Apologia Advanced Biology, Module 13: The Digestive System
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Mastication
The process of chewing
Digestion
The breakdown of food molecules into their individual components
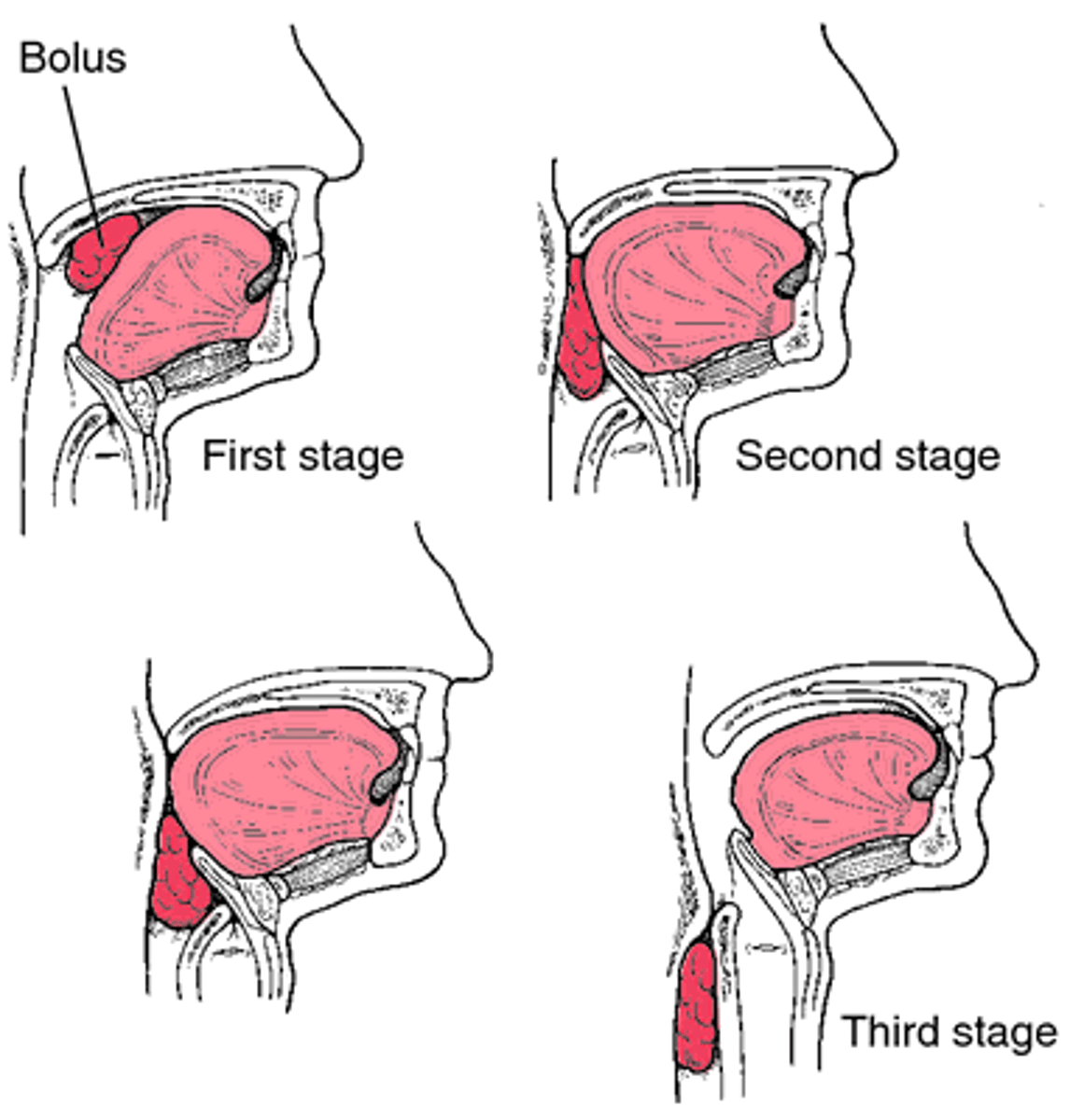
Deglutition
The act of swallowing
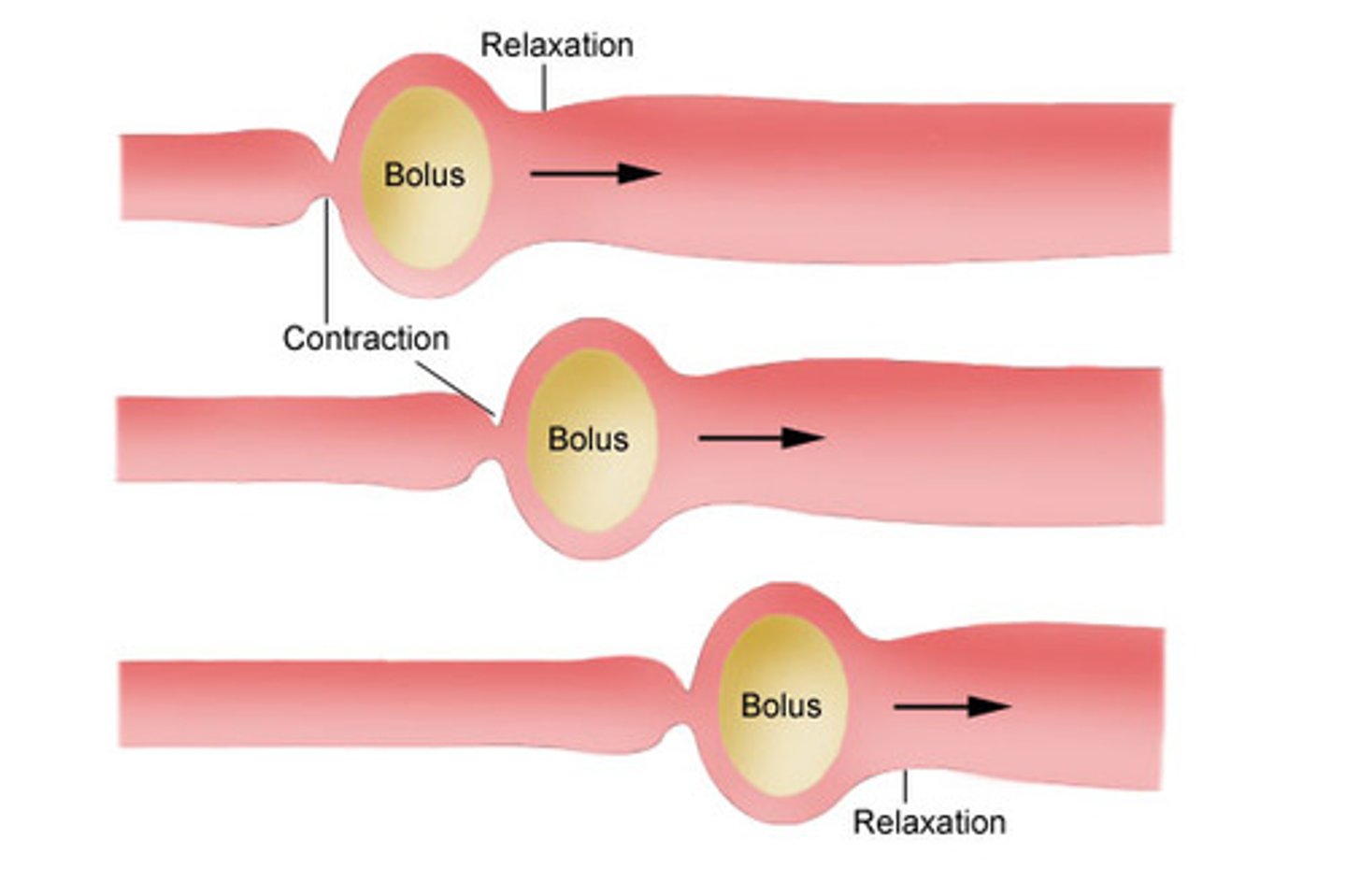
Peristalsis
The process of contraction and relaxation of circular smooth muscles which pushes food through the alimentary canal
Gastric Juice
The acidic secretion of the stomach. The liquid that includes hydrochloric acid and pepsin and that is responsible for the chemical digestion of protein in the stomach.
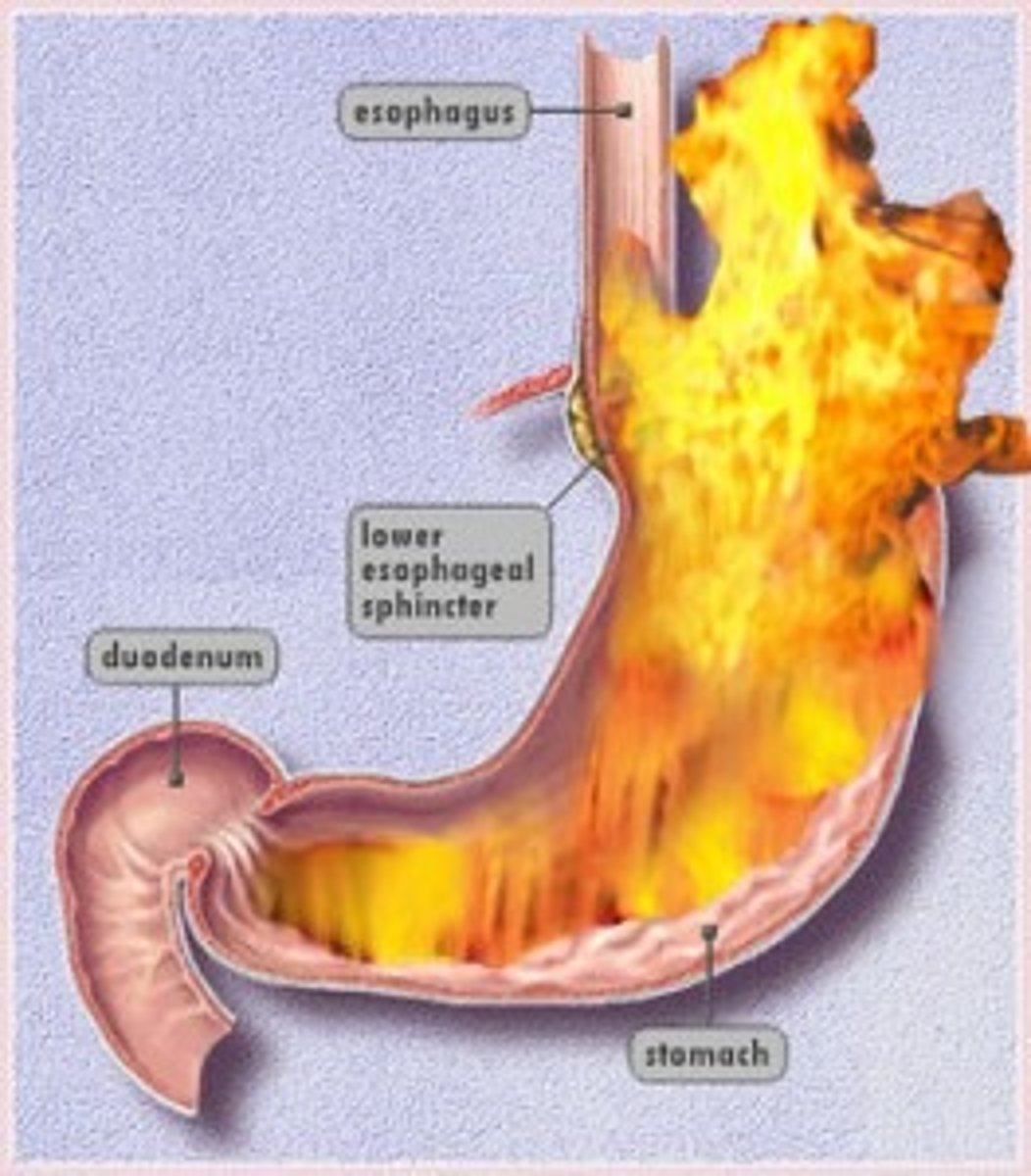
Adventitia
A thin layer of loose connective tissue that binds an organ to surrounding tissues or organs
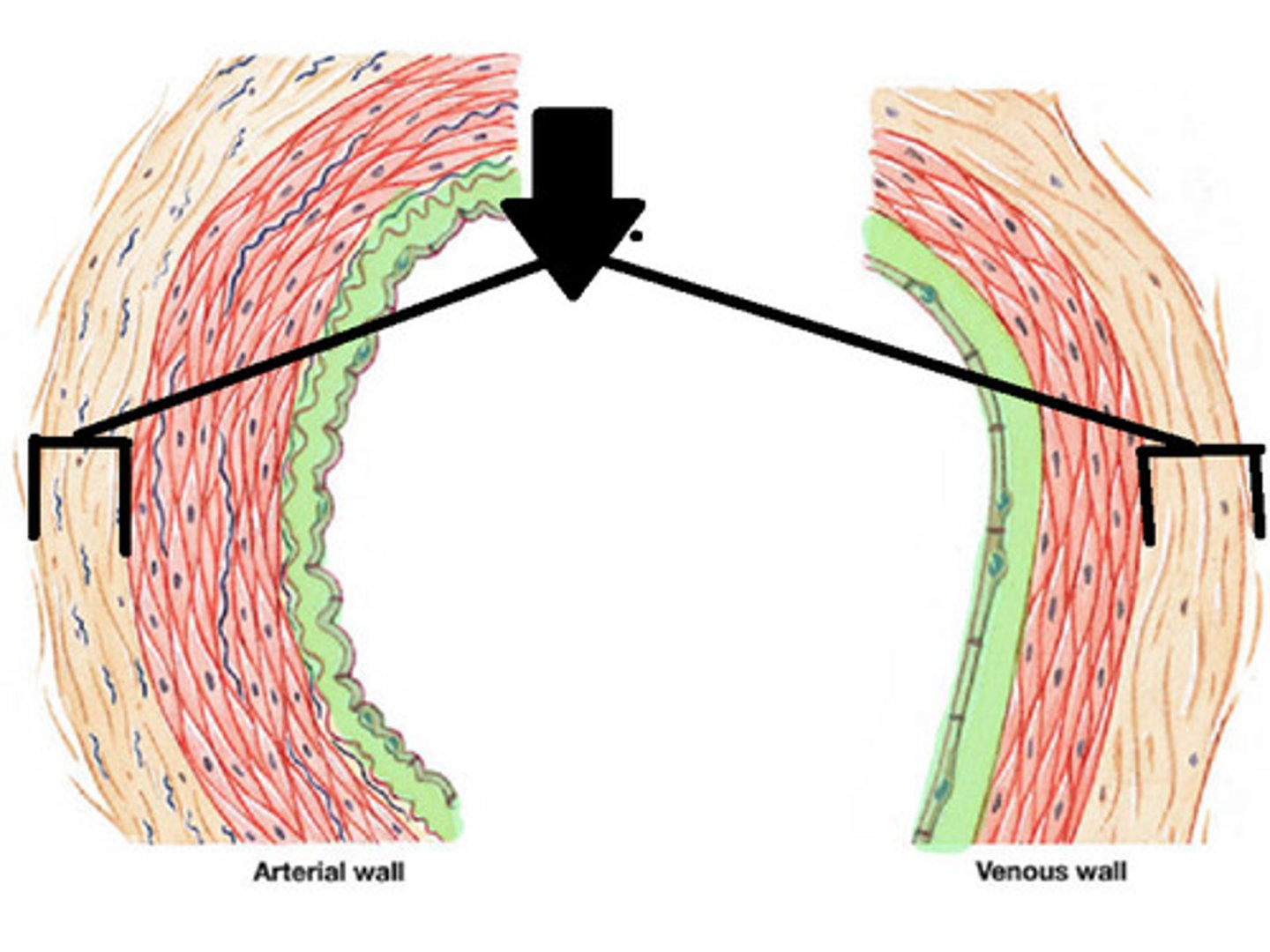
Lumen
The hole in the center of a tube; the pathway in blood vessels in which the blood moves through
Macronutrients
The nutrients the body needs in large amounts: carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which are necessary for building and maintaining body tissues and providing energy for daily activities
Micronutrients
The nutrients the body needs in small amounts, such as vitamins and minerals. An element that an organism needs in very small amounts and that functions as a component or cofactor of enzymes
Pancreas
An organs in the abdominal cavity with two roles. The first is an exocrine role: to produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are delivered to the small intestine via the pancreatic duct. The second is an endocrine role: to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
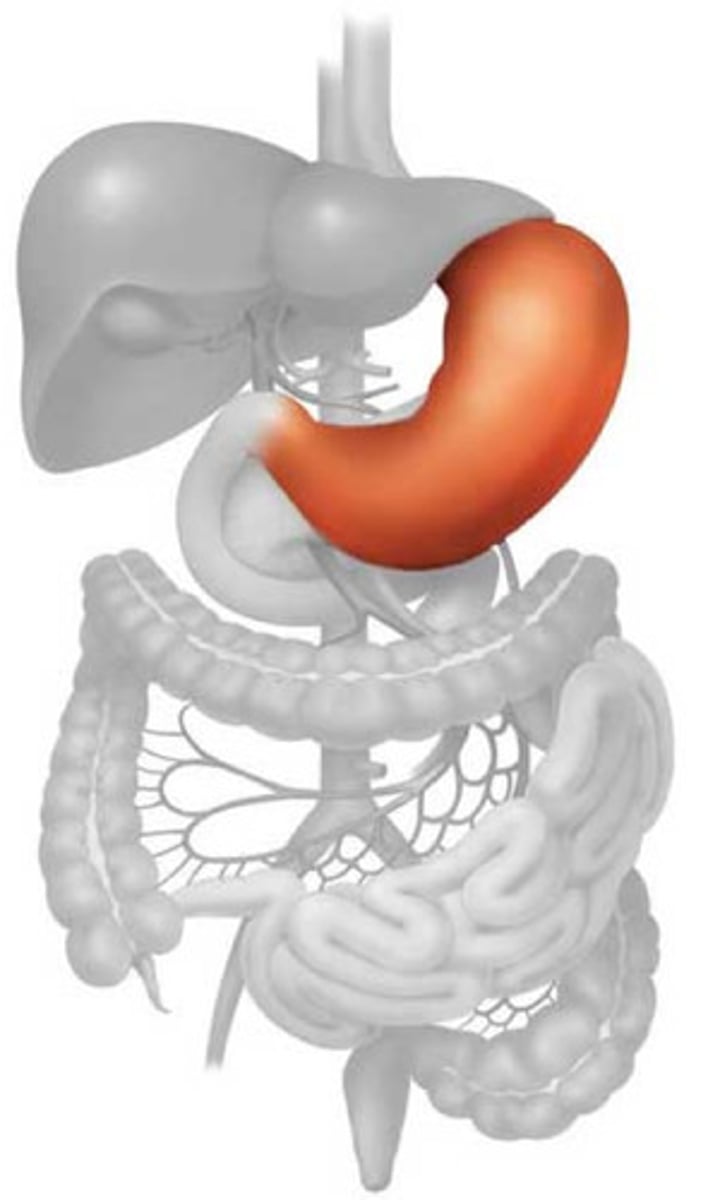
Stomach
A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat.
Small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place. Contains glands which produce secretin, which is a hormone that inhibits the secretion of gastric juice and increase the secretions of substance that reduce the acidity of chyme.
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Its purpose is to move food from the pharynx to the stomach
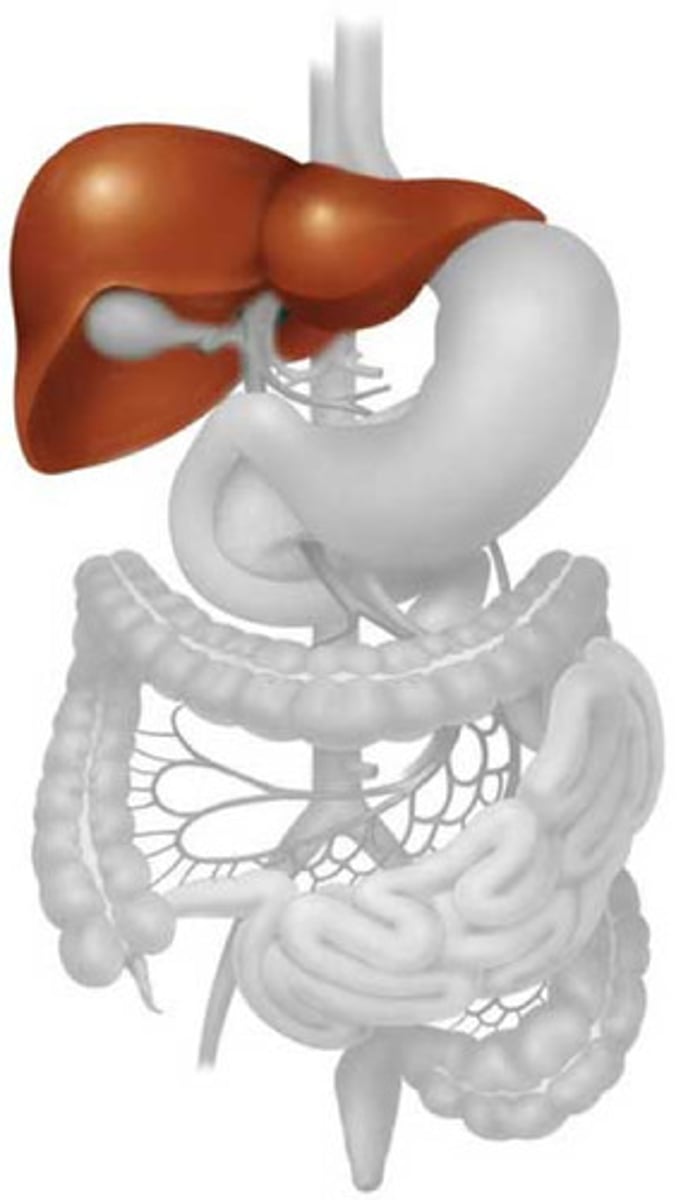
Liver
Stores excess glucose as glycogen
A large solid organ that lies in the right upper quadrant immediately below the diaphragm; it produces bile, stores glucose for immediate use by the body, and produces many substances that help regulate immune responses.
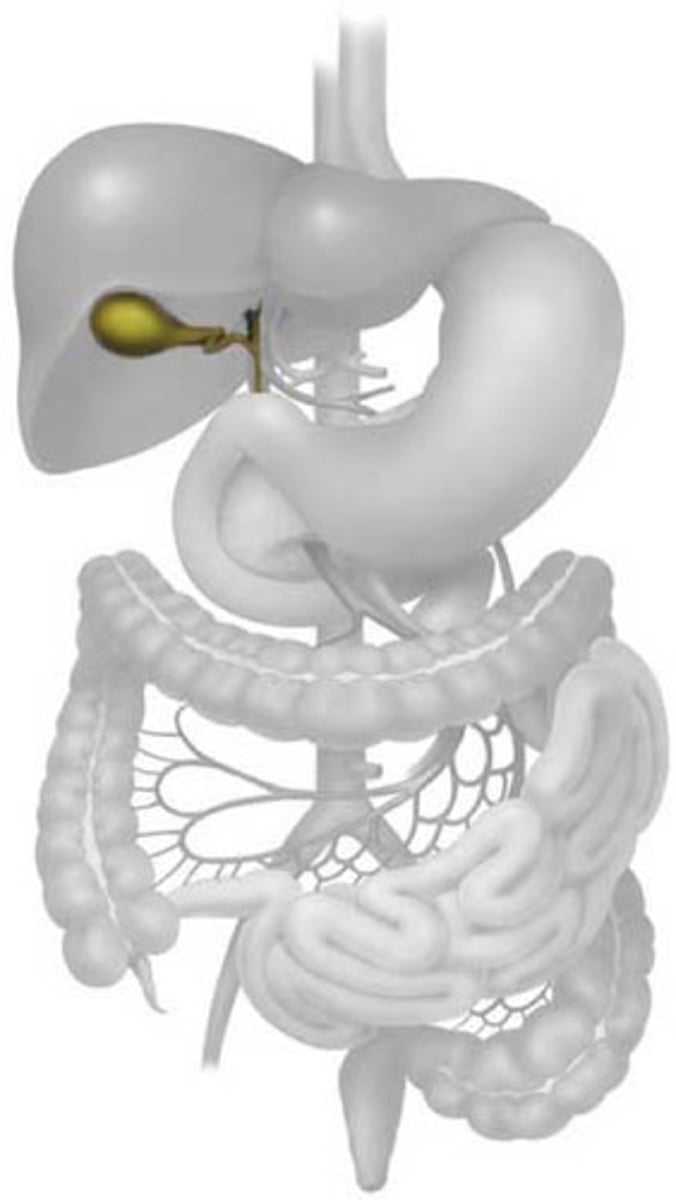
Gall bladder
An organ that stores bile and releases it as needed into the small intestine
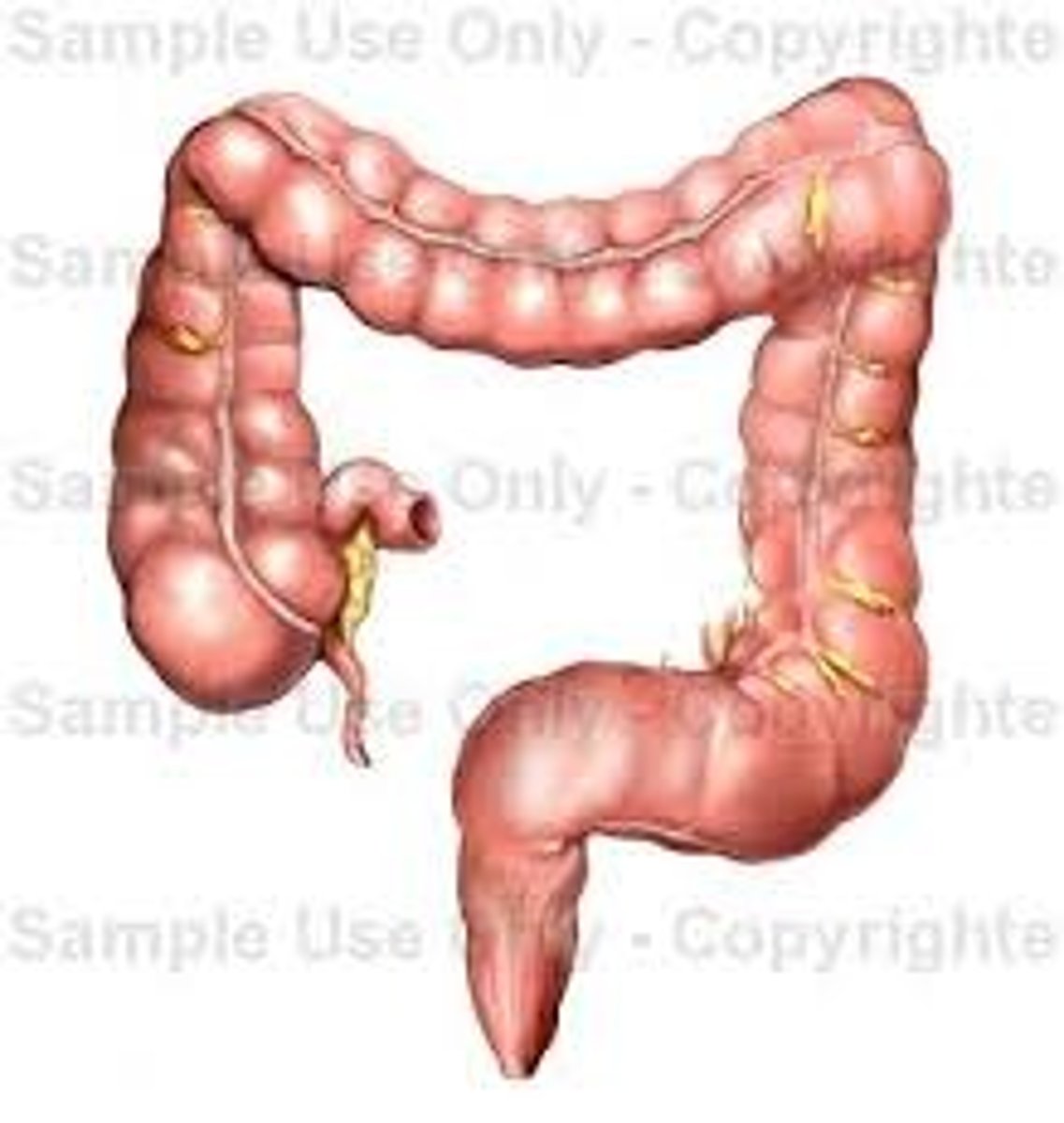
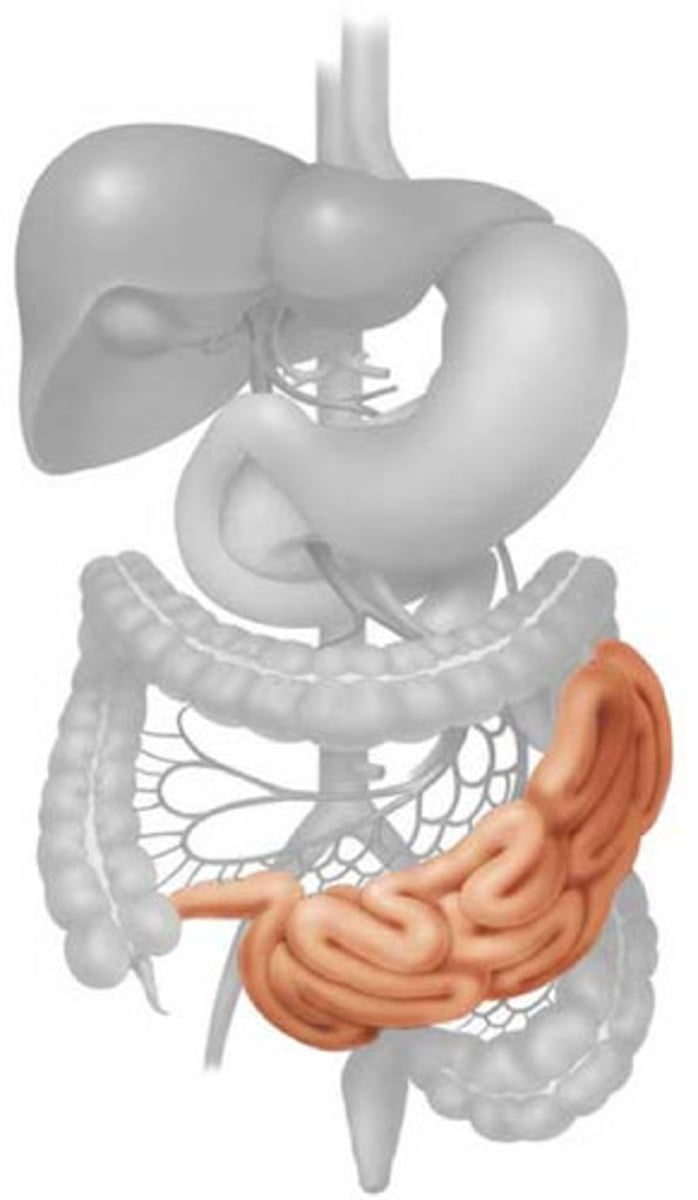
Colon
Another name for large intestine. The Transverse part passes across the interior abdomen. The ascending travels upward from the cecum to the undersurface of the liver. The descending travels down the left side of the abdominal cavity to the sigmoid colon

Vermiform appendix
A small worm-like projection that is in the cecum of the ileum of the small intestine and may play a minor role in immunology
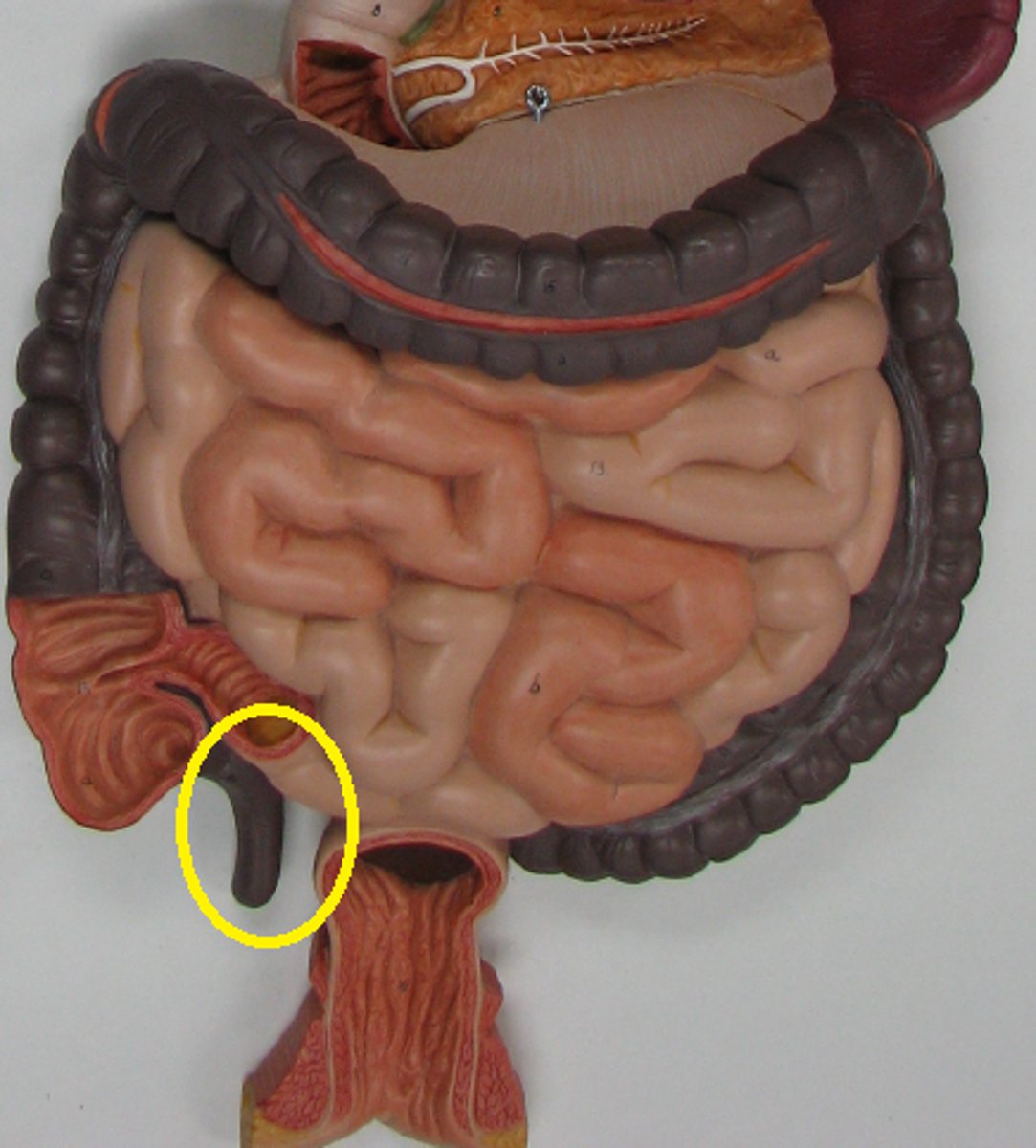
Rectum
A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated. Holds feces and triggers the defecation reflex.
Alimentary canal
digestive tube that extends from the mouth to the anus
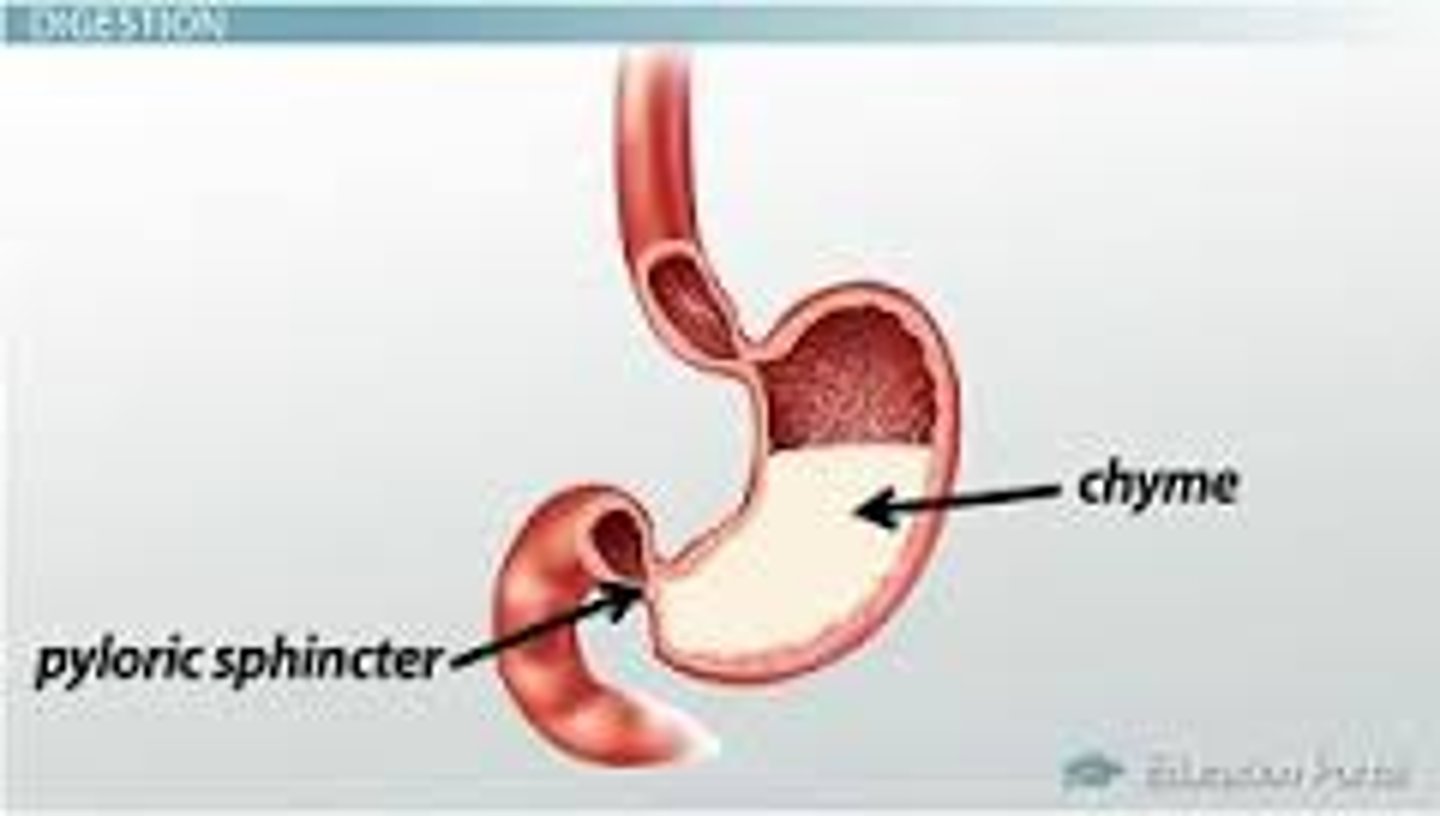
Chyme
Partially digested, semi-liquid food mixed with digestive enzymes and acids in the stomach.
Feces
undigested food material and other waste products that exit the body through the anus
Bile
A mixture of salts and phospholipids that aids in the breakdown of fat
Amylase
a digestive enzyme found in saliva (secreted by the salivary glands) that helps to break down polysaccharides into smaller carbohydrates
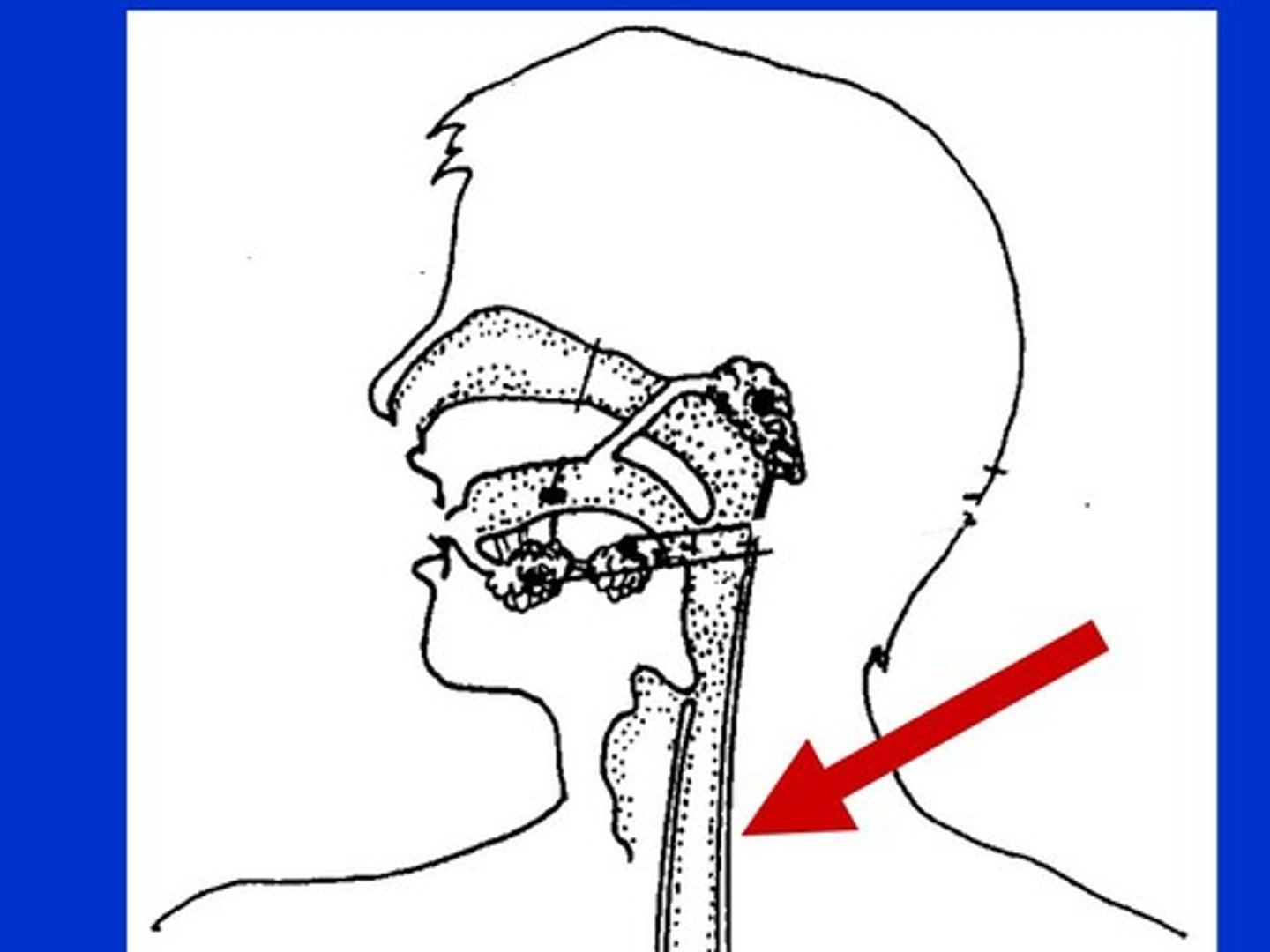
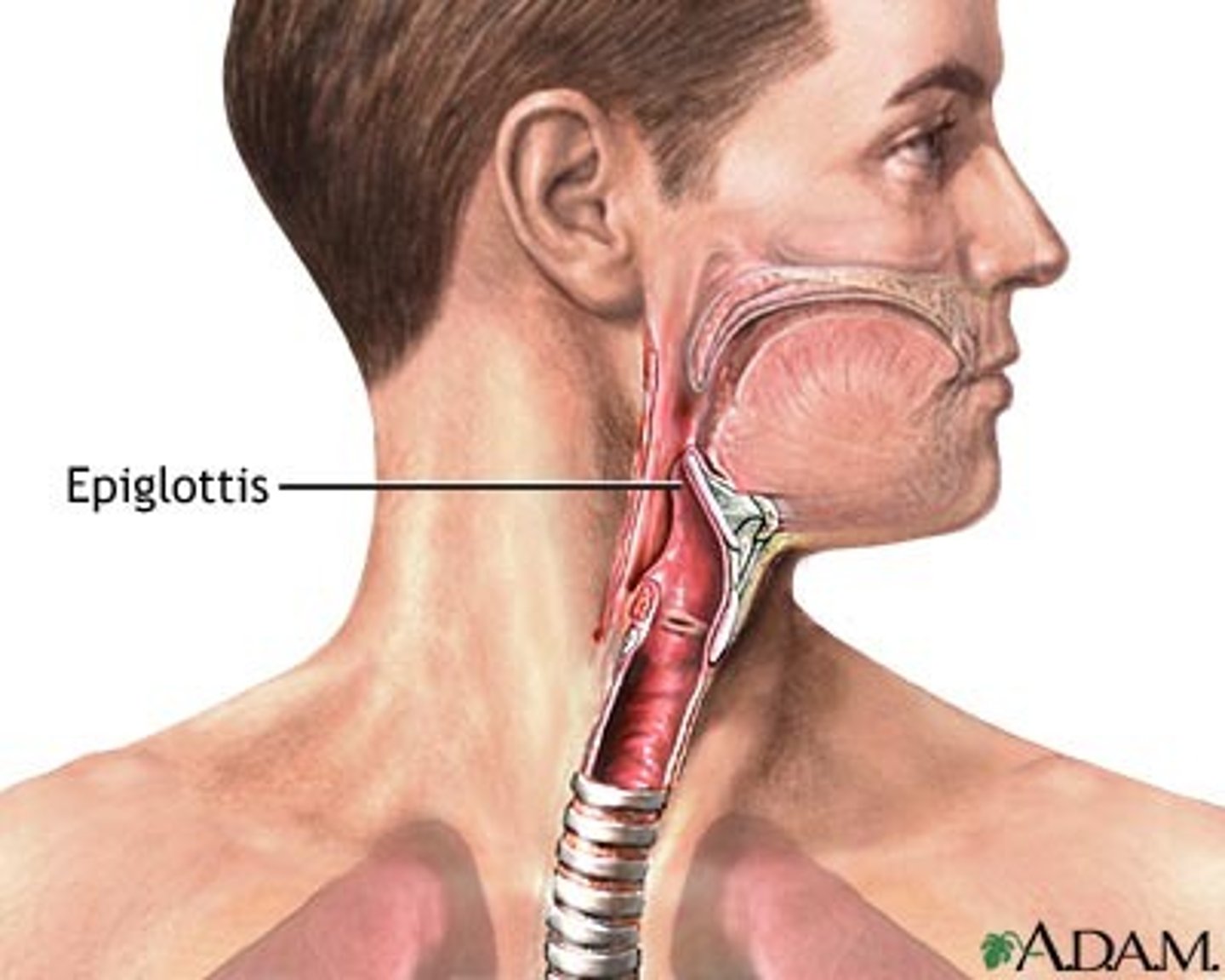
Epiglottis
closes off the larynx to prevent food from entering the airways
Soft palate
seals the nasal cavity to prevent fluid or food from entering the nasal cavity.
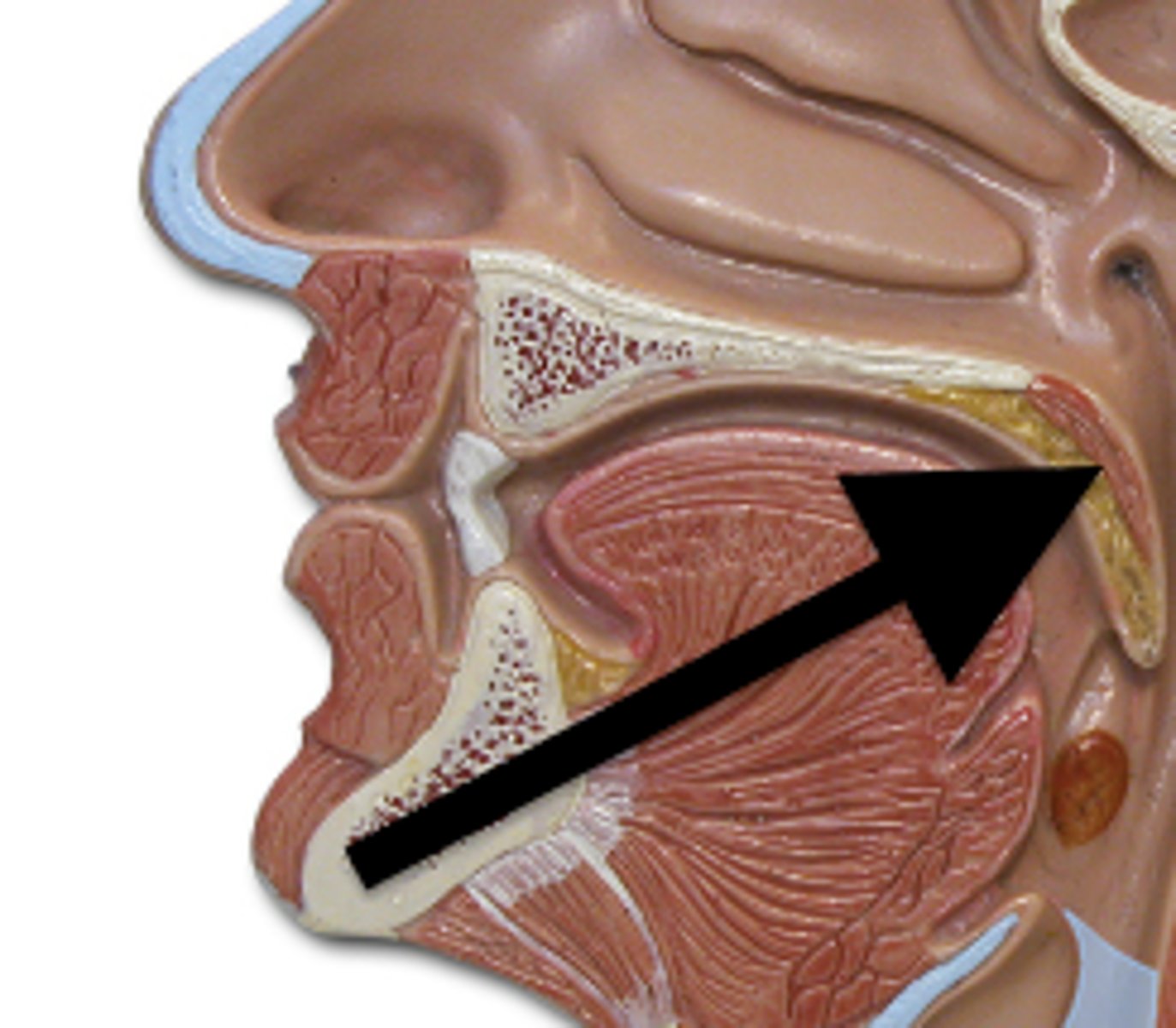
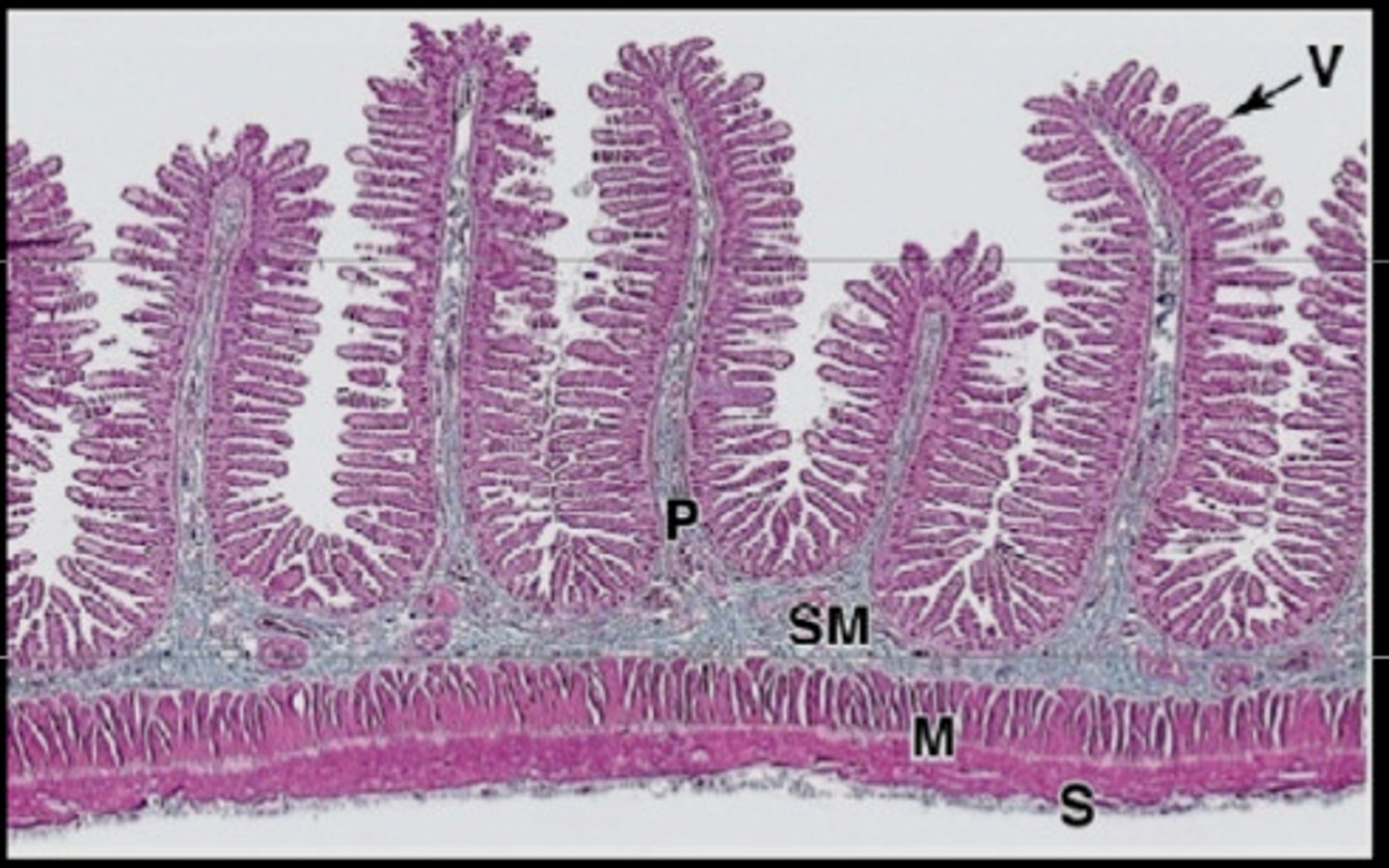
Intestinal villi
millions of tiny projections in the small intestine that greatly increases it's surface are. This is where the nutrients are absorbed.
Pepsin
an enzyme that breaks down proteins into smaller chains of amino acids. It does not completely break them down to amino acids. This would be bad because your cells have tons of proteins in them.
A protein-digesting enzyme secreted by the chief cells of the gastric glands. This is secreted in its inactive form (pepsinogen) and is activated by gastric acid. It is unusual in that its pH optimum is around 1-2; most of these enzymes in the body function best at neutral pHs
Intrinsic factor
A glycoprotein produced by the mucosa of the stomach and intestines that is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12 by the small intestine
Vitamins D
A fat soluble hormone that helps to build bone by increasing absoprtion of calcium from foods in gastrointestinal tract. It is created by exposure to sun.
Vitamin K
Fat soluble hormone necessary for blood clotting. Insufficient amounts of this vitamin can cause hemorrhagic disease. Injections of this vitamin are routinely given postpartum to infants. Made in the intestines by good bacteria
Salivary glands
The three pairs of __________________________ in the mouth that secrete saliva; the parotid, submandibular (submaxillary), and sublingual
Large intestine
larger tubular structure that receives the liquid waste products of digestion, reabsorbs water and minerals, and forms and stores feces for defecation. Cecum, colon and rectum are part of this system.