3.09 Review
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
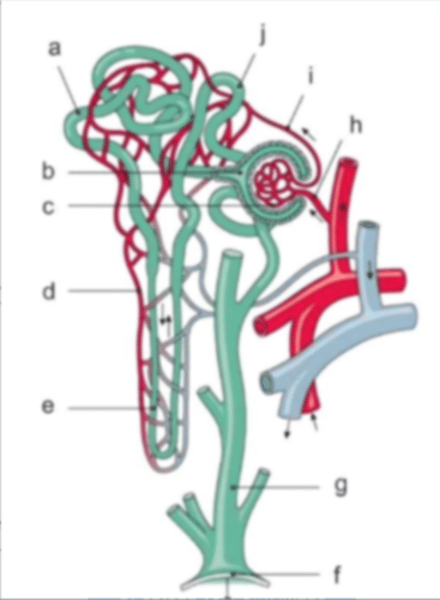
Endothelial cells which form part of the filtration barrier
C
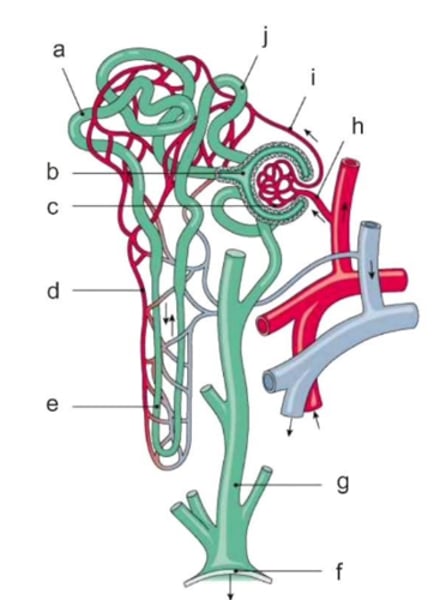
The structure ultimately responsible for medullary hypertonicity
E
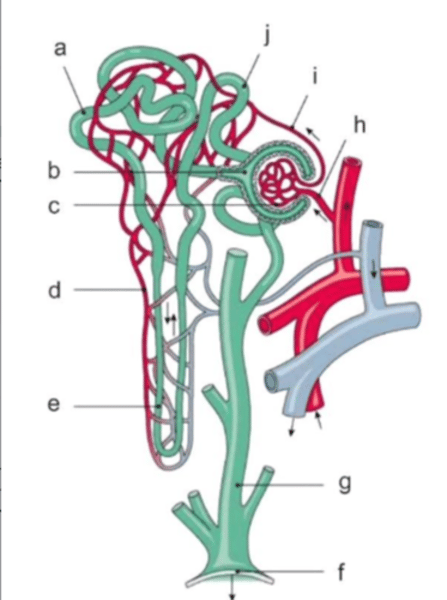
The structure responsible for glucose reabsorption
A
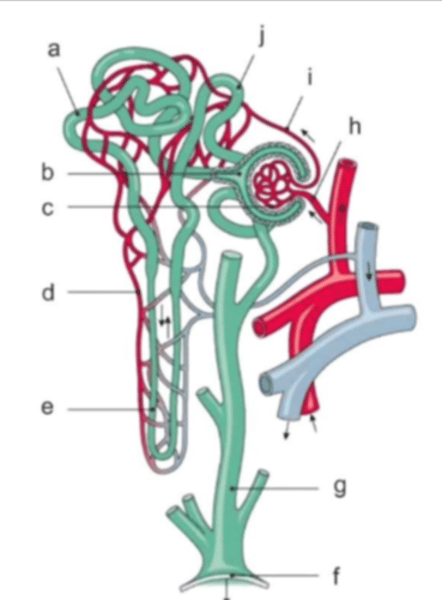
The structure sensitive to vasopressin
G
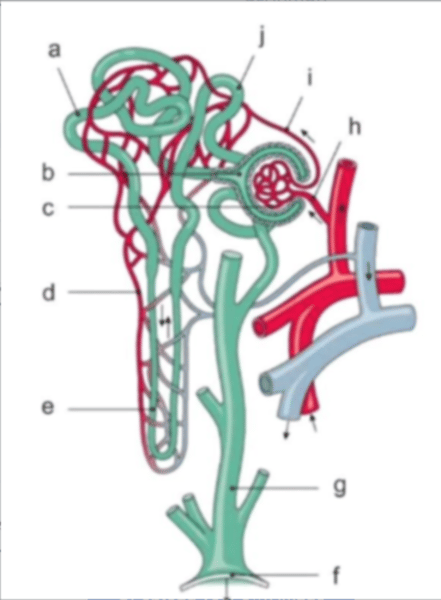
Changes in the diameter of this are a key component in renal autoregulation of blood flow
H
Identify the consequence of nephrotic syndrome
Oedema
Identify the consequence of reduced erythropoietin synthesis
Anaemia
Identify the consequence of failure of renal bicarbonate reabsorption
Metabolic acidosis
Identify the consequence of loss of volume regulation
Secondary hypertension
Identify the consequence of hypocalcaemia and phosphate retention
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Where bone loss, usually from periodontal disease, affects the base of the root trunk of a tooth where two or more roots meet
Furcation lesion
The hypothetical process leading to the loss of cervical tooth structure due to a combination of abrasion, erosion, and/or occlusal forces; data supporting this term as a discrete clinical entity a
Abfraction
A reactive overgrowth possibly in response to local irritation or trauma. This vascular mass often is ulcerated and may be smooth or lobulated and pedunculated or sessile
Pyogenic granuloma
A change from one adult cell type to another form which is not normal to that tissue.
Metaplasia
Loosely adherent, white curds of matter composed of dead cells, food debris, and other components of the dental plaque found on the tooth.
Materia alba
Annual number of kidney transplants in the UK
3000
The number of cases of CKD in the UK (thousands)
3000
The likelihood of CKD in BAME communities compared to other groups (percentage)
500
The number of CKD related premature deaths annually in the UK (thousands)
50
The number of children in the UK with CKD
1000
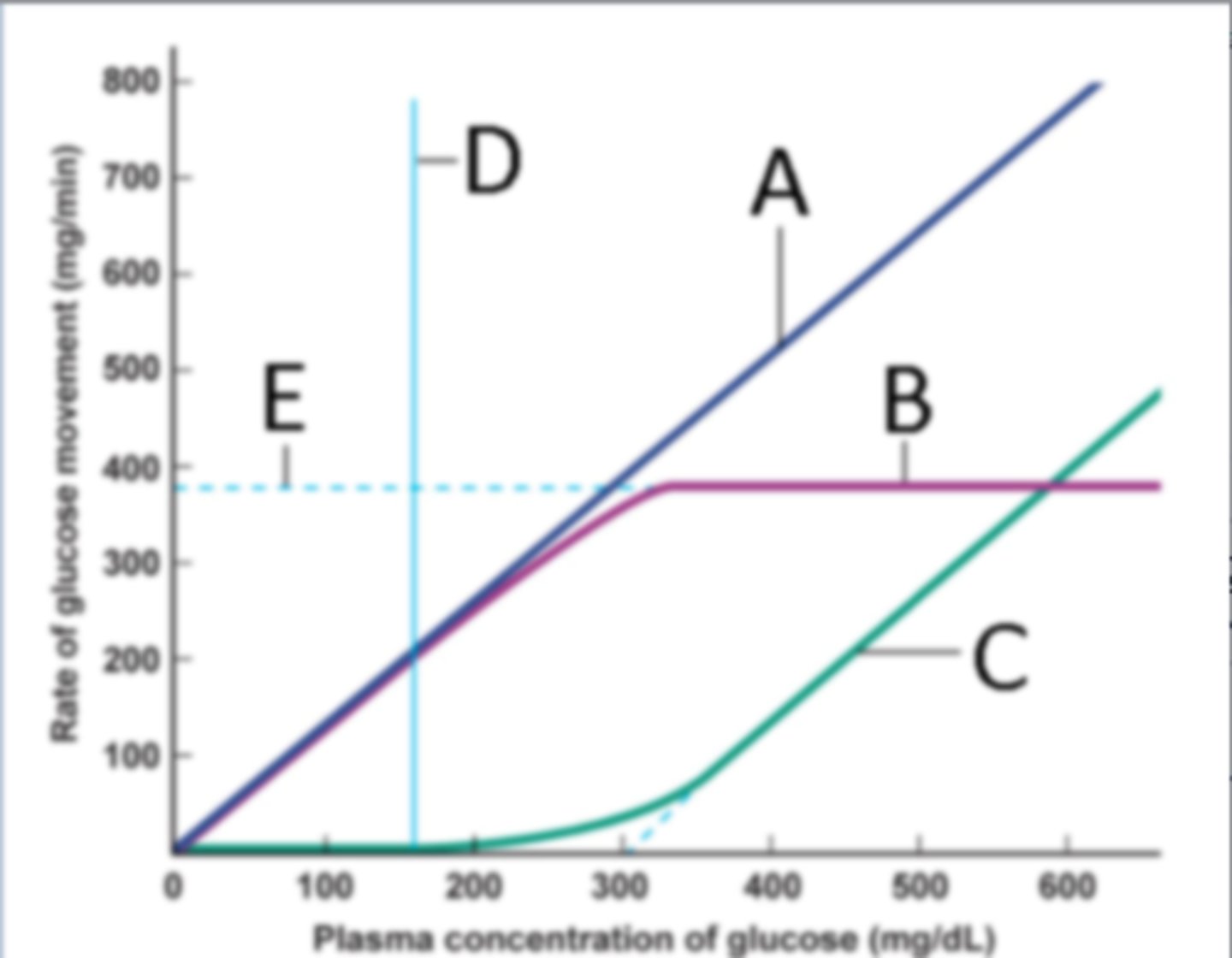
Identify the process at label A
Filtration
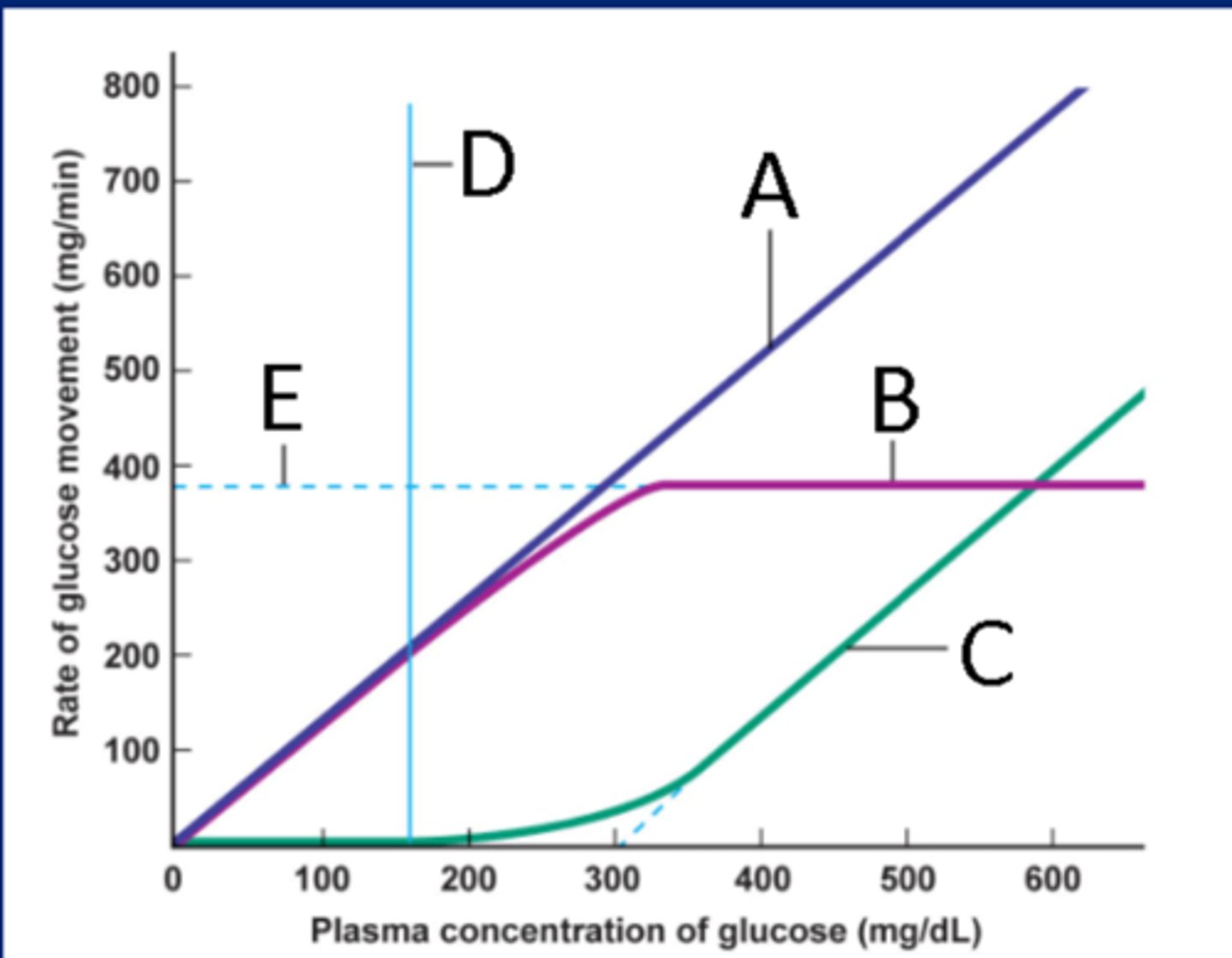
Identify the process at label B
Reabsorption
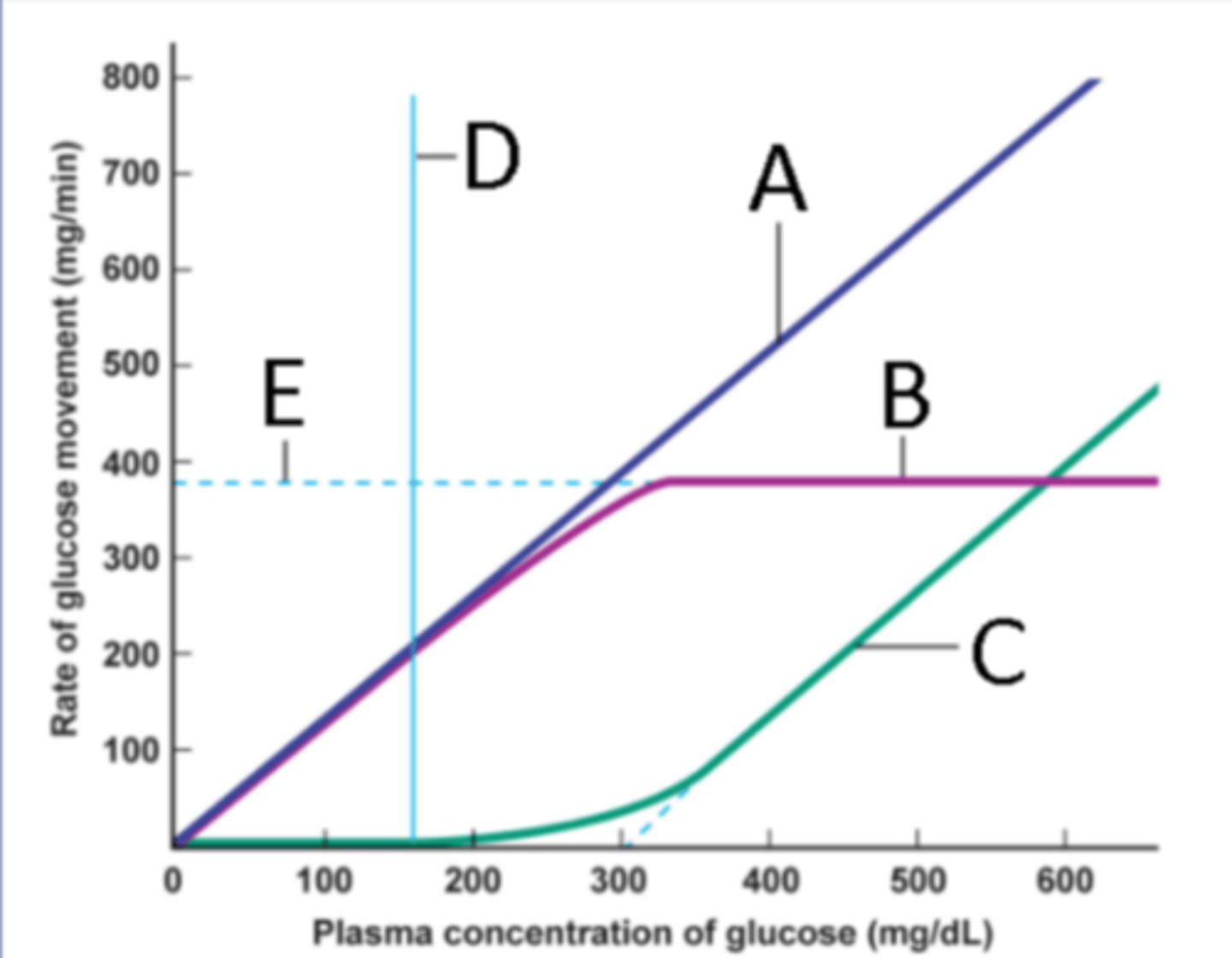
Identify the process at label C
Excretion
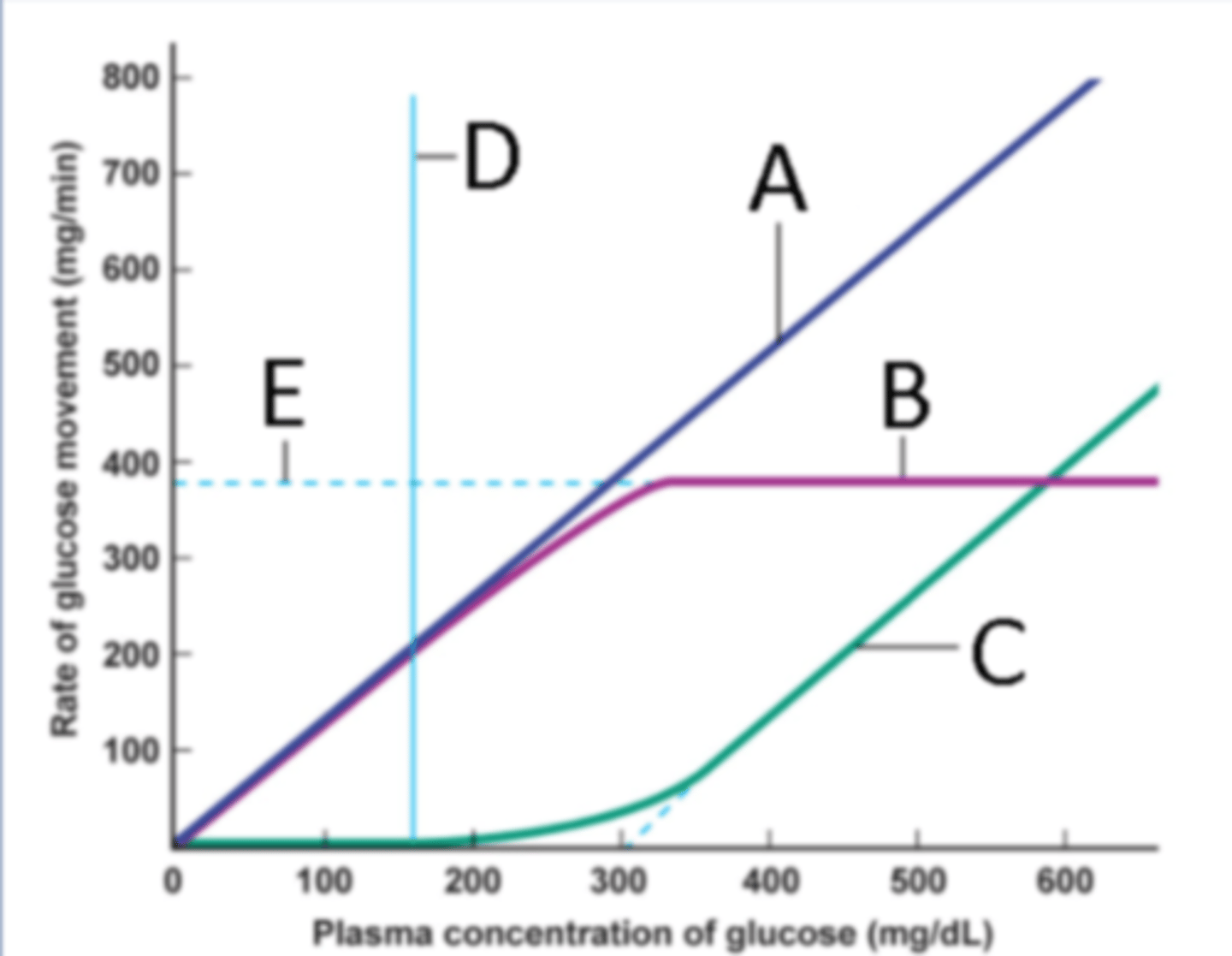
Identify the process at label D
Renal threshold
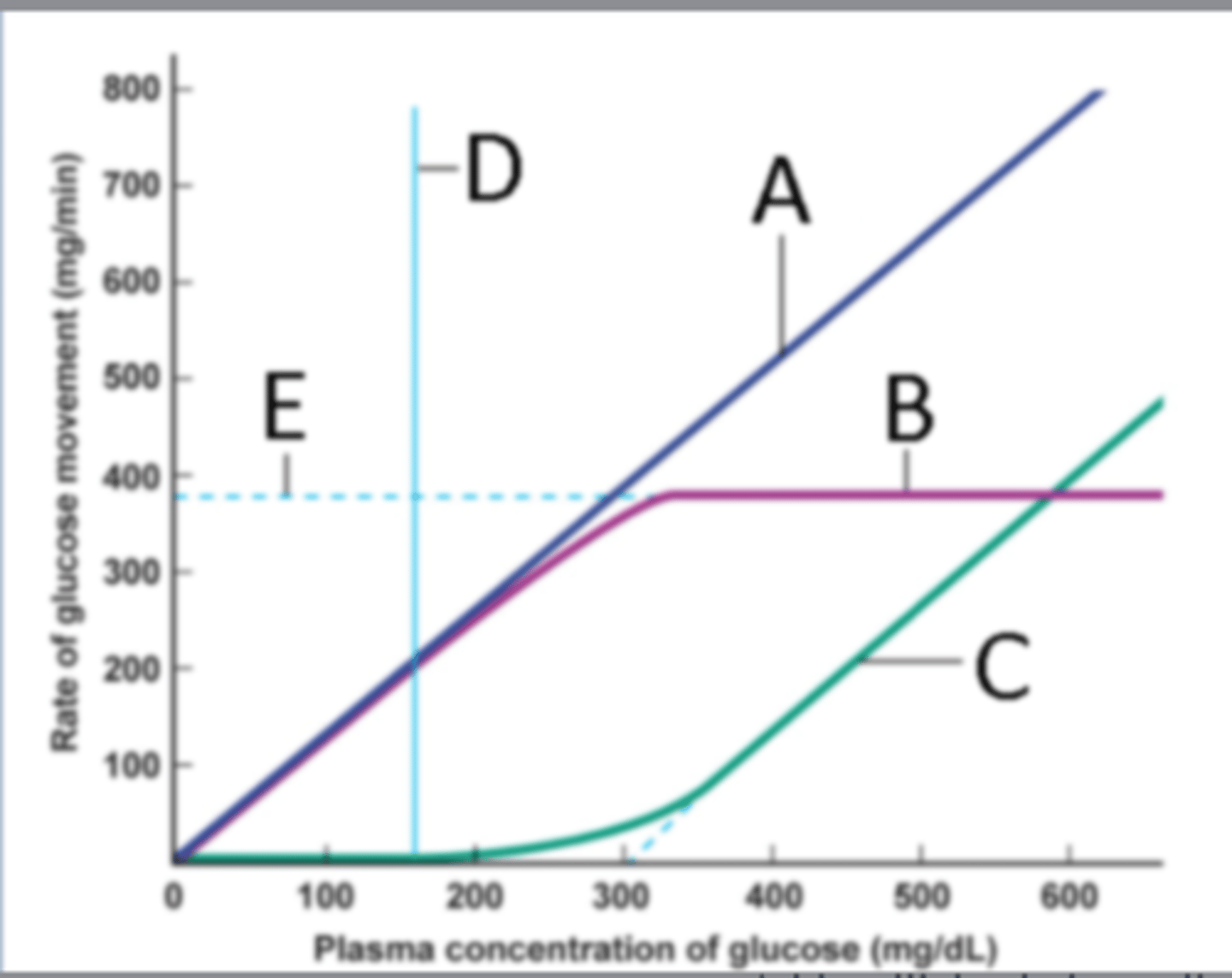
Identify the process at label E
Transport maximum
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) age 20-29 (ml/min/1.73m2)
120
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) age 50-59 (ml/min/1.73m2)
100
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) indicative of stage 5 CKD (ml/min/1.73m2)
15
Urinary volume associated with stage 5 CKD (ml/hour)
50
Target systolic blood pressure for patients with stage 3 CKD (mmHg)
140
A model providing guidance for a shift from an acute, episodic health system focus to one that is required for effective chronic disease care
Chronic Care Model, CCM (Wagner, Austin & Von, 1996)
A model to integrate medical science with redesigned health care delivery systems so chronic patients in any setting can receive prompt diagnoses and care
Improving Chronic Illness Care, ICIC (Wielawski, 2011)
This model recognizes the broader policy environment that involves patients, their families, health care organizations, and communities.
Innovative Care for the Chronic Conditions, ICCC (WHO, 2002)
This model aims to provide participants with the self-efficacy and skills required to optimally manage their chronic conditions regardless of specific diagnosis.
Stanford Model (Stanford University, 2012)
A set of actions designed to ensure the coordination and continuity of healthcare as patients transfer between different locations or different levels of care within the same location
Transitional Care model (Naylor et al., 2004)