Lecture 6b: Needle Selection & Suture Patterns
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
selection of needle depends on:
type of tissue to be sutured
topography of the wound
characteristics of the needle
most surgical needles are made of what? & why?
stainless steel wire because it is
strong
corrosion free
does not harbor bacteria
surgical yield:
the amount of angular deformation a needle can withstand before becoming permanently deformed
ductility:
the needle’s resistance to breaking under a specific amount of bending
sharpness
is related to the angle of the point and the taper ratio of the needle (the sharpest needles have a long, thing, tapered point with smooth cutting edges)
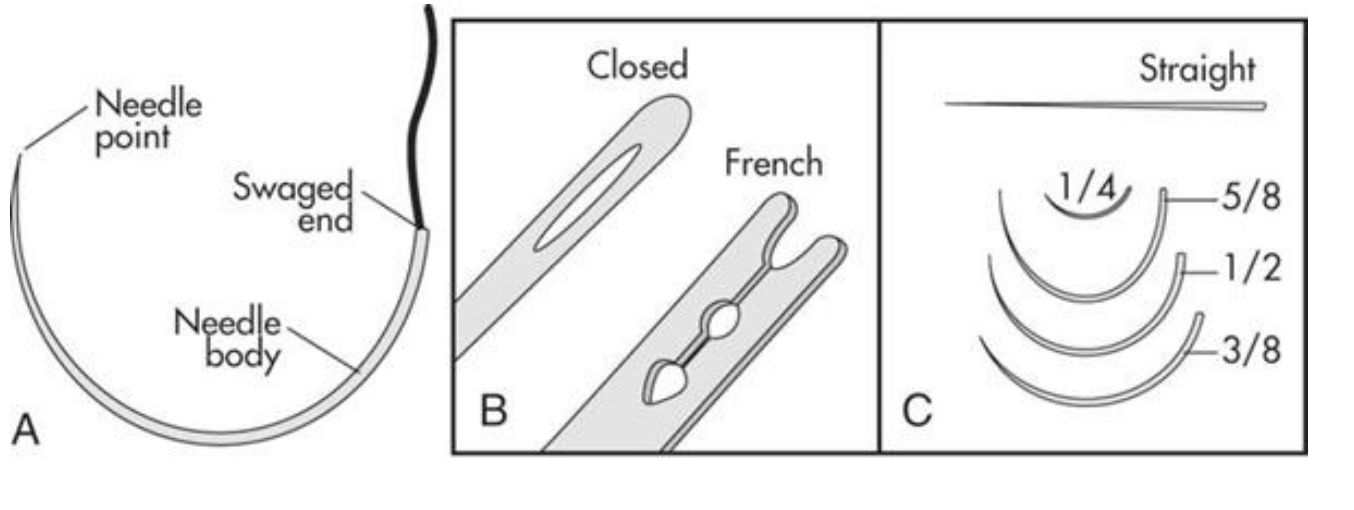
A. basic components of needle
B. types of eyed needles
C. shapes and sizes of needle bodies
selecting a curved needle
depth and diameter of wound are important in selection
¼ circle needles are primarily used in opthalmic procedures
which types of needles are most commonly used in veterinary medicine?
3/8 and ½ curcle needles
a one-half circle or 5/8 circle needles, despite requiring more pronation and supination of the wrist, are easier to use where?
in confiend locations than a 3/8 curved needle
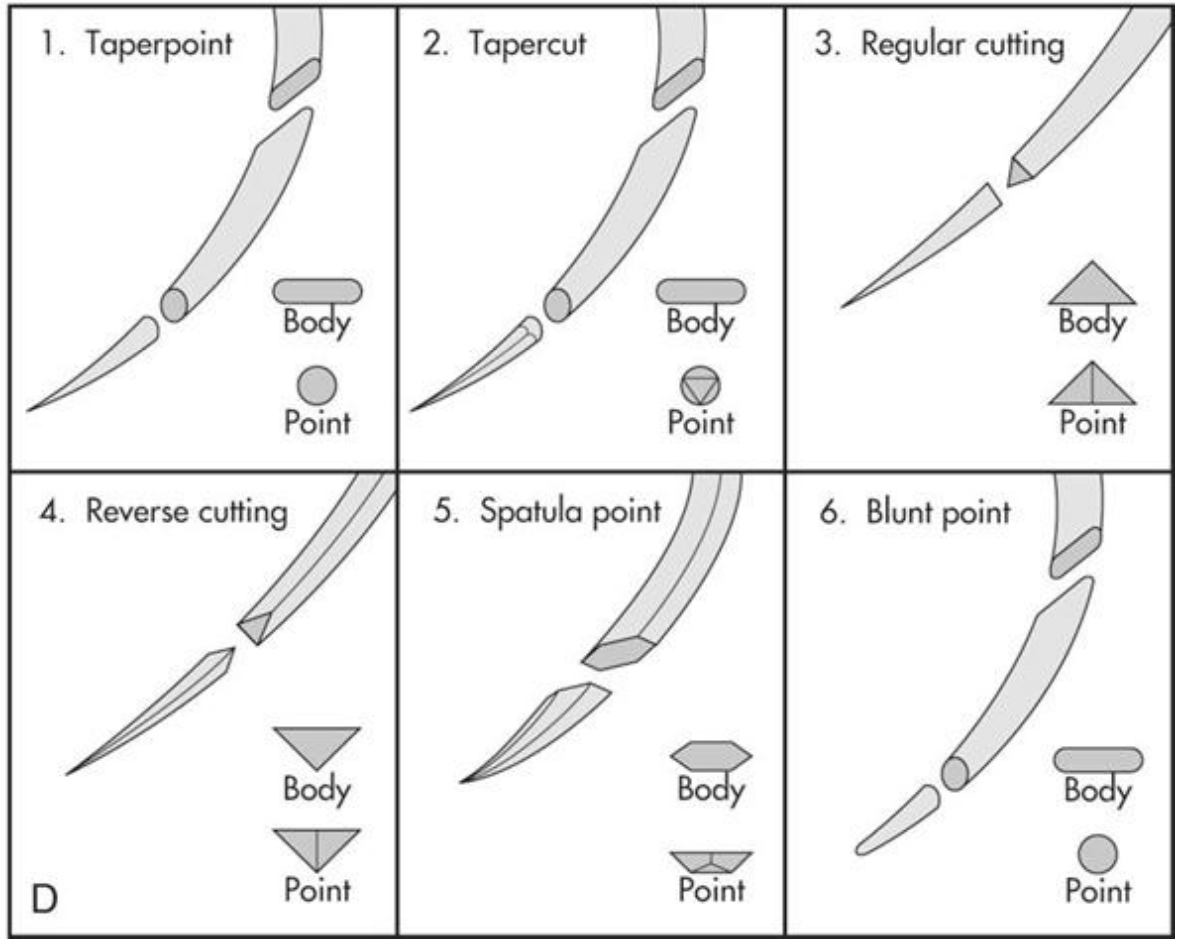
detail of surgical needle points
Suture patterns can be classified as:
interrupted or continuous by the way they appose tissue
appositional = one tissue edge apposed to another
everting = turn the tissue edges outward, away from the patient and toward the surgeon
inverting = turn tissue away from the surgeon, or toward the lumen of a hollow viscous organ
or by which tissues they primarily appose
SQ
Subcuticular/intradermal
point of subcutaneous sutures
eliminate dead space
provide some apposition of skin so that less tension is placed on skin sutures
generally, are placed in a simple continuous manner
in some instances, such as when draining might be necessary, simple interrupted sutures are preferable
subcuticular sutures may be used in palce of:
skin sutures
reduce scarring
eliminate the need for suture removal
suture line is begun by burying the knot in the dermis and then suture is advanced in the dermal tissue, bites are parallel to the long axis of the incision, suture line is completed with a buried knot, no suture is visible externally when complete, absorbable suture materials with a cutting edge are preferred in which suture pattern?
subcuticular sutures
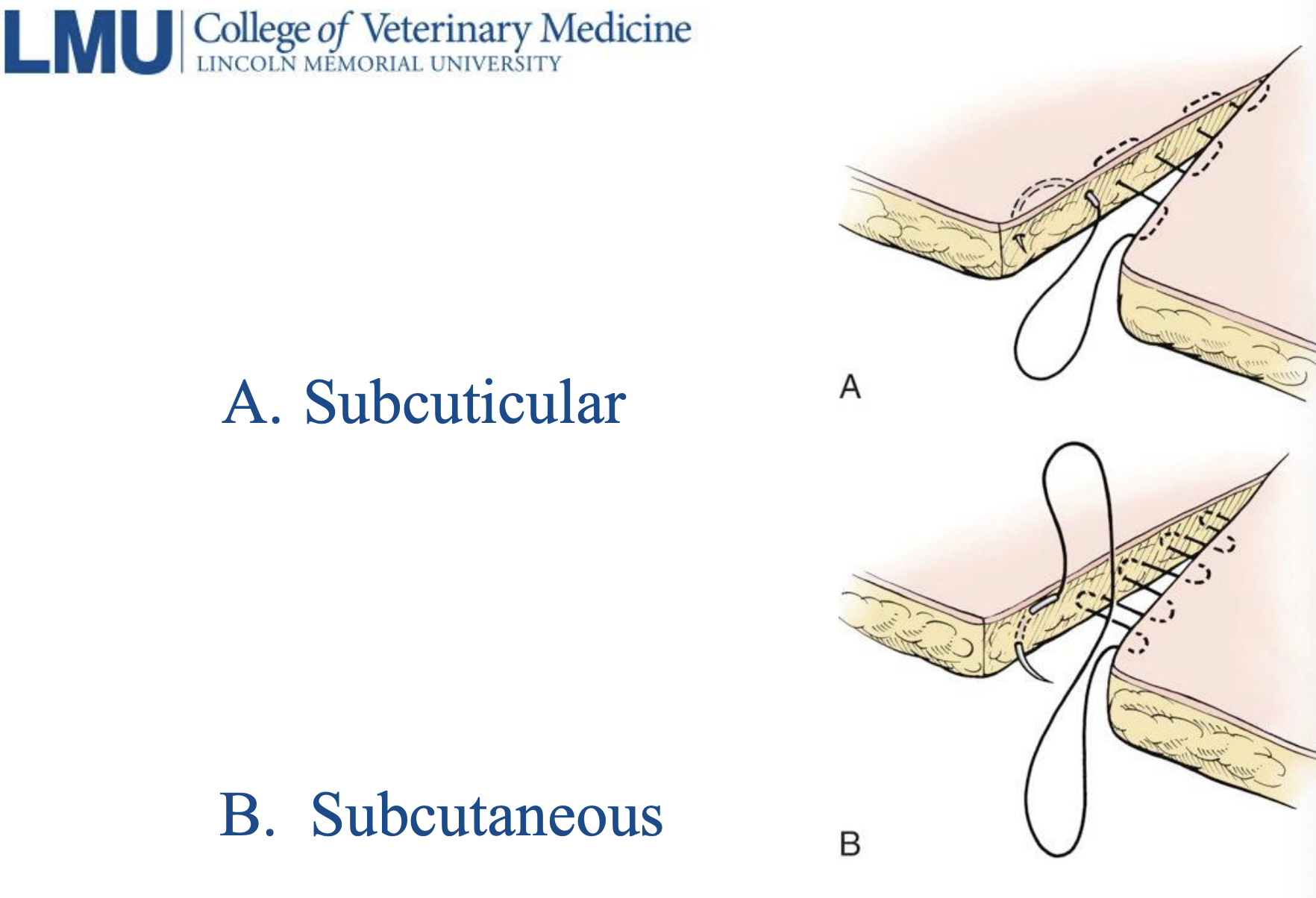
subcuticular vs subcutaneous
list of interrupted suture patterns:
simple interrupted
horizontal mattress
cruciate
vertical mattress
halstead
gambee
simple interrupted suture patternare made by:
inserting the neelde through tissue on one side of an incision or wound, passing it to the opposite side, and tying
knot is offset so that it does not rest on top of the incision
ends of the suture are cut (for skin sutures, the ends are left long enough to allow them to be grasped during removal)
Simple interrupted suture pattern
sutures should be placed approx 2 to 3mm away from skin edge
right-handed surgeons place sutures from right to left in a horizontal fashion. Left-handed are opposite
(dominant to nondominant!!)
simple interrupted sutures are:
appositional (unless excessive tension is applied)
primary advantages and disadvantages of simple interrupted sutures is that:
disruption of a single suture does not cause the enture suture line to fail
however they take more time than continuous patterns
result in more foreign material (knots) in the wound
horiztonal mattress suture pattern are used primarily:
in areas of tension
can be placed rapidly
often cause tissue eversion (care should be exercised to appose, rather than evert, tissue margins)
suture should be angled though the tissue so that it passes just below the dermis
generally, are separated by 4 to 5 mm
can be bolstered using rubber stents and buttons
cruciate suture pattern
formed when 2 simple interrupted sutures are placed parallel to each other and then tied across the incision to create an X
appositional
can relieve low to moderate tension across an incision
less suture material is used to close a skin incision than with simple interrupted
affords the security of an interrupted pattern
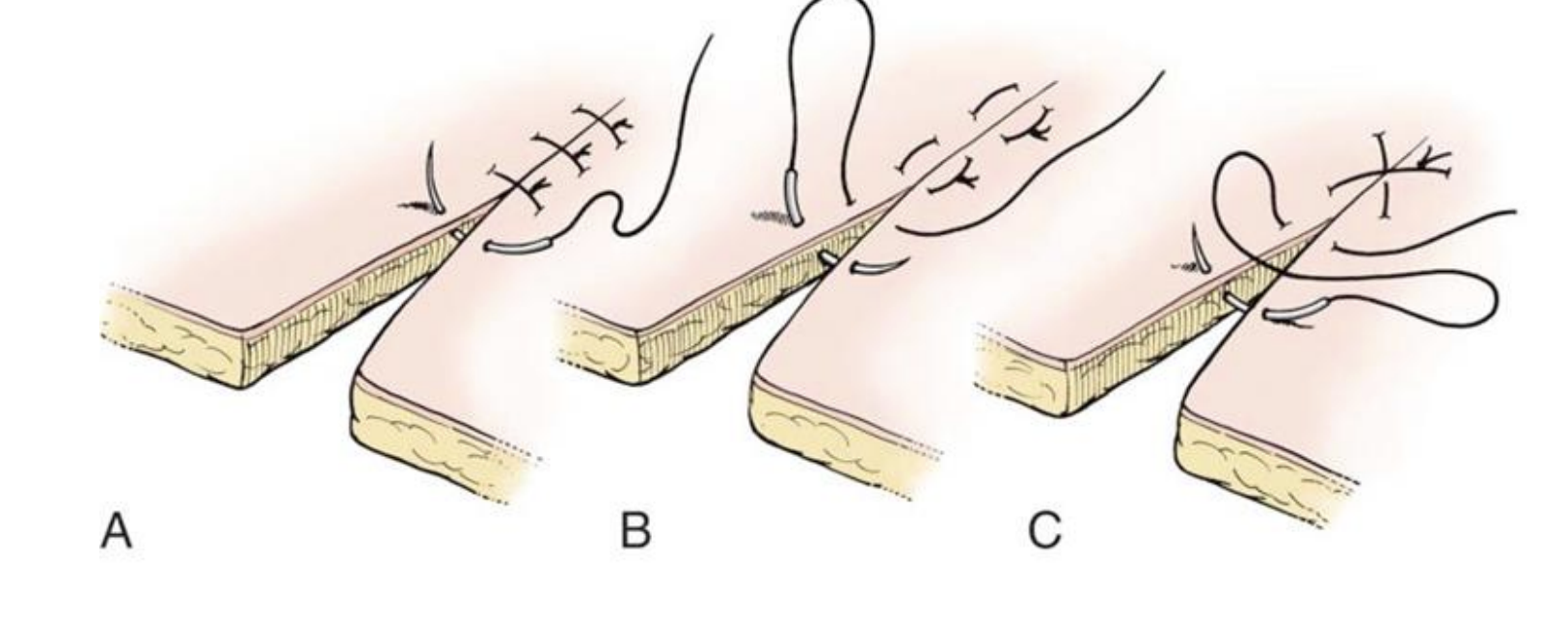
A. Simple interrupted
B. Horizontal mattress
C. Cruciate
Vertical mattress suture pattern
stronger than horizontal mattress sutures
preferred when addressing tension in skin closure
less disruption to the blood supply of the wound edges
each bite approx 4 mm from skin edge
relatively time consuming
eversion of skin margins is less of a proglem than with horizontal mattress sutures
can be bolstered using rubber stents and buttons
stents
placing padded material beneath the suture loops is stenting
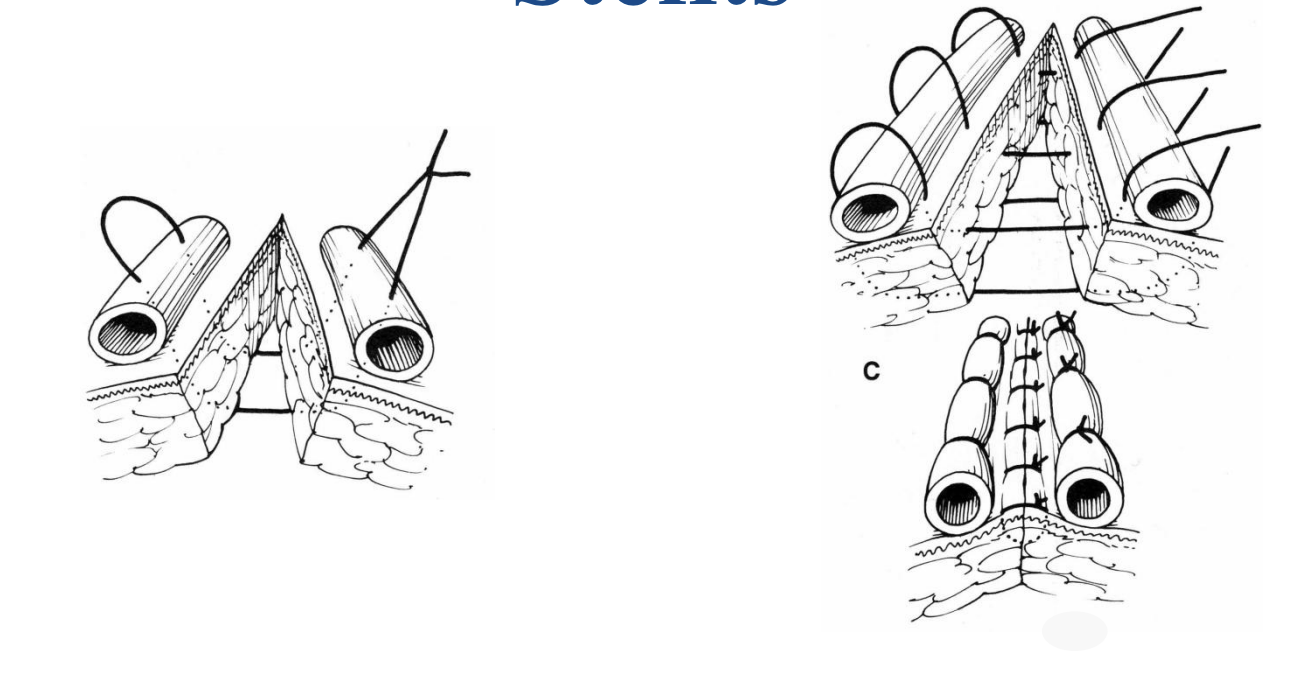
halstead suture pattern
an interrupted mattress pattern that is a modification of a continuous Lembert pattern
infrequently used in vet med
provides exact skin approximation
Gambee suture pattern
interrupted pattern used in intestinal surgery to reduce mucosal eversion
also reduces mucosal inversion and may reduce wicking of material from the intestinal lumen to the exterior
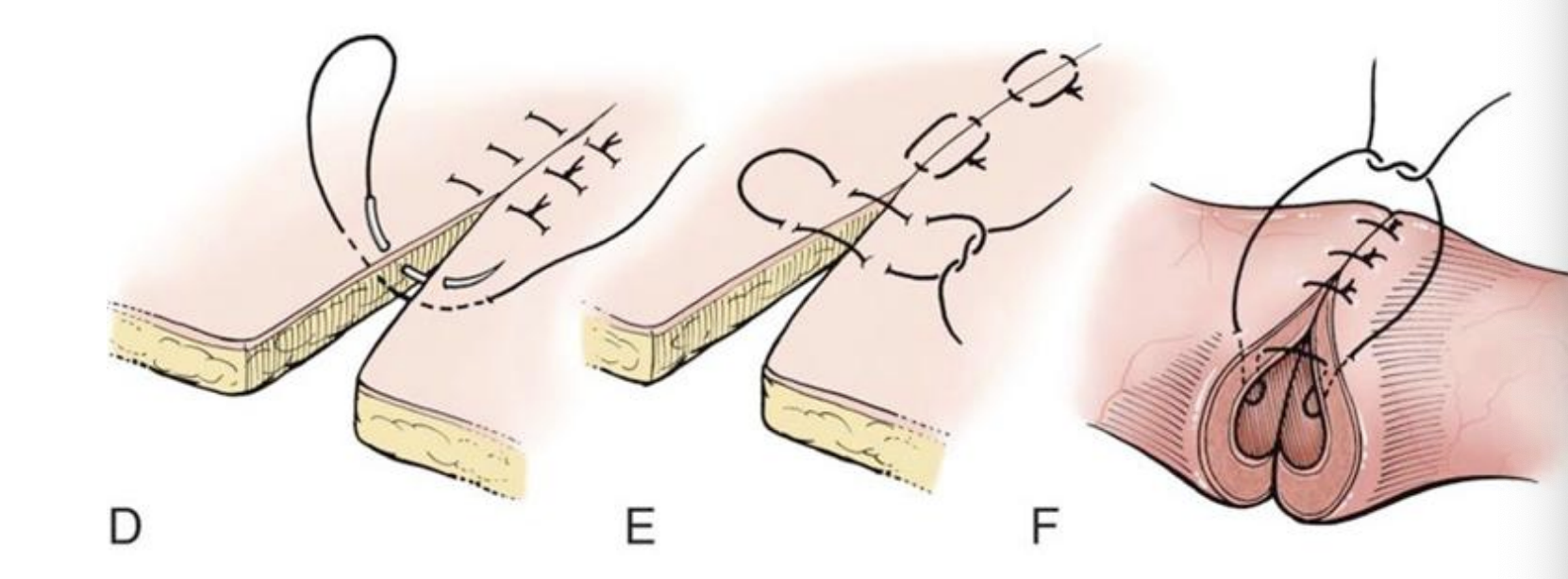
D. Vertical mattress
E. Halsted
F. Gambee
Continuous suture patterns
simple continuous
running
ford interlocking
Lembert
Connel
Cushing
simple continuous pattern
consists of a series of simple interrupted sutures with a knot on either end
provides maximum tissue apposition
relatively air and fluid tight compared with series of simple interrupted sutures
frequently used to close the linea alba and subcutaneous tissue
care should be taken when placing continuous suture lines in areas where tightening of the suture may result in purse-string like effect (such as with an intestinal anastomosis)
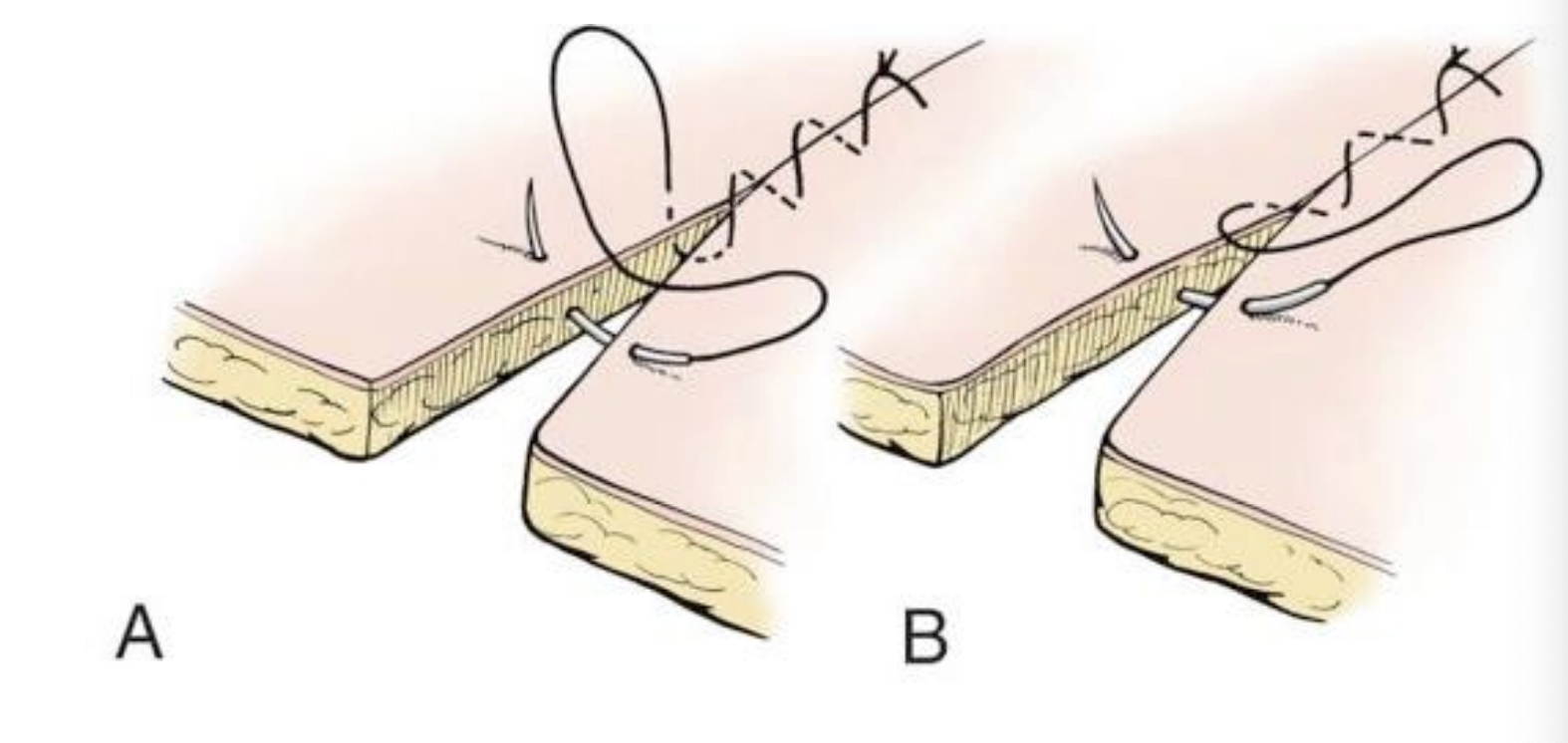
A. Simple Continuous
B. Running
We won’t be performing at LMU really!!
simple continuous suture pattern, how is the needle passed?
rthe suture is advanced above the incision line at a diaganol
running suture
a running suture is created if the suture is advanced above and below the incision line, but this is not as secure as less tissue is purchased
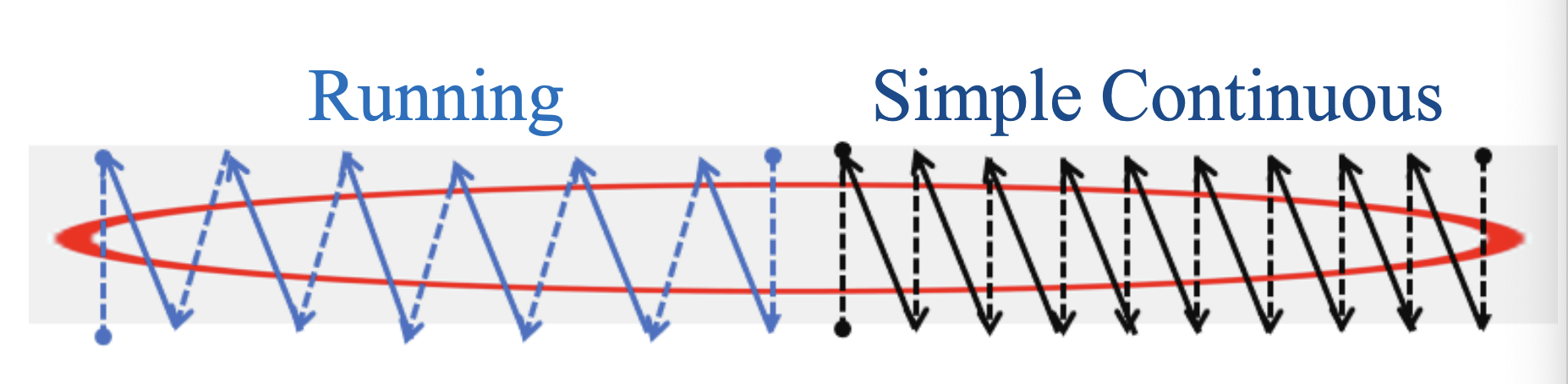
running:
created much like simple continuous, but the suture is advanced above and below the incision line
it is not as secure as a simple continuous since less tissue is purchased
simple continuous
needle passed through the tissue from one side to the other, perpendicular to the incision
the suture is advanced above the incision line at a diagonal
Ford interlocking pattern
Modification of a simple continuous pattern
Each passage through the tissue is partly locked
Each pass through the tissue is linked to the previous passage as the suture exits the tissue through a created loop of material
May be placed quickly
May appose tissue better than a simple interrupted pattern
Provides greater stability than a simple continuous pattern in the event of a partial break along the line
Larger amount of suture material is used
Sutures may be more difficult to remove
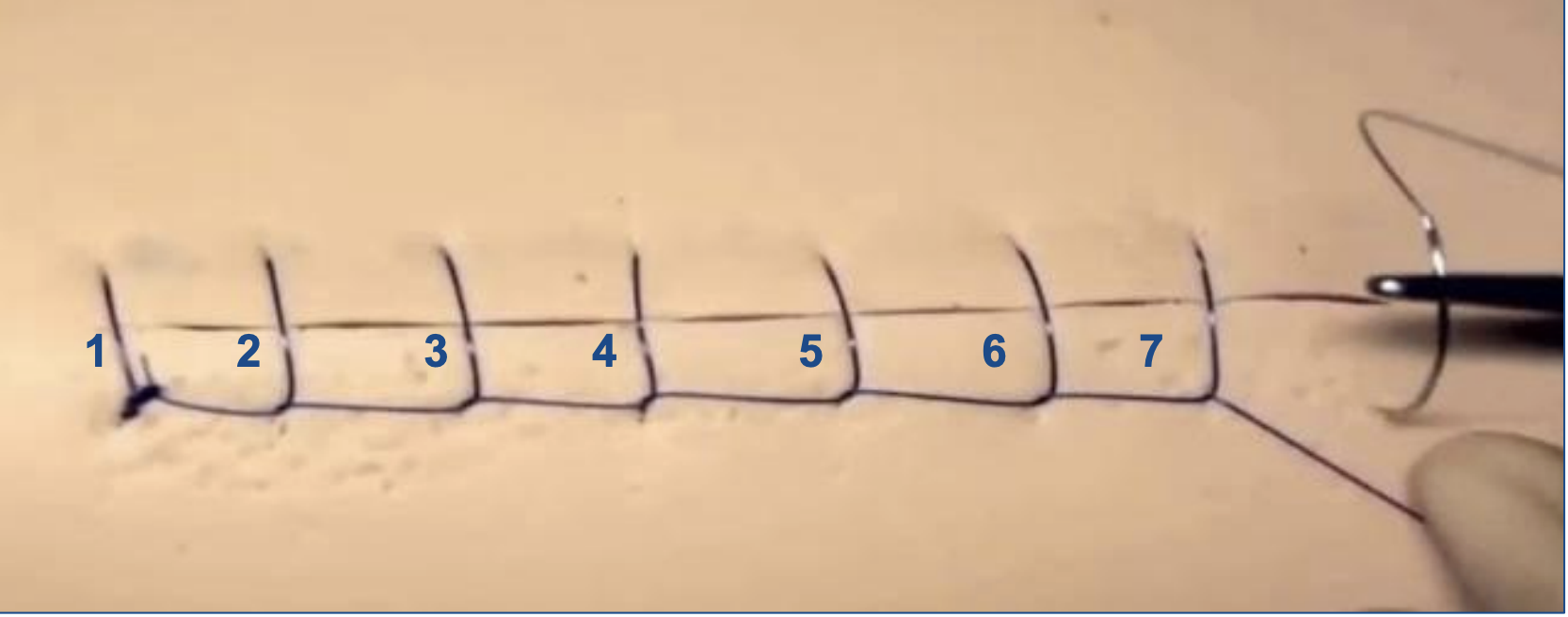

ford interlocking suture pattern
place from nondominant to dominant hand for a right-handed surgeon (only pattern like this!)
Lembert suture pattern
a variation of a vertical mattress pattern applied in a continuous fashion
inverting pattern that often is used to close hollow viscera
Cushing and Connell suture pattern
• Inverting patterns that are used to close hollow organs
• Watertight seal is created by the inversion
• Patterns are similar, except that a Connell pattern enters the lumen, whereas a Cushing pattern extends only to the submucosal layer
• It was previously thought that a Cushing pattern would be preferable to a Connell for cystotomy closure because suture material in the lumen might be calculogenic; however, the use of rapidly absorbed monofilament sutures negates this concern
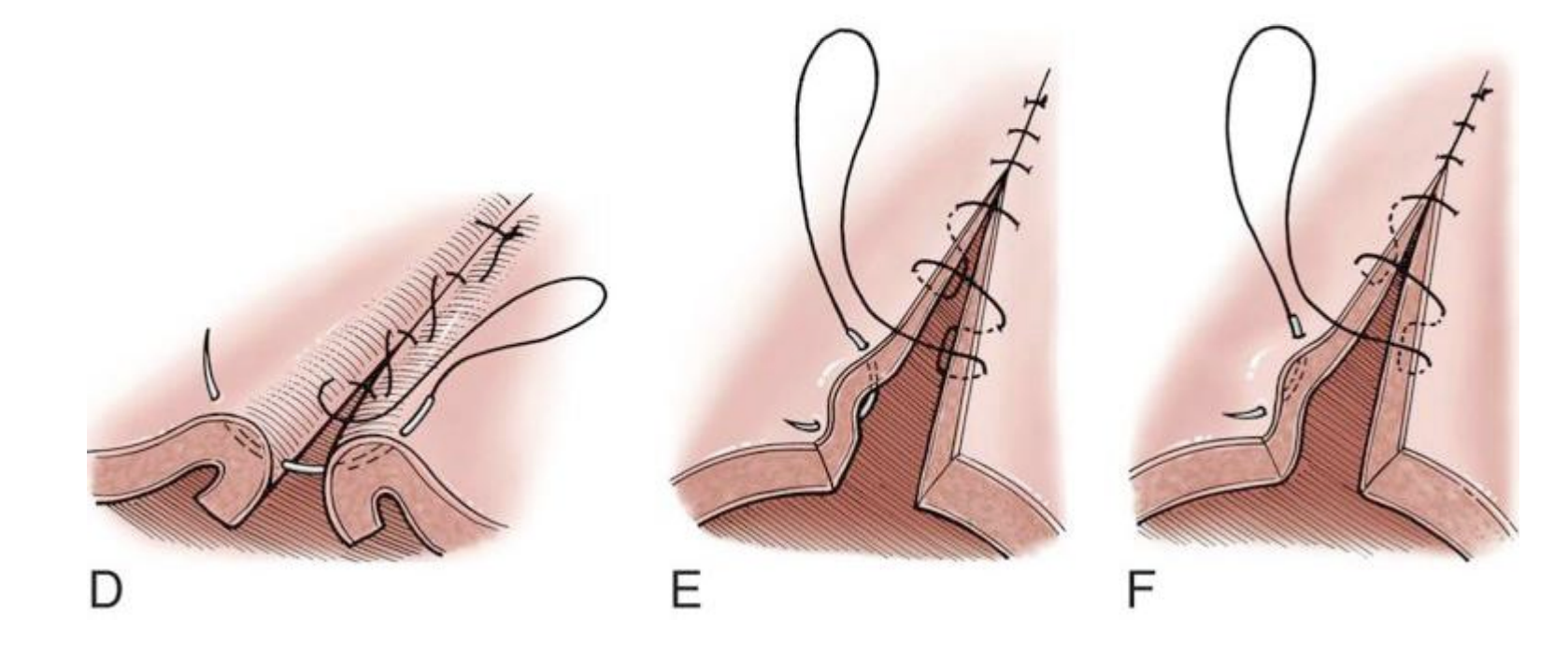
D. Lembert
E. Connell
F. Cushing
Parker-Kerr Oversew
2-layer closure for inverted closure of a transected, clamped, stump of hollow viscera
begins with Cushing/Connell, followed by an inverting seromuscular pattern
seldom used because it causes excessive tissue inversion
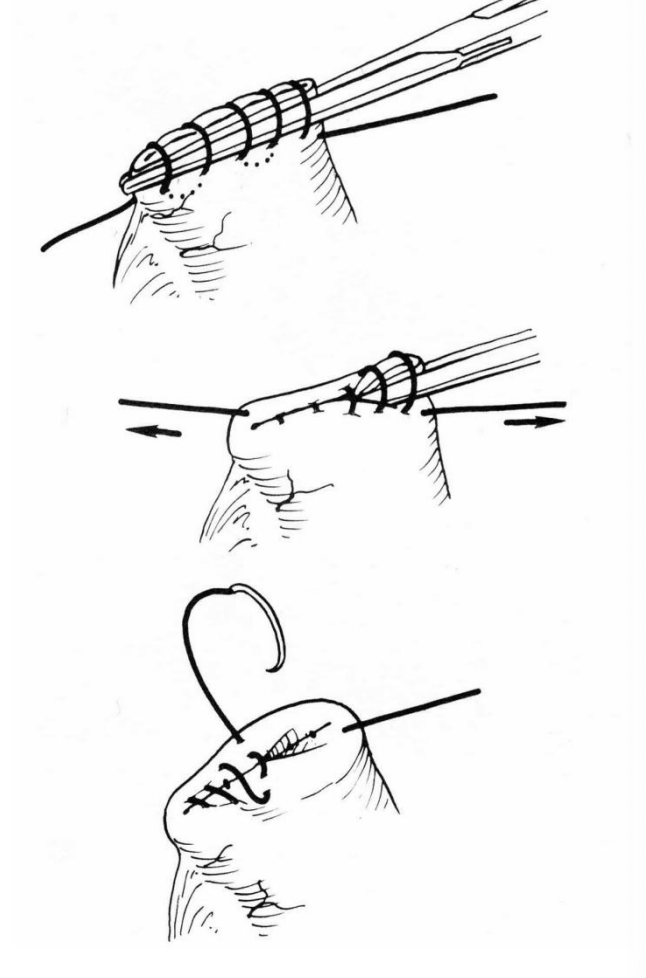
Parker-Kerr Oversew
Tendon Sutures
specific suture configurations are used to approximate severed ends of a tendon or to secure one end of a tendon to bone or muscle
Kessler locking-loop
Bunnel-Mayer
Krackow
Three-loop pulley
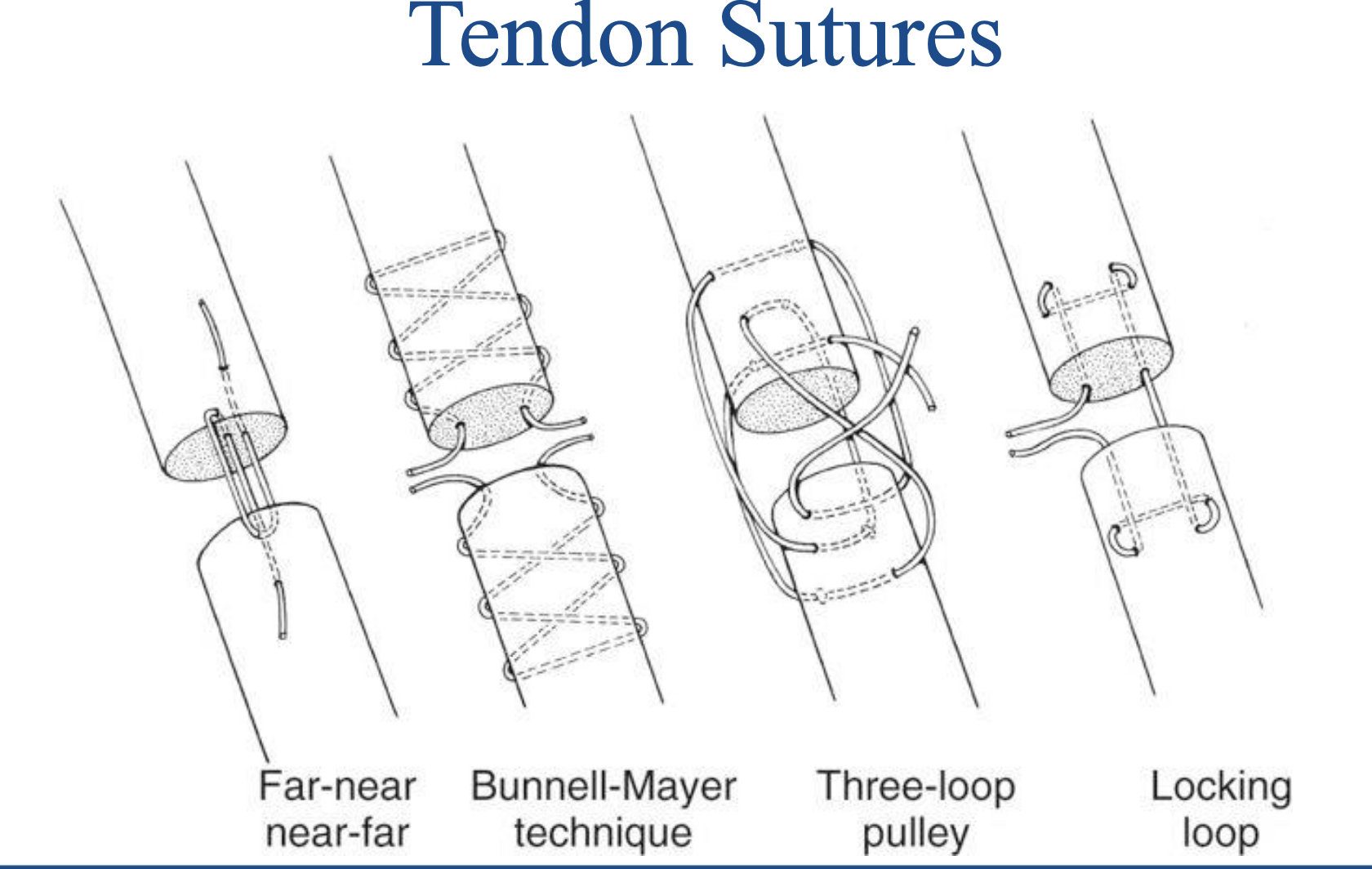
Tendon sutures (cool)