate it and hte digram of it and what does consumer equilbrium mean
It represents the line at which the utility or happiness you get from the points in the line are the exact same, so you would still get the same amuotn of utlility as 5pizzas and 5 coffees just as you would from 2 pizzas and 9 coffees
Marginal Utlity (Good X) / Price (Good X)
consumer equlibrium = utility is maxamised given the budget constraints
Explan in this scenario
Budget = $18
Price of biscuits = $3
Price of cofee = $3
Current status, 5 cofee = MU of coffeee = 1
Current status, 1 biscuits = MY of biscuits = 8
is lily maxamising her utility? if not waht shoudl we do to improve the siutaiton
so it is assumed that the last biscuit made lily 8 times as happy as the last coffee, so based on preferences, she should be willing to trade 8 coffees for one more biscuit to maintain her current level of utility
compare the marginal utility with the market exchange rate for coffee too
she could increase her utility by swapping coffee for biscuits and having less coffee will increase MU of coffee and having more biscuits will reduce the marginal utility of biscuits
therefore she needs less coffee and more biscuits
Explain in this scenario
Budget = $18
Price of biscuits = $3
Price of cofee = $3
Current status, 5 cofee = MU of coffeee = 1
Current status, 1 biscuits = MU of biscuits = 8
Is Lily maximizing her utility? If not, what should we do to improve the situation
(Use the marginal utility per dollar spent method)
MU per dollar spent on biscuit is 8 /3
MY per dollar spent on coffee is 1/3
Biscuits provide 8 times as much MU per dollar as coffee, so increase the consumption of biscuits and decrease the consumption of coffee
Therefore, having less coffee will increase MU of coffee, adn having more biscuits will decrease MU of coffee
Why does marginal utility fall as more is conusmed and wha tis utiltiy
utility
total satisfaction from consuming a particular good or service
marginal utility
the satisfaction from consuming one more unit of a good, the marginal utility will fall as more is consumed and will increase when less is consumed